Arenes - Benzene
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What are arenes (aromatic compounds)
Compounds with a delocalised π system
In terms of bond lengths, comment on the accuracy of the Kekulé structure of benzene.
Not accurate - all carbon-carbon bonds in benzene are same length, there are no longer discrete C—C and shorter C=C present.
How many π electrons are there in a benzene molecule
6 (one per carbon)
What is needed for the hydrogenation (reduction) of benzene
Nickel catalyst
What is the extra thermochemical stability associated with the delocalisation of the π electrons in benzene
152kJ/mol (360-208)
What happens when cyclohexene is added to bromine water
Decolourises
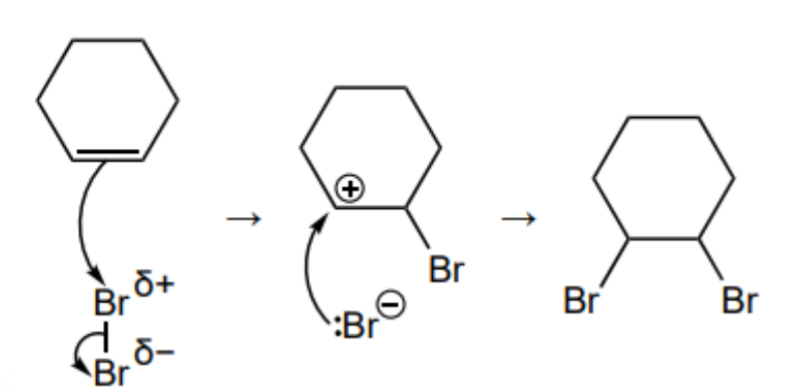
Name and outline the mechanism for the reaction between cyclohexane and bromine
Electrophilic addition
What happens when bromine water is added to benzene and how does this provide evidence for the delocalised model of benzene
no reaction
Delocalisation provides extra stability
Electrophilic addition reaction would remove stable arrangement as it would involve the loss of a double bond
Why does benzene undergo electrophilic substitution, not addition
it would involve the loss of delocalisation
Retains stability
Requires stronger electrophiles and more forcing conditions
What are the conditions for the nitration of benzene
mixed with conc nitric acid and conc sulfuric acid
Below 50˚C
Give the equation between conc nitric acid and conc sulphuric acid.
2H2SO4 + HNO3 → NO2+ + 2H2SO4- + H3O+
NO2 + acts as electrophile
Draw the mechanism for the reaction between NO2 + and benzene
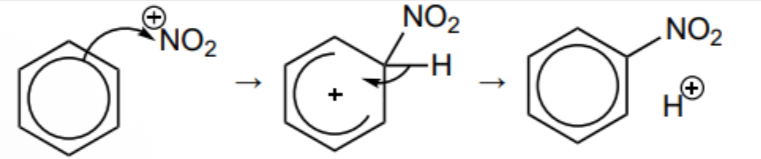
What does H2SO4 act as in the nitration of benzene and why
Catalyst, the H+ lost from the benzene reacts with the HSO4 - to regenerate H2SO4
Why does the temperature of the nitration of benzene need to be kept below 50˚C
Prevents the likelihood of multiple substitution of the benzene ring, potentially producing a hazardous, explosive product (TNT)
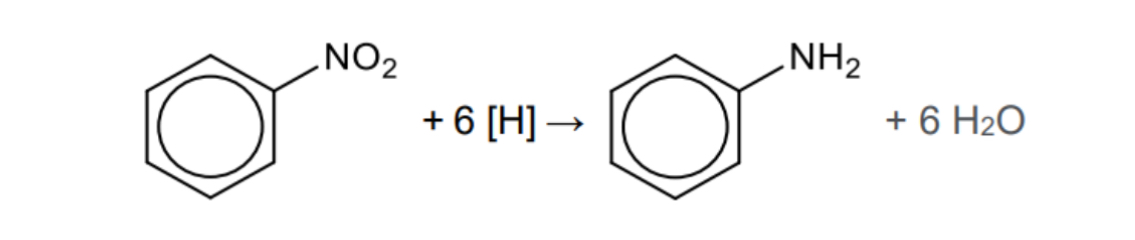
What is needed for the formation of aromatic amines from nitrobenzene and what type of reaction is it
Tin and concentrated hydrochloric acid
Reduction
What is a common use of aromatic amines
Used to make as azo-dyes, used to treat textiles, leather and some foods
What is the name of the reaction between acyl chlorides and benzene
Freidel-Crafts Acylation of Benzene
What is needed for freidel-crafts acylation and alkylation of benzene
anhydrous AlCl3 catalyst
Give the chemical equation for the reaction between an acyl chloride (RCOCl) and AlCl3
RCOCl + AlCl3 → AlCL4- + RCO+
Draw the mechanism between benzene and RCO+ (electrophile)
H+ produced reacts with the AlCl4 - forming HCl and reforming AlCl3
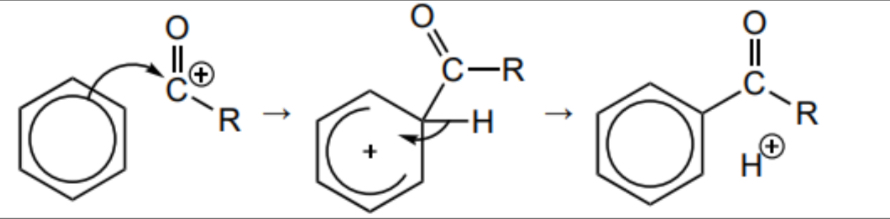
What is the name for the reaction between chloroalkanes and benzene
Freidel-crafts alkylation of benzene
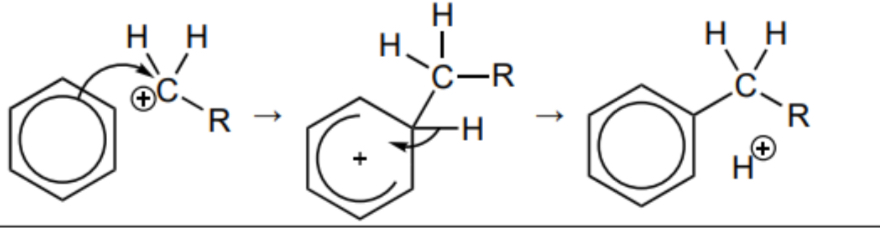
Give the equation for the reaction between a chloroalkane (RCH2Cl) and AlCl3
AlCl3 + RCH2Cl → AlCl4- + RCH2 + + AlCl4-
Draw the mechanism for the reaction between benzene and RCH2+
What is needed for the bromination of benzene (benzene + bromine)
AlBr3 (or iron) catalyst
Give the mechanism for the reaction between benzene and Br+
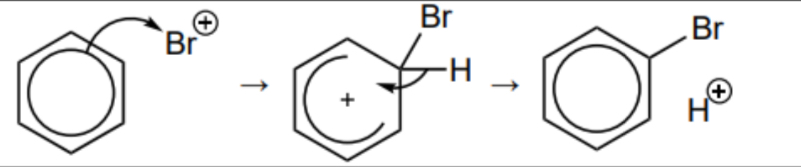
Give the chemical equation for the reaction between bromine and AlBr3
AlBr3 + Br2 → AlBr4- + Br+
Br+ is used as an electrophile for the bromination as the delocalisation within the ring is too stable for just bromine water.
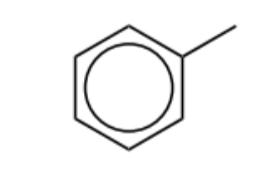
Name this molecule
Toluene
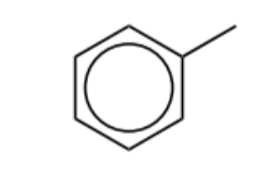
State and explain the reactivity of toluene compared to benzene
more reactive
Alkyl groups have positive inductive effect pushing electron density to ring
Ring more electron dense, more attractive to electrophiles
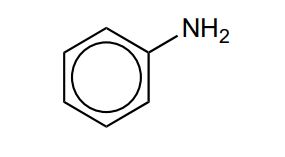
State and explain the reactivity of phenylamine compared to benzene
more reactive
Lone pair on nitrogen delocalised into ring
More electron dense, more attractive to electrophile
State and explain the reactivity of chlorobenzene compared to benzene
less reactive (ignore lone pairs)
Very electronegative, negative inductive effects, electron pulling
Benzene ring less electron dense, less attractive to electrophiles
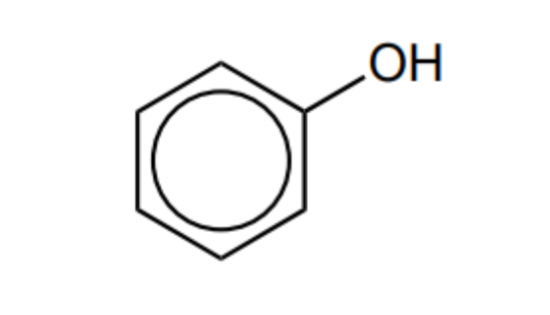
State and explain the reactivity of phenol compared to benzene
more reactive
Lone pair delocalises into ring
Increased electron density, more attractive to electrophiles
How does phenol react with bromine (in the absence of a catalyst
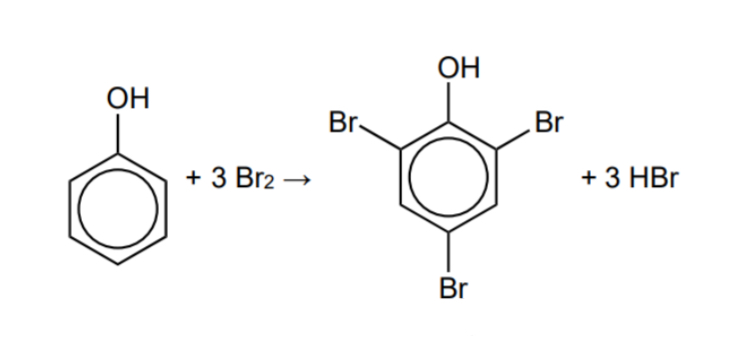
Complete the mechanism