Chem2 Quiz 1
1/192
Earn XP
Description and Tags
includes TDM, seperation techniques and blood gasses for testing and forensics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
193 Terms
What is the best specimen for qualitative testing?
Urine
What type of testing is used for screening drugs/ drug mtabolites?
Immunoassays
What type of testing is the gold standard for confirmation testing?
GCMS ad LCMSMS
What is the difference between clinical toxicology and forensic pathology?
clinical - monitors pt status for treatment
forensic-analysis for medicolegal proceedings
pharmacokinetics
activity of drugs in the body over time (what the bod does to drugs)
pharmacodynamics
study of physiological response to drugs (what the drug does to the body)
pharmacogenomics
The genetic programming for handling drugs
CYP
Cytochrome P450 a generic term for mixed- function, oxidative enzymes (especially secretion)
Steady state
when quantity of drug absorbed at target tissue is equal to quantity being cleared
MEC
The lower level of a drug in the body that will still be effective
MTC
The lowest level at which a drug is toxic
Half life
time required for 50% of an administered drug o be lost throuch metabolism/elimination
What is the range between MEC and MTC? Goal?
the range is called therapeutic range
t he goal is steady state, which occurs at ~ 5.5 half lives.
Why do we test for the peak and trough?
they help determine the dose and frequency of administration to achieve steady state
how many half-lives does it take to reach steady state?
~5.5
How many half- lives does it take to clear the drug when stopped?
~5.5
When should we be doing therapeutic monnitoring?
When steady state is reached
Describe what ADME stands for?
absorption
distribution
metabolism
excretion
what are the differences between passive diffusion, active transport, facilitated diffusion?
Passive diffusion: high concentration to low concentration with no energy
Active: requires energy to transport against a gradient
Facilitated diffusion: Uses carrier molecule in the membrane, combines reversibly and needs no energy
distribution depends on what characteristics?
molecular size
degree of ionization
lipid solubility
extent of protein binding (albumin)
body composition
Proteins distribution depend on what characteristics?
only free, uncharged drugs pass through membranes
Ph depends on what characteristics?
acids: bind albumin
Basics bind alpha 1 glycoproteins or lipids, metals/minerals bind globulins
what does phase one metabolisms do?
make the drug more polar by adding functional groups
What three reactions can happen in phase 1?
oxidation
reduction
hydrolysis
What is the most important enzyme involved with this phase?
cytochrome P450
what does phase II do?
Conjugation to link functional groups to make them more soluble
What 3 reactions can happen in phase II?
glucuronidation
acetylation
sulfation
The moieties attached are ______ soluble
water; because most are excreted in the urine
How are these drugs excreted?
urine and bile
What factors can change pharmacodynamics?
Drug-Drug interactions
Genetics
Age
What is the definition of Vd (volume of distribution)?
the total amount of drug in systemic circulation divided by the plasma drug concentration
What is the equation for half-life?
t1/2=0.7xVd/Cl
Vd=volume of distribution, Cl=clearance
application: Quantity remaining= (original quantity((1/2)n
n=number of half lives
Gentamicin, Amikacin, Tobramycin
Aminoglycosides, antibiotics
monitor toxic ranges to prevent damage to hearing and kidneys
Vancomycin
Glycoprotein, antibiotics
monitor toxic ranges to prevent damage to hearing and kidneys
Digoxin
antiarrhythmics and cardioactive
dec. K and Mg
Procainamide
antiarrhythmics and cardioactive
Must monitor metabolite NAPA
Lidocaine
antiarrhythmics and cardioactive
short half life
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Anti-epileptic
Phenobrbitol
Anti-epileptic
Valproic acid
Anti-epileptic
Other common anticonvulsants→
carbamazepine
Tricyclics
Psychotropics
Amptriptyline
Psychotropics
metabolized to notriptyline
Lithium
Psychotropics
used to treat bipolar disorder
Theophyline
Bronchodilators
Caffeine is an active metabolite
tested through immunoassay
LC
Caffeine
Bronchodilators
Caffeine is an active metabolite
tested through immunoassay
LC
Cyclosporine and tacrolimus (FK509)
immunosuppressant - Calcineurin inhibitors
used to prevent rejection
whole blood specimens
Sirolimus (Rapamycin) and Everolimus
immunosuppressant - mTOR inhibitors
used to prevent rejection
whole blood specimens
What is the major difference between Forensic samples and therapeutic drug testing?
method collection
looking for toxic compound and drugs
these analyses and interpretations are conducted in a manner to be defensible in court
What must all forensic samples have to be tested?
controlled collections
temperature monitored
tamper proof seal
chain of custody
What kind of forensic testing is used for screening?
immunoassay
What kind of testing is used for confirmation?
GCMS and LCMSMS
What three thing validate a urine drug screen?
creatinine
pH
Oxidizing agent
What specimen and testing do we use for drugs of abuse testing?
urine screening by immunoassays
What specimen do we use for ethanol, salicylate and acetaminophen testing?
Salicylates and acetaminophen: Plasma and serum
Ethanol: blood, plasma or serum
what are the 4 main substances that can cause acute poisoning and that we routinely test for?
acetaminophen
salicylate
alcohols
carbon monoxide
What are the 4 main categories of DOA and what drugs are in those categories?
sedatives/depressants
analgesics
stimulants
hallucinogens
What is the detection time for opioids?
2 days
What are some examples of opiates?
morphine
Codeine
6-monoaetyl morphine
Hydromophone
Hydrocodone
oxymrphone
oxycodone
What are the 2 main sedatives we test for and what are they taken for?
Barbituates
Benzodiazepines
What is the other name for Tylenol and aspirin?
tylenol- acetominophen
Aspirin- salicylate
What kind of acid base problems do Tylenol and aspirin cause?
Tylenol- metabolic acidosis
aspirin- respiratory alkalosis→ metabolic acidosis
How do NSAIDS work vs opioids?
block the effects of prostaglandins
what are the effects of cocaine on the body?
binds dopamine re-uptake transported inhibits re-uptake
vasoconstriction, hypertension, heart attack, stroke, seizure
What is the metabolite of cocaine?
benzoylegonine
How long can we detect this drug?
2-4days
What effect has meth users feeling like they have super powers?
dopamine reuptake inhibition
What is the active ingredient that is tested for on cannabinoids?
THC derivatives
What are the 2 drugs that cause hallucinations?
PCP and LSD
What is the Ph of adulterated urine?
<3 or >11
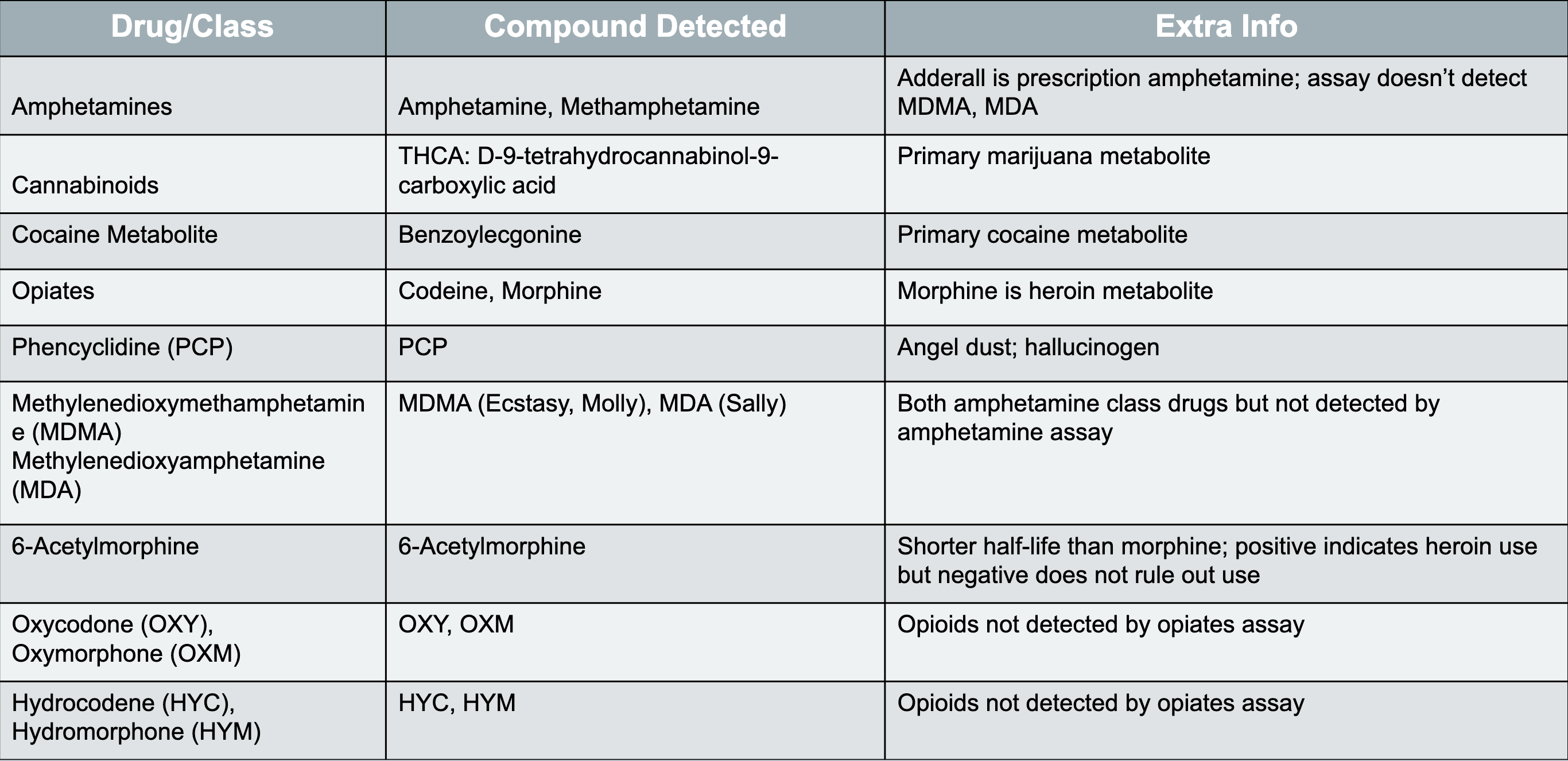
key summary slide for DOA and what is detected for specific drugs
Chromatography
physical process whereby the components of a sample mixture are separated as a result of their differential distribution between stationary and mobile phase
mobile phase
a gas or liquid that flows ina chromatographic system and carries the sample past the stationary phase
stationary phase
a solid liquid or gass that interacts with the components of the mobile phase
Eluent
fluid entering the column
Eluate
fluid exiting the column
analyte
mixture whose individual components have to be seperated and analyzed
mass spectrometry
study of matter through the formation of gas-phase ions that are characterized using mass spectrophotometers by their mass, charge, structure, and/or physicochemical properties
adsorption
solutes of a sample are seperated according to their attraction to the stationary phase vs the mobile phase
partition
solutes of a sample are seperated by differences in their distribution
What is the principle of chromatography?
separates mixture into individual components on basis of specific differences in physical characteristics
What is the difference between normal phase and reverse phase?
Normal phase: Stationary phase is polar and mobile phase is non-polar, carries no polar analytes
Reverse: is the opposite, carrier polar analytes
Ion exchange
must identify the charge of the target substance
initial charge inducement-final charge neutrality
thin layer
used to identify drugs, lipids, carbohydrates, and amino acids
Rf value equation
distance compnent traveled/ distance solvent travelled
Rf value and what it means for solute and solvent distance
seperation is based on differences in solubility between two liquid phases
high performance liquid chromatography
aqueous or organic solutions are pumped through columns under high pressure, which allows high resolution with fast and accurate quantitation
what is the difference between the isocratic and gradient in HPLC?
Isocratic: mobile phase is consistent in composition
Gradient: the composition of the mobile phase is altered as the run occurs
HPLC: high pressure error is caused by
Blockage
HPLC:noisy baseline is caused by
Bubbles
HPLC:drifting baseline is caused by
contamination
HPLC:loss of column resolution is caused by
overloading column with sample or degradation of column packing
gas liquid chromatography is the best method to measure…
blood alcohol
gas-liquid chromatography is used as confirmatory testing for what?
GCMS for regulated drugs of abuse
what are the 4 steps in how Mass spec works?
ionization of compound
sorted by m/z through deflection
signal detected/counted
results are displayed
How are ions sorted in mass spec?
by size and charge
What applications can we use for mass spec for?
TDM
Drugs of abuse
heavy metals
metabolic disorders
O2 in the blood is necessary for _______ metabolism
aerobic
What are the three properties of arterial blood?
arterial pO2 high enough to create a diffusion gradient
O2 binding capacity is normal
Hemoglobin can bind O2 in the lungs/ release it in tissues
Methemoglobin
cannot bind to O2
Hgb containing iron oxidized to Fe3+