Test 2 - Ch 4 Hybridization and MO Theory
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Simple molecules
Overlap of atomic orbitals - look at unpaired e-
Example: H2 - 1s1 (Simple molecules)
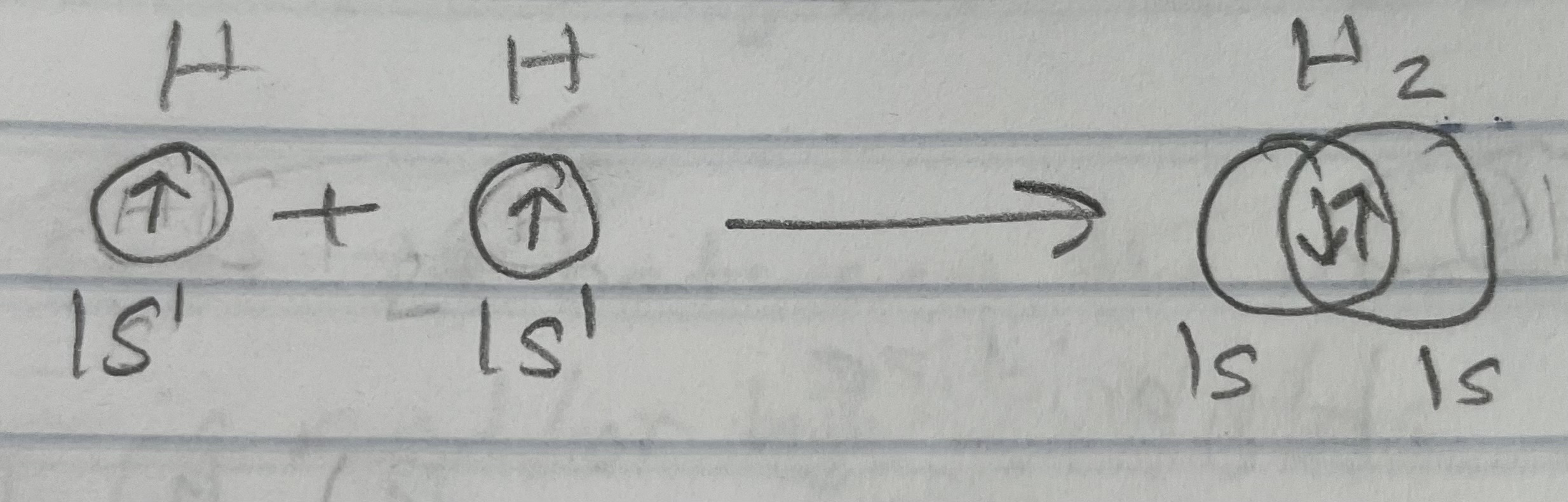
Example: Cl2 - [Ne]3s2 3p5 (Simple molecules)
Filled 3s orbital so use unpaired e- in 3p orbital
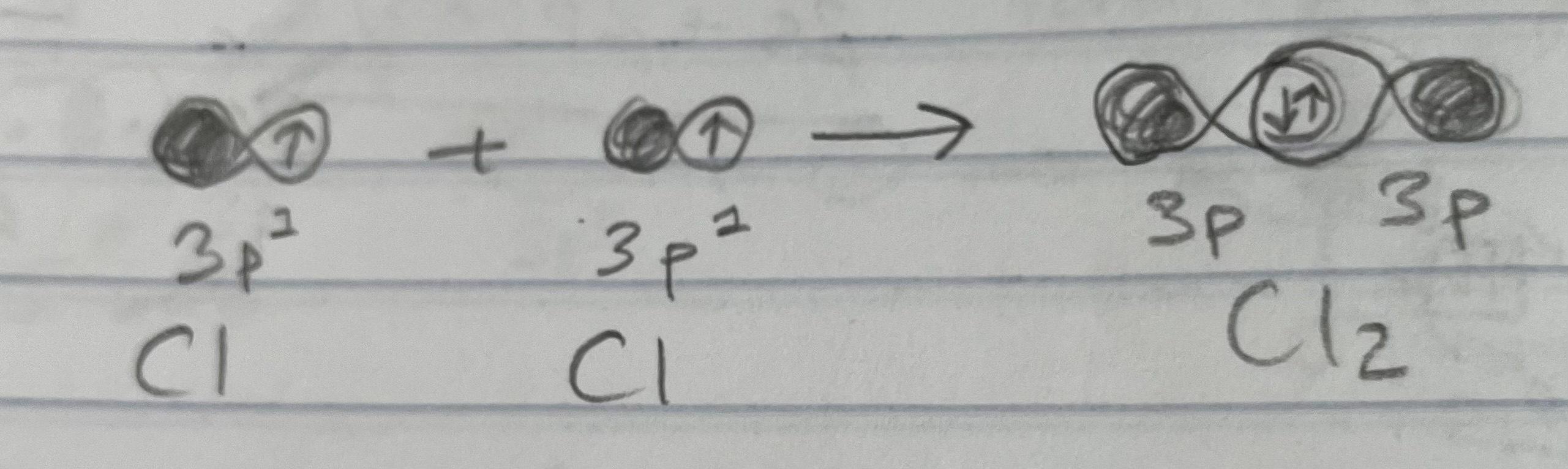
Example: HCl, H: 1s1, Cl: 3p1 (Simple molecules)
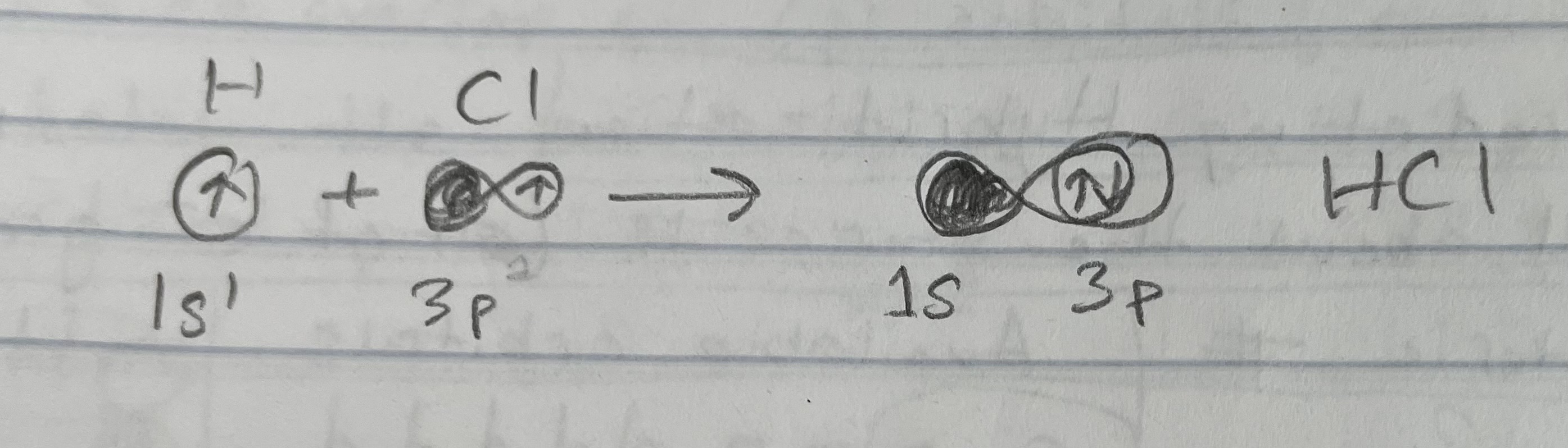
Types of Orbitals: sp
Geometry: linear
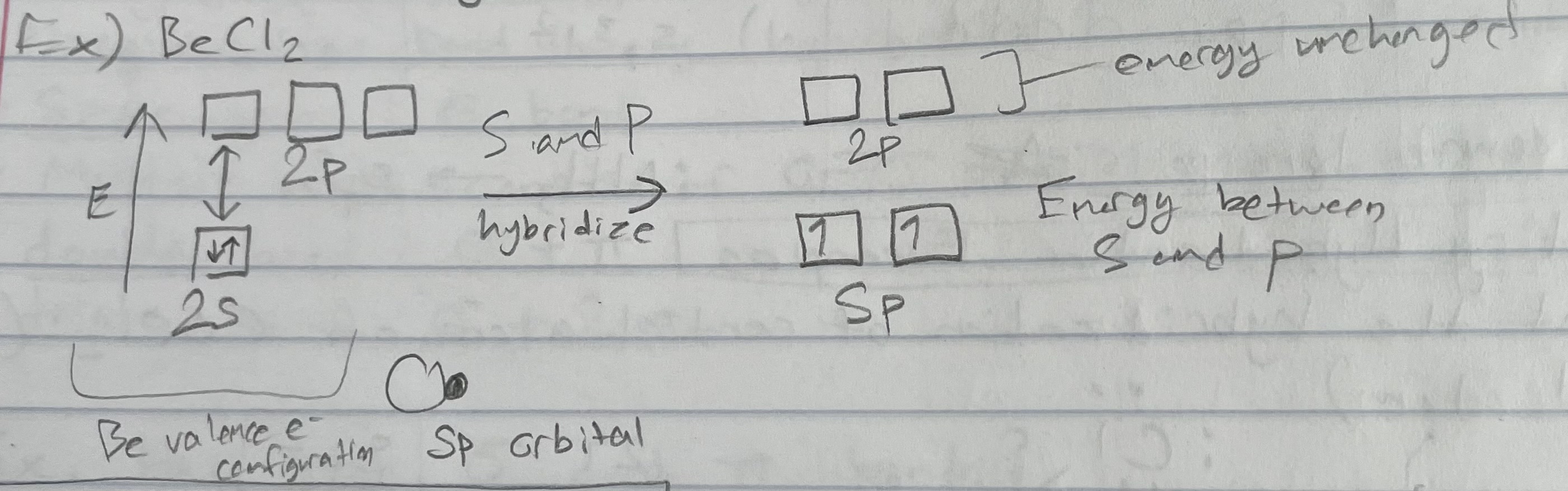
Types of Orbitals: sp2
Geometry: Trigonal Planar
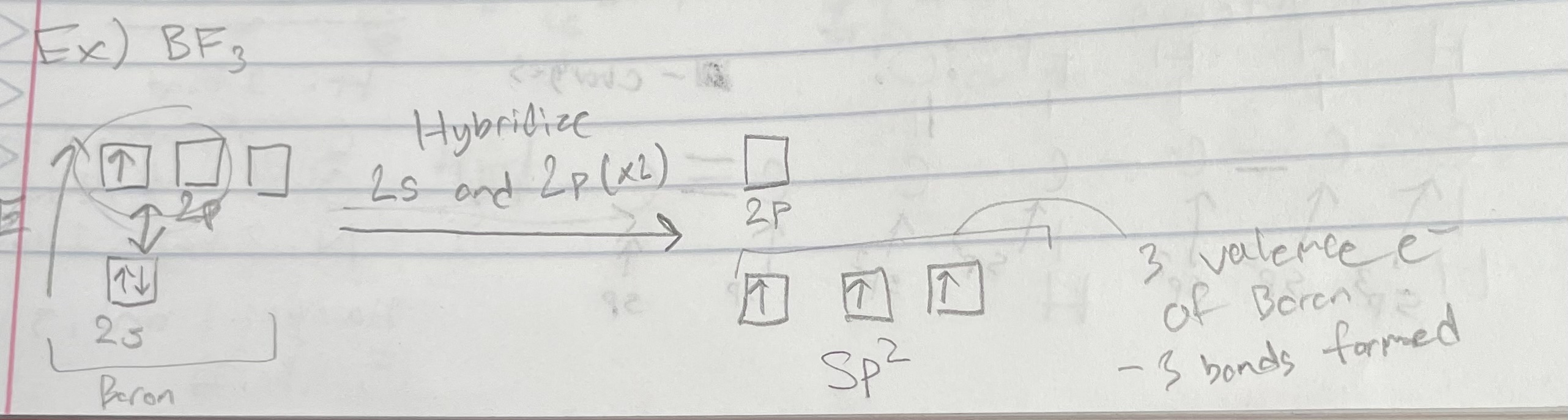
Types of orbital: sp3
Geometry: tetrahedral
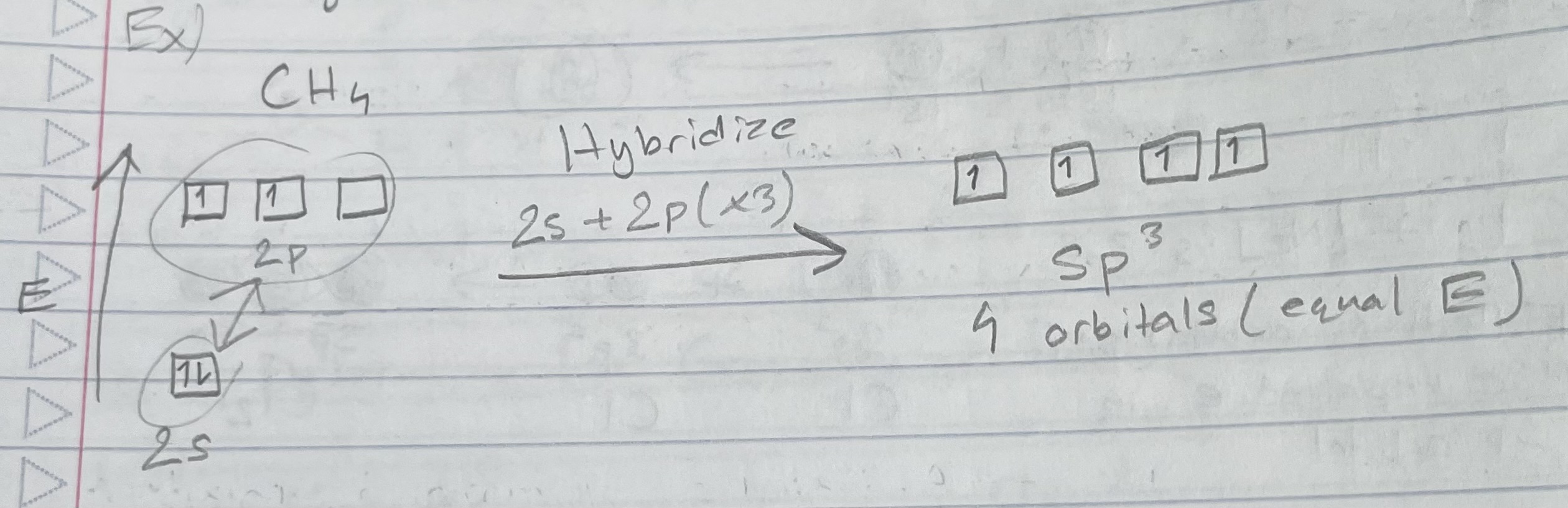
Predicting hybridization
all about the steric # (# of e- groups)
Also count lone pairs(Ex:NH3 - sp3)
Steric # 2 - sp
Linear
Steric # 3 - sp2
Trigonal planar
Steric # 4 - sp3
Tetrahedral
Steric # 5 - sp3d
Trigonal bipyramidal
Steric # 6 - sp3d2
Octahedral
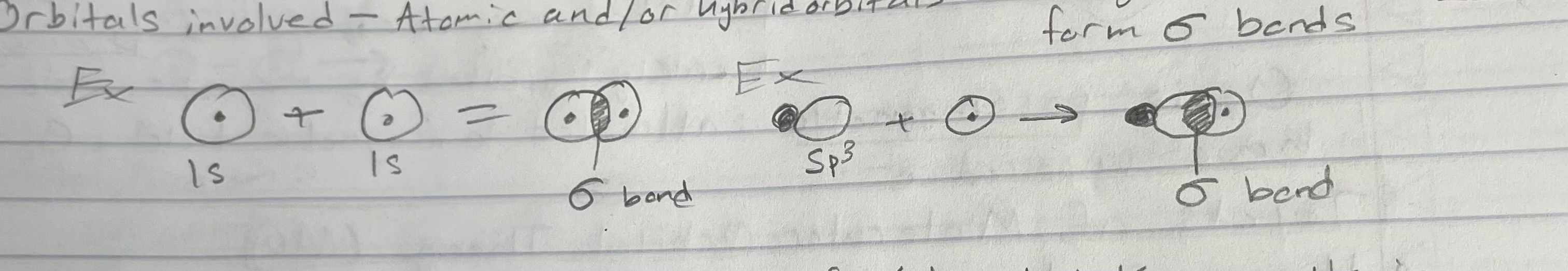
Sigma (σ) bonds
Bonds formed by end-to-end overlap of atomic hybrid orbitals
e- density greatest in between the nuclei: right along the bond axis
Orbitals involved - atomic and/or hybrid orbitals (hybrid orbitals only form σ bonds
Pi (π) bonds
side-to-side overlap of p orbitals, results in e- density above and below the bond axis
Orbitals involved - unhybridized p orbitals ONLY
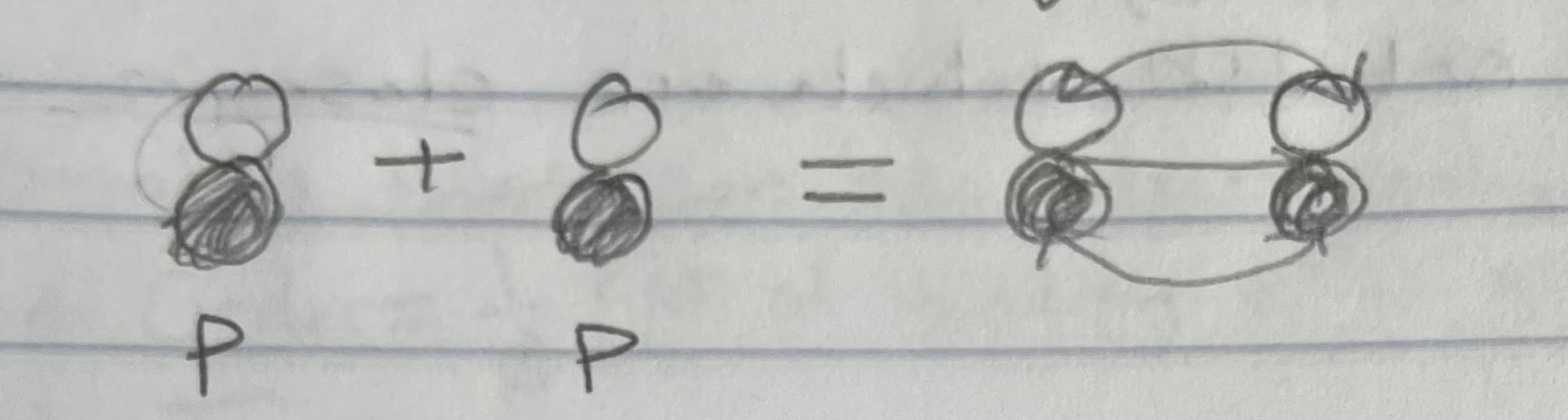
Single bond
σ bond
Double bond
σ + 1π bond
Triple bond
σ + 2π bond
Example of pi/sigma bond
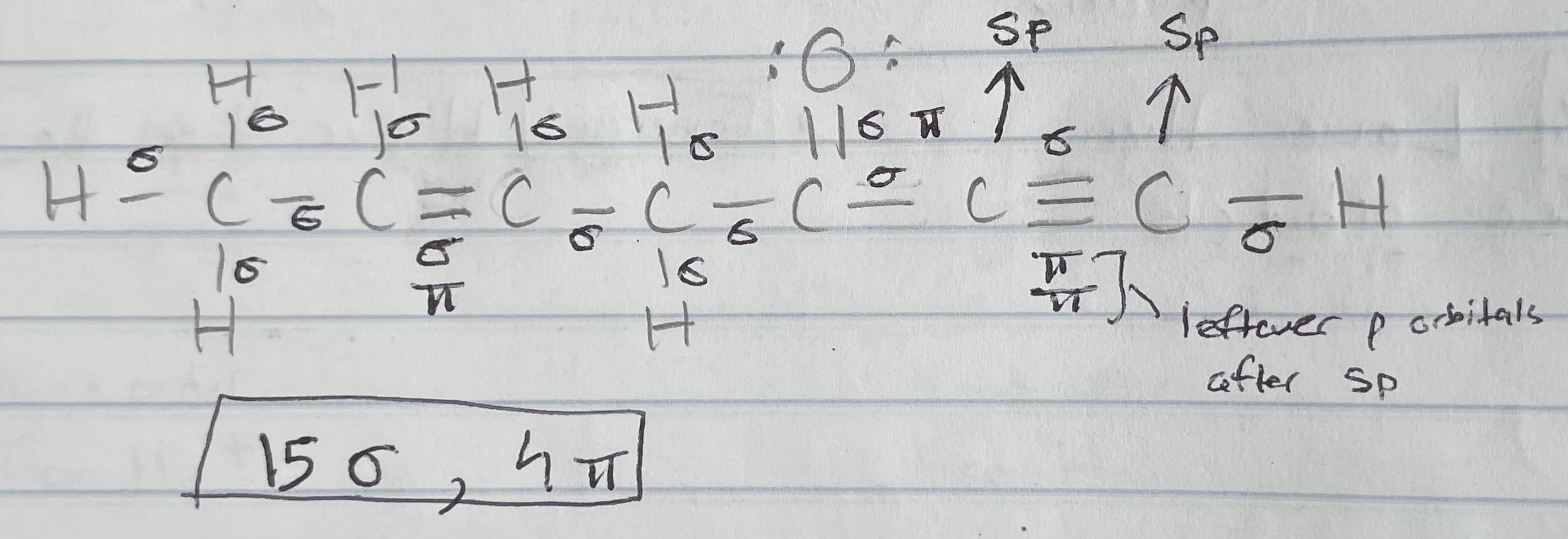
Diamagnetic
Weakly repelled by magnetic field
Paramagnetic
Attracted to magnetic field. Must have unpaired e-
Tenets of Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
Mixing of atomic orbitals: atomic wave fxn’s mathematically combined (linear combination add/subtract) to form delocalized molecular orbitals
Energy considerations: only valence orbitals which are close in energy can mix
VALENCE ORBITALS
Bonding Orbitals (types of orbitals)
Wave fxn: AO1 + AO2 (additive combination - in phase)
e- density: greater along the bond (between nuclei)
Energy: lower than the AO’s
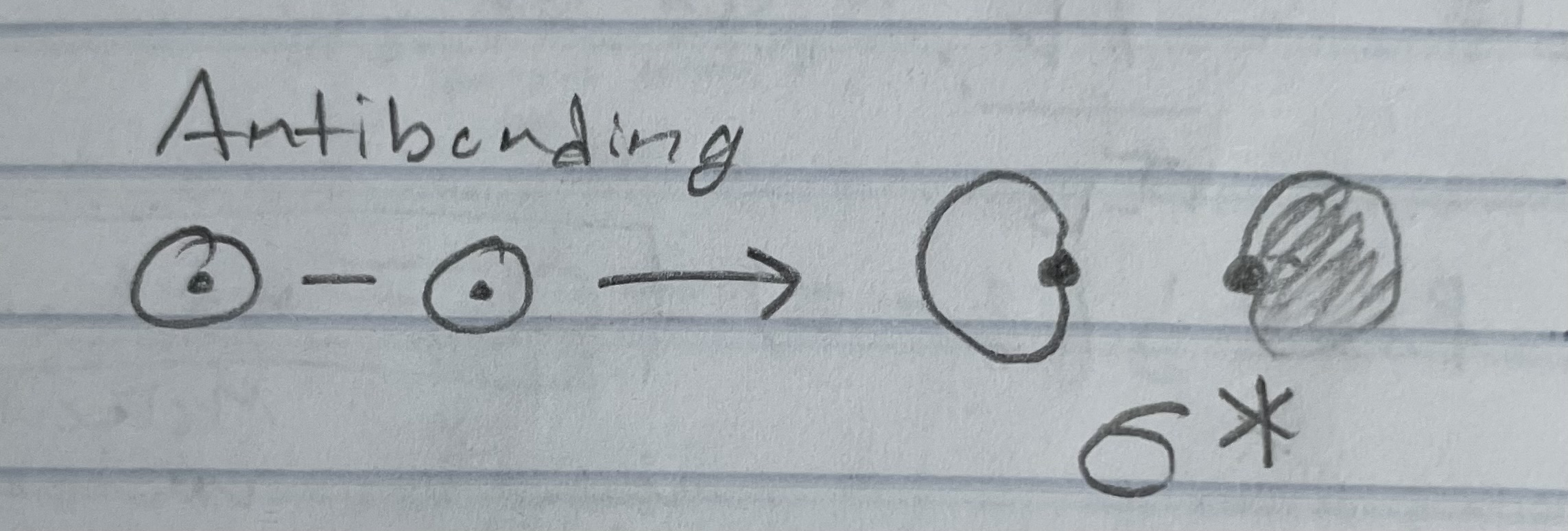
Antibonding orbitals (types of orbitals)
Wave fxn: AO1-AO2 (subtractive combination - out of phase)
e- density: greater outside the internuclear region
Energy: higher than the AO’s
Shapes: bonding orbital (MO’s for 1s orbital)
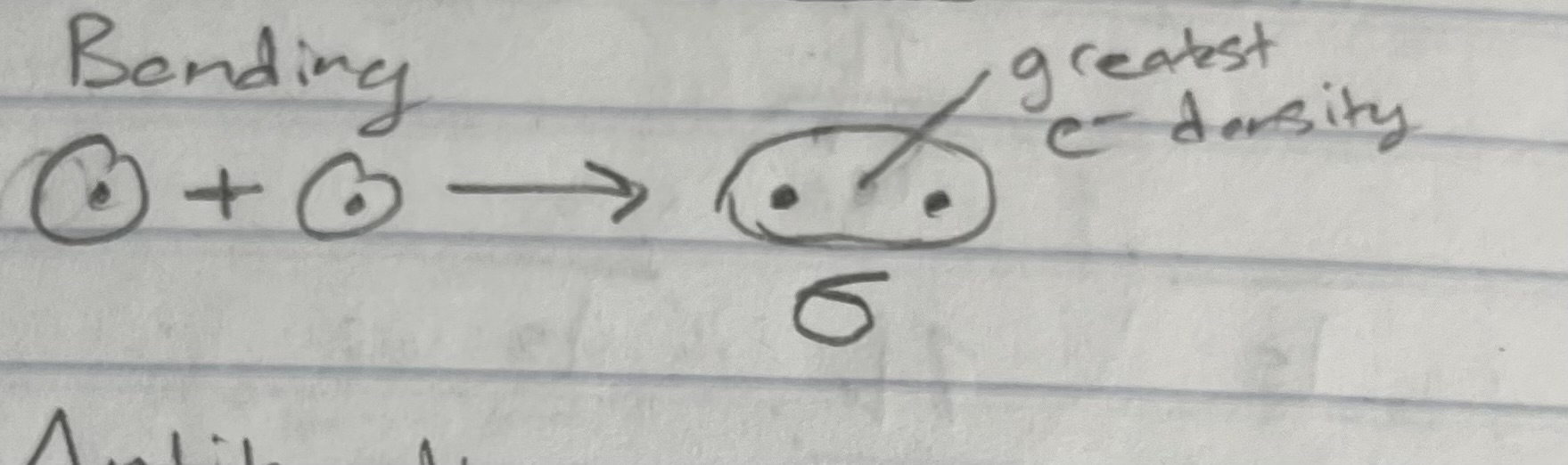
Shapes antibonding orbital (MO’s for 1s orbital)
Orbital diagram structure
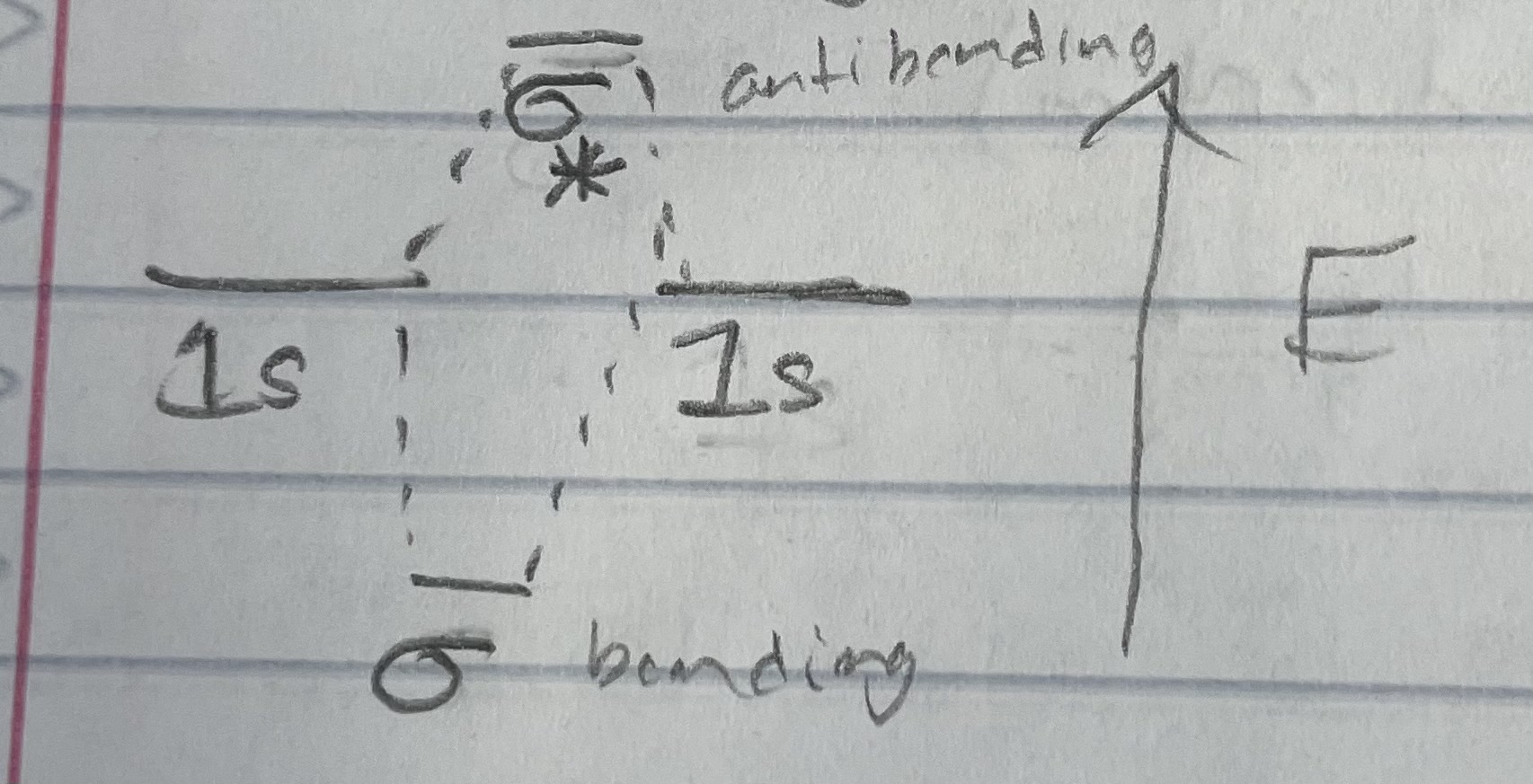
Parameters than can be determined from MO Diagram
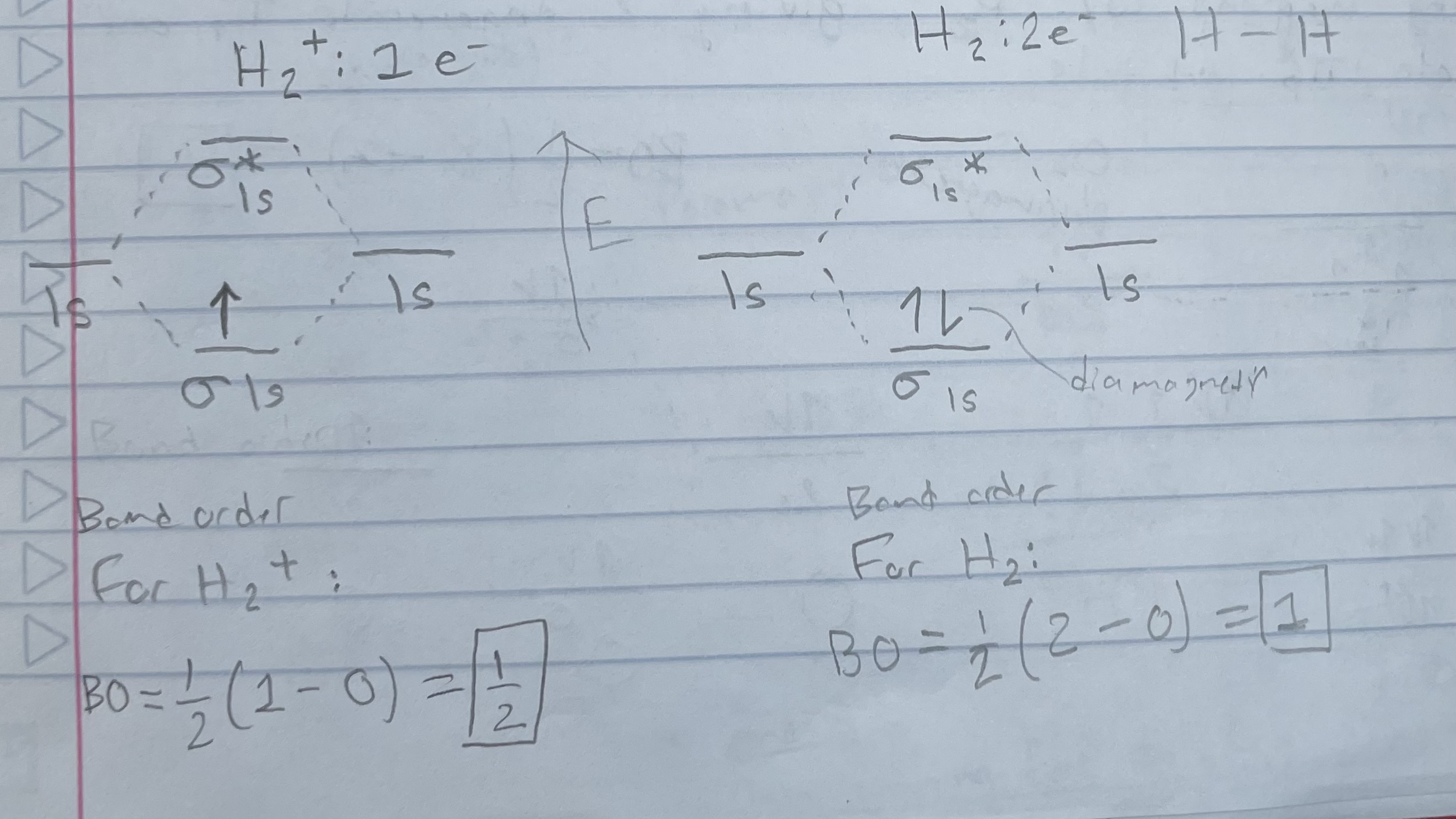
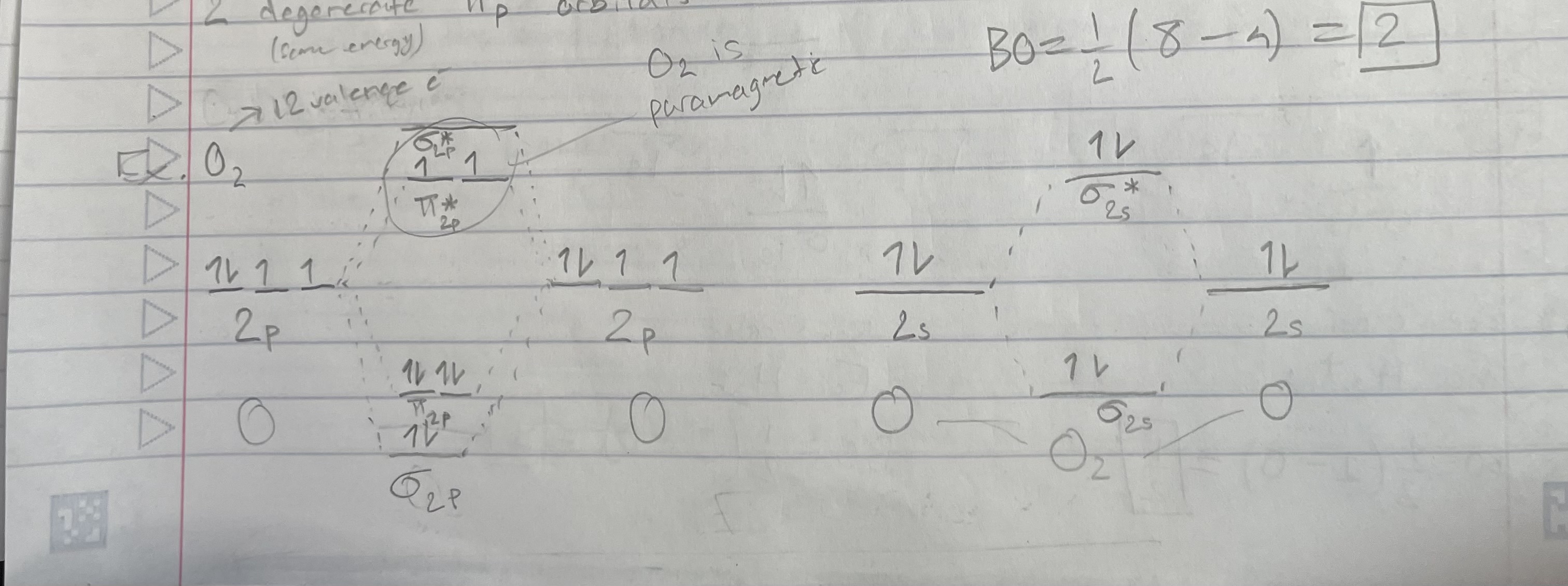
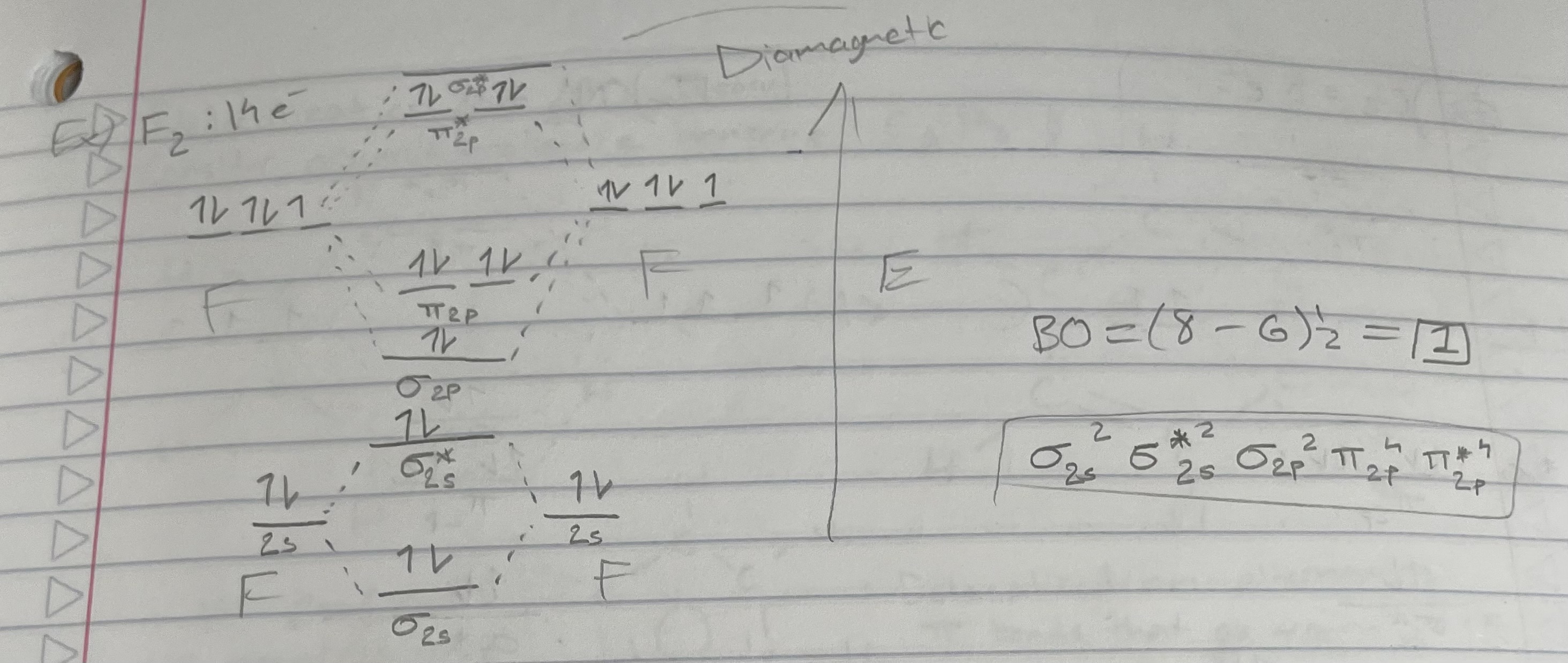
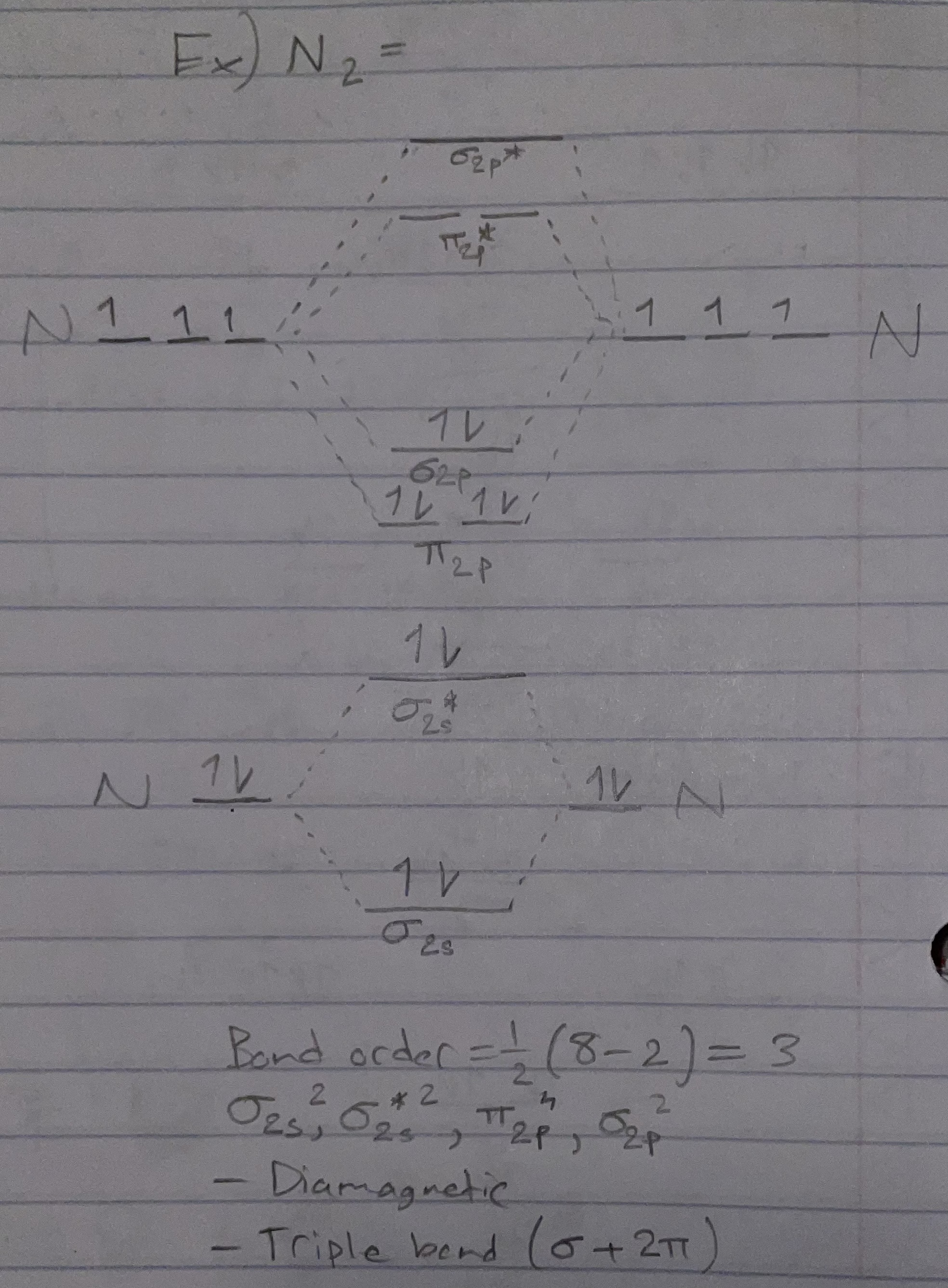
Bond order = 1/2(# bonding e - # antibonding e)
Bond types: sigma vs pi
Magnetic properties:
Diamagnetic: all e- are paired
Paramagnetic: 1+ unpaired e-
H2+ vs H2 (orbital diagram)
H2- and He2 (orbital diagram)
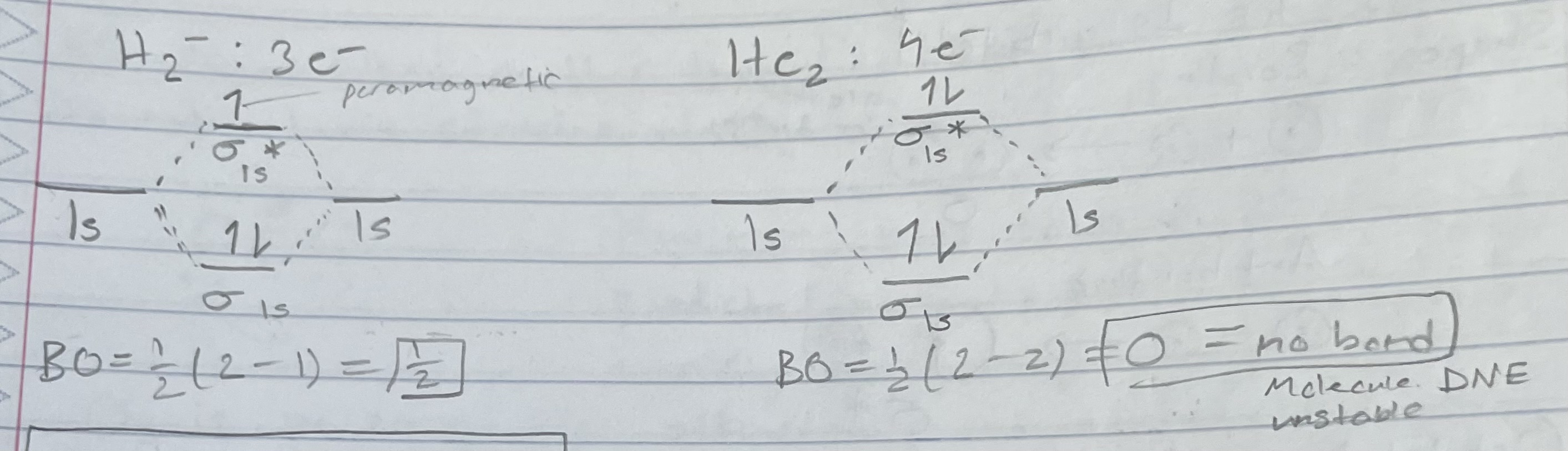
Sigma p MO’s (what about p orbitals?)
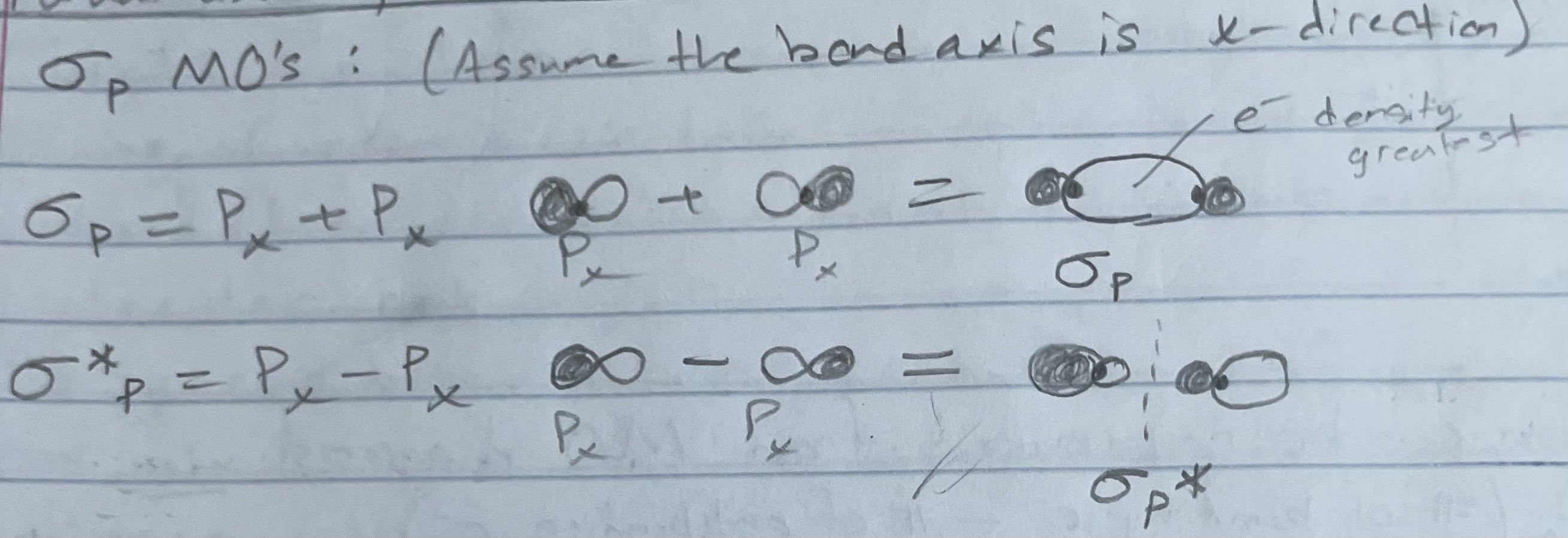
Pi p MO’s (what about p orbitals?)
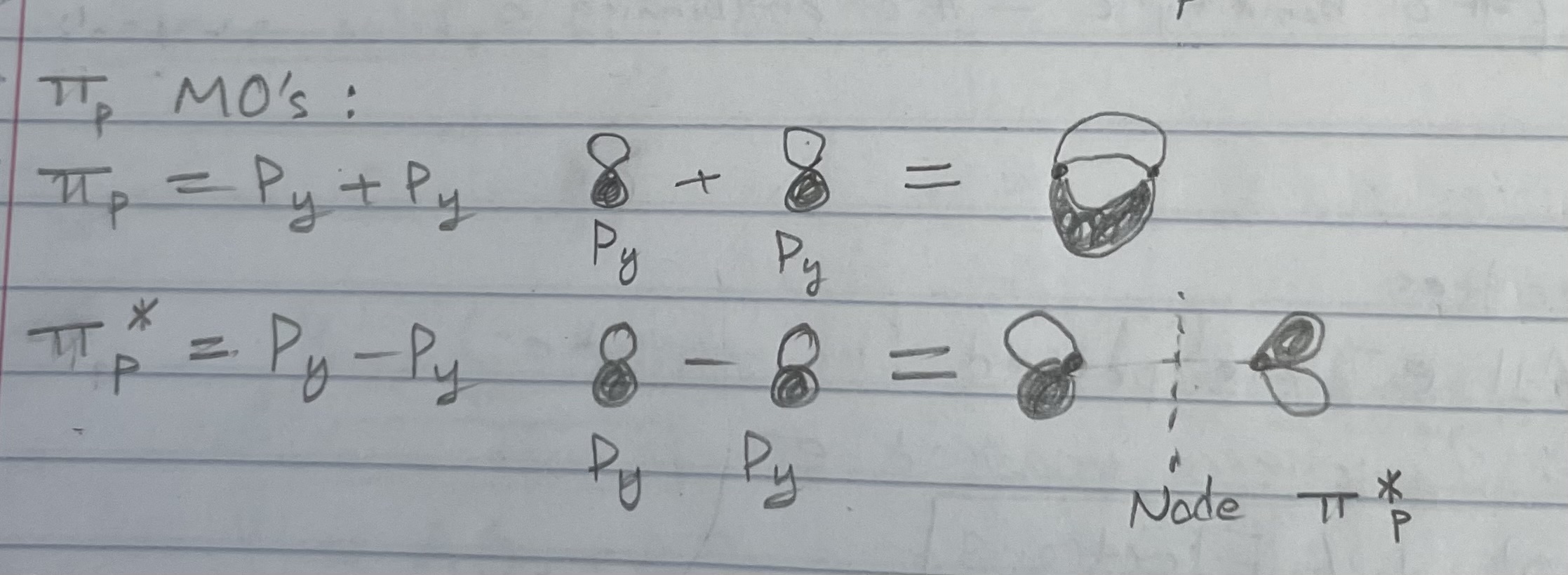
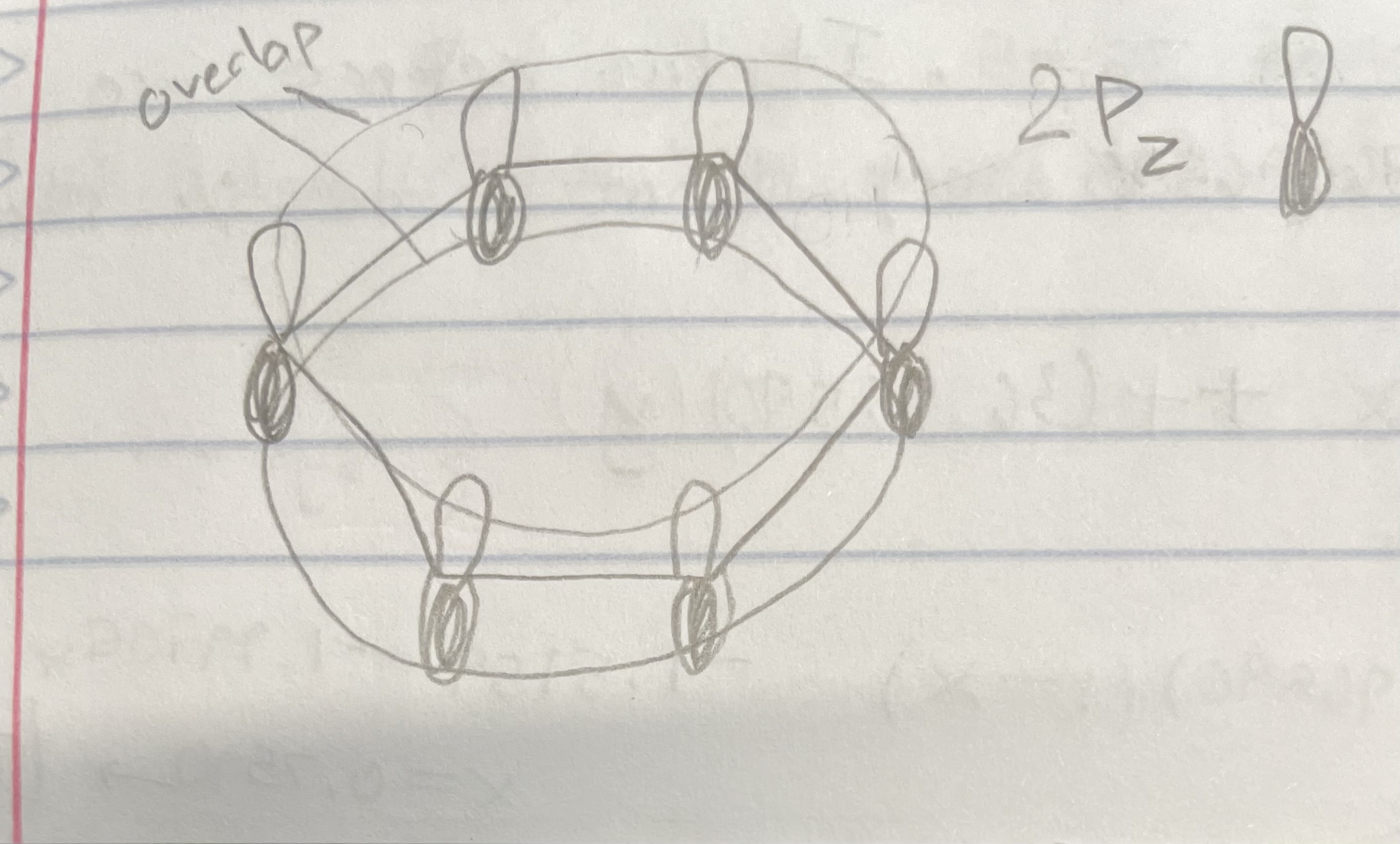
Pz (what about p orbitals?)
Same thing happens w/ Pz, giving 2 degenerate Pi p and 2 degenerate Pi*p orbitals
O2 (orbital diagram)
F2 (orbital diagram)
Ne2 (orbital diagram)
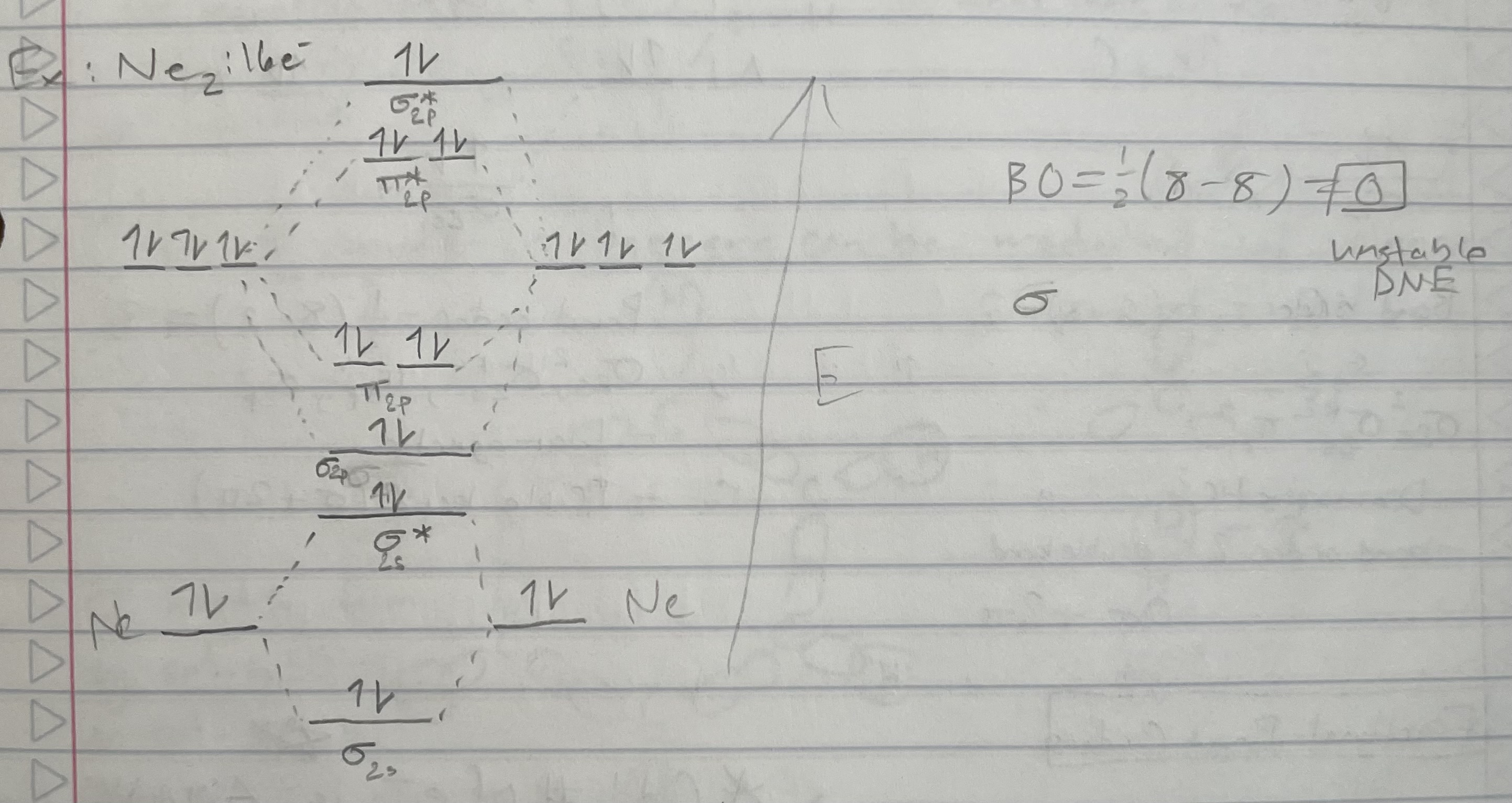
B2 (orbital diagram)
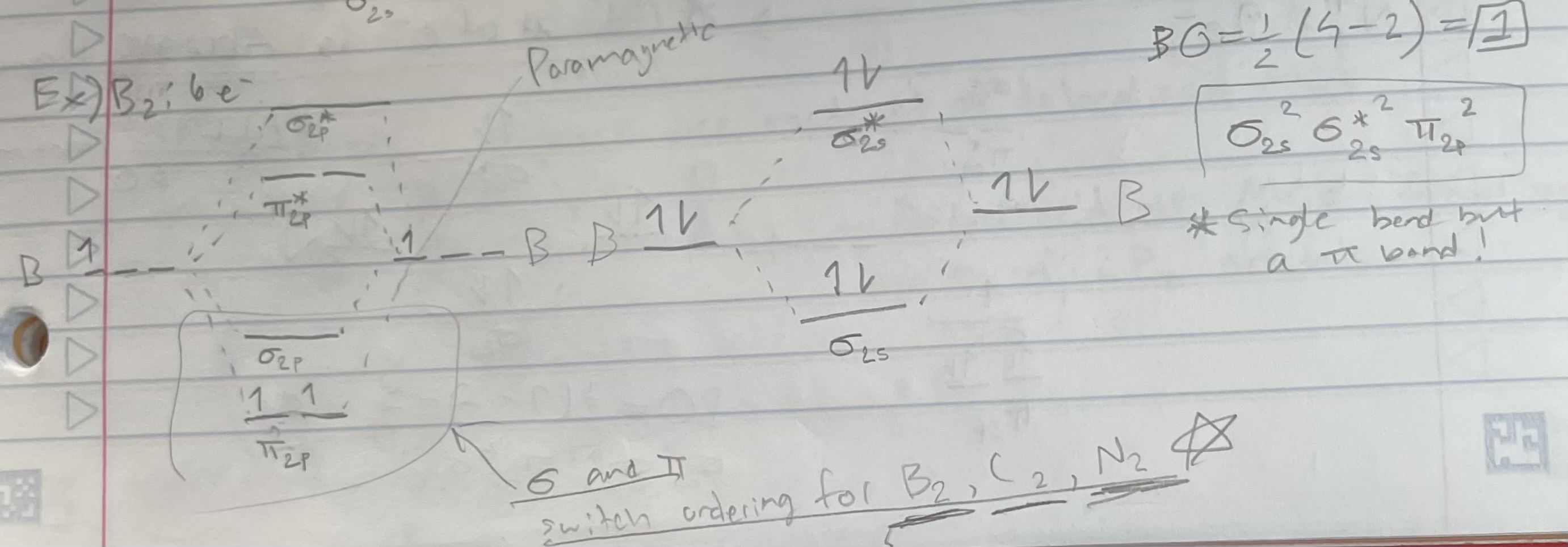
C2 (orbital diagram)
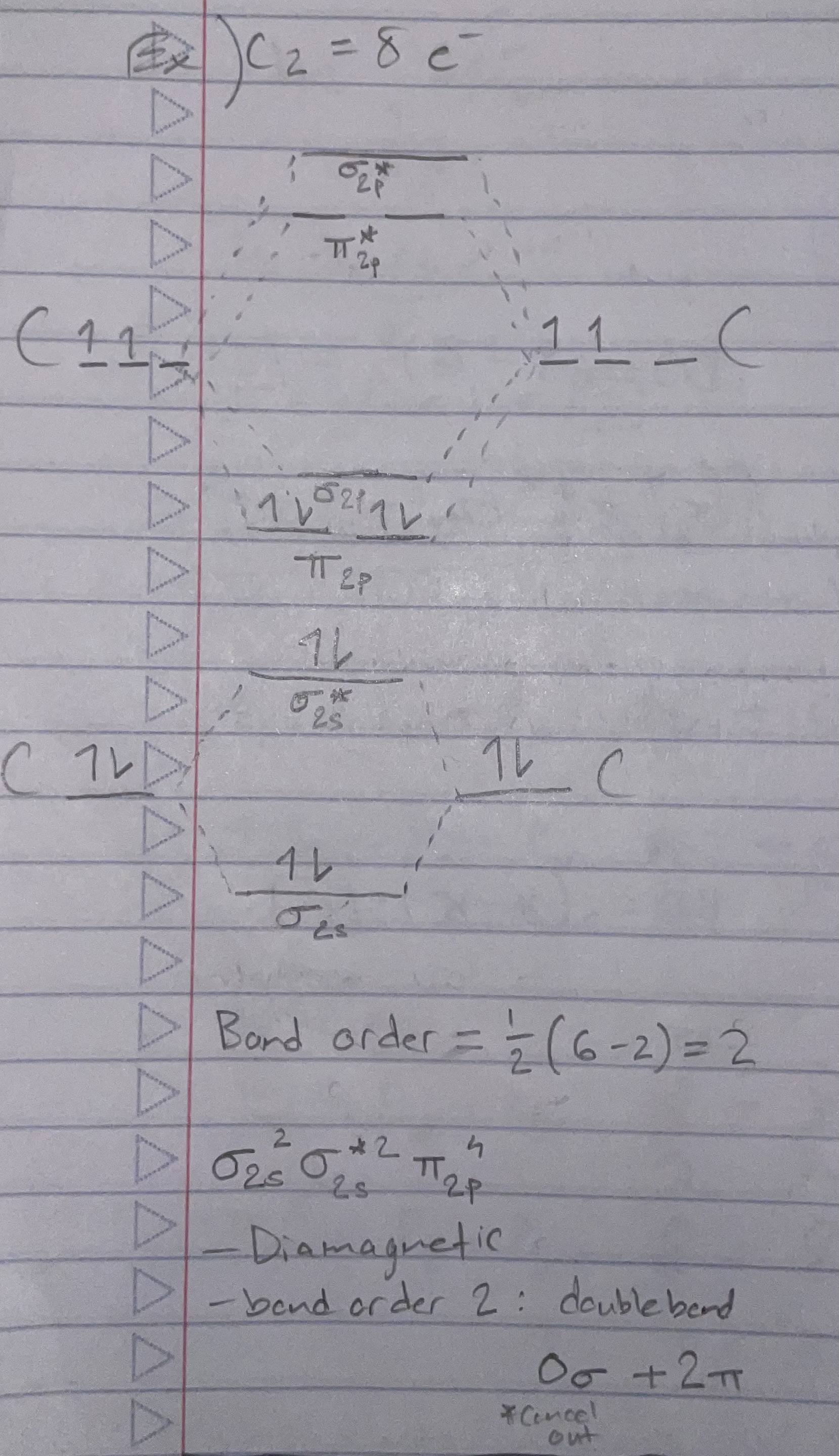
N2 (orbital diagram)
Fractional bond orders: N2+
Shortcut: ODD # OF e- IS ALWAYS PARAMAGNETIC AND ALWAYS FRACTIONAL BOND ORDER
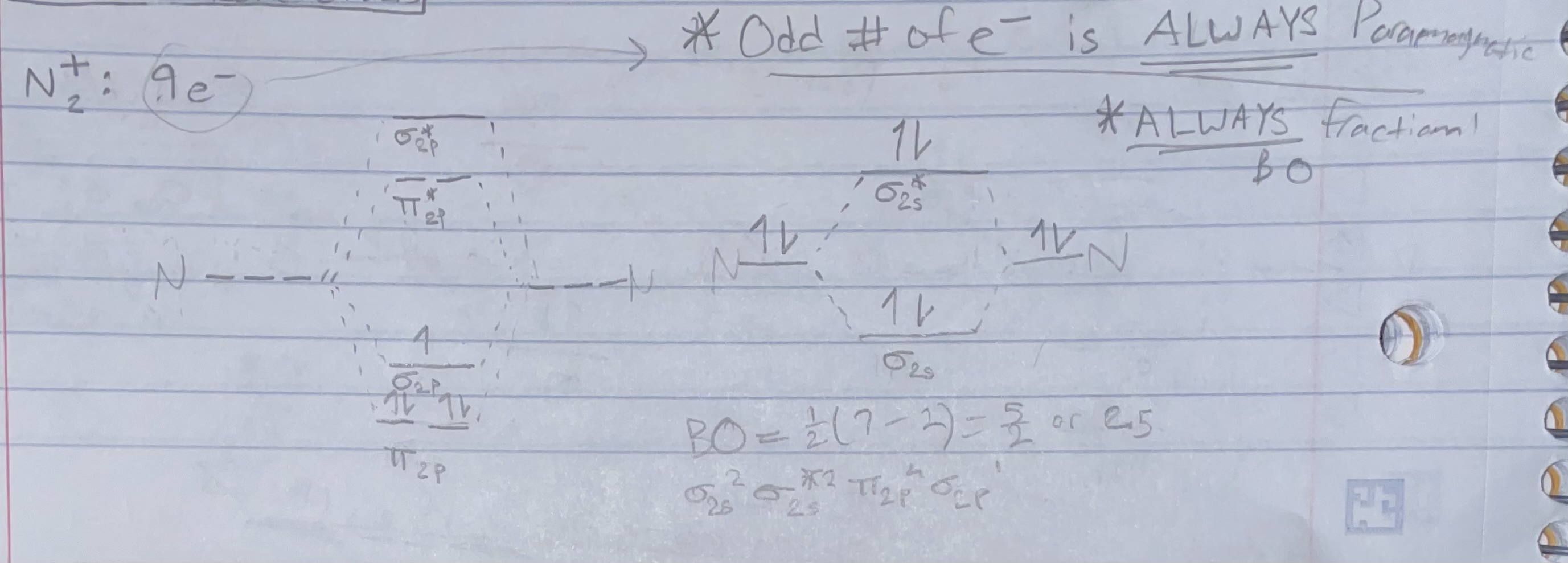
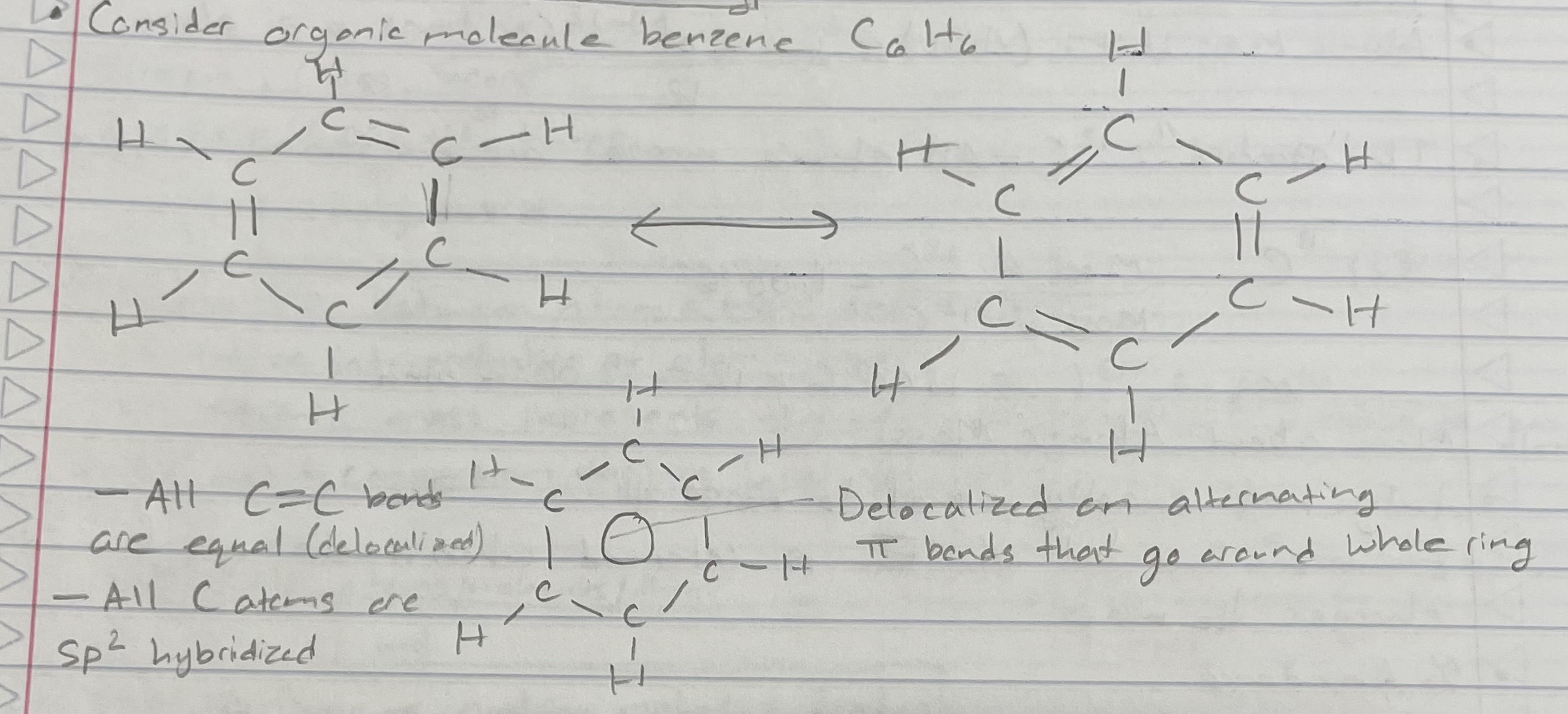
Benzene C6H6 (Delocalization and MO Theory)
All the C=C bonds are equal (delocalized)
All C atoms are sp2 hybridized
Delocalized and alternating pi bonds that go around whole ring
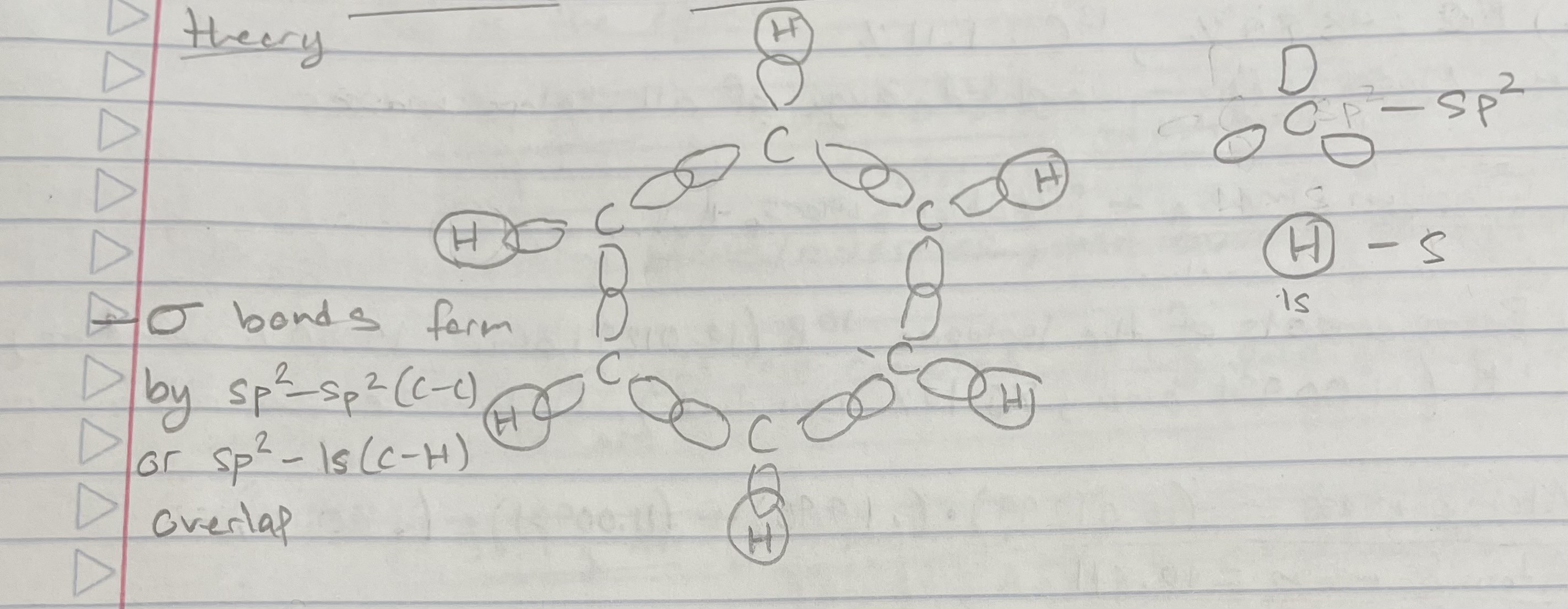
The sigma bonds in benzene can be modeled w/ valence bond theory (Delocalization and MO Theory)
Sigma bonds are formed by sp2-sp2 (C-C) or sp2-1s (C-H) overlap
The pi bonds in benzene are modeled as delocalized MO’s
Delocalized pi MO’s, formed by overlap of 2Pz orbitals