Biomechanics MT 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Biomechanics
the application of mechanical principles to living organisms
Center of Mass
average position of an objects mass.
Elasticity
the ability of an object to return to its original shape after being deformed
Momentum
mass x velocity
Newton’s first law
an object maintains its state of rest or uniform motion unless acted on by another force
Newton’s 2nd law
acceleration of an object depends on the mass of the object & the force applied
Newton’s 3rd law
for every action there will be an equal & opposite reaction
Plasticity
the propensity of a material to undergo permanent deformation under load
Pressure
applied force divided by the surface area to which the force is applied
Viscoelasticity
the property of a material that allows it to behave both as a viscous & elastic structure
On the stress-strain diagram of collagen, in what phase is little energy required to elongate the collagen fibers, no major bonds are disrupted, & crimp is being removed?
Past the yield point
Plastic zone
Toe phase
Linear phase
Toe phase
why are twisting movements associated annulus injury?
Twisting movements squeeze out the water content of the annulus.
Twisting does not cause injury to the annulus.
Half of the fibers of the annulus undergo tension; half relax.
The spine is only designed to withstand compressive forces.
Half of the fibers of the annulus undergo tension; half relax.
What is the term that describes the loss of energy with repetitive loading & unloading cycles in the physiologic zone?
Hysteresis
Creep
Fatigue failure
Relaxation
Hysteresis
Which of the following are more likely to cause a disc herniation?
A major traumatic event
Repetitive microtrauma
Repetitive microtrauma
Which cells maintain & repair the disc matrix?
Discocytes
Chondrocytes
Fibroblasts
Lymphocytes
Chondrocytes
Fibroblasts
What is the orthogonal listing for the malposition below?
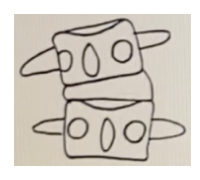
a. -Tz, +Ry, +Rz
b. -Tz, -Ry, +Rz
c. -Tz, +Ry, -Rz
d. -Tz, -Ry, -Rz
-Tz, -Ry, -Rz
What is the standard listing for the malposition below?
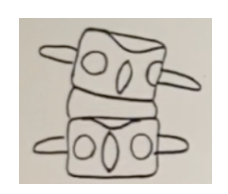
a. PLS
b. PRI
c. PRS
d. PLI
PRI
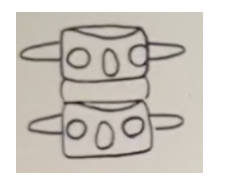
What is the standard listing for the malposition below?
a. RP
b. PR
c. PL
d. LP
PR
What is the standard listing for left rotation restriction, right lateral flexion restriction?
a. PRI
b. PLS
c. PLI
d. PRS
PLI
11. Select all the listings that correctly describe the malposition below.
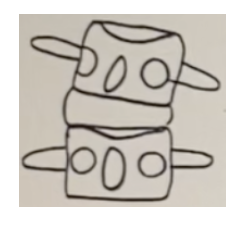
a. Right rotation malposition, right lateral flexion malposition.
b. Left rotation restriction, left lateral flexion restriction.
c. PLS
d. PRS
e. -Tz, -Ry, +Rz
f. PRI
a. Right rotation malposition, right lateral flexion malposition.
b. Left rotation restriction, left lateral flexion restriction.
c. PLS
e. -Tz, -Ry, +Rz
Select all the listings that correctly describe the malposition below.
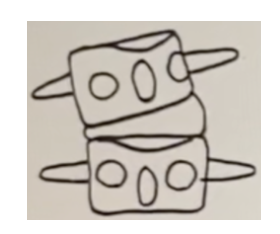
a. -Tz, +Ry, -Rz
b. PLI
c. PRS
d. -Tz, -Ry, +Rz
e. Left rotation malposition, right lateral flexion malposition.f. PRI
-Tz, +Ry, -Rz
PRS
Which glycosaminoglycan has the highest water binding capacity?
a. Phosphorous sulfate
b. Hyaluronic acid
c. Chondroitin sulfated. Keratin sulfate
Chondroitin sulfate
Annulus fibrosus
60-70% water
resists tension
type I collagen fibers
Nucleus pulposus
70-90% water
resists pressure
type II collagen fibers
Which IVD injury is most likely to occur with high-rate compression loading?
a. End plate fracture.
b. Circumferential annular tear
c. Radial annular tear
d. Disc herniation.
End plate fracture.
When the spine undergoes compression, the bracing mechanism of the IVD stabilizes & protects the FSU. Place the following steps of the bracing mechanism in chronological order.
a. Compression of FSU
b. Height of IVD decreases pressure exerted on nucleus pulposus.c. Nucleus pulposus expands radically.
d. Annulus fibrosus undergoes tension.
e. Annulus fibrosus reaches maximum tension.
f. Equilibrium established, bracing mechanism successful.
b. Height of IVD decreases pressure exerted on nucleus pulposus.
c. Nucleus pulposus expands radically.
d. Annulus fibrosus undergoes tension.
e. Annulus fibrosus reaches maximum tension.
Bending
half of the fibers undergo tension; half of the fibers undergo compression
Compression
all the fibers undergo tension.
Distraction
all fibers undergo tension
Shear
half of the fibers undergo tension; half of the fibers are relaxed
Torsion
half of the fibers undergo tension; half of the fibers are relaxed
Which of the following corresponds with Contact Point (segmental & doctor)?
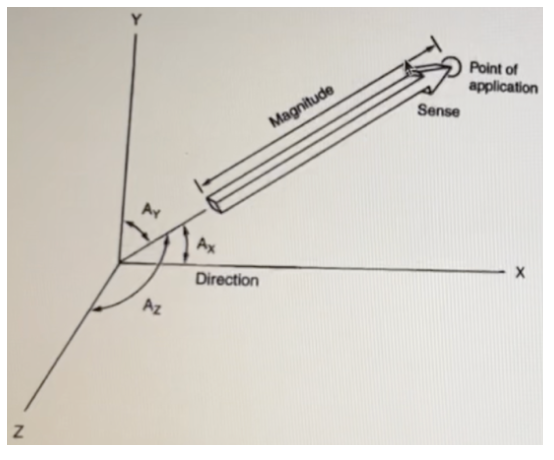
a. Arrowhead
b. Angle of application
c. Point of application
d. Magnitude
c. Point of application
Scalar
time, temperature, speed
Vector
force, velocity, acceleration
While performing a posture analysis, you notice that your patient has a high right shoulder & low left shoulder indicating left lateral flexion through the thoracic spine. What is the orthogonal listing for this postural imbalance?
a. -Rz
b. +Rz
c. +Rx
d. -Rx
-Rz
What anatomical plane does lateral flexion occur in?
a. Sagittal
b. Transverse
c. Frontal/coronal
Frontal/coronal
What ligament limits extension of the FSU?
a. Intertransverse ligament
b. Supraspinous ligament
c. Posterior longitudinal ligament
d. Anterior longitudinal ligament
Anterior longitudinal ligament
The physiologic range of motion is made of what two zones?
a. Neutral zone
b. Plastic zone
c. Failure
d. Elastic zone
Neutral zone
Elastic zone
Bone is ananisotropic material. What is the definition of anisotropic?
a. A material in which the strength & stiffness are different with loads applied in different positions.
b. A material that has mechanical properties that are time dependent.
c. A material that will stretch & deform at a greater rate when load is applied with greater force or for longer periods of time.
d. A material in which the strength and stiffness are the same regardless of orientation.
A material in which the strength & stiffness are different with loads applied in different positions.
How would left rotation restriction & right lateral flexion restriction be described in the orthogonal system?
a. O+Ry, O-Rz
b. O-Tz, O+Rx
c. O+Ry, O+Rz
d. O+Rx, O+Rz
O+Rx, O+Rz
During axial rotation of the IVD:
a. Half of the annular fibers undergo tension.b. All the annular fibers undergo tension.
c. None of the annular fibers undergo tension.d. All the annular fibers undergo compression.
a. Half of the annular fibers undergo tension.
The primary function of the vertebral body is to absorb & transmit shear loads.
a. True
b. False
False
The IVD contains mostly type I & II collagen. What kind of stress does type I withstand & where in the disc is it concentrated?
a. Pressure, nucleus pulposus.
b. Pressure, annulus.
c. Tensile, nucleus pulposus.
d. Tensile, annulus
Tensile, annulus
Biomechanics of the spine is the best class ever because:
a. It will help me understand the mechanisms of spinal disorders I will experience in the real world.
b. It is the foundational knowledge needed to understand normal and abnormal motion of the joints of the spine.
c. I simply love biomechanics.
d. It will help me on my journey to become the best adjuster in the universe.
a. It will help me understand the mechanisms of spinal disorders I will experience in the real world.
b. It is the foundational knowledge needed to understand normal and abnormal motion of the joints of the spine.
c. I simply love biomechanics.
d. It will help me on my journey to become the best adjuster in the universe.
Mark any affirmation for credit and have a wonderful rest of your week.
a. I am a beautifully unique soul.
b. I am perfectly enough.
c. I am putting in the work, I will be successful.d. I am intelligent and bright.
a. I am a beautifully unique soul.
b. I am perfectly enough.
c. I am putting in the work, I will be successful.
d. I am intelligent and bright.