Chapter 11 : Standard Costs and Variances
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
The Flexible Budget Variance shows
the variance caused by factors other than volume
The Volume Variance shows the
variance caused by selling more or less than planned
Input
what we put into the good
Output
The good itself
Standard Unit Cost
Budgeted cost for a single unit of product
Calculation of Standard Unit Costs
Direct Materials:
• Standard DM Cost per Unit = DM Standard Quantity X DM Standard Price
Standard quantity per unit often referred to as
Input Ratio
Calculation of Standard Unit Costs
Direct Labor:
• Standard DL Cost per Unit = DL Standard Quantity X DL Standard Rat
Manufacturing Overhead Standard Unit Cost Calculation
Standard MOH Cost per Unit = Standard Quantity of Cost Driver(s) X POHR(s)
Calculation of Standard Unit Costs
Overall Standard Unit Cost = Standard DM Cost per Unit + Standard DL Cost per Unit + Standard MOH Cost per Unit
When and how are these standard unit costs used
• Beginning of the period to determine budgets.
• End of the period to evaluate performance and adjust operation
What do we learn from a Price Variance?
• Comparison of the actual cost of an input to the standard cost of an input.
• Did we pay more or less for the inputs than expected
What do we learn from a Quantity Variance
• Comparison of what we actually used to make product versus what we should have used.
• Did we use more or less pounds, feet, ounces, etc. than expected
Variances can be labeled as Favorable (F) or Unfavorable (U)
• Favorable: input cost less than expected or used less than “allowed.”
• Unfavorable: input cost more than expected or used more than “allowed
Materiality also applies to these variances
When evaluating Direct Materials variances, the manager will likely discuss
• The direct materials price variance with the purchasing manager because the purchasing manager should be aware of purchasing deals/contracts.
• The direct materials quantity variance with the production supervisor because the
production supervisor should be aware of how much direct material is being used in production
Direct Materials Variances Summary
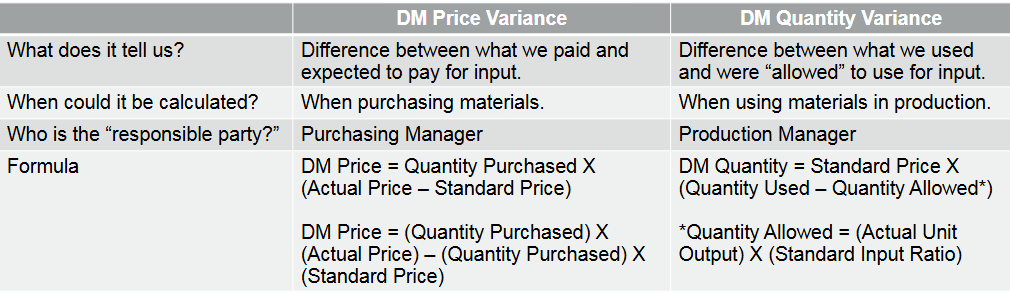
Total Direct Material Variance : If Quantity Purchased ≠ Quantity Used
= (Quantity Used X Actual Price) – (Quantity Allowed X Standard Price)
Total Direct Material Variance : If Quantity Purchased = Quantity Used
= Price Variance + Quantity Variance
What do we learn from a Rate Variance?
• Comparison of the actual cost of an input to the standard cost of an input.
• Did we pay our employees more or less than expected
What do we learn from an Efficiency Variance?
• Comparison of what we actually used to make product versus what we should have used.
• Did it take more or less time to make the product than expected
Direct Labor Variances:
Variances can be labeled as Favorable (F) or Unfavorable (U).
• Favorable: input cost less than expected or used less than “allowed.”
• Unfavorable: input cost more than expected or used more than “allowed”
Materiality also applies to these variances
When evaluating Direct Labor variances, the manager will likely discuss:
The direct labor rate variance with the HR and the production supervisor because these groups would be aware of changes in wage rates of workers.
• The direct labor efficiency variance with the production supervisor because the production supervisor should be aware of how long it takes workers to complete job
Direct Labor Variances Summary
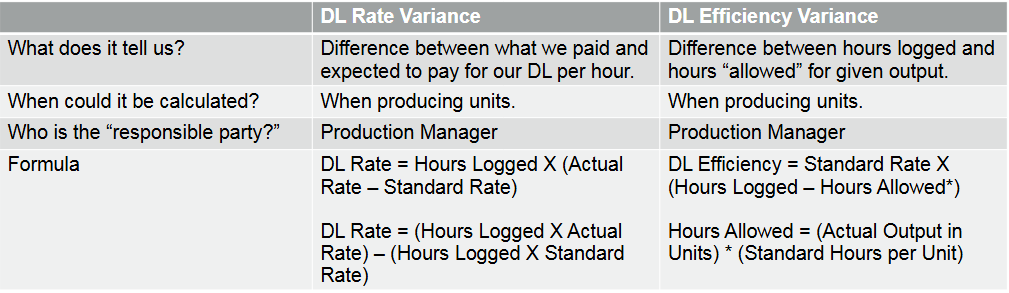
Total Direct Labor Variance Formula
• Actual – Budget = (Hours Logged) X (Actual Rate) – (Hours Allowed) X (Standard Rate)
• OR = DL Rate Variance + DL Efficiency Variance
What do we learn from a Rate Variance?
Comparison of the actual cost of an input to the standard cost of an input.
• Did our overhead cost more or less than expected?
• For example: price per hour of overhead (POHR)
What do we learn from an Efficiency Variance?
Comparison of what we actually used to make product versus what we should have used.
• Did it take more or less time (labor hours, etc.) to make the product than
expected?
• For example: number of machine hours needed to produce the good
Variable Overhead Variances :
Variances can be labeled as Favorable (F) or Unfavorable (U).
• Favorable: input cost less than expected or used less than “allowed.”
• Unfavorable: input cost more than expected or used more than “allowed.”
Materiality also applies to these variances
Approach to answering Variable Questions
Here is how I would recommend you approach each of the questions asked in this chapter:
1. Scan the problem. Do you see Direct Materials, Direct Labor, Variable MOH, or All?
2. Identify and draw “fork(s)” needed for the question.
3. Read the problem and fill in everything you can (don’t solve as you go)!
4. Start at beginning of problem and solve for unknowns.
5. Answer the questions asked
T/F
The amount of direct materials purchased is usually equal to the amount of direct materials used in production that period.
False - "It is common in practice that companies purchase more or less than they actually use in production."
For which of the following cost categories do manufacturers prepare standards?
a.Manufacturing Overhead
b.Direct Material
c.Direct Labor
d.All of the Above
D. all of the above
Which of the following could be a variance that would be highlighted through standard costing?
A.Wage increases
B.Materials price increases
C.Excess overtime hours
D.Fixed cost reductions
E.All of the above
E. All of the above
The standard direct material cost is equal to:
Standard quantity × Standard price
Which of the following statements best defines the direct material price variance?
a. The difference between the actual cost per unit of input and the standard cost per unit of input.
b. The difference between the actual quantity of input used during the period to the standard quantity of input allowed during the period.
a. The difference between the actual cost per unit of input and the standard cost per unit of input.
T/F : The flexible budget variance is equal to the difference between actual costs incurred and budgeted costs.
False ; ”The flexible budget variance is the difference between actual costs incurred and costs that would have been expected to be incurred at standard rates given the actual level of production.”