Halide Ions
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
What is the trend in reducing power down group 7?
How easy it is for a halide ion to lose an electron depends on the attraction between the nucleus and the outer electrons.
As you go down the group, the attraction gets weaker because ions get bigger, so electrons are further away from the positive nucleus
There is also increased shielding
Therefore reducing power increases down the group
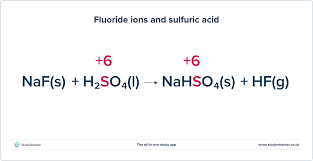
How does NaF or NaCl react with sulfuric acid?
NaCl/ NaF reacts for form either HCl or HF
You will see misty fumes as the gas comes into contact with moisture in the air.
HF and HCl aren’t strong enough reducing agents to reduce sulfuric acid so the reaction stops
This is an acid base reaction, not a redox reaction
How does NaBr react with sufuric acid?
1st reaction: NaBr + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HBr
This gives misty fumes of hydrogen bromide gas. But the HBr is stronger reducing agent than HCl and reacts with the H2SO4 in a redox reaction
2nd reaction: 2HBr + H2SO4 O2 and orange fumes of Br2
How does NaI react with sulfuric acid?
1st reaction: NaI + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HI
HI then reduces H2SO4
2nd reaction: 2HI + H2SO4 → I2 + SO2 + 2H2O
But HI keeps going and reduces the SO2 to H2S
3rd reaction: 6HI + SO2 → H2S + 3I + 2H2O
The reaction produces fumes of H2S and solid iodine
What is the test for halides?
Add dilute nitric acid to remove ions which might interfere with the test.
Add a few drops of silver nitrate solution
A precipitate is formed (of the silver halide)- Chloride is white, bromide is cream, iodide is yellow
You can also test your results by adding ammonia solution. Each silver halide has different solubility in ammonia
Chlorides dissolve in dilute ammonia
Bromide dissolves in conc. ammonia
Iodide is insoluble in conc. ammonia