combo mombo
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
What is marginal thinking?
Marginal thinking involves making decisions based on the cost and benefit of one more unit of something.
What happens to marginal benefit and marginal cost as one consumes more?
Marginal benefit tends to decrease, and marginal cost tends to increase as one consumes more.
What are examples of marginal benefits of drinking beer?
Liking taste, less social anxiety, killing time.
What are examples of marginal costs of drinking beer?
Lots of calories, getting tipsy, risk of a hangover.
When will an individual decide to drink the beer?
When the marginal benefit equals the marginal cost.
What is efficiency?
Efficiency is accomplishing tasks with minimal waste of time, energy, or resources.
What can result from a focus solely on efficiency?
It can lead to neglect in detail and lack of thoroughness.
What is effectiveness?
Effectiveness is achieving desirable outcomes with precision and quality.
What can result from a focus solely on effectiveness?
It can lead to delays and frustration from stakeholders.
What is needed for a balance between efficiency and effectiveness?
Equilibrium, which requires a deep understanding of the task in question.
What is demand?
Demand is the amount of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at various prices during a particular time period.
What is the law of demand?
There is an inverse relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity demanded.
What does a shift in the demand curve indicate?
A change in factors like income, tastes, prices of related goods, number of consumers, or expectations.
What is the difference between a change in quantity demanded and a change in demand?
A change in quantity demanded is a movement along the demand curve due to a price change, while a change in demand is a shift of the demand curve.
What is supply?
Supply is the amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to supply at various prices during a time period.
What is the law of supply?
There is a direct relationship between price and quantity supplied.
What factors can shift the supply curve?
Resource prices, technological or organizational innovations, taxes and subsidies, prices of related goods, natural causes, number of suppliers.
What is equilibrium in the context of supply and demand?
It is when quantity demanded equals quantity supplied, creating a state of rest.
What happens in a surplus?
Quantity supplied is larger than quantity demanded, leading sellers to lower prices.
What happens in a shortage?
Quantity demanded is larger than quantity supplied, leading buyers to bid up prices.
What is elasticity?
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded or supplied to a change in one of its determinants.
What is price elasticity of demand?
It measures how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good.
What factors affect price elasticity of demand?
Availability of close substitutes, type of market, proportion of income devoted to the product, time horizon, type of good.
What is perfectly inelastic demand?
Demand where quantity demanded does not change with price changes, e.g., insulin.
What is relatively inelastic demand?
Demand where quantity demanded changes very little with price changes, e.g., necessary products with no substitutes.
What is unit elastic demand?
Demand where a percentage change in price results in an equal percentage change in quantity demanded, e.g., clothing brands.
What is relatively elastic demand?
Demand where quantity demanded changes significantly with price changes, e.g., products with many substitutes.
What is perfectly elastic demand?
Demand where any price increase will cause quantity demanded to drop to zero, e.g., two neighboring vending machines.
Who are consumers in economic terms?
Economic agents who aim to maximize utility based on their income constraint.
What is rational behavior in consumer behavior?
Consistent choices where more is always better and consumers aim to maximize utility.
What assumptions are made in the optimization of utility with two products?
Goods are homogenous, prices are given, and there is perfect information on price, quality, and location of supply.
What is an indifference curve?
It shows consumption bundles that give the consumer the same level of satisfaction.
What is the marginal rate of substitution (MRS)?
The rate at which a consumer is willing to trade one good for another while maintaining the same level of utility.
What does the budget constraint represent?
It limits the consumption bundles that a consumer can afford.
What determines the slope of the budget constraint?
The price ratio between the two goods.
What is the optimum point in consumer behavior?
Where the budget constraint reaches the highest attainable indifference curve.
What does the cost of production depend on?
Budget, production function, factor market, and governmental policies.
What is the production function?
It is the relationship between the quantity of input used to make a good and the quantity of outputs.
What does the factor market involve?
It involves the quantity and price of labor and capital.
What is the goal of producers?
To maximize profit.
What are the characteristics of the short run in production?
Production techniques are fixed, and there are fixed and variable costs.
What are the characteristics of the long run in production?
Production techniques are flexible, all costs are variable, and all production inputs can vary.
What is the law of diminishing (marginal) returns?
Increasing the quantity of a certain input will eventually lead to a decline in the marginal product of that input.
What is marginal product?
It is the extra output generated by adding an additional unit of an input.
What happens when more workers are added beyond a certain point?
The marginal product of labor will decline.
What is an isoquant?
It depicts all combinations of labor and capital that can be used to produce a given level of output.
What is the marginal rate of technical substitution (MRTS)?
It is the amount of capital a firm would decrease to increase labor while holding the level of production the same.
What is the iso-cost line?
It shows combinations of productive inputs that have the same cost.
What happens when the budget changes?
The iso-cost line moves outward or inward.
What happens when there is a change in the price of one input?
The intersection point on the respective input axis will change.
What is the least-cost input combination?
It is the combination of labor and capital that minimizes the cost of production.
What is the profit optimization rule?
Produce where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MR=MC).
How is total profit calculated?
Total profit = total revenue - total cost (TR - TC).
What does total revenue depend on?
It depends on the type of product market.
What are the different types of product markets?
Perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, monopoly.
What is the optimal quantity of production?
It is where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MR=MC).
What are the challenges in profit maximization?
Accurately measuring MR and MC, and high profits attracting governmental attention or other objectives.
What is total cost (TC)?
Total cost is the sum of fixed costs and variable costs (TC = FC + VC).
What are fixed costs (FC)?
Fixed costs are costs that do not change with the amount produced (e.g., rented building).
What are variable costs (VC)?
Variable costs are costs that change with the amount produced (e.g., electricity used to produce goods).
What is the optimal production condition for a price-taking firm?
Optimal production is where price equals marginal revenue (P = MR).
What are the steps to find the optimal production for a price-taking firm?
1. Find where MR = MC. 2. Determine quantity. 3. Determine total revenue (TR). 4. Determine total cost (TC). 5. Calculate profit (TR - TC).
What is the break-even point?
The break-even point occurs at the minimum of the average total cost (ATC) curve.
What happens at the shutdown point?
The firm exits the market, occurring at the minimum of the average variable cost (AVC).
What is a monopoly?
A monopoly is a market structure where a single provider supplies the entire market.
How does a monopolist set prices?
A monopolist sets prices based on the quantity produced, with price different from marginal revenue (P ≠ MR).
What are the steps to find the optimal production for a monopolist?
1. MR = MC. 2. Determine quantity. 3. Determine TR. 4. Determine TC. 5. Calculate profit (TR - TC).
What is monopolistic competition?
Monopolistic competition is a market structure with many firms offering differentiated products.
How does monopolistic competition differ from monopoly in the short run?
Demand curve is more elastic for a segment of society wanting the differentiated product.
What happens in the long run in monopolistic competition compared to perfect competition?
In monopolistic competition, firms operate at a slightly higher cost and produce fewer units compared to perfect competition.
What is an oligopoly?
An oligopoly is a market structure with a few large firms that are highly interdependent.
What are the two main strategies oligopolists can follow?
Compete or collude (acting together for mutual benefit).
What is overt collusion?
Oligopolists openly communicate and strategically set prices and outputs to maximize profit (often illegal).
What is covert collusion?
Agreements are made in secret.
What is tacit collusion?
Implied agreements where firms set prices without explicit communication.
What is game theory?
Game theory studies how actors behave in strategic situations, considering the actions of others.
What is a payoff matrix?
A payoff matrix is a table showing possible outcomes depending on the actions chosen by each player.
What is a dominant strategy in game theory?
A dominant strategy is the best strategy for a player regardless of the strategies chosen by other players.
What is Nash equilibrium?
Nash equilibrium is a situation where no player can benefit by changing strategies while the other players keep theirs unchanged.
What are externalities?
Externalities are the positive or negative impacts of an economic activity on third parties.
What is a positive externality?
A benefit received by third parties not involved in the economic activity.
What is a negative externality?
A cost imposed on third parties not involved in the economic activity.
What is general equilibrium?
a state where all markets in an economy are in balance simultaneously. Supply equals demand in every market, ensuring that resources are used efficiently.
delete
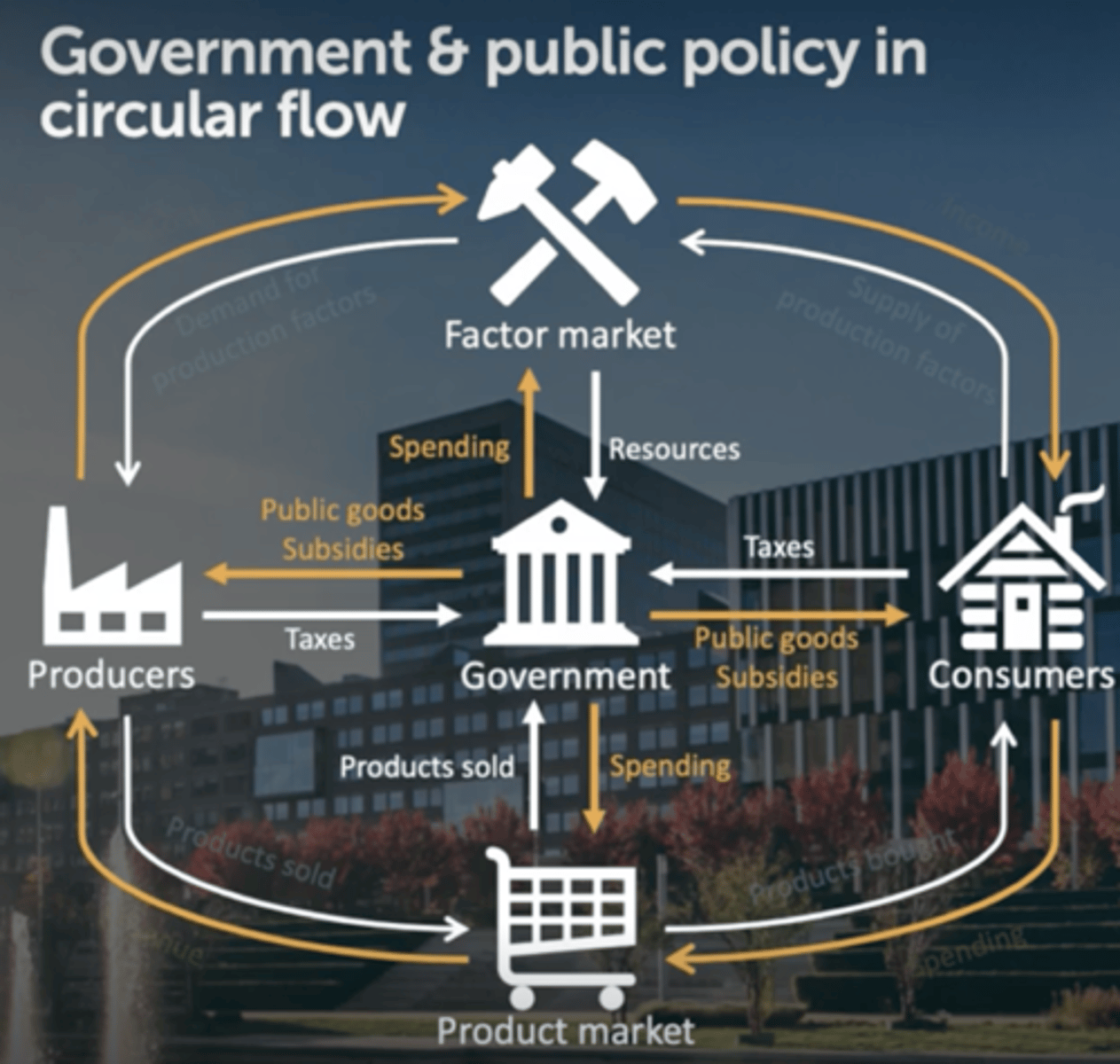
market failure and public policy
new topic
general equilibrium and public policy
new topic
What does government spending consist of? (2)
1) buying from the factor market
e.g. firefighters and teachers
2) buying from the product market
e.g. police cars and laptops
How does a government intervene?
(4)
with money
1) subsidizing merit goods
2) taxing demerit goods
3) maximum or minimum prices
4) taxes in general
If the market would function according to perfect competition...?
... society would be in a general equilibrium
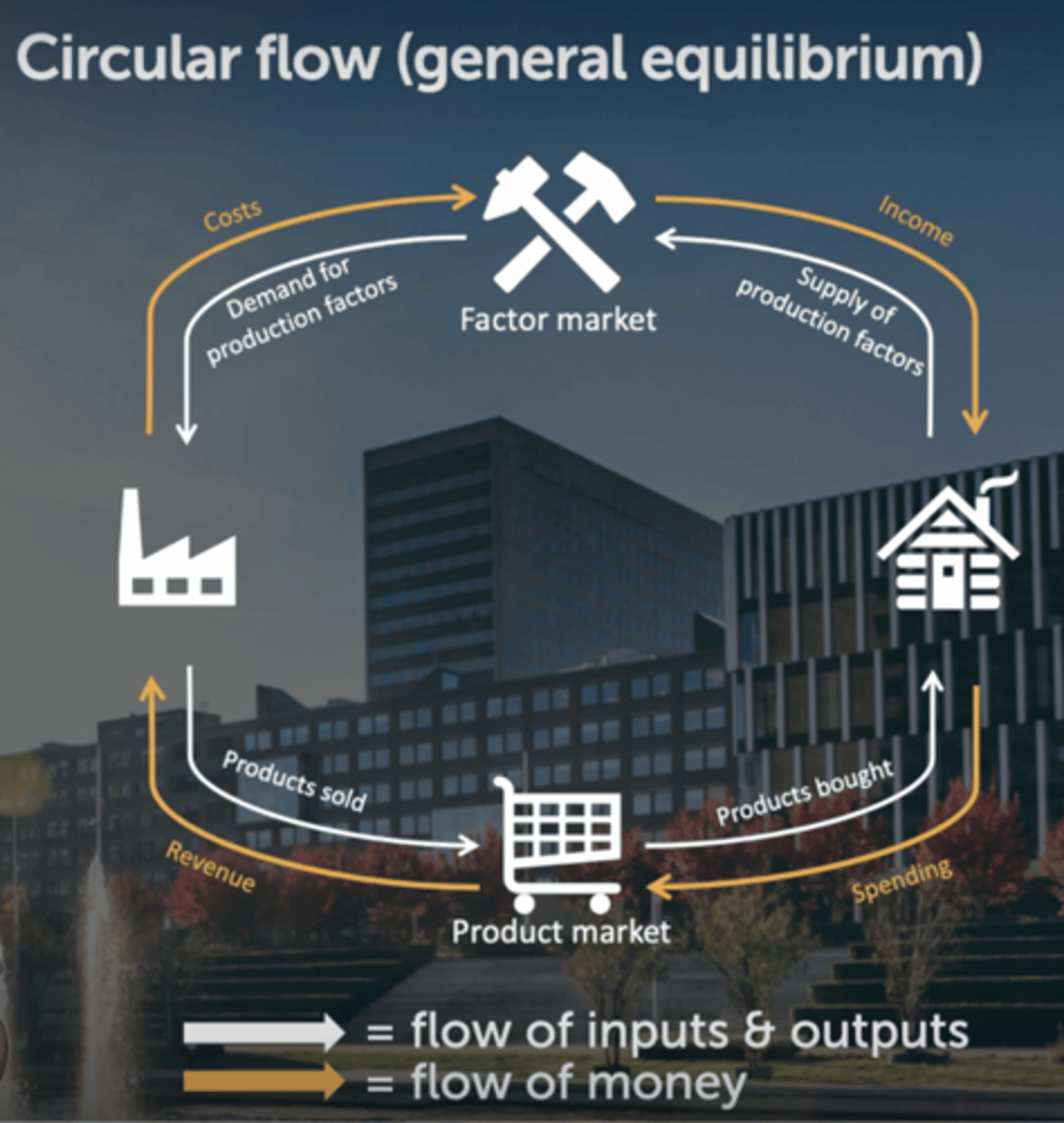
What does the circular flow (economische kringloop) look like?
= circulation of money, goods and services between different sectors of the economy
focus is on the flow of economic activity and income between these sectors which shows how they're interdependent
What are some more characteristics of a general equilibrium? (6)
1) all markets function properly
2) optimal allocation of inputs and outputs is achieved
3) consumers are maximizing utility &
producers are maximizing profit at the minimum average cost
4) no economic agent can increase total economic welfare of society
5) collective utility of society is set to be optimal
6) free markets are the best way to organize economic activity
--> government should not intervene
What can cause government to intervene?
when there is... (6)
1) substantial market power
- market power of producers can cause: higher prices, reduced output, inefficiencies in allocation and production, stifling innovation, and maintaining barriers to entry
- market power of workers can cause unions
2) Common property resources
- tragedy of the commons --> firms, led by self-interest, overuse and exploit a shared source --> which leads to the destruction of that source
- e.g. fishing ground: the ocean is not anyones property but anyone can benefit from it by fishing in it and selling that fish, until eventually there might not be any fish left
3) Side effects of economic activities
- externalities --> side effects of the economic activity for people who did not choose to be involved --> they can be beneficial or harmful
- e.g pollution
4) Provision of public goods
- nobody can get excluded from a public good --> people have no incentive to pay for the good --> free-riding
- e.g. defense
5) Merit goods or demerit goods
= goods that can be produced by the market, but are considered good or bad for society --> if left to production by the market, these goods either get under- or overproduced --> in this case governments will intervene by subsidizing merit goods and taxing demerit goods
- merit goods = beneficial goods that society thinks people should consume (more of)
e.g. eduction
- demerit goods = harmful goods that society thinks people should consume less of
e.g. alcohol and cigarettes
6) Unequal distribution of income
How do governments finance their spending?
by taxing firms and households
What is the relationship between circular flow and general equilibrium?
The circular flow model helps explain how money and resources move through an economy, while general equilibrium focuses on the balance achieved when all markets are in harmony.
The circular flow can be a part of understanding how general equilibrium is reached, but they are distinct concepts
Governments develop all sorts of policies to improve and influence market outcomes. What 4 categories are there of these policies?
1) direct price control
2) indirect price control: taxation and subsidies
3) policies that counter the market power
- especially monopolies and oligopolies
4) policies that focus on (more) efficient allocation of resources
- due to externalities
What is direct price control?
- price ceiling = legal maximum price
- price floor = legal minimum price
With a price floor..
1. minimum price is higher or lower than the equilibrium price?
2. leads to a surplus or a shortage?
3. Qs > Qd or Qs < Qd?
1. minimum price is higher than the equilibrium price
2. leads to a surplus
3. quantity supplied is larger than quantity demanded (Qs > Qd)
With a price ceiling...
1. maximum price is higher or lower than the equilibrium price?
2. leads to a surplus or a shortage?
3. Qs > Qd or Qs < Qd?
1. maximum price is lower than the equilibrium price
2. leads to a shortage
3. quantity supplied is less than the quantity demanded (Qs < Qd)
What are the challenges of direct price control by the government? (2)
1) it can cause undesirable rationing mechanisms
--> to manage the limited supply
2) it can increase inequality among different groups of people
What must governments do before implementing price ceilings and floors?
they must consider potential economic effects
(such as undesirable rationing mechanisms)