Lecture #13: Tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms

What is the terminal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain (ETC)
oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor
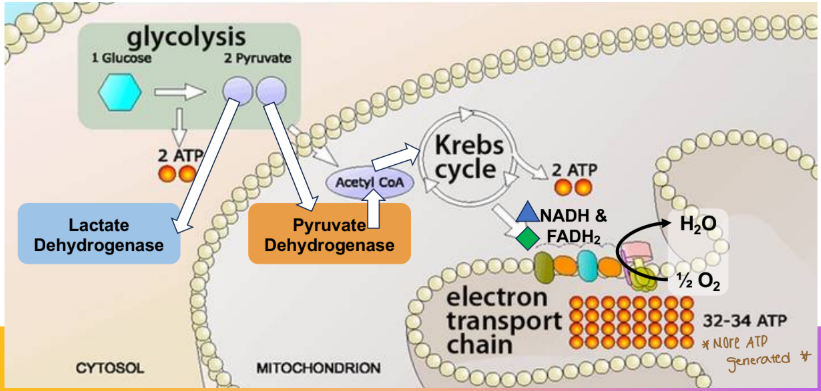
What happens when oxygen is the terminal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain (ETC)
We can get way more ATP than using glycolysis alone
How is glucose catabolized into pyruvate?
Glycolysis
Glucose is catabolized to pyruvate by glycolysis
Two molecules of pyruvate (all 6 carbons left)
Net 2 ATP and 2 NADH formed (2 ATP invested)
Where does glycolysis occur?
Cytosol
What happens wen pyruvate enters the mitochondria to be oxidized?
Much more energy will be captured
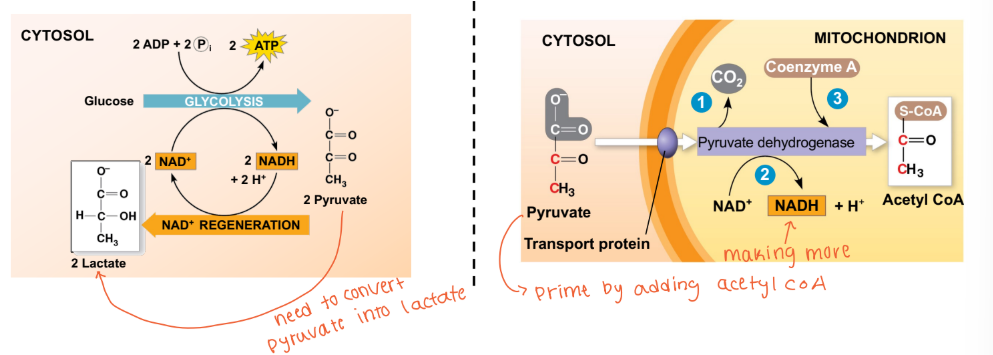
What are the two fates pyruvate has depending on the oxygen status?
Lactate fermentation → low oxygen
Aerobic respiration → normal oxygen
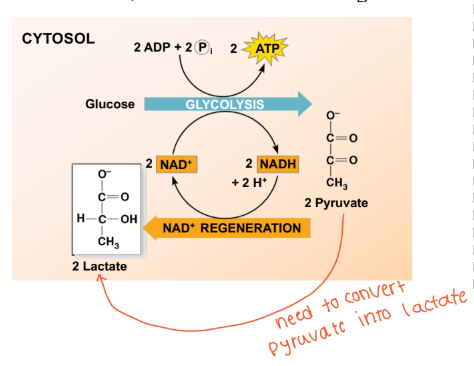
Lactate fermentation → low oxygen
Pyruvate is anaerobically converted to lactate via lactate dehydrogenase
NAD+ is regenerated (oxidized) from NADH (reduced reduced equiv.)
Lowers net energy yield (substrates can’t enter TCA, or ETC that consumes O2)
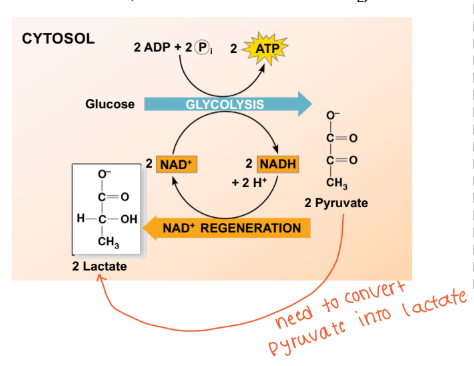
In lactate fermentation (low oxygen) what happed to the NAD+?
NAD+ is regenerated (oxidized) from NADH (reduced reduced equivalent)
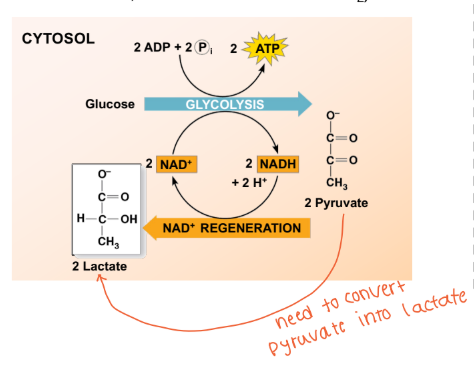
In lactate fermentation (low oxygen) what happed to the total net energy yeild?
It lowers the new energy yields (substrates can’t enter the TCA or ETC bc that consumes O2)
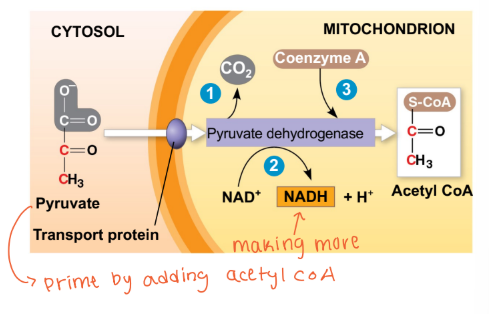
Aerobic respiration → normal oxygen
Pyruvate is aerobically converted to Acetyl-CoA via Pyruvate Dehydrogenase
More NADH is generated (1 per pyruvate molecule)
Higher net energy yield (substrates can enter TCA, and ETC that consumes O2)
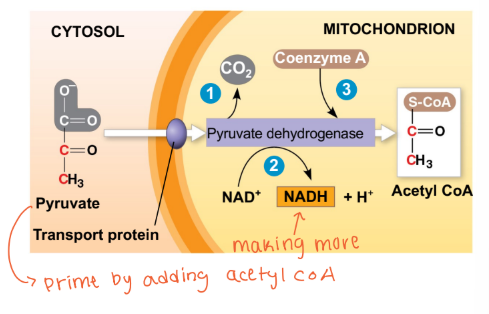
What happens with pyruvate in aerobic respiration (normal oxygen)?
Pyruvate is aerobically converted to acetyl-CoA via pyruvate dehydrogenase
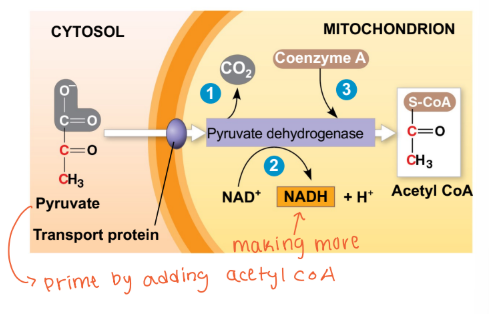
What happens to NADH in aerobic respiration (normal oxygen)?
More NADH is generated (1 per pyruvate molecule)
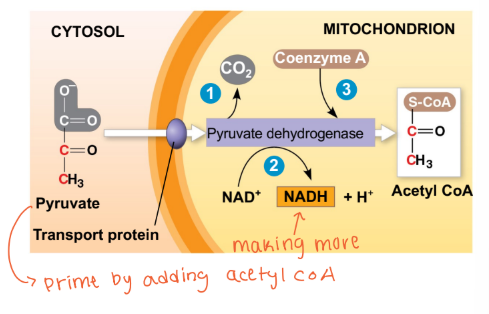
What happened to the net energy yield in aerobic respiration (normal oxygen)?
There is a higher net energy yields (substrates can enter TCA and ETC bc they consume O2)
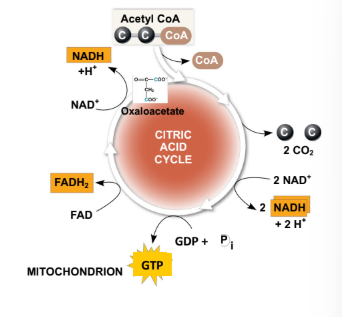
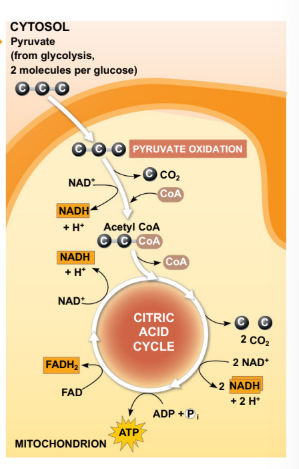
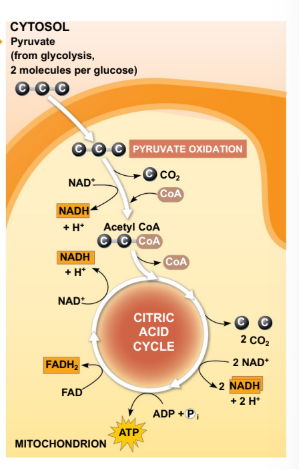
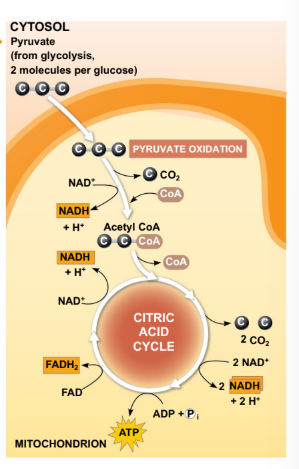
The TriCarboxylic Acid cycle (TCA) is the major source of?
TCA cycle is the major source of reducing equiv. that enter the ETC
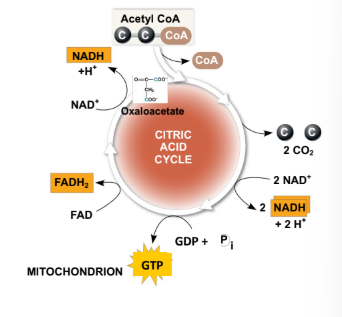
What are the multiple forms that acteryl-CoA molecules generate by entering the TCA?
3 molecules of NADH (NAD+ → NADH)
1 molecule of FADG2 (FAD → FADH2)
1 molecule of GTP (GDP → GTP)
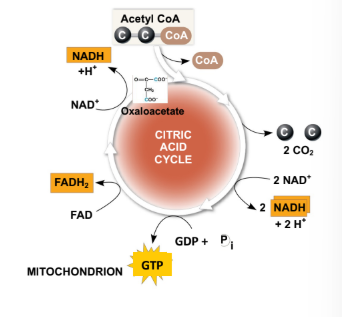
What other end products are generated form the TCA cycle?
2 CO2 (from isocitrate and ⍺-ketoglutarate)
Oxaloacetate (re-enters the cycle! goes back to step 1)
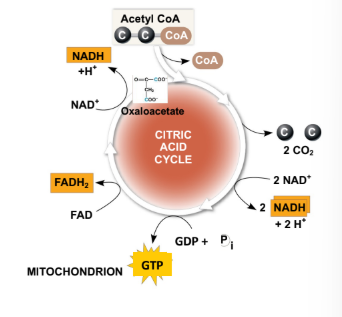
How many times per glucose molecules when doing the TCA cycle it creates these products entering glycolysis?
It happens 2x per glucose molecule entering glycolysis
What are the type of rxns that are part of the TCA cycle?
Synthesis
Isomerization
Dehydrogenation
Phosphorylation
Synthetase
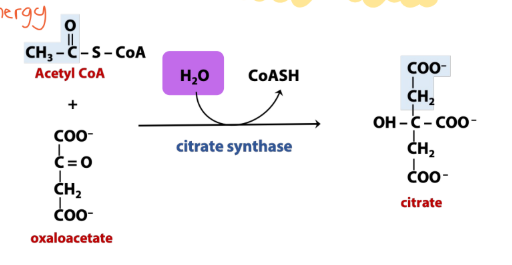
Synthesis (TCA cycle)
Enzyme names: Synthase (Fumarase)
Synthase enzymes synthesize new molecules without using energy.
Reaction type: Water molecule combines with (or derived from) two
separate molecules
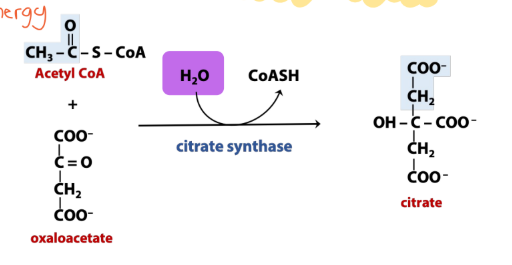
What is the enzyme name for synthesis rxn in the TCA cycle?
Synthase (Fumarase)
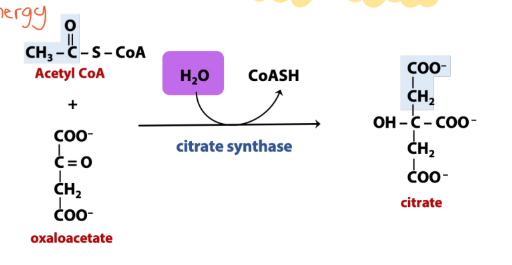
What does synthase enzymes do?
Synthesize new molecules w/o using energy
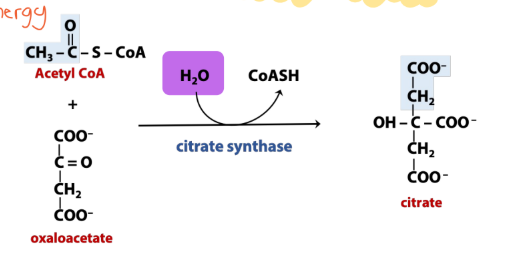
What is the rxn type for synthesis?
Water molecule
(It is combined with or derived from two separate molecules)
Isomerization (rxn in the TCA cycle)
Enzymes: Isomerase (Mutase)
Reaction type: molecule is rearranged, but no atoms lost (isomer formed)
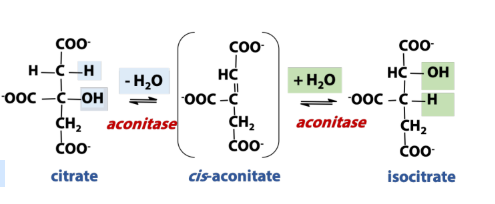

What is the enzyme in isomerization (rxn in TCA)?
Isomerase (mutase)
rearranges functional groups around the molecule
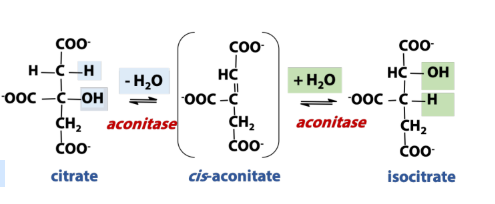
What is the rxn type in isomerization (rxn in TCA)?
Molecules are rearranged, but not atoms lost (isomer is formed)
Dehydrogenation (TCA rxn)
Enzymes: Dehydrogenase
Reaction Type: Removes hydrogen (electron) from molecule – usually to
reducing equivalent
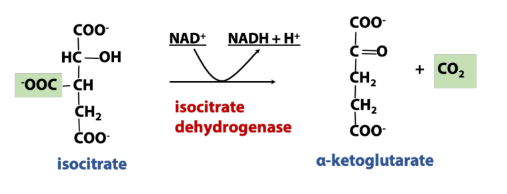
What enzyme is used in dehydrogenation (TCA rxn)
Dehydrogenase
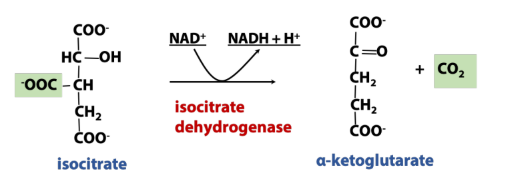
Rxn in dehydrogenation (TCA rxn)
Removes hydrogen (electron) from molecule, usually to reducing equiv.
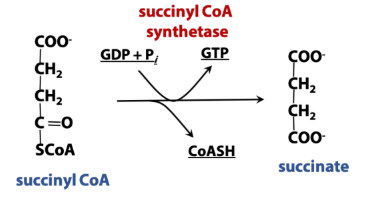
Phosphorylation (TCA rxn)
Enzymes: Synthetase (Kinase)
Reaction Type: Adds phosphate to a molecule (in this case, nucleotide diphosphate to triphosphate)
***This is substrate level phosphorylation *** (can use electrons from the bonds to create ATP)
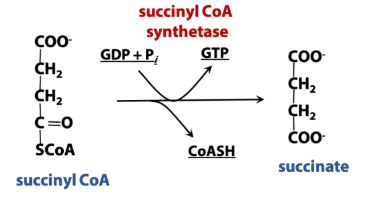
What enzyme is used in phosphorylation (TCA rxn)?
Synthetase (kinase)
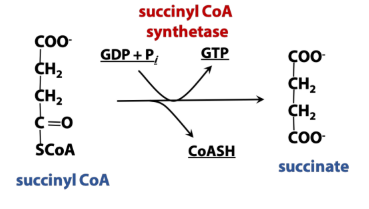
Rxn in phosphorylation (TCA rxn)?
Adds phosphate to a molecule (in this case, nucleotide diphosphate to triphosphate)
***This is substrate level phosphorylation *** (can use electrons from the bonds to create ATP)
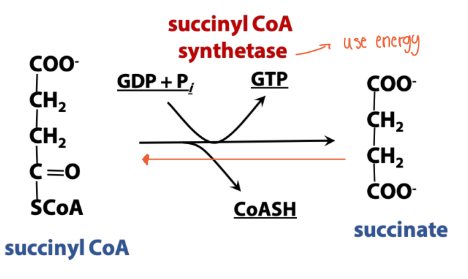
Synthetase (TCA rxn)
Enzyme names: Succinyl-CoA Synthetase
(Synthetase enzymes synthesize new molecules using energy)
Reaction type: uses energy from phosphate-phosphate bond to create a
new bond in the reactant molecule(s).
***This enzyme was named for the reverse reaction than the direction in TCA***
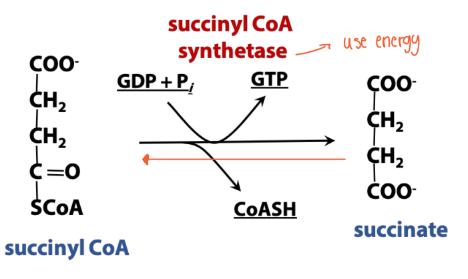
What is the enzyme in synthetase (TCA rxns)?
Succinyl-CoA Synthetase
(Synthetase enzymes synthesize new molecules using energy)
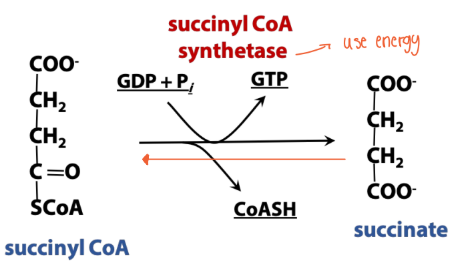
What rxn is in synthetase (TCA rxn)?
uses energy from phosphate-phosphate bond to create a new bond in the reactant molecule(s).
***This enzyme was named for the reverse reaction than the direction in TCA***
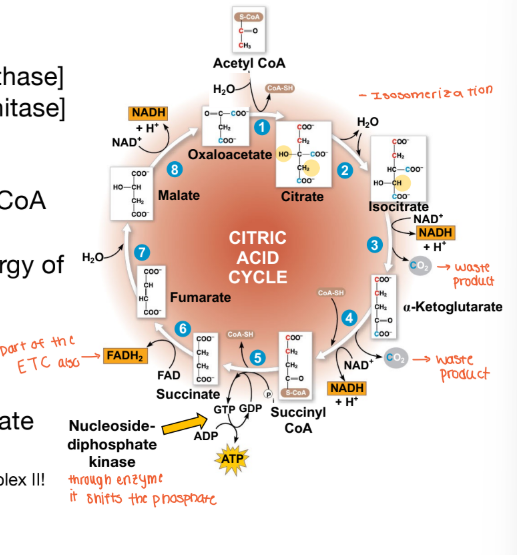
How many total reactions are in the TCA cycle?
8 total reactions
![<p>Step # – Reaction – [Enzyme] in TCA cycle </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5f6f9d0c-bdbc-4fb9-b703-2b28e73408b1.png)
Step # – Reaction – [Enzyme] in TCA cycle
Condensation to form Citrate [Citrate Synthase]
Isomerization of Citrate → Isocitrate [Aconitase]
Oxidation of Isocitrate → ⍺-ketoglutarate [Isocitrate Dehydrogenase]
Oxidation of ⍺-ketoglutarate → Succinyl-CoA [⍺-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase]
Substrate level phosphorylation; uses energy of CoA bond [Succinyl-CoA Synthetase]
Oxidation of Succinate to Fumarate*** [Succinate Dehydrogenase]
Condensation to form Malate [Fumarase]
Oxidation of Malate → Oxaloacetate [Malate Dehydrogenase]
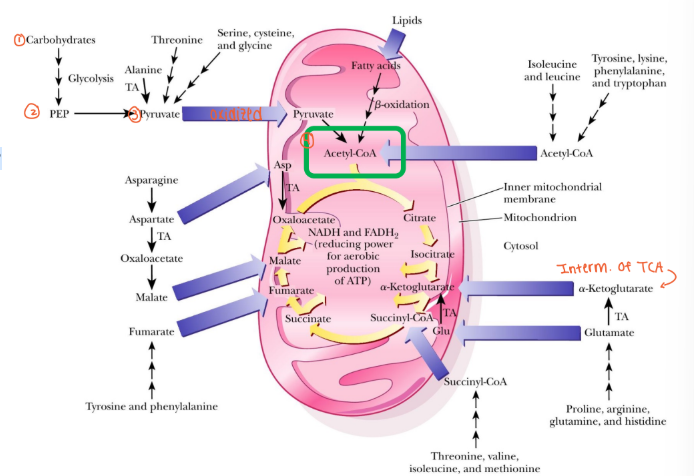
Carbohydrate, protein, and fat metabolism converge at TCA
Most metabolites can enter the TCA cycle at one metabolite or another
The point at which it enters determines how much *ATP will be produced (Acetyl-CoA will go through the entire TCA cycle)
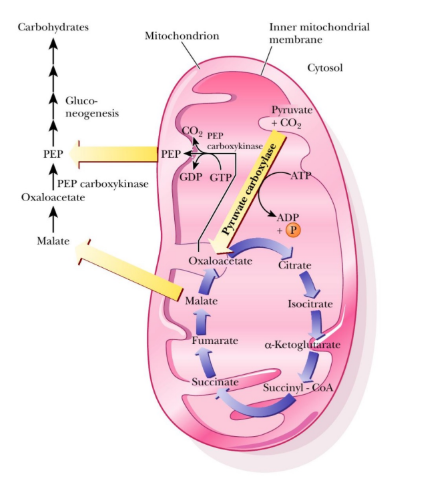
TCA cycle provides gluconeogenic precursors
Most gluconeogenic precursors can either enter TCA (to be oxidized)
or
Can be metabolized to become glucose –particularly through oxaloacetate
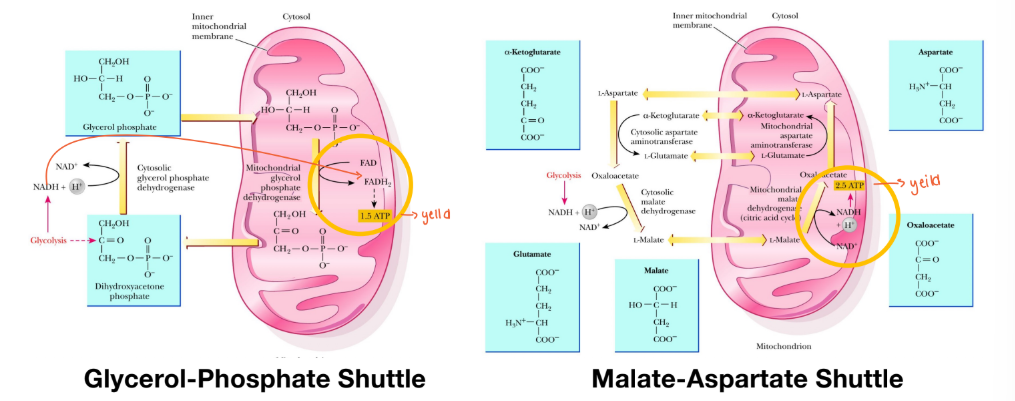
How do reducing equivalents get into mitochondria?
Glycerol-phosphate shuttle
Malate-aspartate shuttle
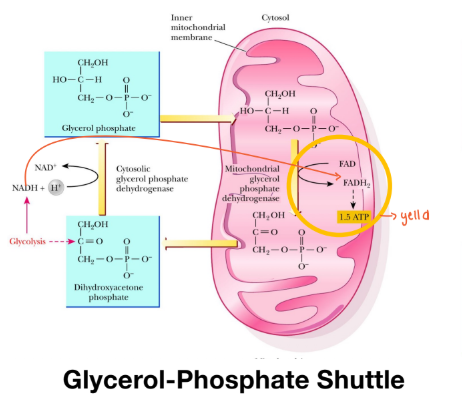
Glycerol phosphate shuttle
Yields 1.5 ATP

Malate aspartate shuttle
Yields 2.5 ATP
What are the products of anaerobic metabolism?
Lactate & NAD+ (reusable in glycolysis)
What are the products of anaerobic pyruvate metabolism?
Acetyl CoA
NADH
CO2
What energy-carrying products are produced from oxidative reactions in the TCA cycle?
Dehydrogenase: end 3 NADH & 2 FADH2
Substrate level phosphorylation: directly gives us ~ ATP
Which metabolite is derived from all 3 macronutrients and
enters the TCA cycle?
Acetyl CoA
How much ATP is derived from NADH?
From FADH2?
2.5 NADH
1.5 FADH2