Pcol II Exam 4
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
Gram POSITIVE vs Gram NEGATIVE bacteria
POS → CM + thick cell wall → purple/blue → mostly cocci
NEG → CM + thin cell wall + outer memb w porins + lipopolysach → red/pink → mostly bacilli
GRAM-POSITIVE SPECIES + identification
Staphylococcus → cluster → catalase + → aureus coag +, epi coag -
Streptococcus → chains → catalase - → a, b, y hemolytic
enterococcus → catalase -
Common infections of STAPHYLOCOCCUS (gram +)
Staphylococcus aureus → 6
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
abscesses, osteomyelitis, food poisoning, TSS, nosocomial, endocarditis
endocarditis, line infxns
UTI
STREPTOCOCCUS SPECIES (gram +)
a hemolytic (partial lysis)
b hemolytic + Lancefield classification (full lysis)
y hemolytic (no lysis)
pneumoniae, viridans
group A pyogenes, B agalactiae, D bovis
enterococcus
Common infections of STREPTOCOCCUS (gram +)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Viridans Streptococcus
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus agalactiae
community adult meningitis, acute sinusitis
endocarditis
soft tissue infxns, pharyngitis, rheumatic fever
neonatal meningitis
Enterococcus ___________ is typically vancomycin RESISTANT (VRE)
faecium
Gram-POSITIVE
shape =
_________ species + diseases (2)
_________ species + disease
+bacilli
listeria → meningitis, food poisoning
bacillus → anthrax
Gram-NEGATIVE
Shape =
____________ gonorrhea, meningitis
-cocci
Neisseria
Gram-NEGATIVE coccobacillus
found in respiratory tract → ________ species
______ species
haemophilus
moraxella
GRAM NEGATIVE DRUGS → SPACE
serratia
pseudomonas aeruginosa
acinetobacter
citrobacter
enterobacter
GRAM-NEGATIVE BACCILI
Enterobacterales (from the GUT) → YES PECKSS
Yersinia
Escherichia
serratia
proteus
enterobacter
citrobacter
Klebsiella
salmonella
shigella
Salmonella can cause (3)
Shigella can cause
Yersina can cause
Which can cause UTIs? (5)
typhoid fever, enterocolitis, sepsis
entercolitis
plague
E. coli, proteus, Klebsiella p, serratia, enterobacter
GRAM-NEGATIVE BACCILI:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
“___________”
Highly ________ to antibiotics
Diseases → 7
non-fermenters
resistant
CF/lower resp, nosocomial, endocarditis, ear infxn, UTI, hot tub folliculitis, burn wound sepsis
GRAM-NEGATIVE BACCILI:
Burkholderia cepacia diseases
CF/lower resp, catheter + IV line infxns
ATYPICAL ORGANISMS
3 major species
all 3 can cause _______
mycoplasma, chlamydia, legionella
pneumonia
ANAEROBIC organisms
_______ species (C diff)
-
clostridium
bacteroides
RESISTANT PATHOGENS → No ESKAPE
Enterococcus faecium (VRE, gram +)
Staph aureus (MRSA, gram +)
Klebsiella pneumoniae (ESBL, gram -)
Acinetobacter (gram -)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (gram -)
Enterobacter (gram -) → C diff, E. coli
Important Resistance Genes:
MRSA
VRE
fluoroquinolone
plasmid mediated resistance in clindamycin + macrolides
E.coli to tetracyclines
P.aeruginosa to carbapenems
MecA
Van A/B/C
GyrA/B, parC
Erm
Tet A/B/C
OprD
AMINOGLYCOSIDES
The 3 most commonly used aminoglycosides
IRREVERSIBLE Inhibitors of __________ → _____ subunit
Mostly used against _________ bacteria
Including __________
Significant toxicities → 2
Other ADEs → 2
Polycationic → amine group is ______ at phys pH
_________ prevents oral absorption / penetration into CSF
Excretion →
How are AGs taken up by bacteria?
gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin
protein synth → 30S
Aerobic gram -
pseudomonas
nephrotox, ototox
neuromusc blockade (myasthenia gravis susceptible), apnea
protonated
polarity
renal
passive porins → then active O2 depend process
Spectrum of Activity - AMINOGLYCOSIDES
Gram + bacteria → combination w cell wall active agent to produce ________ bactericidal effect
Gram - bacteria → active against … (3)
______________ (3) are active against mycobacteria
_________ active against Entamoeba histolytica and other intestinal protozoa
synergistic
enterobacteriaceae, pseudomonas, gram - cocci (neisseria, moraxella, haemophilus)
streptomycin, tobramycin, amikacin
paromomycin
which aminoglycoside is the most active against M. tuberculosis?
streptomycin
Mechanisms of RESISTANCE against Aminoglycosides
Production of _______________ (most common) → 3 reactions
-permeability and -intracellular accumulation of drug → ______ systems seen w P. aeruginosa
Target ________
*inactivating enzymes → acetylation, adenylation, phos
efflux
alteration
AMINOGLYCOSIDES PK/PD
________-dependent killing and __________
Goal of therapy:
Efficacy goal:
Dosing: Traditional vs extended, TYPICALLY GIVEN _____
conc, PAE
maximized concentrations
peak/MIC >10-12
IV
Other Aminoglycosides Dosage Forms
Ophthalmic →
Topical →
Inhalation + use →
gentamicin, tobramycin, neomycin-bacitracin-polymyxin B
neomycin-bacitracin-polymyxin B
tobramycin, amikacin → CF
AMINOGLYCOSIDES ADEs → Ototoxicity differences btwn AGs
strepto, genta → vestibular (balance)
amikacin, kanamycin, neomycin → auditory
tobra → both (equally)
Aminoglycosides Monitoring
Therapeutic effect → 5
Toxicity → 3
vitals signs (BP, HR, T, O2), WBC, procalcitonin, ESR, CRP
renal fx, urine output, hearing fx
AMINOGLYCOSIDES NEW AGENT:
Agent =
Resistant to enzyme _________ (acetyl, adenyl, phos)
Approved for ________
Similar spectrum
Similar ADEs
plazomicin (Zemdri)
modification
complicated UTIs
POLYMYXINS
Used against _______ organisms (last line of defense)
MOA: act as __________ → disrupt the structure of the ________ of GNB → leakage of intracell contents → rapidly bactericidal
Significant toxicity →
Other ADE
ACTIVE AGAINST →
Abs?
Excretion
Resistance?
MDR gram - bacilli
cationic detergents → outer memb
nephrotox
neurotox
gram - ONLY
poor PO abs
colistin → urine (unchanged), polymyxin B → non renal
RARE
POLYMYXIN PK/PD
_____-dependent and _______
Goals of therapy
Efficacy goal
conc, MODERATE PAE
maximize amt of drug received
AUC/MIC >12
Concomitant NEPHROTOXINS → 7
(DDI AGs & polymyxins)
vancomycin
ampho B
cisplatin
ACEi
NSAIDs
diuretics
radiocontrast
Which AG has good oral absorption?
A. gentamicin
B. tobramycin
C. amikacin
D. none
D
Which AG was recently approved for cUTI?
A. amikacin
B. plazomicin
C. gentamicin
D. tobramycin
B
Which is Colistin’s MOA?
A. causes rapid loss of K+ and membrane depolarization
B. inhibits transpeptidase
C. cationic detergents that disrupts bacterial cell membranes
D. bind 30S subunit and inhibit protein synthesis
C
Colistin is also known as polymyxin ____
E
Which is given IV as a prodrug?
A. polymyxin B
B. polymyxin E
B (colistin)
GLYCOPEPTIDES
vancomycin, teicoplanin, telavancin, dalbavancin, oritavancin
MOA: inhib ____________ by inhibiting ________ and is __________
ACTIVE AGAINST →
Mostly used against …
cell wall synth, D-ala-D-ala, bactericidal
gram + → kills staphylococci rel slowly
MRSA
Spectrum of Activity - GLYCOPEPTIDES (5)
MRSA
MRSE
strep
strep pneumoniae (PCN resistant)
enterococcus faecalis
GLYCOPEPTIDE RESISTANCE
_____ is a major concern
Occurs as a result of alteration of the last ________ terminus to either ________ or _____
Some concern about _____ and ______ (rare)
VRE
ala → lac or ser
VRSA/VISA
GLYCOPEPTIDES PK/PD
all have ______ PO abs
Vd → ________ has best CNS penetration
Excretion → RENAL (renal adjust)
Excretion → nonrenal
t1/2
Killing characteristics: ________ and ________ dependent
Goal of therapy:
Efficacy goal: _________ for MRSA
poor
vancomycin
vancomycin, telavancin, dalbavancin (Dalvance)
oritavancin (Orbactiv)
dalba 346 hr, orita 245 hr
conc, time
maximize amt of drug received
AUC/MIC 400-600
Which glycopeptides are given as a SINGLE dose?
oritavancin, dalbavancin
ADEs - VANCOMYCIN
“____________” syndrome → erythematous, urticaria, flushing, tachycardia, hypotension
_________ release from mast cells
*DO NOT EXCEED AN INF RATE OF ________
Reaction NOT observed w _____
Other ADE → ________ → risk factors (4)
red man syndrome
histamine
1 g/hr
teicoplanin
nephrotox → total daily dose >4g, coadmin w piperacillin-tazobactam (Zosyn)/AGs, TR>15, AUC>800
ADES - TELEVANCIN (3)
nephrotox
teratogenic
+QT
GLYCOPEPTIDES: Therapeutic uses
vancomycin
telavancin
dalbavancin
oritavancin
MRSA/MRSE, PO for C diff, sev + non sev infxns
hosp acquired pneumonia, skin + soft tissue infxn
skin + soft tissue infxn
skin + soft tissue infxn
CYCLIC LIPOPEPTIDE
Agent →
MOA: ________ agent that is rapidly ________ for ____________ bacteria
^ causes rapid _________ possibly by pore formation + membrane depolarization
kills _____ than vancomycin
*NOT USED FOR _________
May cause __________
daptomycin
cell memb, bactericidal, resistant gram +
loss of K+
FASTER
NO pneumonia
muscle injury
DAPTOMYCIN PK/PD
Abs
Vd
Excretion
Killing characteristics
goal of therapy
efficacy goal
Dose _______ for more severe infxns (blood stream, joint, etc) & VRE (monitor muscle injury)
poor PO, muscle toxicity → NO IM
very small → ECF
renal
conc, PAE
maximize conc
peak/MIC
inc
Why is daptomycin inappropriate for pneumonia even though it penetrates adequately into the lung?
inactivated by pulmonary surfactants
ADES - DAPTOMYCIN
Usually well tolerated
Monitor _____________ during therapy → rapidly resolves after DC
Daptomycin-induced acute __________________ is very rare, unpredictable, potentially serious AE → fever, hypoxia, pulm infiltrates
DRUG INTERACTIONS →
CPK weekly
eosinophilic pneumonia
statins (+CPK)
Which is vancomycin’s MOA?
A. inhib protein synthesis by binding 30S subunit
B. complex formation in cytoplasmic memb, rapid loss of K+
C. inhib cell wall synth by inhibiting transpeptidase
D. inhib cell wall synth by binding to D-ala-D-ala
D
Which may increase risk of nephrotoxicity with vancomycin?
A. rate >1 gram/hr
B. AUC <400
C. trough of 10-15
D. concurrent piperacillin-tazobactam
D
(A is for red man syndrome
TR >15 and AUC >800 would be risk nephro)
Daptomycin is active vs:
A. E.coli
B. VRE
C. Bacteroides sp
D. Mycoplasma
B (active vs resistant gram+)
Which is a common ADE of daptomycin?
A. nephrotoxicity
B. elevated CPK
C. hepatotox
D. QTc prolongation
B
BETA-LACTAMS
Includes … (4)
All share B-lactam ring and same MOA →
^ these are involved in the final stages of the synthesis of _________
bacterial resistance continues to increase at a dramatic rate, unfortunately there are ________ of resistance
penicillin, cephalosporins, carbapenems, monobactams
inhib PBPs (cell wall synth)
peptidoglycan
multiple forms
BETA-LACTAMS: PENICILLINS
Narrow spectrum → 5
Broad spectrum → 2
BROADEST spectrum (pen + B-lactamase INHIBITOR) → 3
pen G, pen V, nafcillin, oxacillin, dicloxacillin
ampicillin, amoxicillin
ampicillin/sulbactam, amoxicillin/clavulanate, piperacillin/tazobactam
NATURAL PENICILLINS
Agents → 2
Used for _________ infxns →
Significant ADEs →
pen G, pen V
streptococcal → strep throat
allergic rxn, AB assoc diarrhea
Crucial enzymatic activities of PBPs:
___________ → crosslinking of peptidoglycan
___________ → links subunits of glycopeptide polymer
transpeptidase
glucosyltransferase
BETA-LACTAMS MOA OF RESISTANCE:
Decreased __________ to target site → must pass through porin channels
________ of the target site (MRSA, MRSE, PRSP)
________ pump
*MAJOR MOA: ___________ by a bacterial enzyme (AmpC, ESBL, CRE. plasmid-mediated)
penetration
alteration
efflux
inactivation
PENICILLINS PK/PD
Good PO abs = 4
______ distribution
Excretion → Most eliminated _______ 60-90%
EXCEPT …
______ half-lives
Killing characteristic: ____-dependent
Goal of therapy
Efficacy goal
PCN, amp, amox, dicloxa
wide
renally
antistaph → naf, ox, diclox (no renal adj)
short (1-2h)
time
maximize duration of exposure
T>MIC = 50%
ANTI-STAPH PENICILLINS
aka penicillinase-resistant penicillin
Agents → 3
ONLY active against (2)
Resist ________ of penicillinase
Significant ADEs
Dosing:
nafcillin, oxacillin, dicloxacillin
staph, strep (gram +)
hydrolysis
allergic rxn
NO renal adj
EXTENDED-SPECTRUM PENICILLINS
Aminopenicillins + activity →
Ureidopenicillins → almost always used in comb w tazobactam
Significant ADEs →
ampicillin, amoxicillin → strep, enterococci, listeria
piperacillin
allergic rxn, AB assoc diarrhea
B-LACTAMASE INHIBITORS
Have very _______ AB activity on their own
Prevent ______________ of beta-lactam ABs and thus extend the spectrum of activity
Aminopenicillins + BLI activity →
Piperacillin/tazobactam activity →
All extended-spectrum penicillins w or w/o BLI require __________
little
bacterial degradation
+MSSA, MORE GNB and ANAEROBES
MSSA, PSEUDOMONAS, anaerobes, enterobacter
renal adjust
ANTI-PSEUDOMONAL DOSING for piperacillin/tazobactam
4.5 g IV q 6h
1st line agents for diabetic foot infxns / animal bites
amox/clavulanate, amp/sulbactam
Meningitis → AB combination
aminopenicillin (amp/amox) + vanco + 3rd gen ceph
Piperacillin/tazobactam (ZOSYN) reserved for SERIOUS infxns caused by __________ organisms, often ______, often in combination
gram -, nosocomial
PCN ADEs
_______ rash 10%
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea type 1 → higher with ____________ PCNs
Antibiotic-associated diarrhea type 2 → _____ infxn as a concern
______________ contains 1.7 mEQ of K+ → caution cardiac arrest w rapid infusion and hyperkalemia in renal failure
________ at very high blood levels
amp
broader spectrum
C diff
IV Pen G
seizures
SUMMARY - PCNS SPECTRUM OF ACTIVITY
Natural PCNs
Anti-Staph PCNs
Amino PCNs
Amino + BLI (additional)
Piperacillin/tazobactam
enterococcus, strep, minimal GNB + anaerobes
MSSA, strep
enterococcus, strep, listeria, some H influenza + enterobacter
+MSSA, anaerobes, acinetobacter w sulbactam
enterococcus, strep, MSSA, anaerobes, pseudomonas, GNB
CEPHALOSPORINS:
MOA:
Resistance: particular concern w AmpC beta-lactamase producing _______/________
Bind PBPs
SPACE/SPICE -> I = indole + proteus
CEPHALOSPORINS PK/PD:
Killing characteristic: _____-dependent
Efficacy goal
_____ distribution
______ half lives
Elimination
Time
T>MIC 50-70%
Wide
Short
Renal
Which cephalosporins have excellent CNS penetration?
cefotaxime, ceftriaxone, ceftazidime
Which cephalosporin has the longest half-life (5-9h vs 1-3h)?
ceftriaxone
Which cephalosporin is NOT renally eliminated (no dose adj)?
ceftriaxone
1ST GEN CEPHALOSPORINS
Agents =
Often used for …
Spectrum of activity
Cephalexin, cefadroxil, cefazolin
Skin + soft tissue infxn, surg prophylaxis
MSSA, strep, some GNB/anaerobe
2ND GEN CEPHALOSPORINS
Agents = 4
MAY be used for …
Cephamycins may be used for _____ and _____ procedures
Spectrum of activity
Cefuroxime, cefprozil, cephamycins → cefoxitin & cefotetan
Upper resp infxn
Intra-abdominal, gyn
Strep, Less MSSA than 1st gen, better GNB/anaerobe
___________ (2nd gen) or ___ gen cephalosporins used for otitis media in PCN allergic patients
cefuroxime + 3rd
3RD GEN CEPHALOSPORINS
Agents IV = 3
Agents PO = cefpodoxime, cefixime, cefdinir, cefditoren, ceftibuten
WIDELY used for … (4)
Spectrum of activity
Cefotaxime, ceftriaxome, ceftazidime
Pneumonia, meningitis, bacteremia, sinusitis
Strep, Less MSSA than 1st gen, GNB
__________ is therapy of choice for all forms of gonorrhea
ceftriaxone
ANTI-PSEUDOMONAL CEPHS
Agents → ______ and ______ for pseudomonas infection
___________ for RESISTANT pseudomonas infection
___________ and __________ for ESBL + CRE organisms
Ceftazidime (3rd gen), cefepime (4th gen)
ceftolozane/tazobactam (Zerbaxa)
ceftazidime/avibactam (Avycaz), cefiderocol (gen 5)
4th and 5th generation cephalosporins
4th = cefepime
5th = ceftaroline, ceftolozane, cefiderocol
CEFTAZIDIME & CEFTOLOZANE
Spectrum of activity
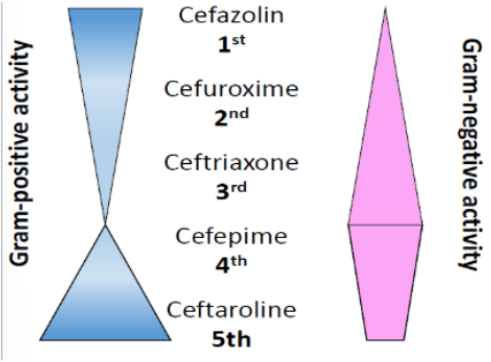
NO STAPH, strep <ceftriaxone, pseudomonas, HIGHLY GNB
4th Generation ceph =
Spectrum of activity =
cefepime
MSSA, strep, HIGHLY GNB, pseudomonas, anaerobes
5th generation ceph =
Spectrum of activity =
Ceftaroline
MSSA, MRSA, VISA, Strep + PRSP (PCN resist strep pneumoniae), GNB
BLI + CEPH COMBINATIONS
Comb 1
Comb 2
Differences
FDA indication: complicated _________________ infections with ________
Avycaz → ceftazidime/avibactam
Zerbaxa → ceftolozane/tazobactam
Zerbaxa ESBL < Avycaz, Zerbax NO CRE (Avycaz does)
Intra-abdominal, metronidazole
ADES OF CEPHALOSPORINS:
_________
_________ problematic in NEONATES → interacts with ________________, also biliary sludging that has produced ________
_________ w _______ at high doses/renal dysfx
_________
Allergic rxns
Ceftriaxone → calcium to form crystal deposits in lungs + kidneys → hyperbilirubinemia
Encephalopathy → cefepime
AB assoc diarrhea
NEW CEPHALOSPORIN AGENT → Gen V
Cefiderocol (Fetroja)
MOA: binds ______
Chelates _____ ions and uses bacterial iron transport systems (Trojan horse strategy)
Spectrum
PBP3
Ferric
MDR GNB
Which class has the BROADEST coverage of all beta-lactams?
Carbapenems
CARBAPENEMS
MOA:
Used in polymicrobial infxns to cover _____
GENERALLY RESISTANT to cleavage by most plasmid/chromosomal beta-lactamases, but _____ is a growing concern
Spectrum of activity
Bind PBP
Resistant GNB
CRE
MSSA, strep, enterococ/pseudomonas/acinetobacter EXCEPT ertapenem, listeria, GNB, anaerobes
CARBAPENEMS PK/PD
Killing characteristics: _____ dependent
Goal efficacy
Time
T>MIC >40%
___________ and __________ are highly active against many CRE (carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae) + difference?
Vabomere - meropenem/vaborbactam
Recarbrio - imipenem/cilastatin-relebactam
Vabomere 3h infusion vs Recarbrio 30 min
Which carbapenem can only be given once a day?
Ertapenem
CARBAPENEMS ADEs (3)
Allergic rxn
CNS tox
AB associated diarrhea
MONOBACTAMS
Agent =
Structural similarities to _______
Active vs
Used for serious infxn in place of an _____ in patients with a history of ________
Spectrum of activity
Elimination
Aztreonam
Ceftazidime
pseudomonas aeruginosa
ESBL → PCN anaphylaxis
GNB
renal
AZTREONAM is resistant to many of the β-lactamases produced by most GNB, including the metallo-β-lactamases but NOT THE ______ B-lactamases
_________ being developed -> activity against class A, class C, and select class D beta-lactamase enzymes
KPC
aztreonam/avibactam
CLINDAMYCIN
Class =
Active against ____ and _____
MOA: binds ______ subunit and suppress protein synth
ADEs → 3
Spectrum of activity
RESISTANCE → 2
GNB are intrinsically resistant due to ________ and ______
Therapeutic uses → 4
lincosamide
GPC, anaerobes
50S
C diff, diarrhea/GI, allergic rxn
staph, strep, CA-MRSA, anaerobes
target modification, inactivation
poor perm, efflux pumps
skin/soft tissue infxn, polymicrobial, TSS, PID
Which agent is active vs CA-MRSA (community acquired)?
clindamycin
CLINDAMYCIN PK/PD
Abs
Vd
Metabolism
Excretion
Killing characteristic: _____ dependent
good PO
poor CSF
CYP3A4 substrate → N-demethyl clindamycin more active
not much renal
time
CLINDAMYCIN should be used with CAUTION in patients receiving _________
neuromusc blockers (clindamycin has some NM blockade)
DIAPHRAGM UP / oral anaerobes → use _______
Diaphragm down → use ______
clindamycin
metronidazole
NITROIMIDAZOLES
Primary tx of ________ and _______ infxns
Therapeutic uses: _________ infections w aerobic + anaerobic
MOA: production of ________ that are toxic to microbe → _________
Drug _______ activation by intracellular transport proteins ONLY IN ANAEROBIC CELLS
ADEs → 2
anaerobic, protozoal
polymicrobial
free radicals → disrupt DNA structure
reduction
GI/altered taste, CNS/disulfiram like
Which drug class used for anaerobic and protozoal infxns?
nitroimidazoles
NITROIMIDAZOLE PK/PD
Metronidazole
Abs
Vd
Metabolism
Excretion
Tinidazole
Abs
Vd
Metabolism
Excretion
good PO
tissues+CSF
hydroxymethyl = active; glucuronide/ox = inactive
renal
good PO
tissues
CYP3A4 substrate, ox/hydrox/conjug
little