Biology - Section 1: Evolution, the Themes of Biology, and Scientific Inquiry
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Properties of Life
Order
Evolutionary Adaptation
Regulation
Reproduction
Response to the Environment
Growth and development
Energy processing
Themes of Biology
Organization
Genetic Information
Energy and Matter
Interactions
Evolution
Biological Organization: Biosphere
• All places on Earth where life exists
• All life on earth
Biological Organization: Ecosystems
• All living organisms in one area
• Co-exist with non-living components
Biological Organization: Communities
• Array of organisms inhabiting a particular ecosystem
Biological Organization: Populations
• All individuals of a species within a community
Biological Organization: Organisms
• Individuals within a population
Biological Organization: Organs
• Within body of an organism, made of multiple tissues
• Carry out specific functions of organism
Biological Organization: Tissues
• Groups of cells within an organ, working together
• Perform specialized tasks
Biological Organization: Cells
• Fundamental unit of structure and function
Biological Organization: Organelles
• Structures within cells that carry out specific functions
Biological Organization: Molecules
• Chemical structures composed of two or more atoms
Biological Organization: Reductionism
Reducing complex systems to simpler manageable units
• Example: studying the molecular structure of DNA
• Incomplete view of life
Emergent properties
Novel properties that emerge at each higher level of organization
• Due to arrangement and interactions of parts as complexity increases
• Example: Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplast but not chlorophyll and the other molecules in a test tube
• Difficult to study
Systems biology
System: network of independent components that function together
Systems biology models dynamic behaviour of biological system by studying interactions among system’s parts
Can be used to study biology at all levels
Examples: blood pressure global warming 14
Biological Organization: Structure and function
Structure and function are correlated at all levels of biological organization
• Leaves
Thin, flat structure maximizes chloroplasts’ ability to capture sunlight
• Hummingbird wings rotate at shoulder, enabling hovering
• Ecosystem function results from interactions among biotic and abiotic components
Nutrient cycling – N in atmosphere converted by plants to a form usable by animals
Cell theory
All living organisms are made of cells
All cells share which characteristics?
Enclosed in membrane
DNA as genetic information
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells
• Membrane-enclosed nucleus
• Membrane-enclosed organelles
• Found in Eukarya
Prokaryotic cells
• Smaller and simpler
• No membrane-enclosed nucleus
• Found in Bacteria and Archaea
Genes
units of inheritance
• Encode information to build the molecules in cell
• Transmitted from parent to offspring
• Transmitted during each cell division within an organism
• Directs development of organism
Molecular Structure of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
Two long strands arranged in a double helix
• Nucleotides
• Adenine (A)
• Guanine (G)
• Cytosine (C)
• Thymine (T)
Specific sequences of nucleotides make up genes
• Structure accounts for ability to store information
Gene expression
Process by which information in a gene controls production of a cellular product (protein).
• Intermediary – ribonucleic acid or RNA
• The gene is a section of DNA within a chromosome with a specific, unique sequence
Transcription
DNA sequence is copied to messenger RNA (mRNA)
Translation
mRNA sequence is translated to amino acid sequence
• Amino acid sequence determines protein produced
• A universal genetic code determines how the RNA sequence is translated to amino acids
• For some genes, RNA itself is the end product
Genome
Entire set of genetic material in organism
Genomics - study of whole genomes of one or more species
Proteome
All proteins expressed within given cell, tissue, or organism
Proteomics - study of sets of proteins and their properties
Large-Scale Analysis of Biological Sequences - Three research developments:
High-throughput technology
Multiple samples analyzed simultaneously
Rapid collection of large amount of data
Bioinformatics
Using computational tools to analyze, store, and organize biological information
DNA, RNA, protein sequences
Interdisciplinary research teams
Transfer and Transformation of Energy and Matter
Sunlight captured by producers is converted to chemical energy for themselves and for consumers
• Living organisms require energy to do work – for movement, growth, reproduction, cellular activities
• Energy input and transformation from one form to another makes life possible
Energy Flow and Chemical Recycling
Chemicals are recycled within an ecosystem ... decomposers
• Energy flows through ecosystem in one direction → light to heat
Feedback regulation
Allows biological processes to self-regulation. Product regulates process.
Negative feedback
• Response reduces/counteracts initial stimulus, returning a system to a balanced state
• Ex: Insulin signaling
Positive feedback
• Response reinforces stimulus, increasing response
• Ex: Platelets and injury
Interactions with Other Organisms and the Physical Environment
Organism interact continuously with physical features of environment
Interactions regulate ecosystems as a whole
Organism - Organism interactions
Mutually beneficial
Parasitic (1 beneficial, 1 harmful)
Mutually harmful
Commensal (one species benefits, the commensal, while the other, the host, neither benefits nor is harmed).
Human Interactions with Environment
• Increased burning of fossil fuels last 150 years
• Excess CO2 release leading to trapped heat and global warming – 1oC since 1900
• Climate change – directional change to global climate lasting 30 years or more
• Consequences: loss of habitat, range shifts, population declines or species extinction, population increases
Examples:
• Increased mortality of polar bears
• Ivory gull population decline by 80%
• Mountain pine beetle outbreaks
Evolution
All living organisms are modified descendants of common ancestors.
→ Descent with modification
→ Explains both the unity and diversity of life
→ Accounts for adaptations of organisms to particular environments
Each species given two-part name:
✗ Genus – plural general
✗ Specific epithet – unique to species
✗ Example: Homo sapiens
The Three Domains of Life
• Bacteria (prokaryotes)
• Archaea (prokaryotes)
• Eukarya (eukaryotes)
Domains Bacteria and Archaea
• Prokaryotes are single-celled and microscopic
• Cell structure simpler than eukaryotes
Kingdoms of Eukarya
Four Kingdoms:
• Plantae - Photosynthesis
• Fungi - Absorb nutrients
• Animalia - Ingest other organisms
• Protists – Diverse group of single-celled eukaryotes
How can we account for life’s dual nature of unity and diversity?
Process of evolution accounts for life’s similarities and differences
• DNA as the universal genetic language
• Cell structures similar among diverse organisms
• Similar skeletons among vertebrates
History of life as documented by fossils and other evidence
Charles Darwin - Descent with Modification
Contemporary species arose from a succession of ancestors that differed from them.
Explains duality of unity and diversity
Unity due to descent from common ancestor
Diversity due to subsequent modifications in diverged lineages
Charles Darwin - Natural Selection
The cause of descent with modification.
✘ Individuals with inherited traits better suited to environment more likely to survive and reproduce
✘ Over generations, a higher and higher proportion of the population will consist of individuals with advantageous traits
✘ Evolution occurs as as unequal reproductive success leads to adaptation to the environment
Evolutionary Adaptation
The environment “naturally selects” individuals with advantageous traits for propagation
Result – adaptation of populations and species to local environment
The Tree of Life - Explanation
Over time ancestral species to give rise to 2 or more descendent species.
• Similarity due to common ancestor
• Diversity due to modification by natural section
• Example: Bat wing is modified forearm adapted for flight
Common architecture with other mammalian forearms
The Tree of Life - Diagram
• Evolutionary relationships illustrated with tree-like diagrams
• Branch point represents common ancestors
• Closely-related species have more recent common ancestor and share more features
• Shows temporal dimension of biology
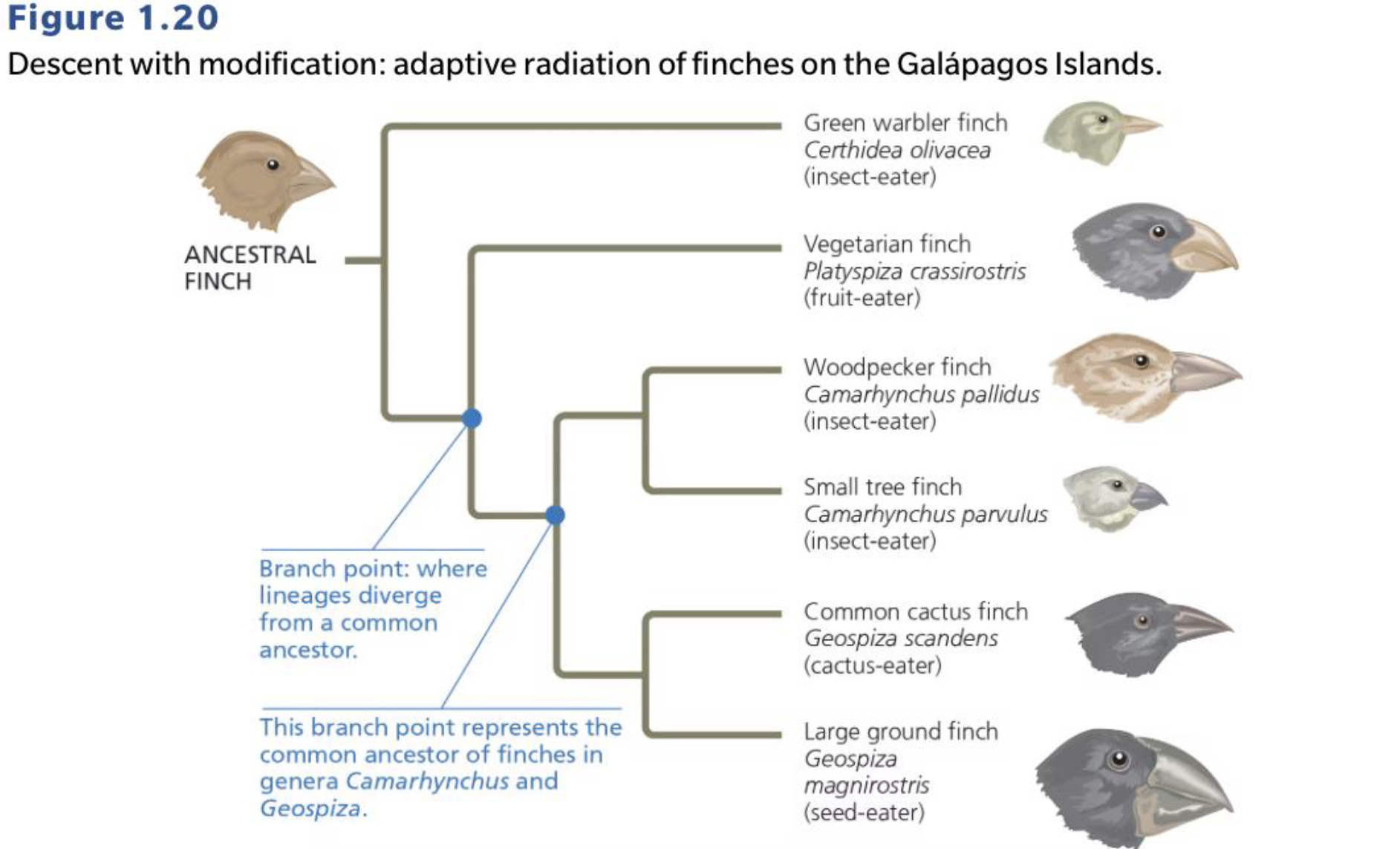
Gathering and Testing Data
✘ Observation – the gathering of information
✘ Data – recorded observations
Qualitative
Quantitative
✘ Statistics – branch of mathematics used analyze and determine significance of data
✘ Inductive reasoning – logic in which generalizations are based on many specific observations
✘ Scientific literature – set of published studies or findings
Forming and Testing Hypotheses
✘ Hypothesis – explanation, based on observations and assumptions, that leads to a testable prediction
Guided by inductive reasoning
✘ Experiment – scientific test carried out under controlled conditions
✘ Scientific method – idealized process of inquiry based on hypothesis testing
✘ Limitations: not all hypotheses can be tested, or meet criteria of science
Deductive reasoning (if hypothesis is not proven correct)
logic in which specific results are predicted from a general premise.
✘ Hypotheses are not proven correct
✘ A hypothesis is supported when not proven incorrect
✘ Repeated testing increases confidence in validity
✘ Scientific consensus – shared conclusion that a particular hypothesis explains the known data and stands up to experimental testing
Variables
Factors being manipulated and measured
✘ Independent variable – factor being manipulated, values set by researcher
✘ Dependent variable – factor being measured, predicted to be affected by independent variable
Controlled experiment – experiment where an experimental group is compared to a control group
• Control group cancels effect of other features of the experimental environment
Theory
Explanation of aspect of natural world
• Broader than a hypothesis
• Generate new hypotheses
• Supported by large body of evidence
• May be modified or rejected upon new information