factors affecting eye witness testimonies
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
it is used as evidence by lawyers to convict a criminal
however research suggests it is very unreliable
what are the 4 factors affecting eye witness testimonies?
leading questions/misleading information
post-event discussion
Anxiety
* leading questions can influence recall
* memories can be inserted
* memories can be changed
what was the IV and DV in Loftus and Palmer?
IV = critical questions being phrased differently using smashed, collided, bumped, hit and contacted
DV = to estimate the speed of a car at the point of impact
what were the results in Loftus and Palmer?
smashed= 40.5
collided =39.3
bumped = 38.1
hit = 34.0
contacted = 31.8
why did Loftus and Palmer do a replication study?
because it doesn’t necessarily show that participants memories were changed by leading questions
what was the replication study for Loftus and Palmer?
2 conditions one used hit and one used smashed in the critical question and a control
1 week later a follow up question of did you see any glass?
what were the results of Loftus and Palmers 2nd study?
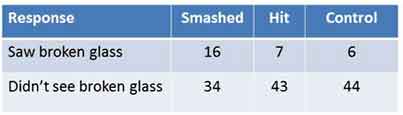
what is post event discussion?
the memory of an event may be altered or contaminated through discussing events with others
what is the conformity effect?
co-witnesses may reach a consensus view of what happened
what evidence is there for post event discussion affecting eye witness testimonies?
Gabbert (2003)
what did Gabbert do?
ps were put into pairs where the partner watched a different video of the same event
they both saw unique items
pairs in one condition discussed the event before each partner was asked to recall the event they had just watched
what were the results of Gabbert’s study?
71% of ps who had discussed the event with their partner mistakenly recalled items discussed by the other partner of which they did not see in their video
what are the strengths of leading questions and post-event discussion for affecting eye witness testimonies?
supporting evidence
real world applications
what is the largest factor in convicting innocent people?
mistaken eye witness testimony
why is Gabbert’s study useful application?
for the police interviews such as avoiding repeat interviewing
how is memory affected by the investigator every time a witness is interviewed?
become increasingly vulnerable to investigator effects as comments from the investigator may incorporate into their memory
what are the negatives of misleading questions and post-event discussion affecting eye witness testimonies?
experiments lack ecological validity
economic implications
how do experiments in misleading questions and post-event discussion lack ecological validity?
as the participants may know they are not watching a real event
what is contrasting research for misleading questions?
Yuille and Cutshall
what did Guile and Cutshall show?
witnesses and very accurate memory of a highly stressful real life event and were resistant to the effects of two misleading questions inserted by the research team
according to what might anxiety affect recall?
Yerkes-Dodson Law
what is supporting evidence for the negative effect of high anxiety on recall?
Deffenbacher et al (2004)
what did Deffenbacher et al (2004)do?
carried out a meta-analysis looking at the effect of anxiety on accuracy of eye witness testimony
what did Deffenbacher et al (2004) conclude?
that high levels of stress had a negative effect on eye witness testimony
what does Yuille and Cutshall argue?
heightened emotion can enhance eye witness testimony accuracy
what did Yuille and Cutshall do?
performed a case study where they interviewed witnesses of a real life incident
what were witnesses memory like in Yuille and Cutshall?
very accurate memory of this highly stressful event
what were the results of when thirteen witnesses were re-interviewed 5 months later?
recall was found to be accurate even after a long time
where exactly were the witnesses who experienced the highest levels of stress?
were actually closer top the event
what is one explanation for why anxiety may harm recall?
the weapon focus effect
what is the weapon focus effect?
where anxiety causes the witness to focus on central details (a weapon) rather than what is going on
so the ability of a witness to identify the offender may be reduced
why may the weapon focus effect reduce the ability of a witness to identify the offender?
all the witnesses’ attention is drawn to the weapon and away from other things
what did Johnson and Scott (1976) do?
asked 2 groups of p’s to discuss situations they saw
1 group saw a man covered in grease holding a pen and the other groups the same man covering in blood holding a pen knife
what were the results Johnson and Scott (1976)?
49% of p’s from group 1 could later identify the man from 50 photos compared to group 2 were only 33% of p’s could identify the man
what is contrasting research to Johnson and Scott?
Pickel (1998)
what did Pickel do?
showed 230 American students a video on an accident in an hair salon
a man entered the salon and approached the receptionist who handed him the money then left
what type of design was this experiment?
independent measures
what was the IV in Pickel?
what the man was holding in the video
what were the five conditions in Pickel?
scissors (high threat/low unusualness)
gun (high threat/high unusualness)
wallet (low threat/low unusualness)
raw whole chicken (low threat/high unusualness)
empty (control)
what were the results of Pickel?
empty condition had the highest mean memory score of 9.02
the non-unusual object condition had a mean memory score of 8.33
unusual condition had a score of 7.52