Chapter 21 (Part 1): Molecular Cloning
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is another name for Gene Cloning?
Recombinant DNA technology
What is Gene Cloning?
Laboratory techniques to manipulate DNA
Example of the usage of Gene Cloning:
Diabetes
lack of insulin
insulin is a polypeptide/hormone
Insulin regulates blood glucose levels
We can inject insulin into patients. Insulin produced from E. coli is working well in humans.
What do we need to make insulin first?
We need the Insulin gene from a human cell. This is because E. colis dont ’t have the insulin gene.
What is a recombinant vector?
When the DNA of the E. coli and the DNA from the human cell are combined.
Where does this Recombinant vector go?
It goes into the E. coli. This allows insulin to be produced in the E. Coli.
What do you do after the insulin is produced in the E. Coli?
You disrupt or lyse E. colis and purify the insulin polypeptide.
Why use E. Coli for this gene cloning for Insulin?
Because E. Coli replicates very fast. (Doubling time is 20-30 mins)
What is the general first step of gene cloning?
We need to purify plasmid DNA (vector DNA) from the E. Coli culture.
use plasmid kit
What is the general second step to gene cloning?
Insert human insulin gene into vector
purify and cut

How can we purify the Insulin gene?
We use Gel electrophoresis.
What is Gel electrophoresis?
Load samples of DNA fragments into wells at the top of the gel.
Apply an electric field. The DNA fragments are moving from negative to positive charge.
Each bond is a group of DNA fragments with the same mass.
lower mass migrate faster.
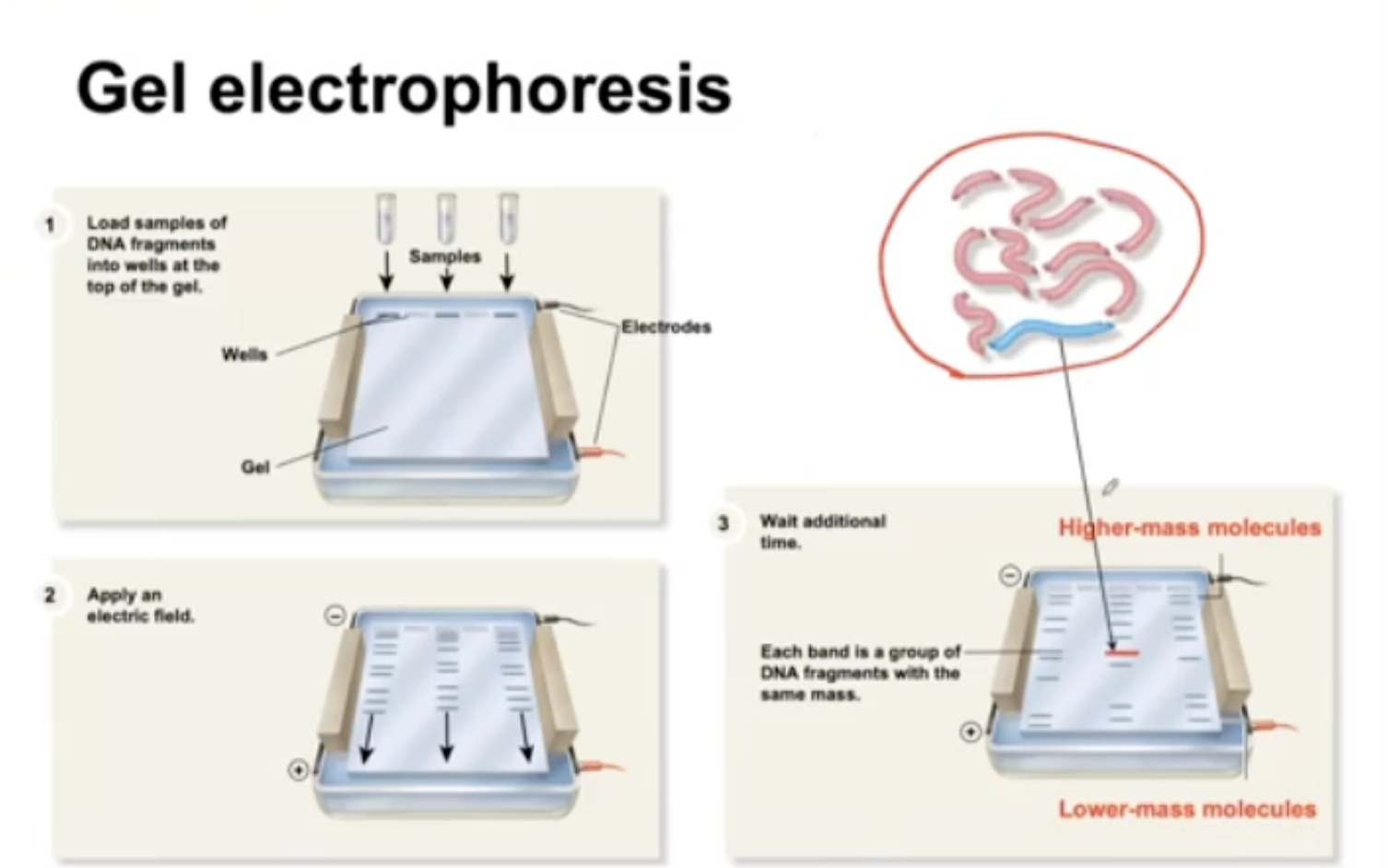
What does the agarose gel serve as?
molecular sieves
Why is the DNA moving to positive charge?
Phosphodiester bond: phosphate has a lot of negative charge
opposite charge attract each other.
How to insert the insulin gene into vector?
Cut plasmid using restriction enzymes
cut at a specific known restriction site
Base pairing
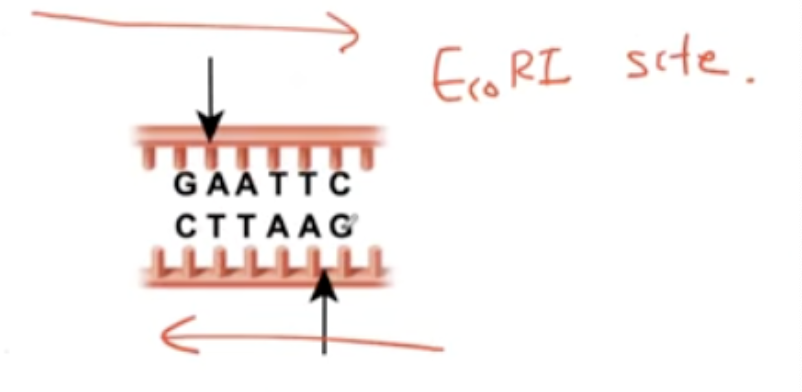
What is the name of the restriction enzyme of E. Coli?
EcoRI site

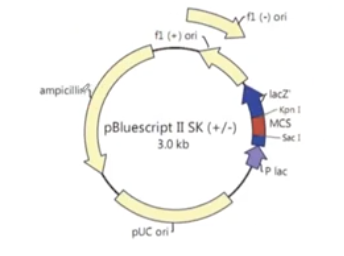
Reading a plasmid map
Ampicillin→ antibiotics
pUC ori → origen
MCS → multiple cloning site
What do we see in the multiple cloning site (MCS)?
Multiple restriction enzymes.
Scientist basically uses the restriction enzymes that only occur at the MCS. (Occurs once throughout the enzyme)
Properties of Restriction Enzymes
Most restriction sites are palindromic
Produce sticky ends (cohesive end)
May produce blunt end
What does palindromic mean?
reads the same forwards and backward
What type of end is created when EcoRI is cut by restriction enzymes?
sticky ends
The AATT is the sticky ends
Try to go back to the original
DNA is inserted based on base pairing
need an enzyme (ligase) to fill the gap
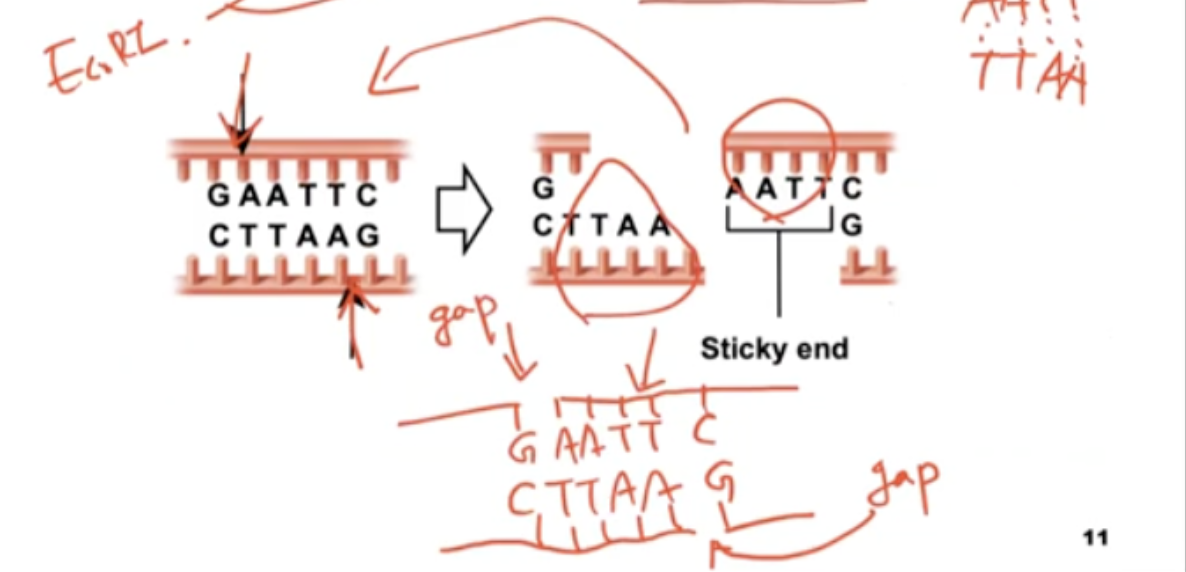
What is a blunt end?
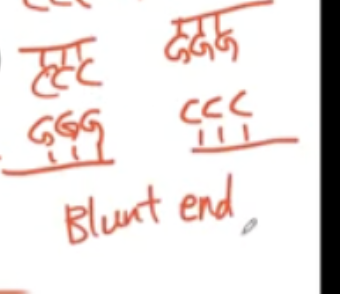
Which enzyme should we use in cutting this human DNA to isolate the insulin DNA?
EcoRI
Use the same enzyme so we can make the recombinant DNA driven by base pairing. The sequence has to be the same.
How to permanently link the DNA?
Use DNA ligase
What is the general third step of Gene Cloning?
Transfer the recombinant plasmid to the E. Coli
this is called transformation
Some will take up a single plasmid, while most fail to take up a plasmid at all. We call the failed ones untransformed.
How to get rid of untransformed cells?
We need a selection method.
Use of antibiotics.
How do we use antibiotics in the selection method?
AmpR on the plasmid confers resistance to ampicillin.
as a result, only these type of E. colis that has the plasmid grow on plates treated with ampicillin

Why is the selection method not prefect?
The sticky ends during the cut can go back to their original form.
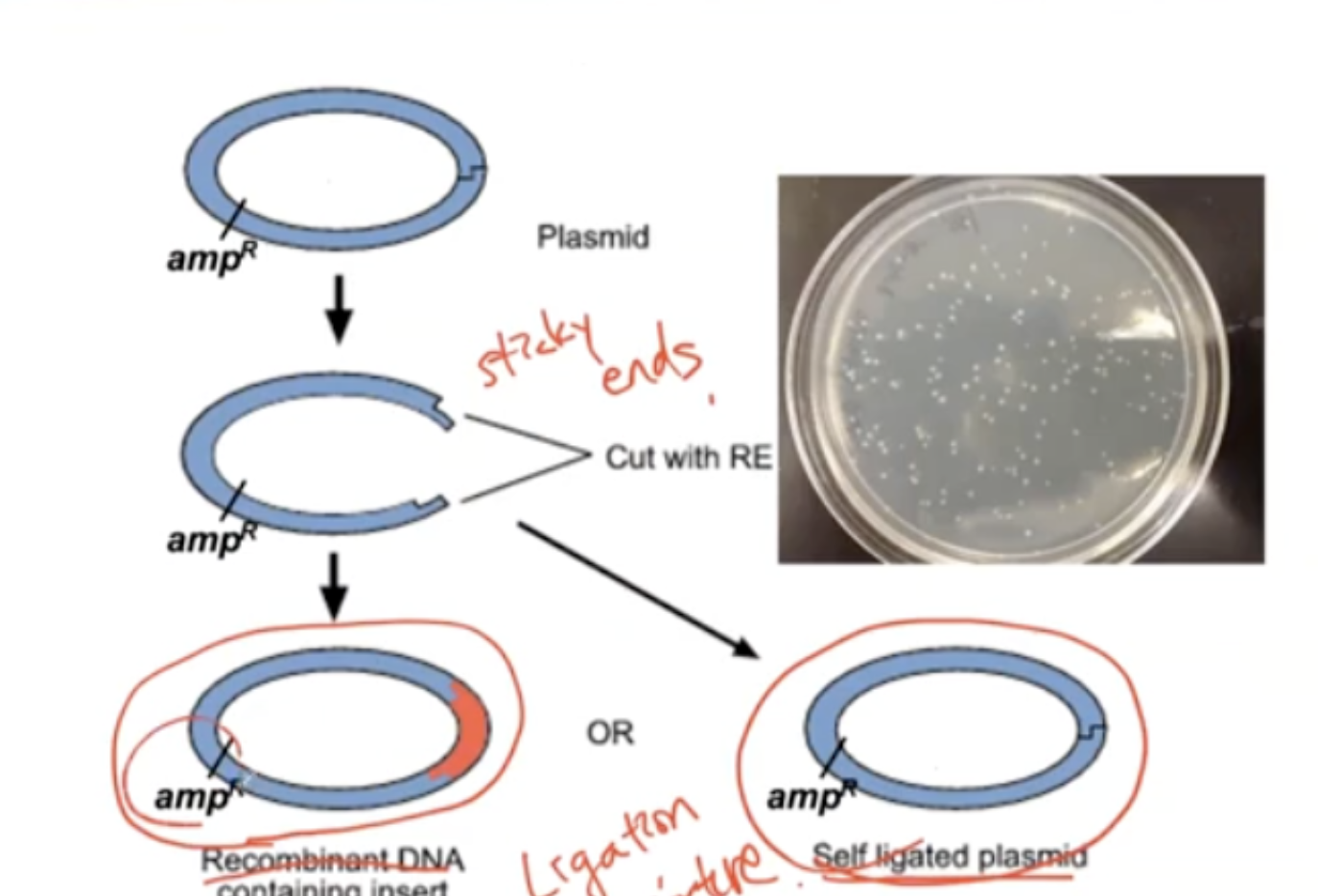
How to fix this issue in the selection method?
To pick up recombinant clones, the lacZ gene is built into the vector located at the MCS.
The purpose of this is to produce a blue color and turn into white color when the lac Z gene is broken by insulin gene.
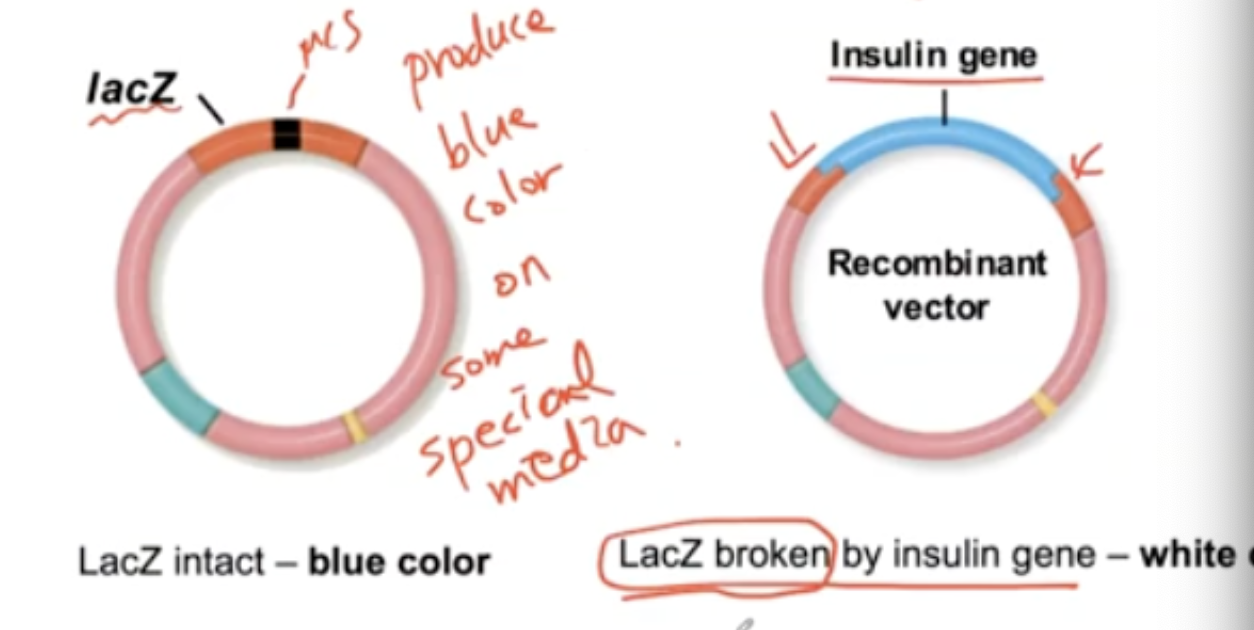
Summary of how Gene Cloning works:
DNA from the Plasmid is purified and cut by an enzyme only found in the MSC.
DNA from a human cell that produces Insulin is purified and cut by the same enzyme.
Use gel electrophoresis to help identify the purified DNA.
The cut DNA has sticky ends, and they join by base pairing.
To fill the remaining gaps, ligase is used to form covalent bonds.
Incorporate the recombinant plasmids into the host cell.
To determine the cells that have the insulin gene, we use a selection method.

Electrophoresis of PURE plasmid vector (Questions on the slide)
1) Because DNA is negatively charged, and opposite attracts
2) The gel separates DNA based on size and shape. The shape is different so that is why there are three bands.
most are super coiled though
What shape migrates faster on gel?
Super coiled.
Uncut and circular are the slowest and are not shown the most
Linear is in medium.
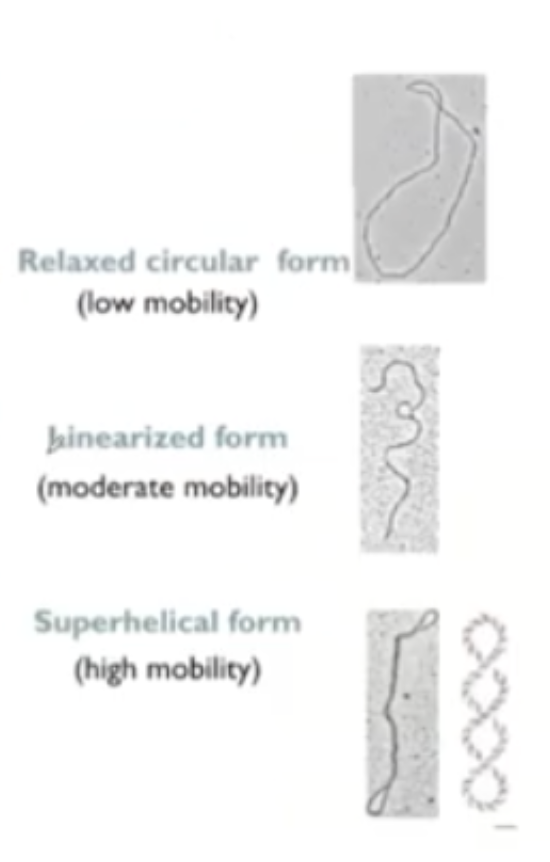

1 Hind II sites (In the data, it says Hind II and Eco RI)
1 EcoRI sites