acid base titration
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Titration Curve Kya Hai?
Jab acid aur base ko mix karte hain, toh pH badalta hai. Titration curve ek graph hai jo "pH" vs "added acid/base ki matra" dikhata hai.
The process of acid base titration is accompanied by a change in pH. A plot between pH of the solution during titration and the amount of acid(or akali) added from a burette is called titration curve
Strong acid vs strong base(Eg:HCl vs NaOH)
Key Points:
24.99 mL to 25.01 mL ke beech (0.02 mL difference):
pH 4 → 10 tak jump karta hai (6 units ka drastic change).
Isko "vertical portion" of titration curve bolte hain.
Indicator Ka Role:
Koi bhi indicator jo pH 4–10 range pe color change kare (e.g., phenolphthalein, methyl red), sahi rahega.
Why Does pH Jump So Fast?
24.99 mL pe: Solution mein H⁺ ions dominate (pH acidic ~4).
25.01 mL pe: Just 2 drops extra NaOH se OH⁻ ions dominate (pH alkaline ~10).
Buffer effect nahi hota strong acid-base mein, isliye sudden change.
Example:
Agar aap phenolphthalein use karte ho, toh:
25.00 mL pe: Colorless (pH 7).
25.01 mL pe: Pink (pH 10) — exact endpoint
dikh jata hai!

Weak acid vs strong base

Bohut kamzor acid (eg: boric acid) vs strong base(eg:NaOH)

Limitation of indicator
1. Acid-Base Indicators Kya Hote Hain?
Indicator ek aisa chemical hota hai jo specific pH range mein color change karta hai.
Example Indicators:
Methyl Red: Red → Yellow (pH 4-6)
Bromthymol Blue: Yellow → Blue (pH 6-8)
Phenolphthalein: Colorless → Pink (pH 8-10)
2. Titration Curves ke Types aur Unke Indicators
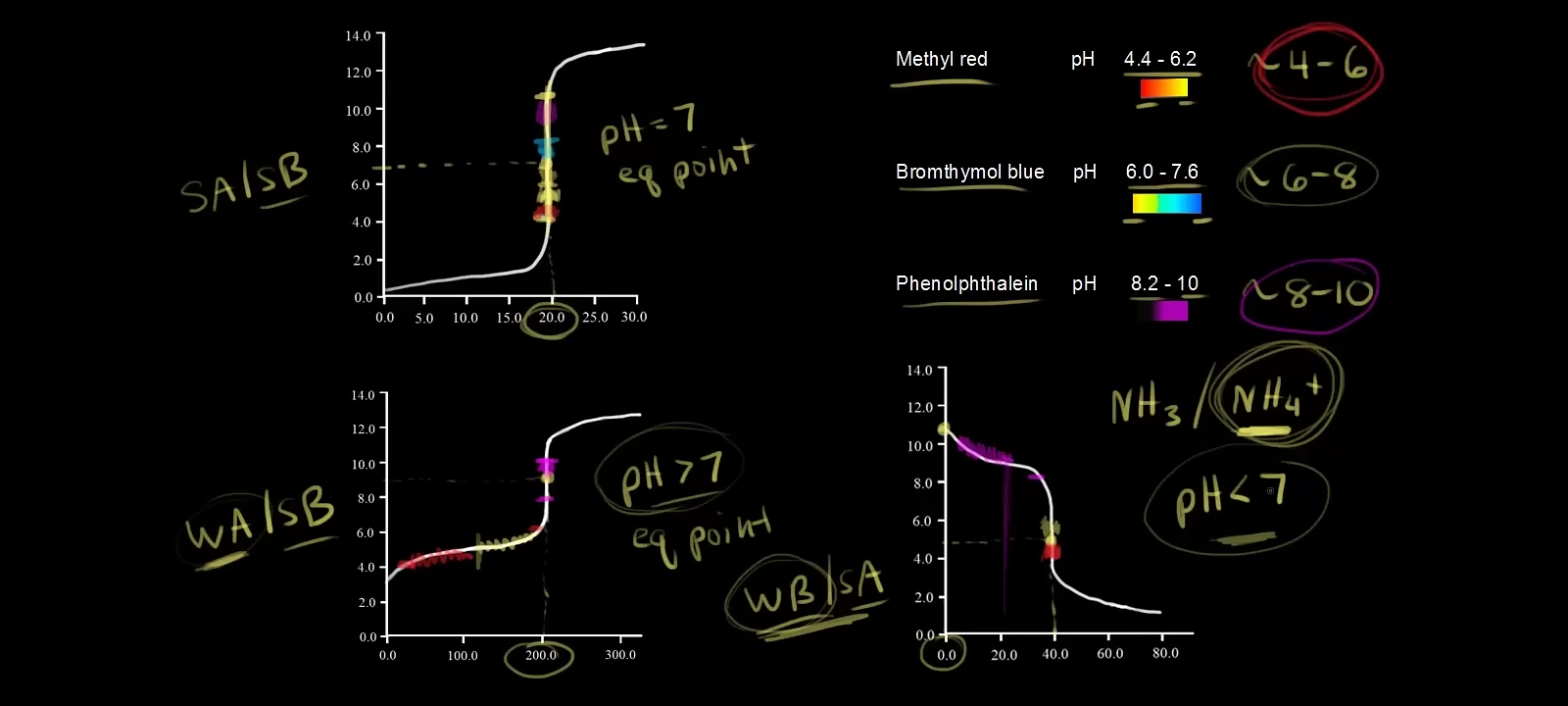
Case 1: Strong Acid + Strong Base (pH = 7 at equivalence point)
Example: HCl (acid) + NaOH (base).
Equivalence Point: pH exactly 7 (neutral).
Kaunsa Indicator Use Karein?
Bromthymol Blue (pH 6-8) best hai kyuki ye 7 ke aas-pass color change karta hai (yellow → blue).
Methyl Red (pH 4-6) ya Phenolphthalein (pH 8-10) bhi use kar sakte hain, lekin Bromthymol Blue zyada accurate hai.
Case 2: Weak Acid + Strong Base (pH > 7)
Example: Acetic Acid (weak acid) + NaOH (strong base).
Equivalence Point: pH 7 se zyada (basic) hota hai (e.g., ~9).
Kaunsa Indicator Use Karein?
Phenolphthalein (pH 8-10) sabse best hai kyuki ye 8-10 ke beech color change karega (colorless → pink).
Methyl Red (pH 4-6) galat hoga kyuki equivalence point (pH ~9) se pehle hi color change ho jayega.
Case 3: Weak Base + Strong Acid (pH < 7)
Example: Ammonia (NH₃, weak base) + HCl (strong acid).
Equivalence Point: pH 7 se kam (acidic) hota hai (e.g., ~5).
Kaunsa Indicator Use Karein?
Methyl Red (pH 4-6) perfect hai kyuki ye 5 ke aas-pass color change karega (red → yellow).
Phenolphthalein (pH 8-10) bilkul kaam nahi karega kyuki ye equivalence point ke baad bhi color change nahi karega.
3. Simple Trick Yaad Rakho:
Strong Acid + Strong Base (pH=7) → Bromthymol Blue.
Weak Acid + Strong Base (pH>
7) → Phenolphthalein.
Weak Base + Strong Acid (pH<7) → Methyl Red.
Ostwald dilution theory
According to Ostwald dilution theory, an acid-base indicator is either a weak organic acid or a weak organic base, in which the undissociated molecule has one color and the ions furnished by it on dissociation has another colour.
Ek acid-base indicator ya to ek weak organic acid hota hai ya ek weak organic base.
Yeh indicator jab water (pani) mein hota hai to poori tarah se toot-ta (dissociate) nahi hai — matlab yeh weak hota hai.
Jo undissociated molecule hota hai (jo abhi tak nahi toota), uska ek alag colour hota hai.
Jab yeh molecule dissociate hota hai, to jo ions (charge wale particles) bante hain, unka doosra colour hota hai.
Hph phenolphthalein
It's a weak organic acid which dissociates as follows:
HPh ⇌H+ Ph-
In the presence of an acid, the hydrogen ion furnished by the acid supress the dissociation of phenolphthalein, shifting the equilibrium towards the left due to common ion effect. As a result the solution remains colourless.
On the other hand, in the presence of a base, the OH⁻ ions furnished by the base combine with H⁺ ions to form undissociated water (H₂O). As a result, the concentration of H⁺ ions decreases. According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the equilibrium shifts towards the right giving more of the pink colored pH ion. So, the solution color turns pink
Methyl orange
