Photosynthetic pigments
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Where are 3/4 pigments found?
They are embedded in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast.
What are the 3/4 pigments?
chlorophyll b, xanthophylls, and carotenoids
What do the pigments and other proteins form?
A light harvesting system
Light harvesting system
- Antennae complexes
- The role is to absorb or harvest light energy of different wavelengths and transfer this energy to the reaction centre
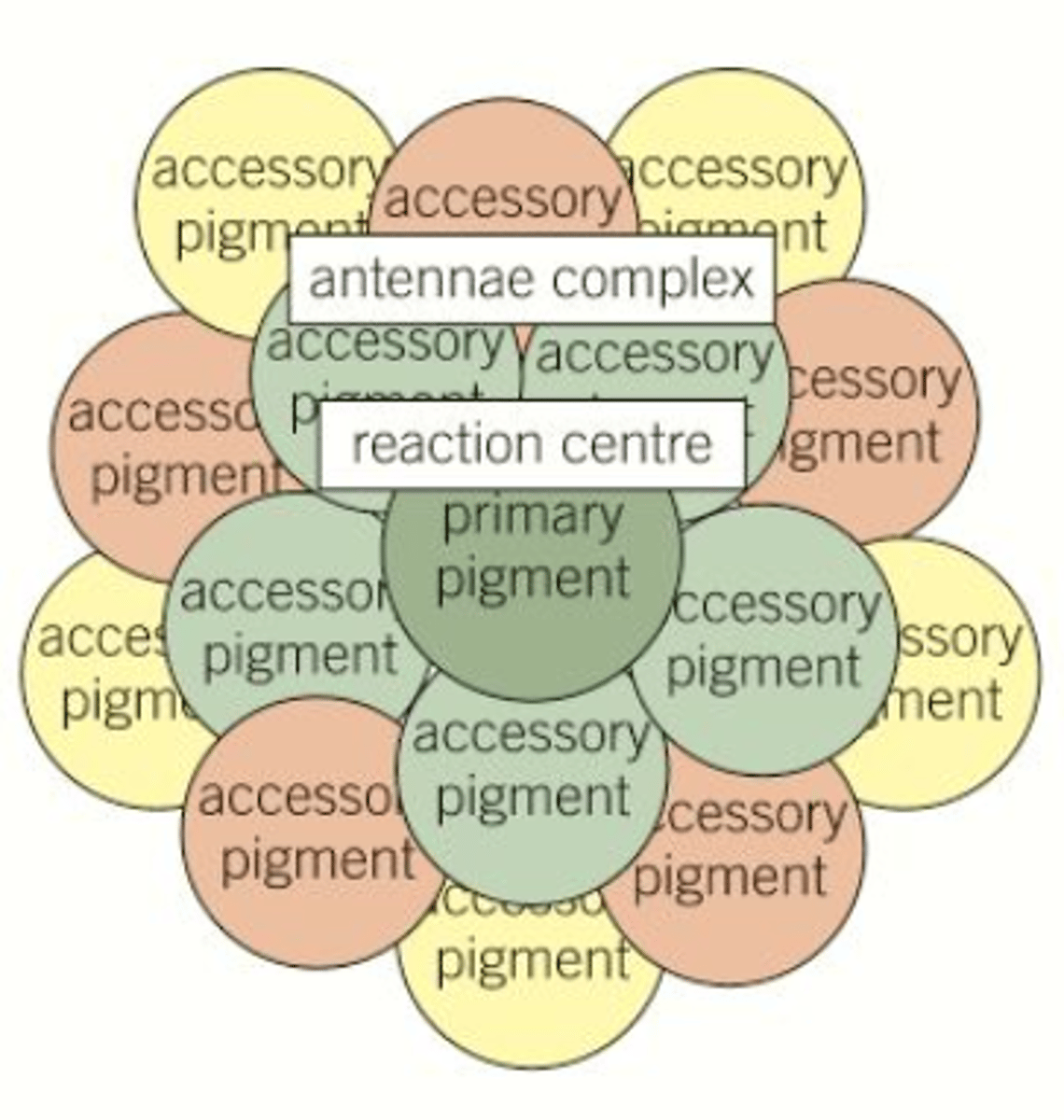
What is the primary pigment?
Chlorophyll a
Where is chlorophyll a located?
In the reaction centre
Accessory pigments
Carotenoids, chlorophyll b
Why are there other accessory pigments?
So they can absorb other wavelengths of light
Different pigments absorb...
....different wavelengths of light
How does it work?
The accessory pigments (carotenoids - xanthophyll or β carotenes) pass the energy to the primary pigment, which is chlorophyll a
Why are there a range of accessory pigments?
It allows a range of wavelengths to be absorbed
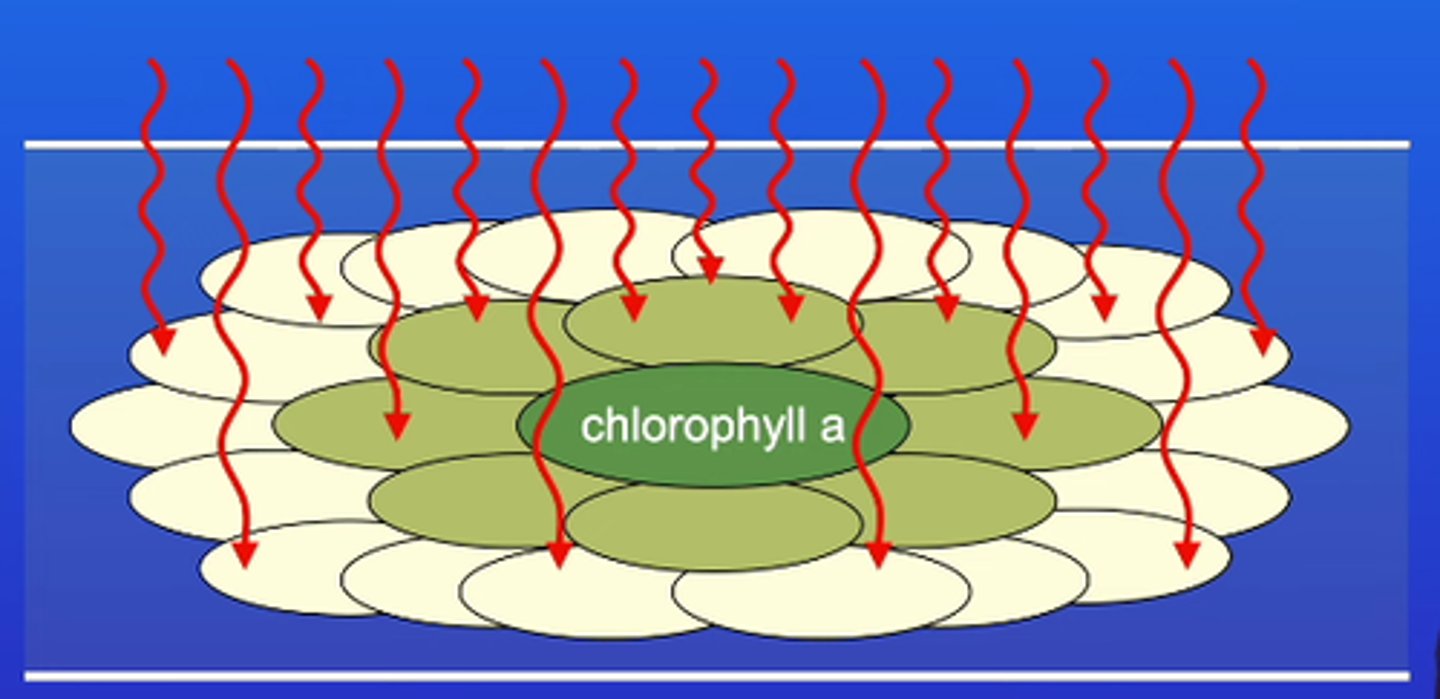
What happens with the primary pigment (chlorophyll a)?
The primary pigment becomes excited and loses the electrons to the electron transport chain. These excited electrons go to a higher energy level to be used in the light dependent reaction
Shorter wavelengths of light can...
penetrate into deeper water in the ocean. Therefore, those plants in deeper waters will have different pigments to those closer to the surface.
TLC of Photosynthetic Pigments
Grind plant sample to break down the cell wall and membrane to release photosynthetic pigments
Use a capillary tube to dot the mixture onto the pencilled line.
Handle the TLC with gloves so the amino acids/oil/fingerprints from your hands don’t get on the plates
Ensure solvent is below the pencil line or the pigments will dissolve into the solvent
Ensure plate doesn’t touch the sides of jar, because condensation/liquid/solvent on walls of the jar may affect movement. It also avoids solvent/spots travelling in the wrong direction
The smaller photosynthetic pigments will travel further up the chromatogram, as there will be less resistance