A6- Unit 1 (Types of circuits, laws, fundamentals)
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 1 flashcards covering the laws of circuits, ohms, resistance, overview of basic fundamentals of electricity.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
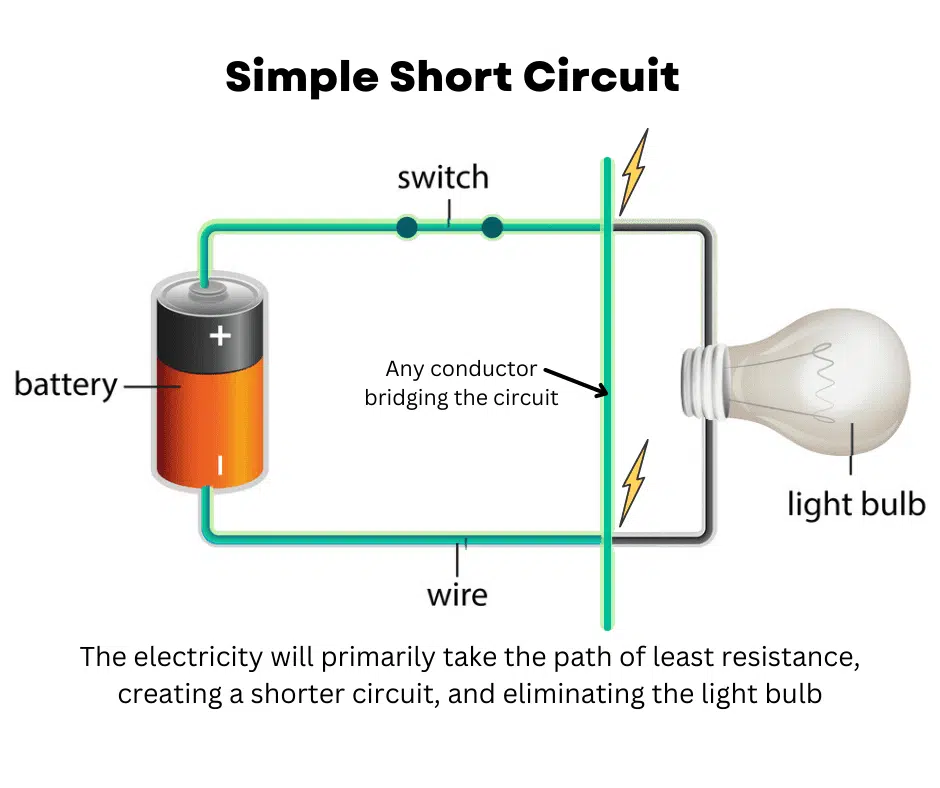
Circuit - short circuit
causes unintended path in a circuit * bypasses a load, low resistance *low resistace > high voltage pressure > high current; in a Short circuit
Circuit - series circuit
A type of electrical circuit where components are a single path for current flow. In a series circuit, the same current flows through all components, and the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances.
Circuit - Parallel circuit
A type of electrical circuit where components are connected in multiple paths for current flow. In a parallel circuit, the voltage across each component is the same, and the total current is the sum of the currents through each path.
Circuit - series / Parallel circuit
A type of electrical circuit configuration where components are both connected along a single path (series) and in multiple paths (parallel), determining how current flows and how resistances combine. (Add the sum of series and sum of parallel resistance to get the sum of the total resistance)
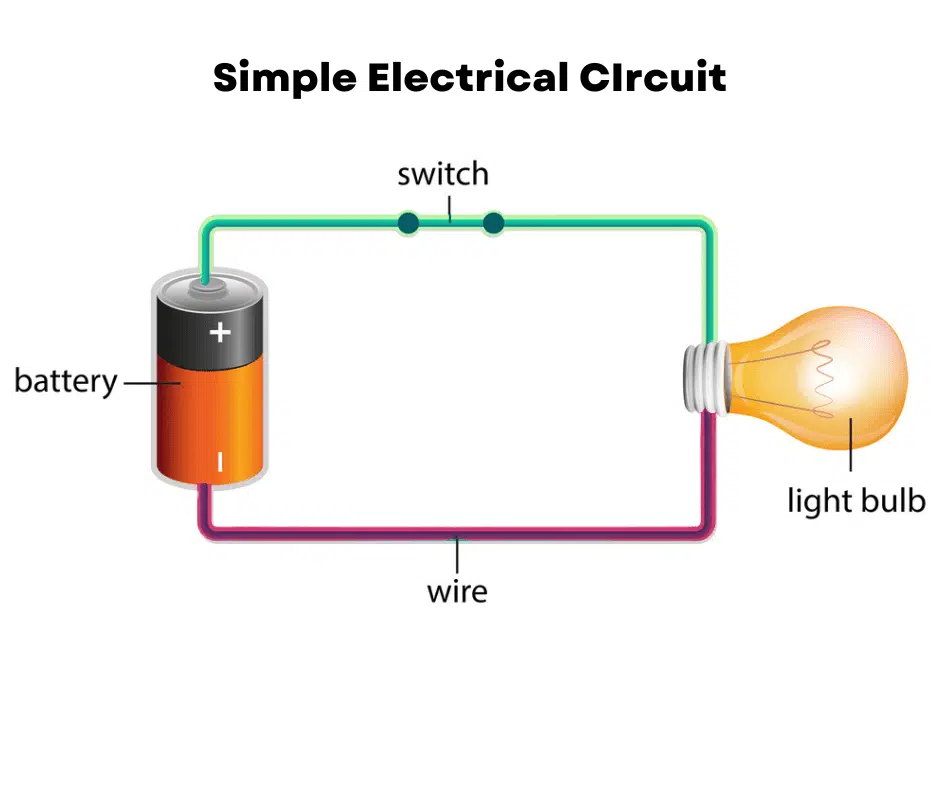
Circuit - open circuit
A type of electrical circuit that is not complete, meaning there is a break in the pathway for current flow. In an open circuit, electricity cannot flow, and devices connected within the circuit do not operate.
Circuit - closed circuit
A type of electrical circuit that is complete, allowing current to flow uninterrupted. In a closed circuit, electrical devices can receive power and operate normally.
Ohms Formula
I = Current / AMP, E = Voltage, R = Resistance; The points of ohms formula is to find the missing variable to a part of the circuit.
Resistance formula
R = V / I; This formula is used to calculate resistance in a circuit by dividing the voltage across a component by the current flowing through it.
Voltage Formula
V = I x R; This formula is used to relate voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit.
AMPs / Current Formula
I = V / R; This formula is used to calculate current in a circuit by dividing the voltage across a component by the resistance.
Definiton of Resistance
Resistance is a measure of the opposition to the flow of electric current in a circuit, expressed in ohms (Ω). It determines how much current will flow for a given voltage.
Definition of Voltage
Voltage is the measure of electric potential difference between two points in a circuit, expressed in volts (V). It indicates how much energy is available to push charge through a circuit.
Definition of Current
Current is the flow of electric charge in a circuit, measured in amperes (AMPs). It represents the rate at which charge passes a point in the circuit.
Whats the difference between current & amps
Current refers to the flow of electric charge, while amps (amperes) is the unit of measurement for that flow. Essentially, current is the concept, and amps quantify it.
how is EMF correlated to Automotive electricity? And how does it do what it does?
Electromotive force (EMF) is the voltage generated by an energy source in a circuit, driving current through it. In automotive electricity, EMF is crucial for powering electrical components and systems, ensuring they operate effectively.
How is EMF created? And how is valence ring correlated in energy?
EMF is created through the chemical process of car batterys in this case; The Valence ring is correlated in the flow of energy because a valence ring contains electrons, a ring with less electrons needs more electrons to balance with other atoms this absorbs atoms from another atom but now the other atom needs more too this creates a chain of reactions
The basic fundamentals of valence ring & law
The Valence ring is the current flow, to split electrons in a valence ring it requires EMF(In the battery); this makes the -(valence ring with less electrons) attracted to +(valence ring with more electrons) conducting energy through conductivity.
Switches
a physical switch that switches the component current to take another path when switched physically.
Relays
acts a switch but instead of needing a physical entity to change the path it uses a Electromagnetic relay to ‘switch‘
Resistor
A Resistor is a component that creates resistance in a load and/or wires.
Wires, loads, power-source, fuses
Wires - Conduct flow
Loads - the components in a circuit that acts a tool for the whole circuits making a purpose.
Power Source - The car battery & alternator
Fuses - Glassbox fuses, Blade fuses, Fuse links; These all melt and need replacement