Cell Biology
1/104
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
What are eukaryotic cells?
plant and animal cells
What are prokaryotic cells?
bacterial cells
What's bigger: eukaryotes or prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes
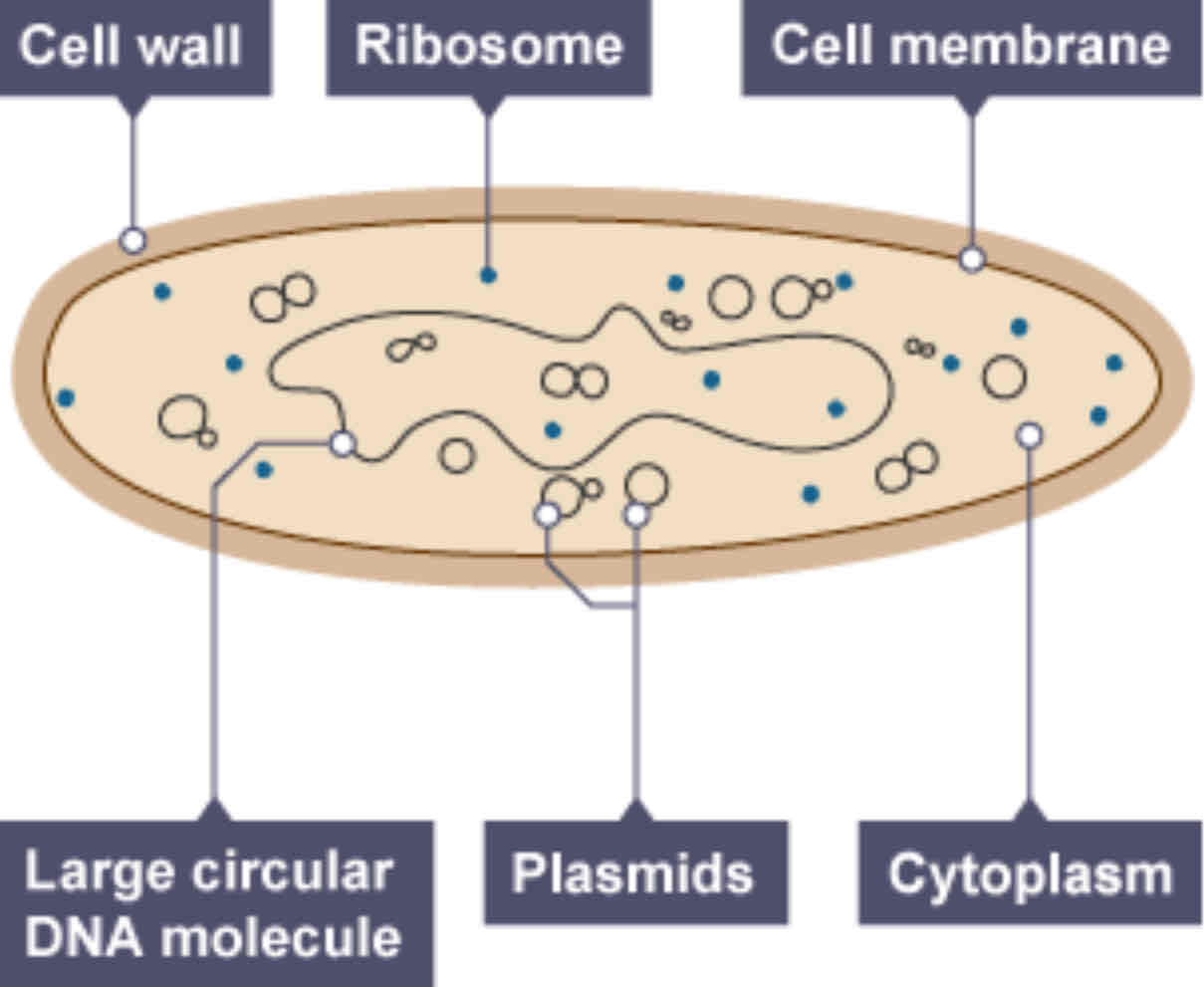
Parts of a bacterial cell
★ Cytoplasm ★ Cell membrane ★ Cell wall ★ Loop of DNA ★ Plasmids (rings of DNA)
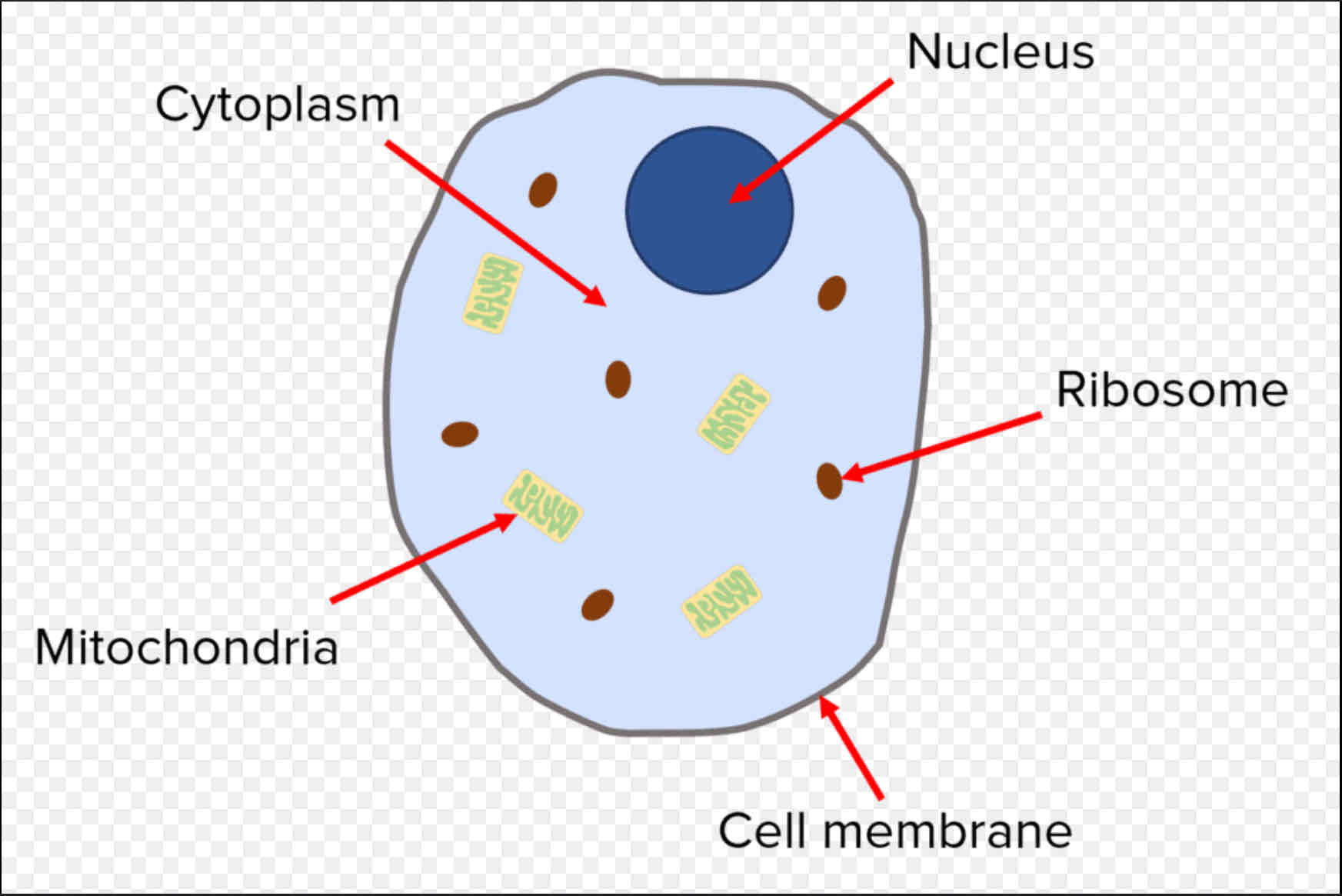
What are the parts of an animal cell?
★ Cell membrane ★ Cytoplasm ★ Nucleus ★ Mitochondria ★ Ribosomes
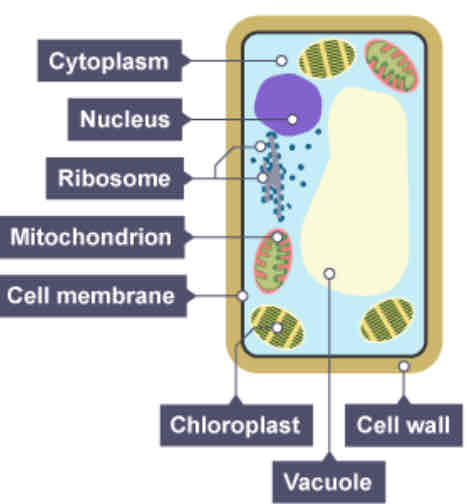
What organelles are part of a plant cell but not an animal cell?
★ Cell wall ★ Permanent vacuole ★ Chloroplast
What's the function of the cell membrane?
Only allows certain substances to enter the cell. The 'gatekeeper' of the cell

What's the function of the Cytoplasm?
Jelly like substance where chemical reactions take place

What's the function of the nucleus?
★ 'brain' of the cell - controls cell activity ★ Contains genetic material
What's the function of mitochondria?
Where aerobic respiration takes place for energy
What's the function of ribosomes?
Where protein synthesis takes place (makes proteins)
What's the function of the cell wall?
provides support and protection
What is the cell wall made of?
cellulose
What's the function of the permanent vacuole?
Contains cell sap
What is cell sap?
A weak solution of sugar and salts
What's the function of chloroplasts ?
Site of photosynthesis
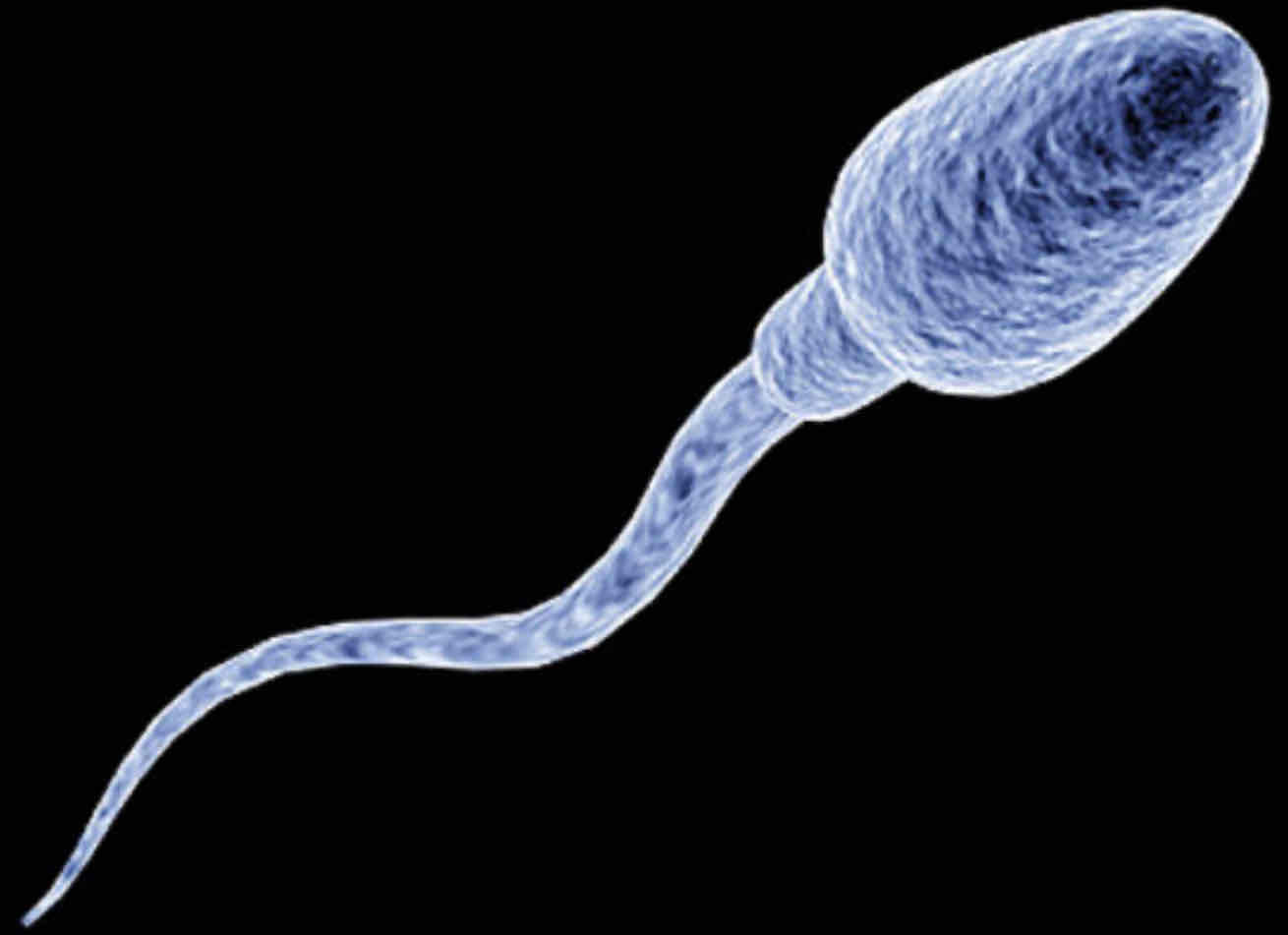
What's the function of a sperm cell?
To fertilise the egg cell
Adaptations of sperm cell
★ Genetic material in the nucleus ★ Tail for swimming ★ Streamlined ★ Lots of mitochondria for energy ★ Enzymes to digest through the ovum
What does streamlined mean?
Shaped to reduce resistance to motion from air or water.
Function of nerve cells
To carry electrical signals from one part of the body to another
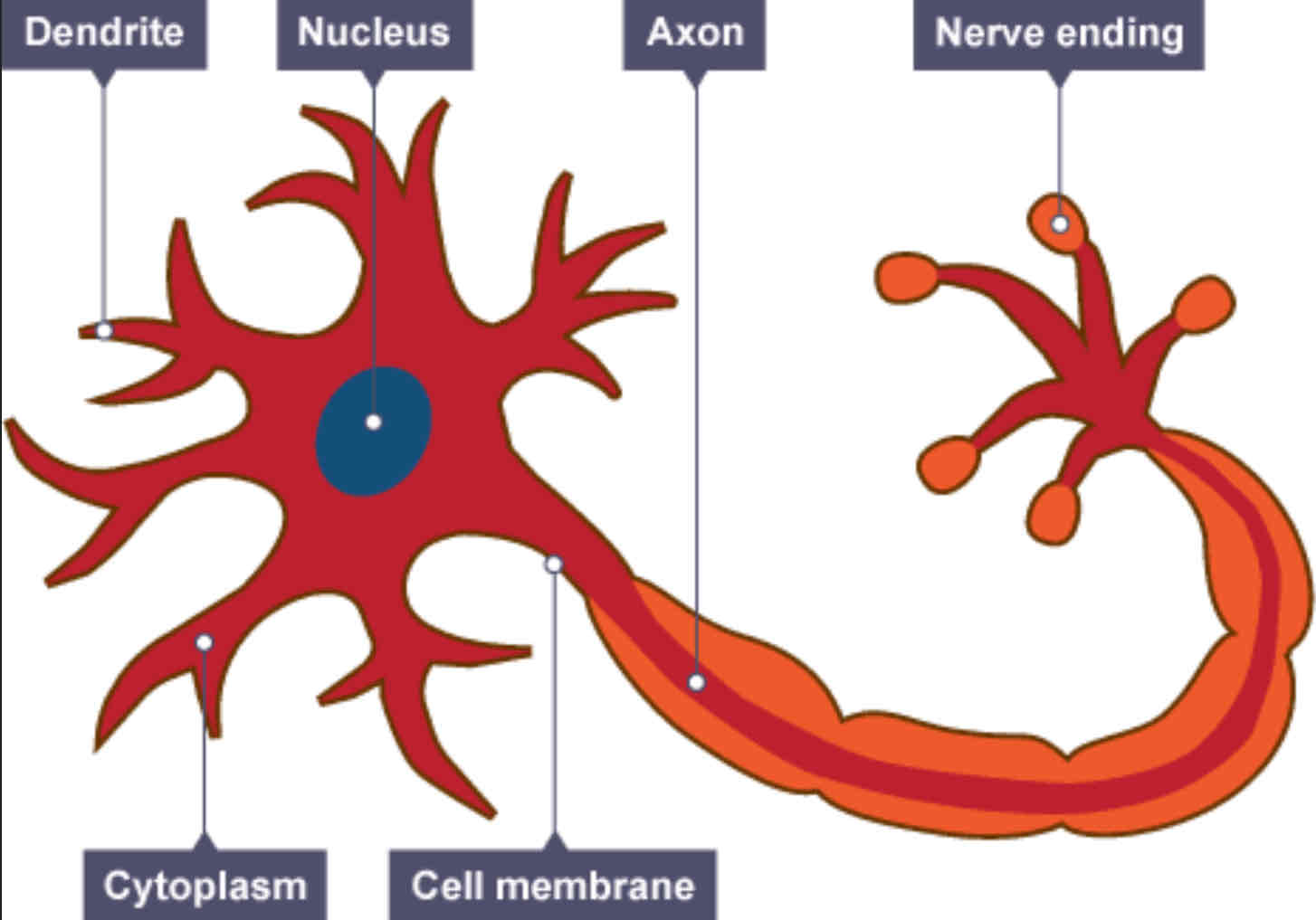
Adaptations of a nerve cell
★ Long axons to carry impulses ★ Myelin speeds up the transmission of impulses ★ Synapses acts as junctions so they can't link to other nerve cells ★ Dendrites so nerve cells can join to other nerve cells more easily
What's the function of a muscle cell?
To contract quickly
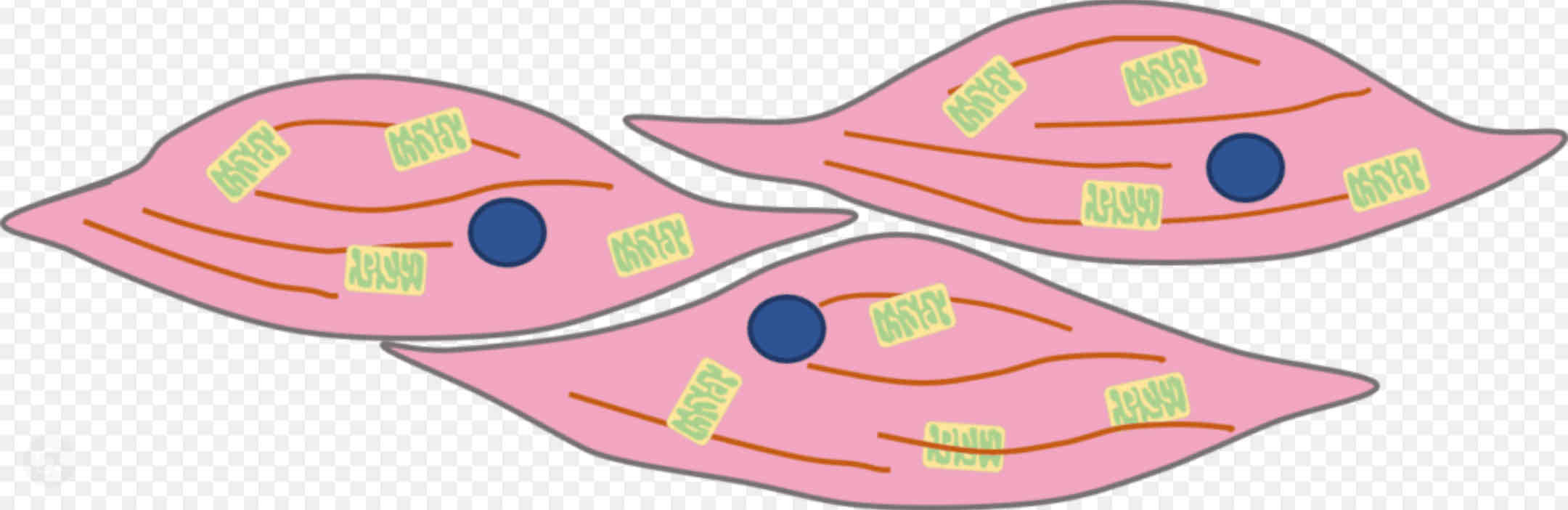
What are the adaptations of the muscle cells?
★ Muscle fibres that can change length ★ Lots of mitochondria for energy
What's the function of a root hair cell?
To absorb water and minerals from the soil
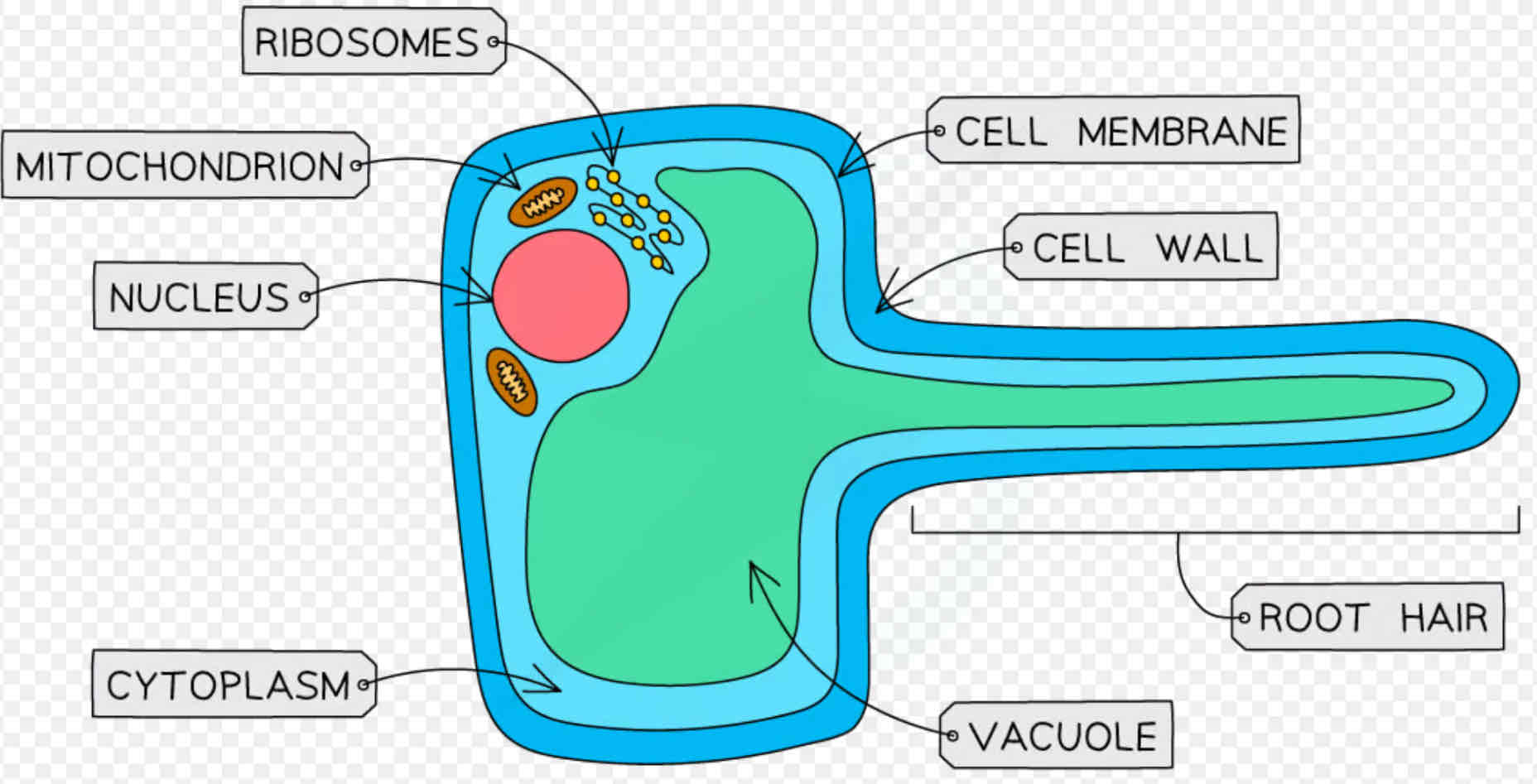
What's the adaptations of a root hair cell?
★ Small hairs to increase SA ★ No chloroplasts as no sunlight underground
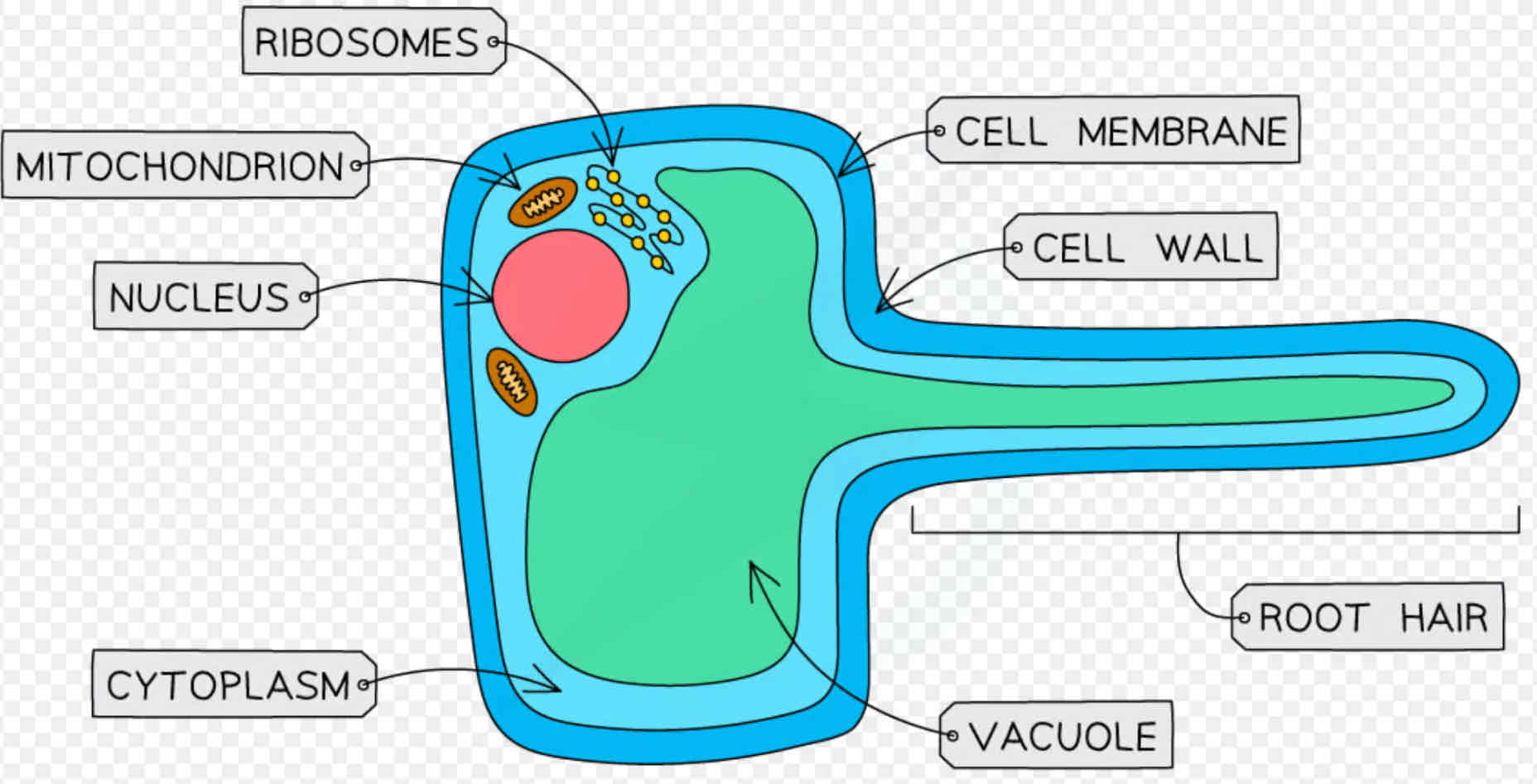
What's the functions of xylem cells?
To transport water and dissolved minerals throughout the plant
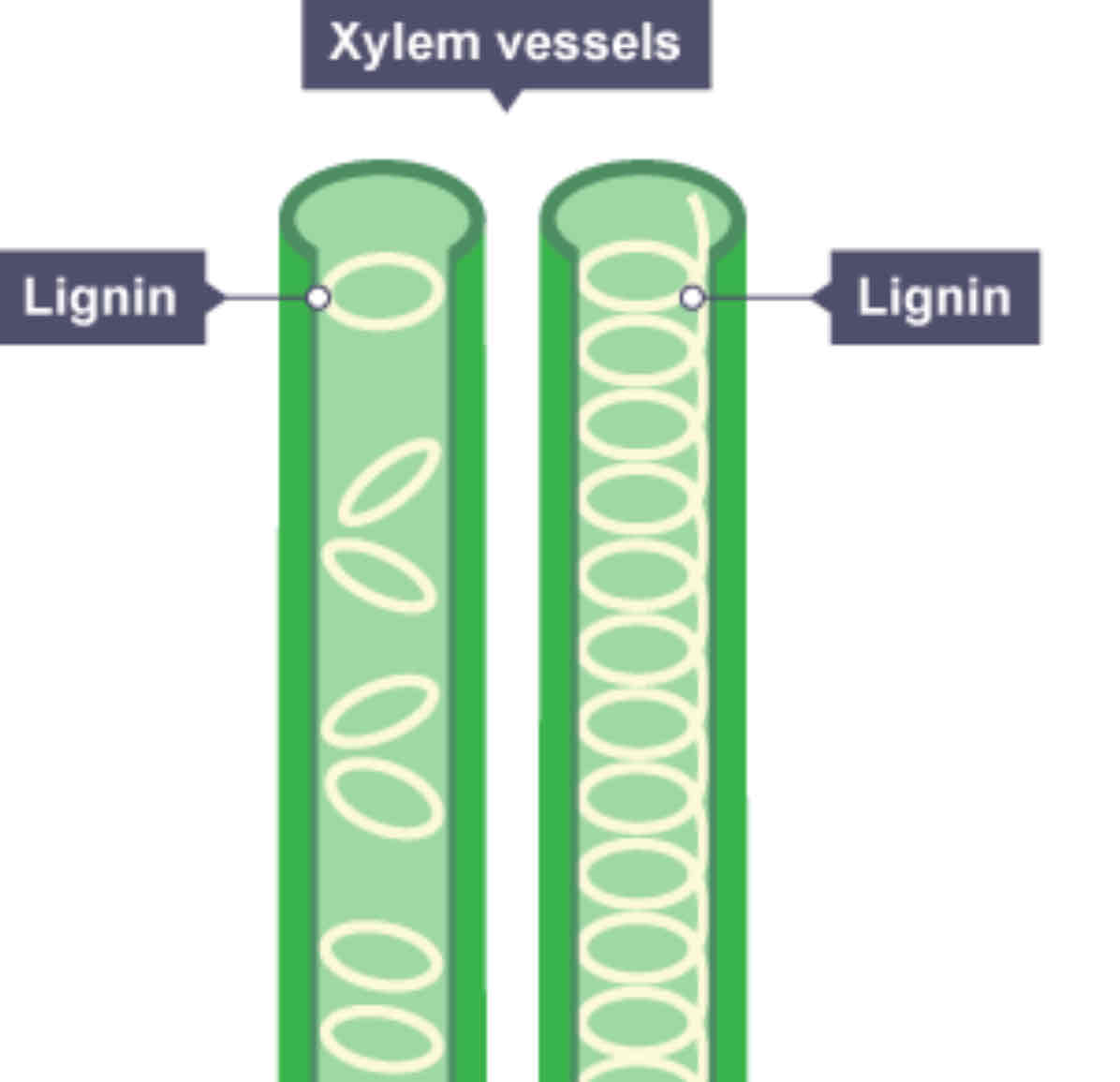
What's the adaptations of a xylem cell?
★ Very thick wall containing lignin providing strength ★ End walls broken down for transport ★Hollow inside for better transportation
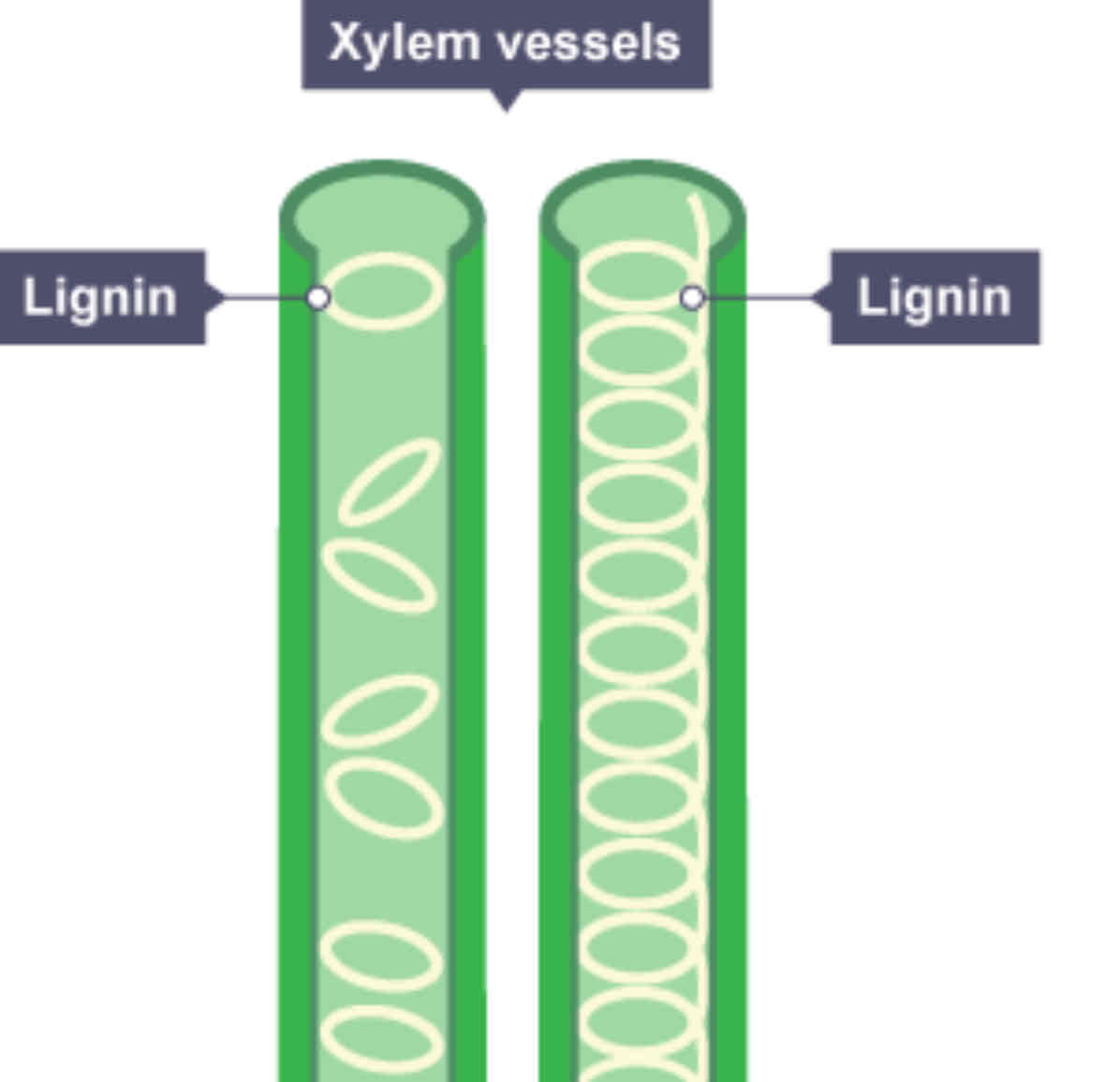
What's the function of phloem cells?
To carry dissolved sugars up and down the plant
What's a pore?
A small opening
What's the adaptations of a phloem cell?
★ Phloem vessel cells have no nucleus and limited mitochondria for more space ★ Pores called sieve plates allow sugars to move throughout the cell interior ★ Companion cells full of mitochondria provide energy to the phloem cells (connected by pores_
Cells differentiate into...
Specialised cells
When do most animal cells differentiate at?
At an early stage of development (as an embryo)
When do most plant cells differentiate at?
Anytime in their lifetime
When does cell differentiation normally happen in mature animals?
Growth and repair
Can specialised cells gain new sub-cellular structures?
Yes
What is the formula for magnification?
Magnification = image size / real size I = AM
What did light microscopes allow us to do?
Allow us to see cells
What did electron microscopes allow us to do?
Allow us to see sub-cellular structures
What are the advantages of light microscopes?
★ Inexpensive ★ Easy to use ★ Portable ★ See in colour
What are the disadvantages of a light microscope?
★ Low magnification ★ Low resolution
What are the advantages of a electron microscope
★ Higher magnification ★ Higher resolution

What are the disadvantages of an electron microscope?
★ Black and white ★ Expensive ★ Inportable

How do bacteria multiply? What is the name of this process?
★ Bacteria multiply by simple cell division
★ This called binary fission
How often do bacteria multiply?
Bacteria can multiply up to twenty minutes
What two things make bacteria multiply quicker?
Two things that make bacteria multiply quicker:
★ If they have enough nutrients
★ Suitable temperature
What two places can bacteria be grown?
Two places bacteria can grown:
★ Nutrient broth solution
★ Colonies on an agar jelly plate
What are uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms required for?
Two places bacteria can grown:
★ Nutrient broth solution
★ Colonies on an agar jelly plate
What are uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms required for?
Uncontaminated cultures of microorganisms are required for investigating the action of
★ Disinfectants
★ Antibiotics.
The disinfectant with the largest zone of inhabitation is the most effective
What does aseptic mean?
Aseptic means sterile and without bacteria
Why must we first sterilise all Petri dishes, bacterial nutrient broth and agar?
We first sterilise all petri dishes, bacterial nutrient broth and agar as:
★ This kills any unwanted microorganisms
★ Prevents contamination
How do we sterilise an inoculating loop before use?
We sterilise an inoculating loop before use by passing it through a Bunsen burner flame
Why must we attach the lid of the Petri dish using adhesive tape?
We attach the lid of the Petri dish using adhesive tape to:
★ Stop the lid from falling off
➜ This would cause unwanted microorganisms to enter
Why do we place the agar plate stored upside down?
The agar plate is stored upside down to:
★ Stop moisture from dripping down
➜ This would disrupt the colonies
Why do we normally incubate bacteria at 25°C in school laboratories?
★ In school laboratories, we normally incubate bacteria at 25°C to prevent harmful bacteria from growing
How do we calculate the area of the zone of inhabitation?
To calculate the area of the zone of inhabitation, we use the formula: A = πr²
★ A = area
★ r = radius
Where are chromosomes located?
nucleus
What a chromosomes made out of?
Genetic material
Are chromosomes found in 3s?
No, they're found in pairs
What is a stem cell?
A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which is capable of giving rise to many more cells of the same type, and from which certain other cells can arise from differentiation.
Where can stem cells be found in animals?
★ Embryos ★ Adult bone marrow
What can bone marrow stem cells differentiate into?
blood cells
What can embryonic stem cells differentiate into?
any type of body cell
When can plant cells differentiate?
Throughout their life
How can stem cells be used to treat leukaemia?
Their old bone marrow can be destroyed and new stem cells can be transplanted into a patient which would produce new blood cells
Problems with bone marrow transplants
★ The donor has to be compatible with the patient. Otherwise white blood cells produced by donated bone marrow could attack the patient's body. ★ There is a risk that viruses can be passed from the donor to the patient.
What happens in therapeutic cloning?
1) A patient’s genetic is used to make an embryo with the same genetics as the patient 2) The embryo develops stems cells 3) Put the stem cells into the patient
What are therapeutic stem cells useful for?
Once inside the patient's body, new stem cells can differentiate into cells that have stopped working properly
What diseases can therapeutic cloning treat?
★ Diabetes ★ Paralysis
What's a downside to therapeutic cloning?
Some people have religious or ethical objections
What are the advantages of adult stem cells?
● fewer ethical issues - adults can consent to have their stem cells removed and used ● an already established technique for treating diseases such as leukaemia ● relatively safe to use as a treatment and donors recover quickly
What are the disadvantages of adult stem cells?
● requires a donor, potentially meaning a long wait time to find someone suitable ● can only differentiate into certain types of specialised cells, so can be used to treat fewer diseases
What are the advantages of embryonic stem cells?
● can treat a wide range of diseases as can form any specialised cell ● may be possible to grow whole replacement organs ● usually no donor needed as they are obtained from spare embryos from fertility clinics
What are the disadvantages of embryonic stem cells?
● ethical issues as the embryo is destroyed and each embryo is a potential human life ● risk of transferring viral infections to the patient ● newer treatment so relatively under-researched - not yet clear if they can cure as many diseases as thought
What are the advantages of cloning plants?
● rare species of plants can be cloned to prevent extinction ● plants with desirable traits, such as disease resistance, can be cloned to produce large numbers of identical plants ● fast and low-cost production of large numbers of plants
What's the disadvantages of cloning plants?
● cloned plants are genetically identical, so a whole crop is at risk of being destroyed by a single disease or genetic defect
Where are meristem found?
The tips of the roots and shoots
What can plant meristem differentiate into
Can differentiate into all cell types they can be used to create clones of whole plants
Diffusion definition
The spreading out of the particles of any substance in solution, or particles of a gas, resulting in a net movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Examples of diffusion
★ Oxygen diffusing into cells ★ CO2 diffusing out of cells due to aerobic respiration ★Used to diffuse urea out (waste product that is excreted by the kidneys)
Factors that affect diffusion
★ The difference in concentrations (concentration gradient) ★ The temperature ★ The surface area of the membrane
Why can single cell organism live off diffusion?
★ It has a relatively large surface area to volume ratio ➜ This allows sufficient transport of molecules into and out of the cell meeting the needs of the organism
Why don't athletes use bottled water?
★ Too little water - Cells lose too much water via osmosis (can't function) ★ Too much water- Cells have too much water via osmosis (swell up)
Isotonic drinks
Contain similar concentrations of salt and sugar (glucose) as the human body
Why can't multicellular organisms live off diffusion
★ The larger an organism gets, the smaller the SA:V ratio ➜ This means that it takes longer to get to the surface and the centre ➜ there's more space to fill up for a smaller amount of surface.
How are alveoli in the lungs adapted for diffusion?
★ Layer of moisture for gases to dissolve faster
What are the exchanges in alveoli in the lungs?
Oxygen in, CO2 out
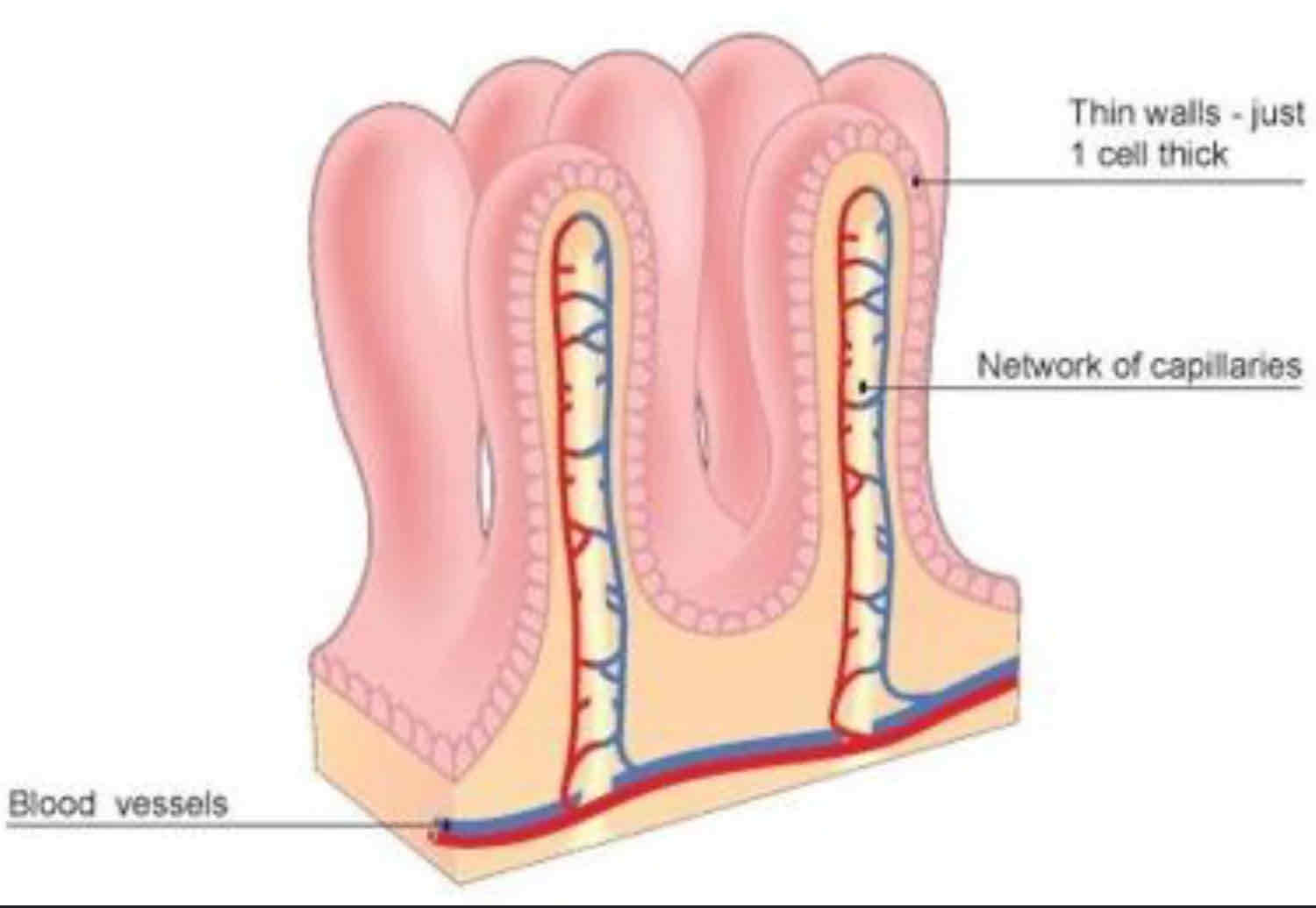
What are the exchanges in villi inside the small intestine?
Glucose, amino acids in
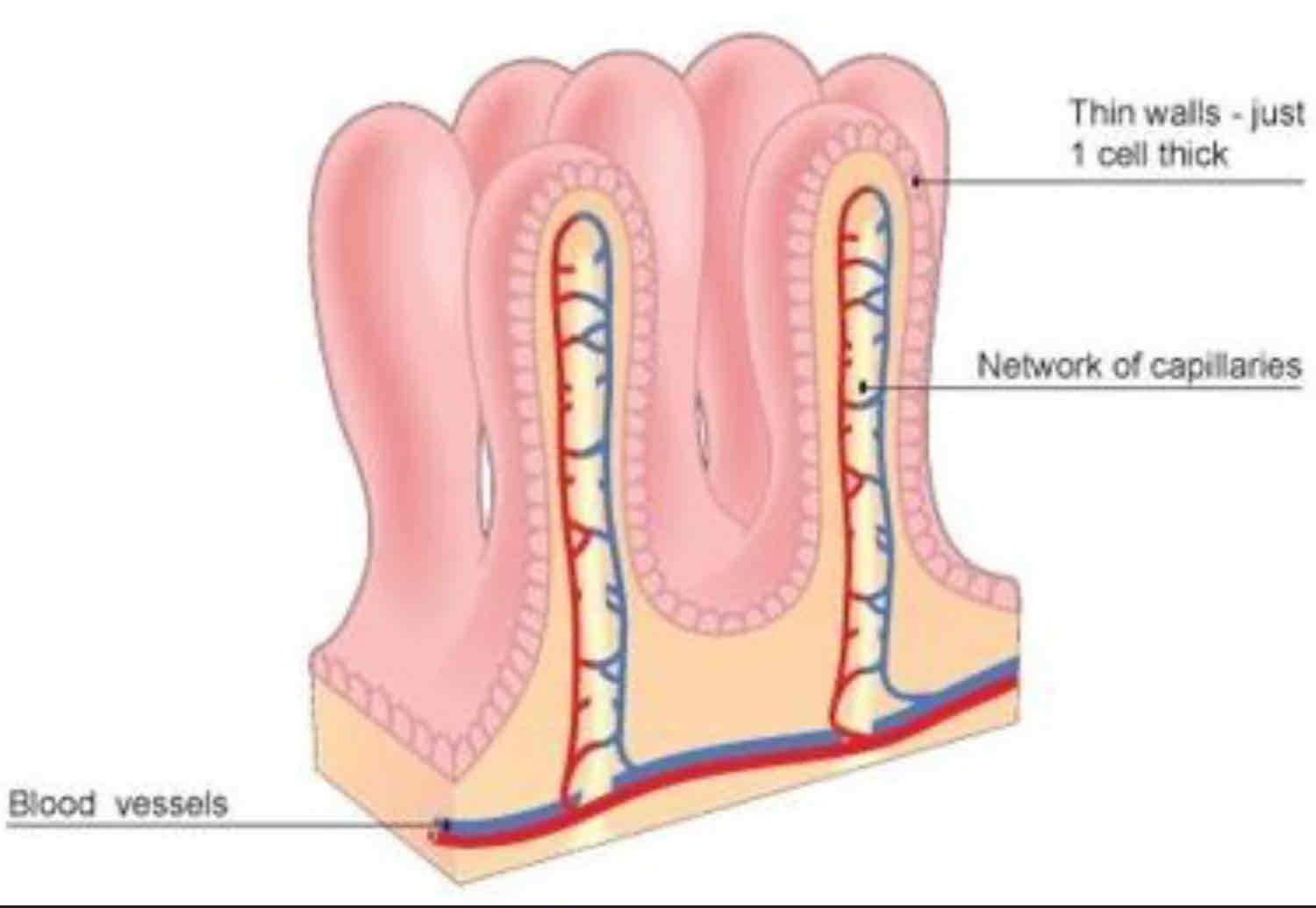
How are villi in the small intestine adapted for diffusion?
★ Lots of blood capillaries
How are leaves in plants adapted for diffusion?
★ Stomata fit for diffusion

Exchanges in the roots of plants
Water, mineral ions in

What are the gas exchanges inside plants?
Oxygen in, CO2 out

General things that help with exchange surfaces
★ Having a large surface area ★ A membrane that is thin, to provide a short diffusion path ★ (In animals) having an efficient blood supply ★ (In animals, for gaseous exchange) being ventilated
Osmosis definition
The diffusion of water from a dilute solution to a concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane
Osmosis potato practical Independent variable
Concentration
Osmosis Potato Practical Dependent Variable
Change in Mass
Osmosis Potato Practical Control Variables
Time, temperature, SA of potato
Active Transport Definition
Movement of substances from a more dilute solution to a more concentrated solution (against a concentration gradient). This requires energy from respiration.
How does active transport help root hair cells?
It allows them to get essential ions into the root hair cell and into the xylem (where it can be transported across the plant)
How does active transport help the small intestine?
It allows the lumens to get essential sugars into the cell and to then be transported into the bloodstream
What organelle does active transport usually require?
Mitochondria