Homeostasis and Human Body Systems Overview
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Homeostasis
Dynamic constancy of the internal environment.
Dynamic
Conditions fluctuate within limits in organisms.
Set Point
Preferred level for internal conditions.
Control Center
Processes information from sensors, often in the brain.
Stimulus
Value determined by the control center.
Effector
Muscles or glands that enact responses.
Response
Action taken by effectors to restore balance.
Negative Feedback Loop
Mechanism correcting deviations from set point.
Sensor
Detects changes disrupting homeostasis.
Water Composition
Body consists of 60% water.
Inorganic Matter
Non-living components like ions and molecules.
Organic Molecules
Contain carbon bonded to hydrogen and others.
Macromolecules
Large organic compounds including carbohydrates and proteins.
Polymers
Long chains of similar chemical subunits.
Dehydration Synthesis
Process forming polymers by removing water.
Hydrolysis
Process breaking down polymers by adding water.
Carbohydrates
Subunits are sugars; store energy.
Monosaccharides
Single simple sugar units.
Disaccharides
Two simple sugars linked together.
Polysaccharides
Long chains of sugar units.
C:H:O Ratio
Carbohydrates contain a 1:2:1 ratio.
Starches
Polymers of glucose for energy storage.
Glycogen
Storage form of glucose in animals.
Polysaccharides
Linked simple sugars for energy storage.
Starch
Polysaccharide for energy storage in plants.
Glycogen
Energy storage polysaccharide in animals.
Cellulose
Structural polysaccharide in plant cell walls.
Lipids
Fats, oils, and phospholipids for energy storage.
Glycerol
Subunit of lipids, combines with fatty acids.
Fatty Acids
Building blocks of lipids, can be saturated or unsaturated.
Saturated Fatty Acids
No double bonds; solid at room temperature.
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
At least one double bond; liquid at room temperature.
Proteins
Polymers of amino acids with diverse functions.
Amino Acids
20 types; building blocks of proteins.
Peptides
Chains of amino acids formed by dehydration synthesis.
Polypeptides
Long chains of amino acids; form proteins.
Nucleic Acids
Polymers of nucleotides; direct cell functions.
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid; carries genetic information.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid; involved in protein synthesis.
Vitamins
Organic compounds essential for growth and development.
Minerals
Inorganic compounds aiding in chemical reactions.
Dehydration Synthesis
Water removal to form larger molecules.
Hydrolysis
Water addition to break macromolecules.
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions.
Active Site
Part of enzyme binding to substrate.
Catalyst
Speeds up reactions without being consumed.
Active Site
Region where substrate binds on an enzyme.
Substrate
Molecule upon which an enzyme acts.
Temperature Effect
Low temperature reduces enzyme flexibility; high temperature alters shape.
Optimal pH
Ideal pH range for human enzymes is 6-8.
Competitive Inhibitors
Molecules that block substrate binding at active site.
Non-competitive Inhibitors
Molecules that change enzyme shape, inhibiting function.
Mechanical Digestion
Physical breakdown of food into smaller pieces.
Chemical Digestion
Hydrolysis of compounds to break down food chemically.
Gastrin
Hormone released by stomach to produce gastric juices.
Chyme
Partially digested food mixed with gastric juices.
Peristalsis
Wave-like muscle contractions moving food through the digestive tract.
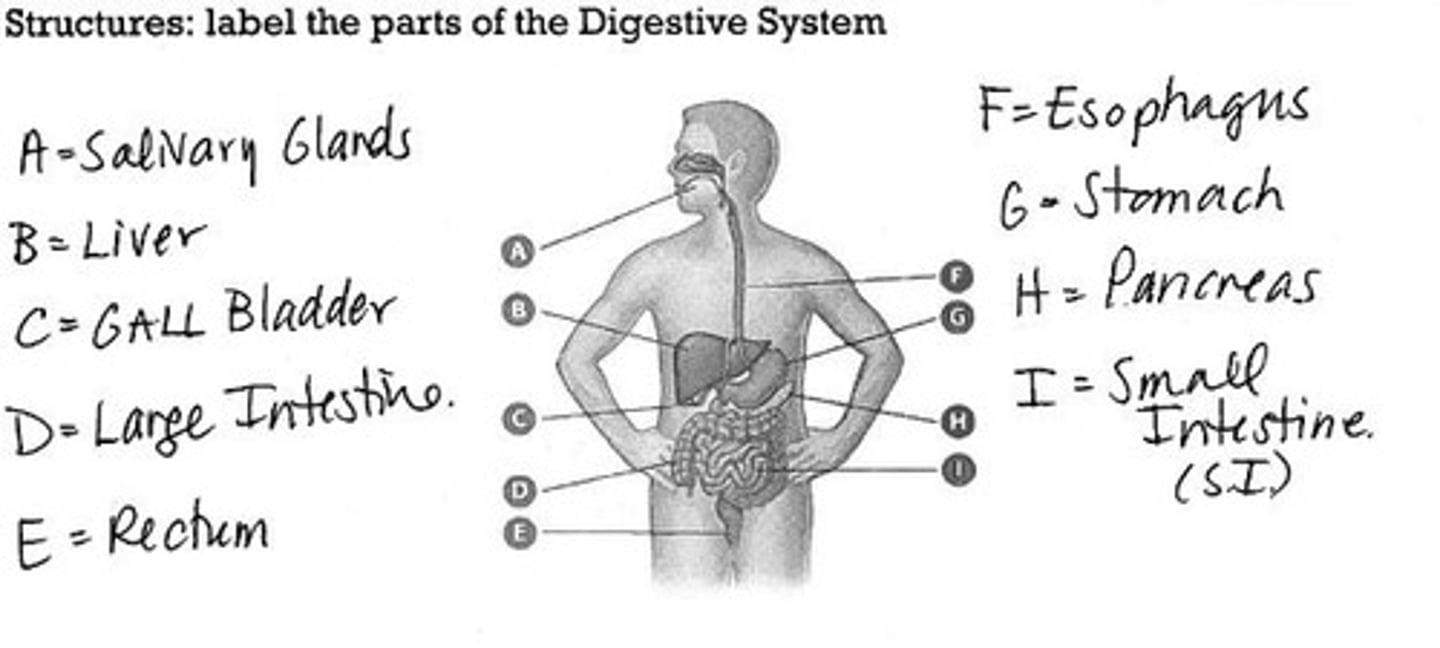
Salivary Amylase
Enzyme in saliva that breaks down starch.
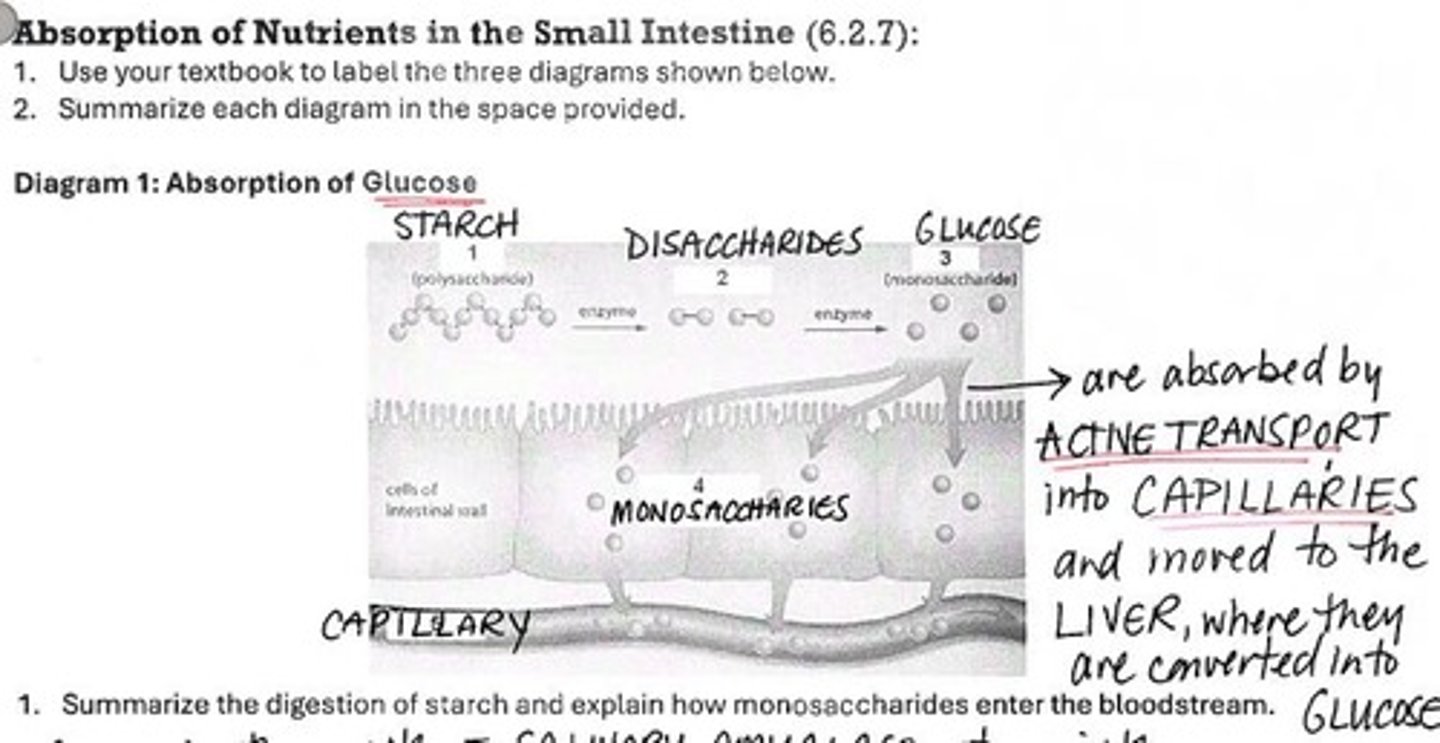
Villi
Small projections in the small intestine that increase absorption surface.
Bicarbonate Ion (HCO3-)
Neutralizes stomach acid in the small intestine.
Liver Functions
Stores glycogen, produces bile, emulsifies lipids.
Gallbladder
Stores bile until needed for fat digestion.
Large Intestine
Absorbs water and salts, forms feces.
Appendix
Vestigial organ, possibly aids immune function.
Rectum
Stores feces before expulsion from the body.
Anus
Controls release of feces via sphincters.
Pepsin
Enzyme that begins protein digestion in the stomach.
Lipase
Enzyme that digests fats in the small intestine.
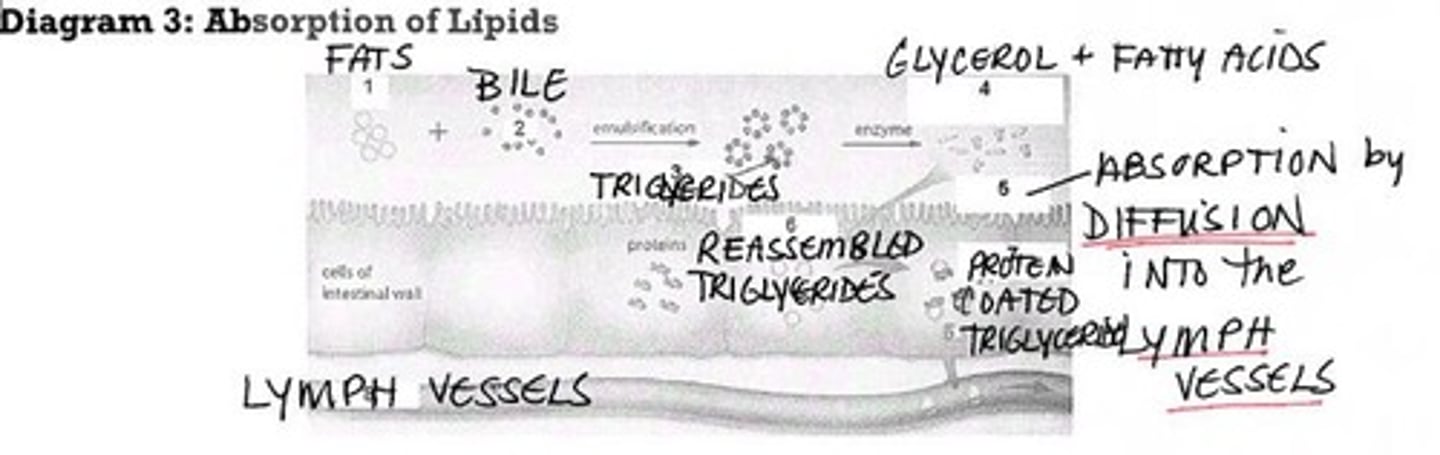
Triglycerides
Reassembled fats that diffuse into lymph vessels.