CH 2 Blood Vessels and Circulation
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
unique feature of capillaries
they have “leaky” walls via either clefts or fenestrations
cleft
incomplete tight junction
pulmonary circuit
moves blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and back to the heart.
systemic circuit
moves blood from left side of the heart to the head and body and returns it to the right side of the heart to repeat the cycle.
walls arteries vs veins
thicker walls, smaller lumen, and elastic membrane
types of arteries
elastic, muscular, arteriole
arteriole
very small artery that leads to a capillary. have the same three tunics as larger vessels but way thinner
perfusion
distribution of blood into the capillaries so they can supply tissues with blood
flow through capillaries is often described as
microcirculation
types of capillaries
continuous, fenestrated, sinusoid
sinusoid capillary
the most leaky, allowing for the largest molecules to pass through. has incomplete basement membrane and intercellular gaps
fenestrated capillary structure
has pores (fenestrations) along with tight juncs allowing for large molecules to pass through
continuous capillaries
least leaky, have complete endothelial lining with incomplete tight junctions between cells allowing for small molecules to pass through
fenestrated capillary locations
small intestine, kidneys, choroid plexus of the brain, and endocrine structures
sinusoid capillary locations
lymph nodes, liver, bone marrow, spleen, pituitary gland + other endo glands
continuous capillary locations
everywhere (all vascularized tissue)
metarteriole function
serve as thoroughfare channels to the venules which bypass the capillary bed, or as conduits to supply the capillary bed with blood
metarteriole
a short vessel arising from a terminal arteriole that branches towards the capillary bed
capillary bed
network of 10–100 capillaries connecting arterioles to venules
precapillary sphincters
smooth muscle sphincters surrounding the entrance to a capillary that can open or close to regulate blood flow
where does blood go if precapillary sphincters are closed
flows directly from the metarteriole to the thoroughfare channel
thoroughfare channel
tube from the metarteriole that bypasses the capillary bed and directly connects to venules
why do pre capillary sphincters need to close? what would happen if all of them stayed open
they would collectively hold all of the blood in the body leaving the veins and arteries empty
when do precap sphincters open
when the surrouding tissue needs oxygen and have excess waste products
vascular shunt
the continuation of metarteriole and thoroughfare channel that allows blood to skip the capillary beds and go straight to venule
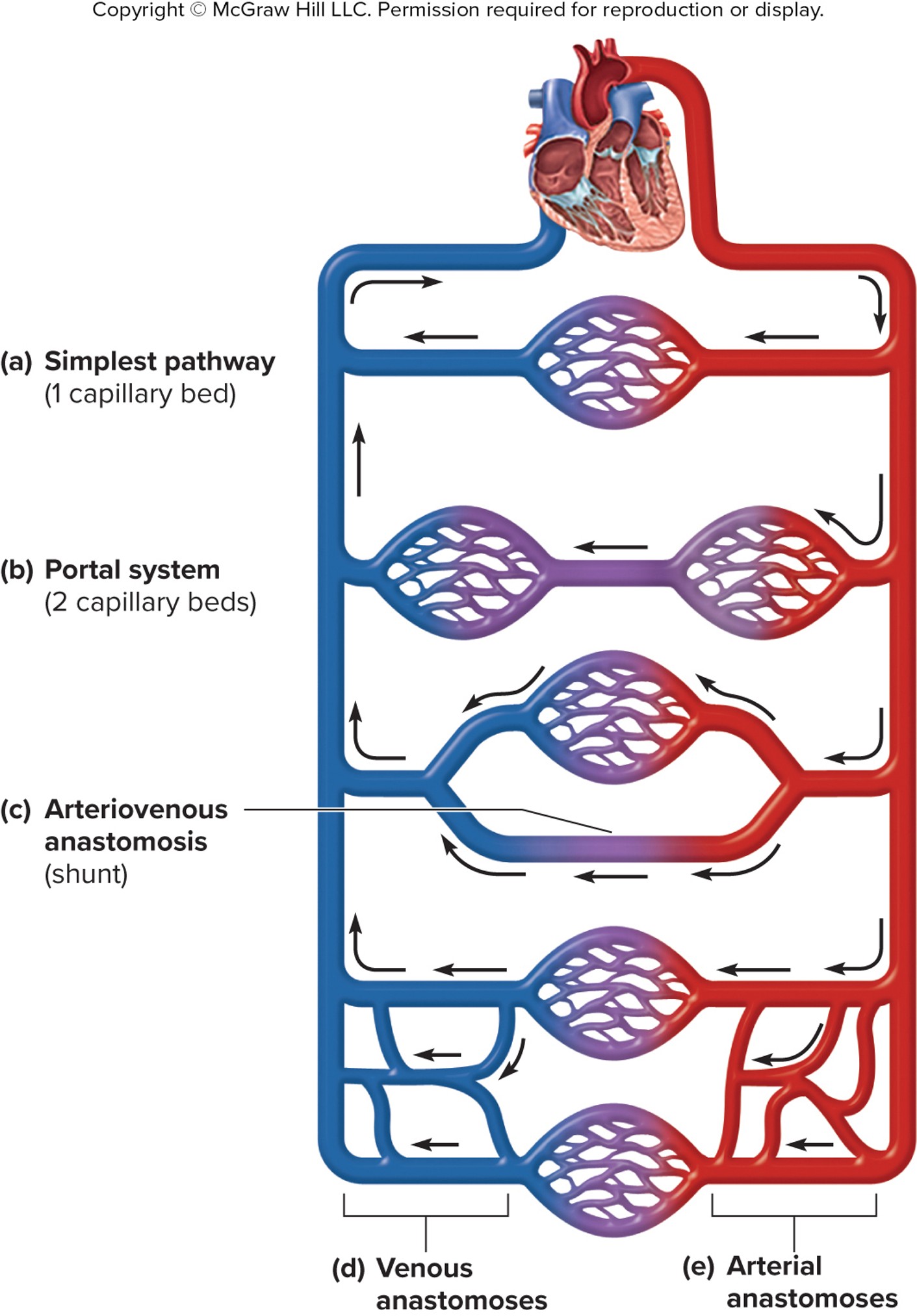
arteriovenous anastomosis
short vessel connecting an arteriole directly to a venule and bypassing the capillary beds
is blood flow through capillary beds smooth or pulsating
pulsating
vasomotion
irregular, pulsating flow of blood through capillaries and related structures
where does blood go if precap sphincters are open
through the capillary bed
veins vs venule
veins are larger and have valves to prevent back flow of blood. venules are basically mini veins without valves
venule
an small vessel leading from the capillaries to veins
skeletal muscle pump
a system promoting venous return of blood during locomotory activity, is done via peripheral veins
peripheral veins
veins in your limbs with one-way valves that direct flow away from the limb and toward the heart
how does the skeletal muscle pump work
when body is in motion skeletal muscles contract, peripheral veins in between them undergo compression causing their valves to open and push blood upwards. when body is relaxed, peripheral veins become decompressed and the blood remains.
variations in circulatory pathways
simple pathway: one capillary bed
portal system: 2 cap beds
arteriovenous anastomosis (shunt/highway)
venous anastomoses
arterial anastomoses
blood flow
refers to blood movement through vessel/organ/tissue, is measured in volume of blood per unit of time
resistance
any factors that slow or counteract blood flow
blood pressure
the force blood exerts on the walls of a vessel or heart chamber
hydrostatic pressure
the force exerted by a fluid due to gravitational pull, usually against the wall of the container its in
systemic arterial blood pressure
blood pressure without any specific descriptors, follows the pressure of blood flowing in systemic arteries
clinical measure of blood pressure
mm/Hg “milimeters of mercury”
why is it measured in milimeters of mercury
because the old historical machine they used to measure BP was a vertical tube of mercury (Hg) and they would measure how high it would get in mm to find BP
systolic and diastolic pressure
expressed as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure, the higher value is systolic and lower value is diastolic
normal adult blood pressure
120/80
systolic pressure
higher value, reflects arterial pressure resulting from the ejection of blood during ventricular contraction (systole)
diastolic pressure
lower value, represents arterial pressure of blood during ventricular relaxation (diastole)
pulse pressure
systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
represents the average pressure of blood in the arteries, formula is diastole + pulse pressure divided by 3
systole
contraction of ventricle muscles to release blood
diastole
ventricular relaxation
pulse sites of head and neck
temporal artery, facial artery, common carotid artery
pulse sites of the limbs
brachial artery, radial artery, popliteal artery, posterior tibial artery, dorsalis pedis artery, femoral artery
variables affecting blood flow and BP
cardiac output, compliance,volume of the blood, viscosity of the blood, blood vessel length and diameter
cardiac output
measurement of blood flow from the heart through the ventricles, usually measured in liters per minute
compliance
the ability of any compartment to expand to accomodate extra content (eg, heart and veins)
what is reduced when an artery is stiffened
compliance
there is a _____ correlation between blood volume, BP, and blood flow
positive
if blood volume decreases, BP and blood flow:
decrease
Hypovolemia
decrease in blood volume
Hyperlovenia
increased blood volume
viscocity of the blood is directly proportional to
resistance
viscocity is inversely proportional to
blood flow
The length of a blood vessel is directly proportional to its
resistance (bc gravity)
2 main determinants of blood viscocity
formed elements and plasma proteins
length of blood vessels during childhood vs adulthood
increase during childhood, stagnate during adulthood
the diameter of blood vessels _______ throughout the body depending on ___
changes, the type of vessel
the diameter of any given BV can _______ throughout the day
change
the diameter of BVs can quickly change in response to
neural and chemical signals that trigger vasoconstriction or vasodialtion
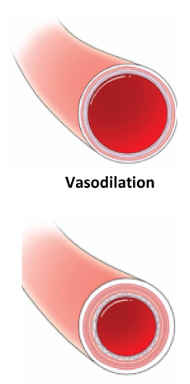
vascular tone
the contractile state of the smooth muscle and primary determinent of diameter
the effect of vessel diameter on resistance is
inverse (given the same volume of blood)
increased BV diameter means:
less blood contacting the walls, lower resistance, increased flow
decreased BV diameter
more blood contacting the walls, higher resistance, decreased flow
review: positive vs negative feedback mechanism
positive: when a product of a reaction leads to an increase in that reaction, strays from equillibrium
negative: when a product of a reaction leads to a decrease in that reaction, maintains equillibrium
example of positive feedback in cardiovascular system
blood clotting
example of negative feedback in cardiovascular system
blood pressure regulation
blood being pumped in the arteries goes from areas of _______ pressure to ______
higher, lower
transcytosis
transport of large molecules across capillary walls
mechanism of vasoconstriction and vasodilation
smooth muscles of the vessel walls either contract or relax to adjust their diameter, regulating blood flow
vasoconstriction/dialation is regulated by:
sympathetic nervous system and hormones
bulk flow
the mass movement of fluids into and out of capillary beds and tissue
bulk flow involves 2 pressure driven mechanisms:
filtration and reabsorption
filtration is driven by
hydrostatic pressure
reabsorption is driven by
osmotic pressure
what does osmotic pressure do
draws fluid back in
what does hydrostatic pressure do
push fluid out
hydrostatic pressure depends on __________ pressure
systolic blood pressure
osmotic pressure depends on
concentration of plasma proteins
elastic artery
arteries located close to the heart with a larger lumen and lots of elastic fibers
elastic artery functions
elasticity causes recoil during blood pumping which helps maintain the pressure gradient that circulates blood, large lumen allows it to accept large amounts of blood
Reabsorption: _____ → _______
tissues (interstital fluid) to capillaries
Filtration: _____ → _____
capillaries to tissue (intersital fluid)