BIO Lab final
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Phenotype
Long or short bill
In H-W equation phenotype frequencies would be p2 + 2pq (long bill) and q2 (short bill) respectively
Genotype
LL, Ll, ll
In H-W equation genotype frequencies would be p2, 2pq and q2 respectively
Allele
L or I
In H-W equation allele frequencies would be p and q respectively
Natural selection
Those individuals with advantageous traits survive better and therefore live to reproduce more, passing
those traits on to the next generation.
These traits exist BEFORE the selection occurs
Genetic drift
Random change in allele frequencies and thus the traits they encode. Can result from random mating if population becomes small (population bottleneck)
Founder effect
A type of genetic drift, in which a new population is founded in a geographically
distinct region.
Monophyletic
Includes common ancestor and ALL its descendants. So every branch that arises from the
common ancestor must lead to species that are part of the group in question.
Paraphyletic
includes common ancestor and but NOT all its descendants. So some branch that arises from the
common ancestor will lead to species that are NOT part of the group in question
Polyphyletic
does not include common ancestor. This will usually be a group that is centered around a trait
that evolved separately (did not come from a common ancestor)
Derived Character
a trait found in a group that is not found in their ancestral group
Homoplasy
a character trait shared between two groups that is NOT inherited from their common ancestor.
Synapomorphy
a trait that is derived from the most recent common ancestor. Found in all its descendants.
PHYLUM PORIFERA
Sponges
No true tissues or organs, pore-bearing
PHYLUM CNIDARIA
Jellyfish, corals, anemones
Radial
tentacles with stinging cells called nematocysts
PHYLUM PLATYHELMINTHES
Flatworms (planaria, tapeworm...)
Bilateral
Dorso-ventrally flattened worms
PHYLUM NEMATODA
Roundworms – (C. elegans, Ascaris)
Bilateral
Smooth, round-bodied worms with tapered ends
PHYLUM ANNELIDA
Segmented worms (earthworms, leeches...)
Bilateral
PHYLUM MOLLUSCA
Clams, mussels, squid, octopus, snails, slugs...
Bilateral
Mantle, muscular foot
PHYLUM ARTHROPODA
Insects, spiders, scorpions, lobster, crab, shrimp…
Bilateral
Jointed appendages, chitinous exoskeleton
PHYLUM ECHINODERMATA
Sea stars, sea urchins, sea cucumbers...
Bilateral & secondary pentaradial
Cephalochordata (invertebrates)
lancelets
notochord extend to front of head
Tunicata (invertebrates)
Tunicates (sea squirts)
Tough outer covering or tunic
pharyngeal slits only
Agnatha
Jawless fish (lamprey, hagfish)
jawless fish
Chondrichthyes
Cartilaginous fish (sharks, skates, rays)
Fish with skeleton made of cartilage
pharyngeal slits (gills), dorsal nerve cord, post-anal tail,
a few have notochord but most do not
Osteichthyes
Bony fish
fish with skeleton made of bone
pharyngeal slits (gills), dorsal nerve cord, post-anal tail
Amphibia
Frogs, salamanders...
incompletely adapted to life on land
Respire at least partially through their skin
dorsal nerve cord, post-anal tail (many)
A few have gills as adults, but most do not
Reptilia
Snakes, crocodiles, turtles
completely adapted to life on land, amniotic egg, scaly skin
dorsal nerve cord, post-anal tail
Aves
Birds
feathers, beaks
dorsal nerve cord, post-anal tail
Mammalia
Horse, cow, cats, humans, etc.
hair, mammary glands
dorsal nerve cord, post-anal tail (in most)
Exponential
growth continues indefinitely
Not usually seen in nature
Graph does not level off
Population increases exponentially
Logistic
Common in nature
Graph looks sigmoidal (S-shaped)
Plateau is at carrying capacity
Environmental resistance causes curve to
level off
Density-dependent
only affect population growth when the population is large. This is the type of factor causing the environmental resistance (leveling off) in the logistic curve above. The curve is unaffected at low populations (starts off looking exponential) but when the population gets large growth is affected.
often necessary resources, such as food and water. When population is low there is plenty, but become limiting when population is large
Density-independent
affect population growth even when population is small
natural disasters, etc.
Lincoln-Petersen
𝐍 = (𝐌 ∗ 𝐂)/𝐑
N = the population estimate
M = number of animals marked in first capture
C = number of animals in recapture
R = marked animals in recapture
Schnabel
Mi = number of previously marked animals at capture i
Ci = number of animals captured at capture i
Ri = previously marked animals captured at capture i
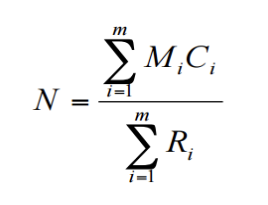
Tragedy of the commons
If a resource is open access (freely available for people to use in an unregulated way) it will eventually be destroyed.
Stream biodiversity simulation
Pollution had no effect on the total number of invertebrates caught
Pollution decreased the number of different species caught
Thus, biodiversity (variety of life) in the stream decreased
Plant biodiversity simulation
Certain types of plan thrived in the dry (xeric) environment while others did better in the moist (mesic) environment.
Notochord
a flexible skeletal rod that runs lengthwise through the animal closer to the dorsal (back) side. It is made a material similar to cartilage
Dorsal nerve cord
a hollow tubular chord of nervous tissue running lengthwise through the animal usually dorsal to the notochord
Pharyngeal slits
a series of parallel slits in the pharynx. They are modified into various structures in different chordates, for example gills in fish
Post-anal tail
a tail that extends posteriorly from the location of the anus
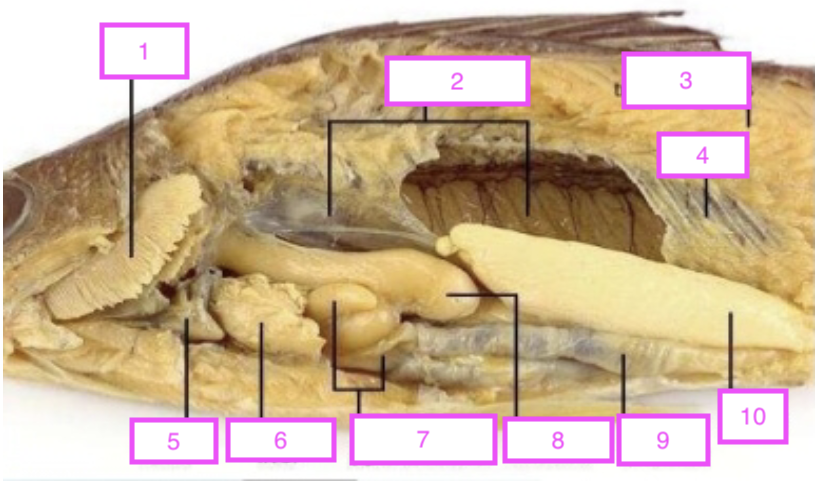
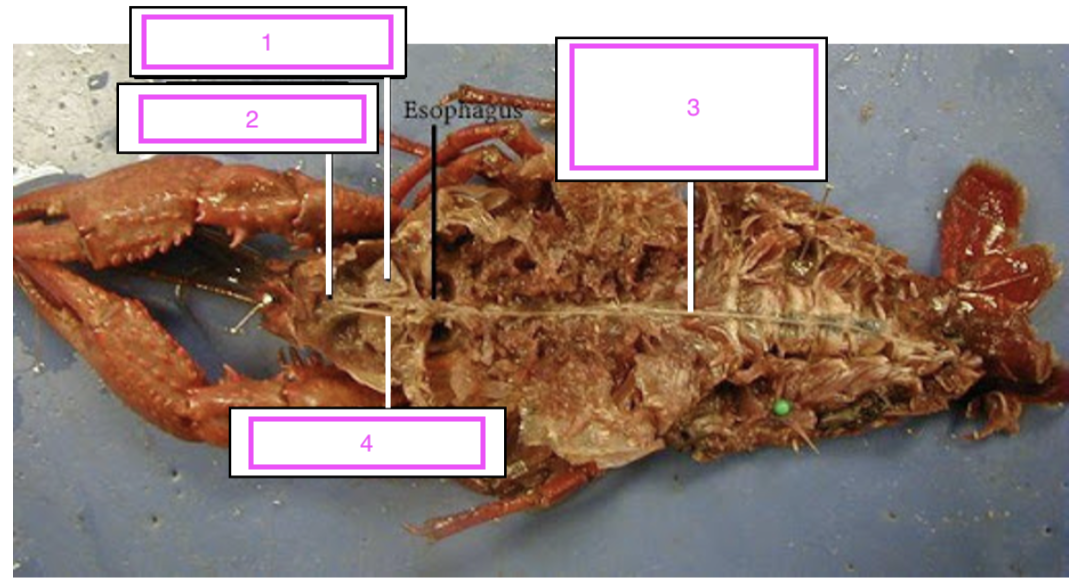
Cardiac stomach
Digestive gland
Heart
Gills
label numbers
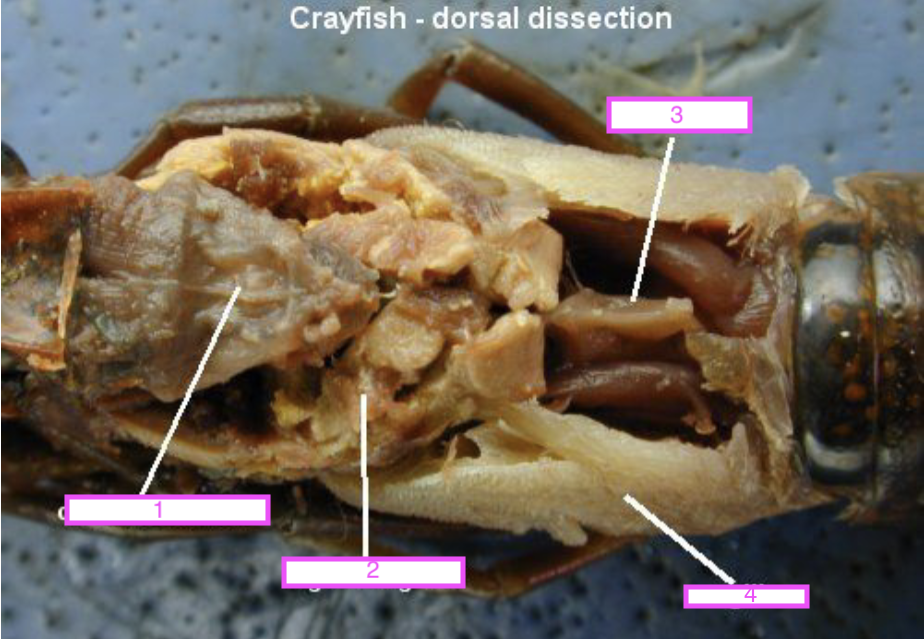
Green gland
Brain
Ventral nerve cord
Nerve cords
label numbers
gills
air bladder
trunk muscles
ribs
heart
liver
pyloric ceaca
stomach
intestine
gonad
label numbers