week 7 - antimicrobial therapy
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
prophylactic therapy
to prevent infection
consider in individuals at increased risk of developing infection
empiric therapy
given when infection is suspected before organism identified
antimicrobial selection guided by patient’s presentation and history
targeted therapy
treatment selected to target specific organism known to be causing infection
selection guided by organism culture results and sensitivities
stepwise approach to antimicrobial therapy
assessment
empiric therapy
monitoring
targeted therapy
follow up
components of assessment
gather information
is there an infection and any infectious history
sample collection
gram staining (less than 24 hours)
culture (24-48 hours)
PCR
antibiotic susceptibility (over 48 hours)
when to collect sample
before antimicrobial agents
having antimicrobial agent decreases chance of isolating organism
how to select appropriate empiric therapy
host/patient factors
med hx, age, allergies, prior infection/hospitalizations, prior antimicrobial use, prior drug colonization, hx of resistance
drug factors
pharmacokinetics
pharmacodynamics
infection factors
pharmacokinetics
movement of drugs within the body
absorption: route of administration
distribution: will drug reach site of infection
metabolism
excretion
pharmacodynamics
the action of the drug in the body
drug spectrum of activity, MOA, combination therapy, resistance
drug factors- antimicrobial spectrum
broad spectrum: active against large variety or organism
increased chance of activity against unknown
promote development of resistance
used for empiric therapy
narrow spectrum: active against limited group of organism
associated with reduced development of drug resistance
risk of poor activity/lack of effect against unknown organism
used as targeted therapy
drug factors- MOA (bacteriostatic vs bactericidal)
bacteriostatic
inhibits/shows bacterial growth
requires a functioning immune system to clear infection
used in less serious infections
bactericidal
causes bacterial death
preferred in serious infections or immunocompromised hosts
drug factors- MOA (time dependent vs concentration dependent killing)
time dependent killing
drug concentration must remain above minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) for effect
the absolute amount above MIC does not impact activity
concentration dependent killing
the peak drug concentration determines effect
demonstrate a post antibiotic effect where activity continues even when drug concentration is less than the MIC
drug factors- combination therapy
synergism
combining different antimicrobials to produce an effect that exceeds the sum of their individual effects
broadens spectrum
combining antimicrobials with different spectrum to fill gaps in coverage
double coverage
combining 2 different antimicrobials with activity against the same organism of interest
increases likelihood od success
reduces development of antimicrobial resistance
drug factors- antimicrobial resistance
the ability of certain organisms to develop a tolerance to specific antimicrobials to which they were once susceptible
must occur naturally over time, but accelerated by the musse of overuse of antimicrobials
risk factors for developing:
prior antibiotic exposure
underlying disease (ex. hemodialysis)
prior hospitalization
invasive procedures in healthcare settings
drug factors- mechanism of resistance
preventing the antimicrobial from reaching its target at sufficient concentrations
decreased uptake
inactivating enzymes (ex. beta lactamases)
increased efflux
modifying the target of the antimicrobial
altering the target
alternative enzymes
monitoring
symptoms
can take 2-5 days to improve
therapeutic drug monitoring
cultures and sensitivities
antimicrobial side effects
therapeutic drug monitoring
measuring drug levels in blood to guide dosing to ensure efficacy and safety
timing of blood collection is essential component
different antimicrobials require levels to be drawn at various time points
trough level (lowest serum concentration)
= draw blood 30 minutes prior to next dose
peak levels (highest serum concentration)
= draw blood immediately after the dose has been administered
why is targeted therapy important
minimize risk of developing antimicrobial resistance
reduce risk of toxic side effects
antibiotics that target cell wall synthesis
B lactams
penicillin
cephalosporins
monobactams
carbapenems
glycopeptides
vancomycin
bacitracin
bacterial cell walls
peptidoglycan is the major component
transpeptidation: the last step of cell wall synthesis
penicillin binding proteins (PBPs) form cross links in the cell wall
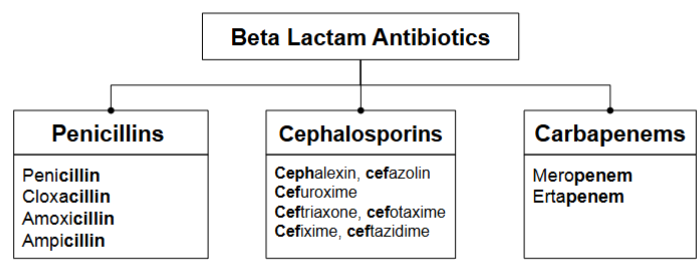
beta lactam classifications and common naming
beta lactam MOA
interrupt cell wall synthesis by:
binding to PBPs
inhibiting transpeptidation
results in:
improper cell wall formation → inability to withstand osmotic pressure → cell ruptures → cell death
bactericidal, time dependent killing
beta lactams- penicillins

beta lactams mechanism of resistance
bacterial cell production of beta lactamases
modification PBP binding site (ex, MRSA)
changes to porin channels
drug efflux pumps
beta lactamases
produced by some bacteria
enzymes that cleaves the beta lactam ring through hydrolysis
inactivates beta lactam antibiotics
beta lactamase inhibitors
some beta lactamases are paired with beta lactamase inhibitors to overcome resistance
inactive beta lactamases to extend spectrum of activity → MSSA, gram -ve, anaerobes
increase risk of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
ex of pairs:
amoxicillin- clavulanic acid (IV, PO)
piperacillin-tazobactam (IV)
beta lactams-cephalosporins

beta lactams- carbapenems

beta lactam allergies
up to 10% of pts have penicillin allergy
less than 1% true allergy
many outgrow true allergy
true penicillin allergies
type 1 IgE mediated: anaphylaxis, hypotension, angioedema
avoid all penicillins and cephalosporins with similar side chain
cross reactivity between beta lactams
around 1% between penicillins and cephalosporins
around 0.1% between penicillins and carbapenems
severe non IgE mediated hypersensitivity reactions
type IV non IgE mediated: stevens-johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
avoid all beta lactams
vancomycin
MOA:
inhibits cell wall synthesis
binds to the terminal end of peptidoglycan precursor → prevents polymerization → weakens the cell wall → cell death
bactericidal, time dependent killing
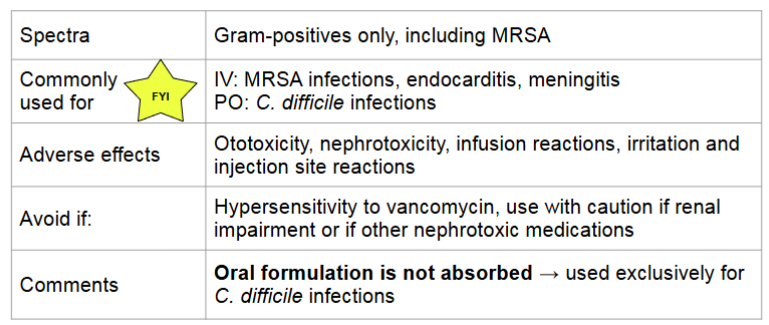
vancomycin infusion reaction (flushing syndrome)
characterized by pruritus, flushing, and erythema of the face and upper torso (NOT life threatening)
due to rapid infusion of the drug leading to histamine release
related to infusion rate
managed by slowing infusion rate
in contrast, vancomycin allergy:
anaphylaxis, hypersensitivity, hives, angioedema, bronchoconstriction, can be life threatening
managed by stopping infusion and administering epinephrine
vancomycin monitoring
nephrotoxicity
monitor for increasing serum creatinine (SCr) and decreasing urine output
therapeutic drug monitoring
serum trough levels once at steady state (pre fourth dose)
if trough is out of range let pharmacist know for dose adjustments
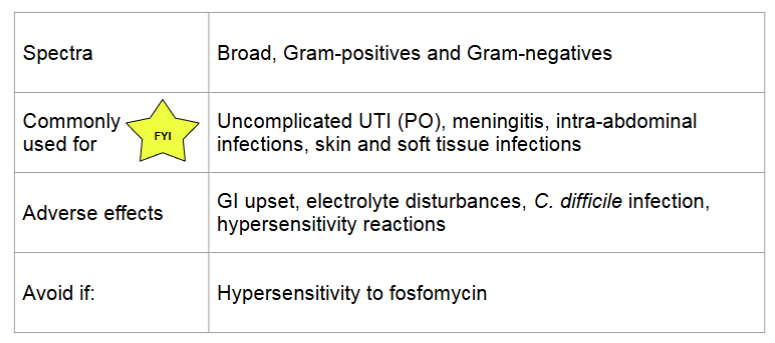
fosfomycin
MOA:
inactivated MurA enzyme involved in peptidoglycan synthesis → weakens cell wall → cell lysis
also inhibits adherence of bacteria to epithelium
bactericidal, concentration dependent killing
antibiotics that target the plasma membrane
polymyxins
polymyxin B
colistin
lipopeptide
daptomycin
daptomycin
MOA:
binds to cell membrane leading to depolarization, efflux of potassium, and inhibition of DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis
bactericidal, concentration dependent killing

daptomycin monitoring
rhabdomyolysis: rapid breakdown of skeletal muscle
can be life threatening
monitor: patient reported muscle pain, creatine kinase (CK) and dark urine
eosinophilic pneumonia
monitor: eosinophils, new onset fevers and dyspnea
antibiotics that target DNA and RNA synthesis
DNA synthesis
fluoroquinolones
ciprofloxacin
levofloxacin
moxifloxacin
RNA synthesis
rifamycins
rifampin
fluoroquinolones
MOA:
inhibits DNA synthesis by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV → promotes the breakage of DNA
bactericidal, concentration dependent killing time
ends in “…floxacin”
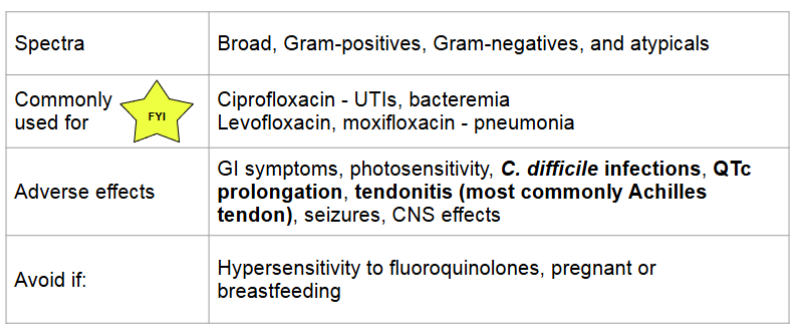
fluoroquinolones and metal cations
bind bivalent or trivalent cations → decrease absorption
avoid administering oral with bivalent or trivalent metal cations by 2 hours
this includes supplements like zinc, magnesium, iron, calcium
antibiotics that create free radicals
metronidazole
nitrofurantoin
metronidazole
MOA
becomes reduced by anaerobic organisms → becomes cytotoxic free radical that breaks DNA, inhibits nucleic acid synthesis and results in loss of DNA integrity → cell death
bactericidal, concentration dependent killing

antibiotics that target metabolic pathways
folic acid synthesis
sulfonamides
sulfones
trimethoprim
mycolic acid synthesis
izoniazid
sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim
MOA:
the 2 work synergistically
inhibit folic acid synthesis which is necessary for DNA synthesis
bactericidal, time dependent killing

antibiotics that target ribosomes
30S subunit
aminoglycosides
tetracyclines
60S subunit
macrolides
lincosamides
chloramphenicol
oxazolidinones
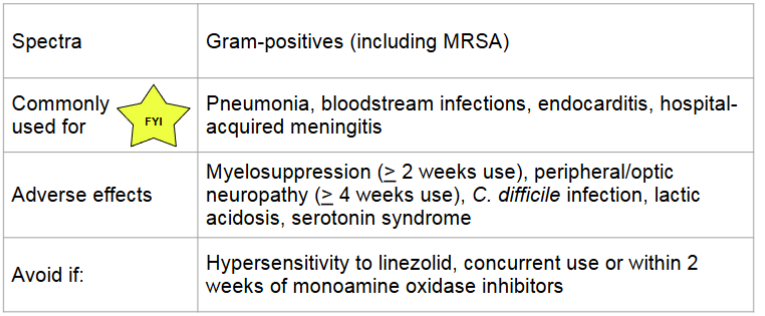
linezolid (oxazolidinone)
MOA:
binds to P site of 50S ribosomal unit → prevents formation of 70S complex
bactericidal against streptococci and bacteriostatic against staphylococci and enterococci
time dependent killing
macrolides
MOA:
reversibly binds to 50S subunit → prevents transpeptidation → protein synthesis inhibited
bacteriostatic, time dependent killing
ends in “..mycin”

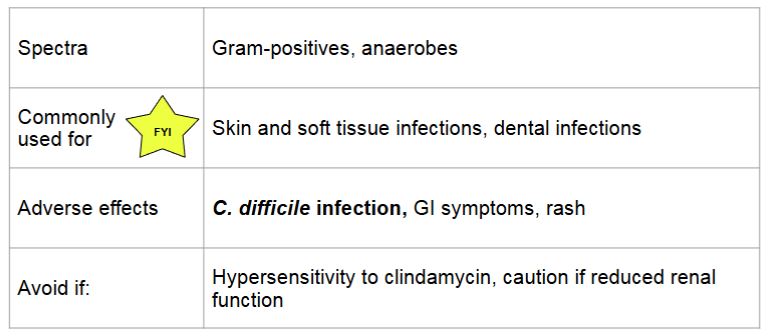
clindamycin (lincosamides)
MOA:
similar to macrolides; reversibly bind to 50S ribosomal subunit → inhibits transpeptidation → protein synthesis inhibited
bacteriostatic, time dependent killing
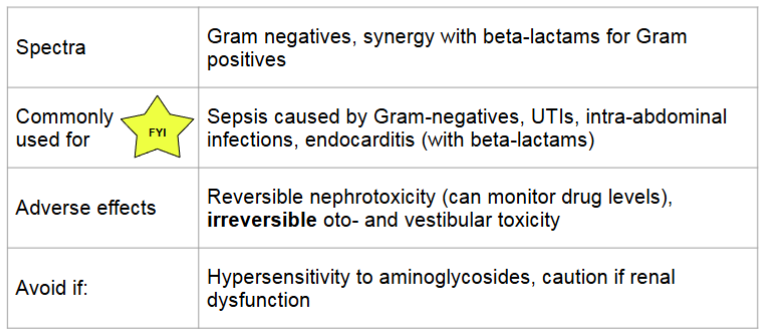
aminoglycosides
MOA:
binds irreversibly with 30S subunit → prevents transpeptidation → protein synthesis inhibited
bactericidal, concentration dependent killing
aminoglycosides dosing
extended-interval dosing: single, large dose once daily
more rapid bactericidal activity and less toxic
recommended for most infection in most patients
traditional dosing: smaller doses given multiple times a day
used when can’t use extended-interval dosing and for synergy
aminoglycosides therapeutic monitoring
troughs are used to monitor for toxicity: drawn 30 minutes prior to next dose
peaks are used to measure efficacy: drawn 20 minutes after infusion end
targets levels vary
tetracyclines
MOA:
bind to 30S subunit → blocks attachment of tRNA to mRNA ribosome complex → protein synthesis inhibited
bacteriostatic, time dependent killing

are fungi eu or prokaryotic
eukaryotic
3 types of fungi
yeast
single celled, budding reproduction
mold
multi cellular, branching filaments
dimorphic fungi
yeast at higher temps (37 degrees)
mold at lower temp (25)
fungal structure
cell membrane made of ergosterol
azole and terbinafine target ergosterol synthesis
cell wall of chitin and beta glucan
polyoxins inhibit chitin synthase
echinocandins inhibit beta glucans synthesis
antifungal medications
polyenes
nystatin
amphotericin B
echinocandins
azoles
terbinafine
polyenes MOA
binds to ergosterol in the fungal membrane → form a pore through the membrane → electrolyte leakage → cell death
resistance: rare, due to decrease or change in structure of ergosterol
fungicidal
polyenes: nystatin
oral suspension: swish and swallow/spit
poorly absorbed, cannot be used for systemic infections
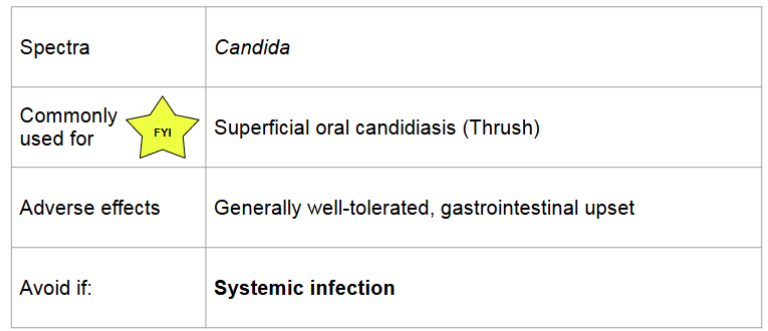
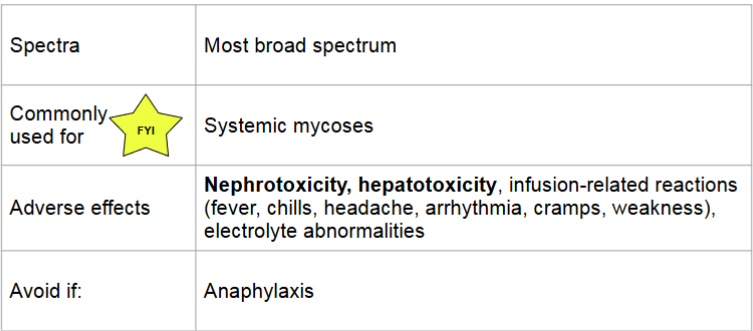
polyenes: amphotericin B
lipid formulation available
less nephrotoxic and fewer infusion related reactions
can reduce adverse effects by pre-treating with medications, prolonging the infusion, nad providing patient with adequate hydration
pre treatment includes: fluids, antipyretics, antihistamines
echinocandins
inhibits synthesis of beta (1,3)-D-glucan (component of the cell wall) by inhibiting Beta (1,3)-D_glucan synthase
impaired cell wall synthesis → cell rupture and death
fungicidal (candida) or fungistatic (aspergillus)

echinocandins monitoring
monitor for potential infusion reactions (ex. facial swelling , flushing, rash)
monitor liver function (caspofungin requires dose adjustment in hepatic impairment)
echinocandins extra info
IV only: if oral therapy is clinically warranted and the infection is susceptible, a switch to an alternate antifungal would be required
poor penetration to CNS, vitreal fluid and urine
very few drug interactions
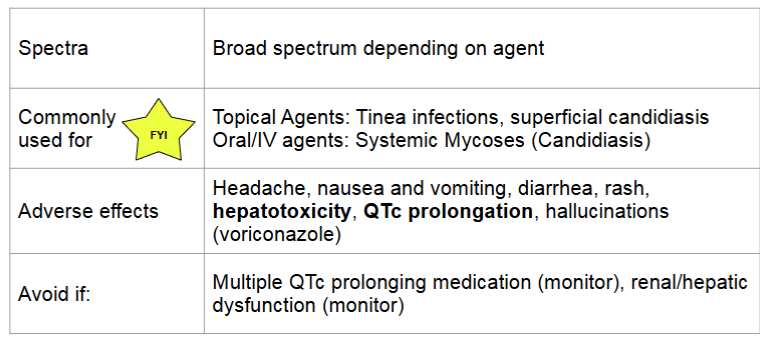
azoles
MOA:
inhibits cytochrome P450 14-alpha lanosterol demethylase → inhibits conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol → increases permeability and accumulation of toxic steroles → cell death
resistance: altered drug binding site
fungicidal or fungistatic
azoles agents

azoles extra info
IV to oral stepdown: bioavailability is typically high and oral may be used even for deep seated infections
many drug interactions
renal and hepatic function must be monitored on oral/IV therapy: QTc prolongation can occur with any systemic azole
if susceptible, use fluconazole as it has the best safety profile and excellent oral bioavailability and good penetration into CNS/vitreal fluid
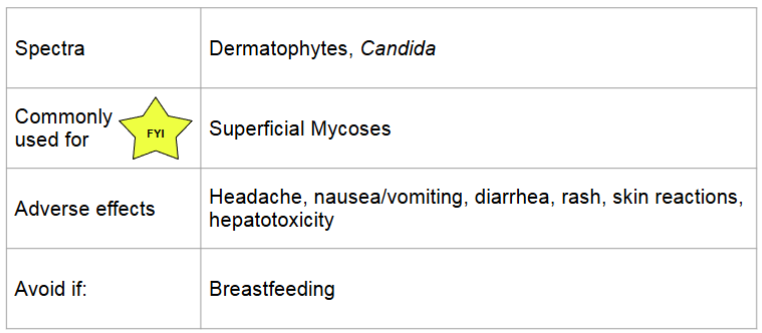
terbinafine
MOA
interferes with squalene epoxidase → inhibit ergosterol biosynthesis → alter cell membrane permeability and accumulation of toxic sterols → cell death
resistance: mutation in squalene epoxidase
fungicidal
viruses
consist of DNA or RNA within a protein outer shell
require use of host cell machinery to replicate; cannot replicate on own
infect host cells and “re-program” to replicate and the virus
types of antivirals
neuraminidase inhibitors
polymerase inhibitors
neuraminidase inhibitors
MOA:
it is an influenza viral enzyme that facilitates the release of new viruses
these drug inhibit this process- preventing the virus’ ability to spread adn replicate further
resistance:
mutations in the neuraminidase enzyme prevent the antivirals from binding

polymerase inhibitors
MOA
DNA polymerase is responsible for DNA synthesis
polymerase inhibitors incorporate into viral DNA by competing for DNA polymerase → inhibits DNA synthesis
resistance:
mutations in viral DNA polymerase or thymidine kinase
narrow spectrum polymerase inhibitors
acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir

broad spectrum polymerase inhibitors
ganciclovir, valganciclovir
