Lec 16 Adaptive Immunity
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
FUCK bro you got this i belive in you, we will win
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What are B cells?
A type of lymphocyte, they are made and matured in the bone marrow?
Where are B cells made and matured?
Made and matured in the bone marrow
What are the functions of B cells?
Make and secrete antibodies
Where can you find B cells?
Spleen, lymph nodes, and MALT
Do B cells have receptors?
Yes, they are called B cell Receptors (BCR)
What type of antibody are BCR?
B cell receptors are a surface antibody, the antibody itself serves as the receptor
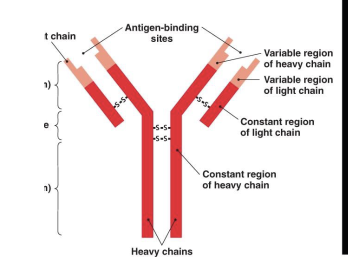
In the BCR, what are the variable regions?
This is where the antigens bind to, it is specific for the particular antigen, each BCR can hold two antigens
In term of antibody function, how do antibodies activate complement cascade or inflammation?
Antibody attaching to antigen triggers complement cascade as well as inflammation
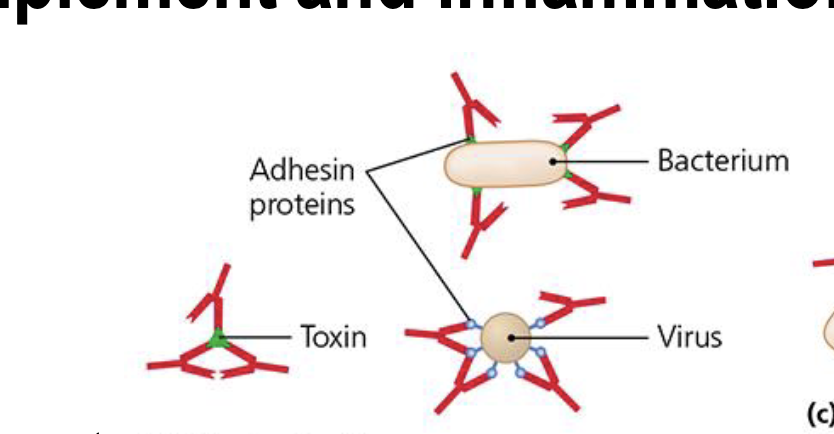
How does neutralization work for anitbody function?
• Antibody binding to pathogen, stopping spread, it eventually get phagocytksed, or spleen
• Antibody can bind to essential spike protein/Glycoprotein blocking essential food source for pathogen
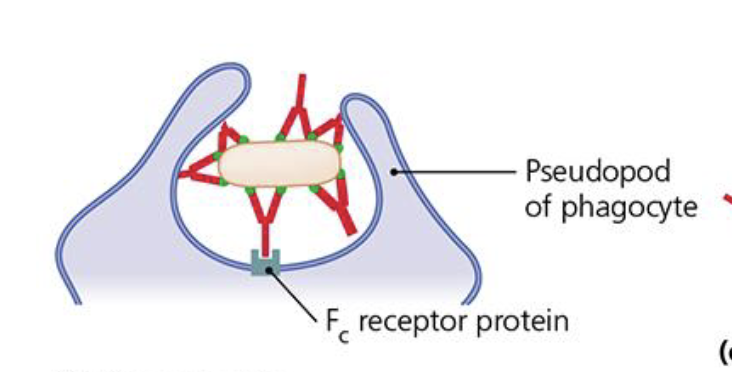
How does oponization work in antibody function?
Phagocytic cells have Fc receptors that only bind when antigen is binded to antibody
Phagocytic cell can work on own, but can also be triggered by antibodies
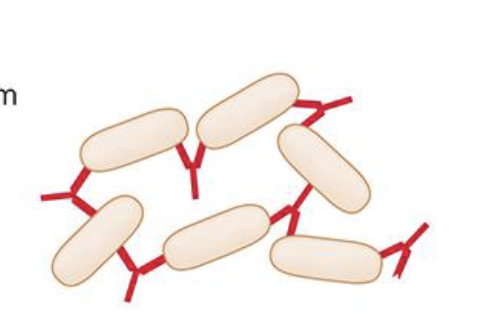
How does Agglutination work in antibody function?
•A single antibody can hold two antigens, this allows for easier phagocytosis as well as other processes to happen
•Prevents spread
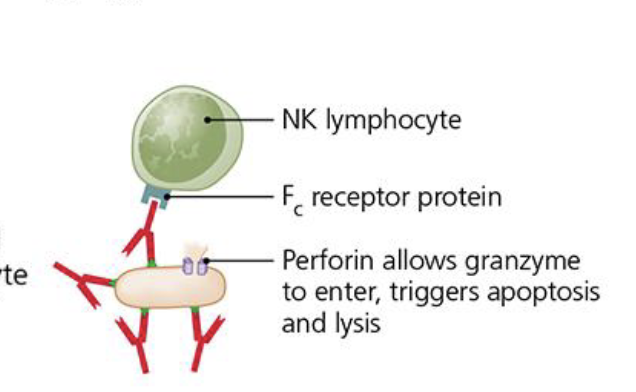
How does Antibody-Depedent Cellular cytotixcicity (ADCC) work?
•NK cells have Fc receptors that bind to antibodies attached to antigens
•NK cells can now release proteins perforin and granzymes that can kill cell
What does NK cells release when attatched to antigen bonded to antibody?
Perforin and Granzymes
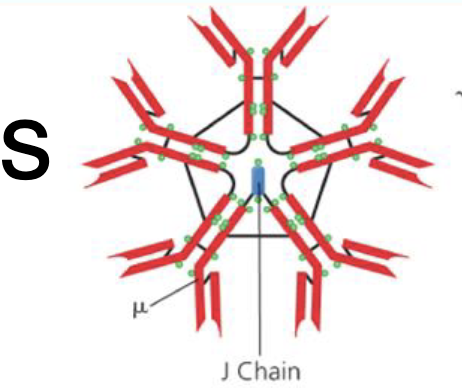
What is the structure of IgM antibody?
Monomer
Pentamer when joined together 5 of them
•5 antibodies joined meaning 10 binding sites
What is the function of IgM antibody?
Trigger phagocytosis
Most antibody functions
How are IgM connected?
J chains
What is the concentration of Igm In the body
5-10%
What is the structure of IgG
Monomer
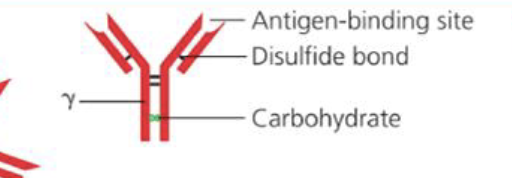
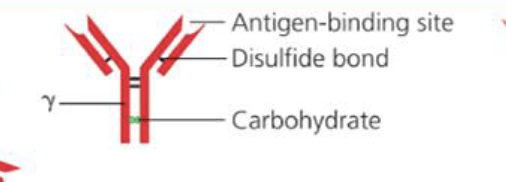
What is the percentage of IgG in the body?
75-80%
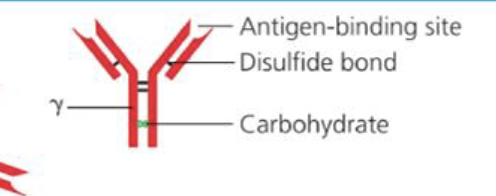
What is the function of IgG
Most antibody function, does most of the work due to the high amount of them
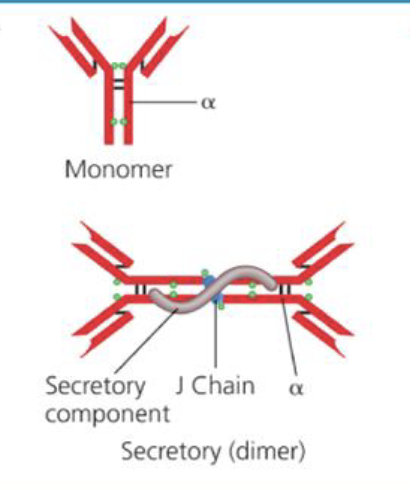
What is the structure of IgA
Monomer
Able to form a dimer via J chain
What is the amount of IgA in the body?
10%
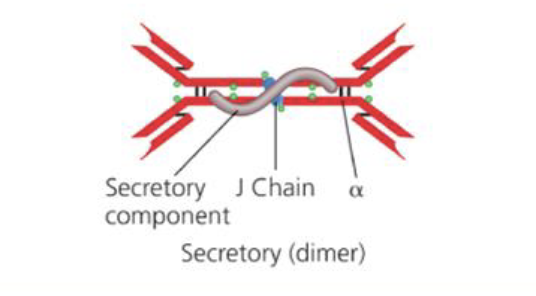
Why is it important that IgA can form a dimer?
When two IgA join together, it can be secreted, and can be pushed into mucousal secretions to help kill shit
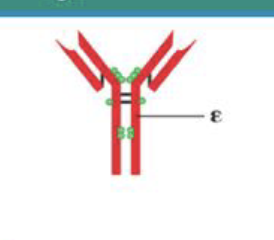
What is the structure of IgE?
Monomer
What is the function of IgE?
Triggers histamine causes allergic response
What is the percentage of IgE?
Less than 1%
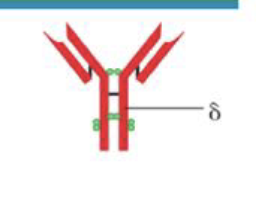
What is the structure of IgD
Monomer
What is the function of IgD
Unknown
What are cytokines?
Small signaling proteins that are released by immune cells to communicate with other cells
What are Interleukins (ILs)?
WBC that communicate with other WBC
What are Interferons (IFNs)?
Block viral replication by making antiviral proteins
What are growth factors?
Cause colonial expansion, causes cells to grow quickly
What are Tumor Necrosis factor (TNF)?
Protein responsible in help fighting cancer
Secreted by macrophages and T cells
What are Chemokines?
Used in movement, such as diapedesis or margination
Signals leukocytes to move
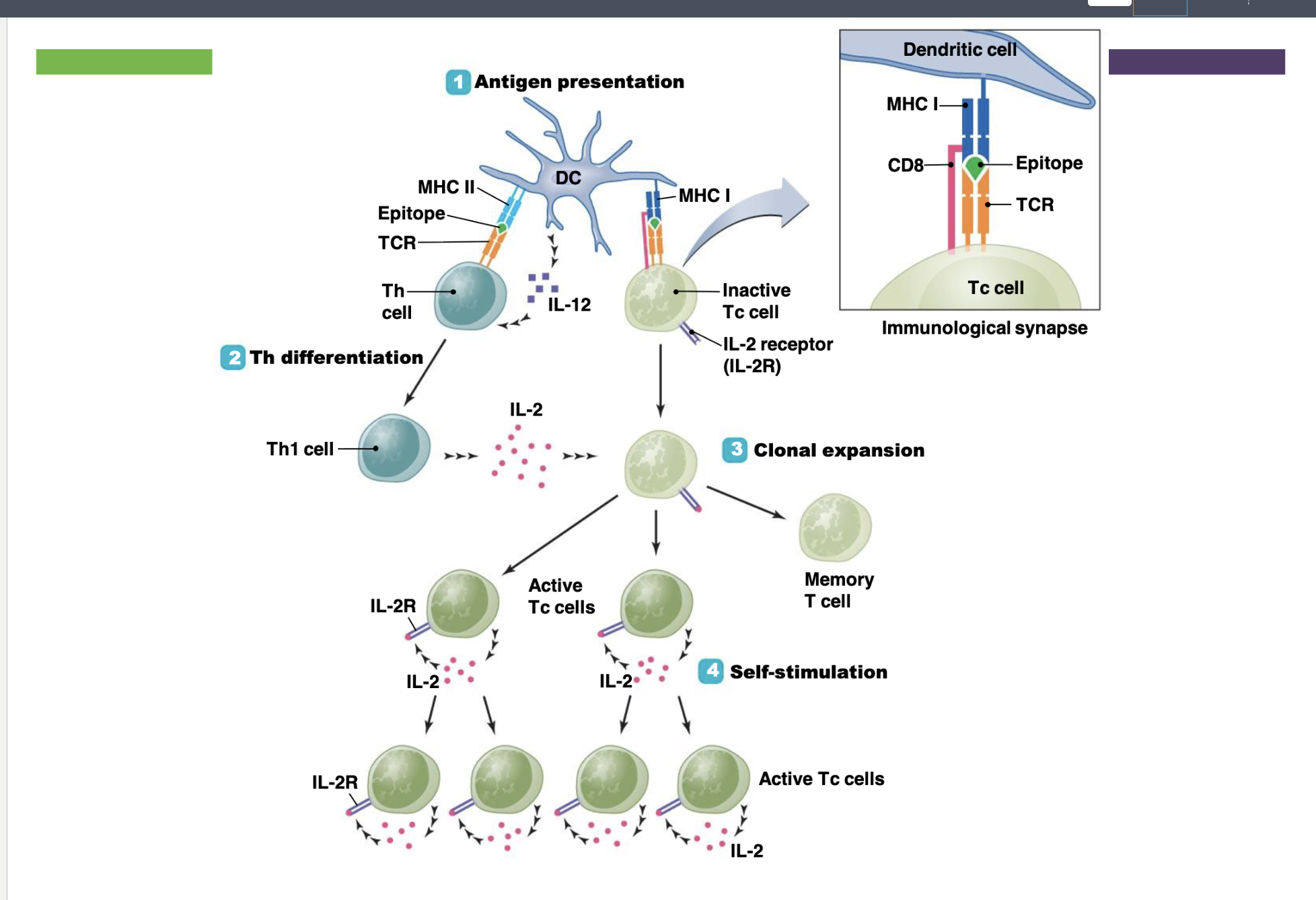
What are the steps of activation of cytoxic T cells?
Antigen Presentation: TCR from both CDH 8+ and CDH 4+ bind to both MHC and the CD8 Glycoprotein stablizes the synapse
Helper T Cell Differentiation: Once binded the infected cell will release IL-12 to the undifferentiated Th cell, now the Th cell is Th-1. At the same time when CD8 is bonded to MHC class 1 it formed a IL- 2 receptor
Colonial Expansion: Th-1 releases IL-2, it binds to the receptor, now the Tc cells can secrete their own IL-2 which allows them to colonaly expand. Some Tc cells are active and some become memory cells
Self Stimulation: Daughter Tc cells active and keep on producing their on IL-2 Receptors and IL-2, they no longer need a Th cell
How does the Perforin Granzyme pathway method work for killing pathogens?
•Two enzymes Perforin and Granzyme are in vesicles in cytotoxic T cells
•When attached to pathogen Tc cells release enzymes, and then apoptosis of the cell occurs
How does the CD95 Cytotoxic pathway method work for killing pathogens?
•Cells have glycoprotein CD95
•Activated Tc cells have CD95L which is the receptor for CD95, once they bind it starts apoptosis
Where do memory t cells live in?
Lymphoid tissue, they become active one they bond with specific epitope to their TCR
When is cell mediated immunity initiated?
When the pathogen is within cell (Endogenous)
When is Humoral Immunity initiated?
When the pathogen is Exogenous, floating in body fluids
How does T dependent humoral immune response work?
APC with MHC 2 complex presents antigen to Th cells, eventually finding the write one with the correct antibody
MHC 2 and TCR bind together, releases IL-4, This differentiates the Th cell into Th-2 cell
Th-2 cells binds to inactive B cells, then activating them by binding to B cell’s MHC 2, as well as binding to B cells CD40, with the Th-2 cells CD40. This releases IL-4
B cells can now colonaly expand while some stay as memory cells
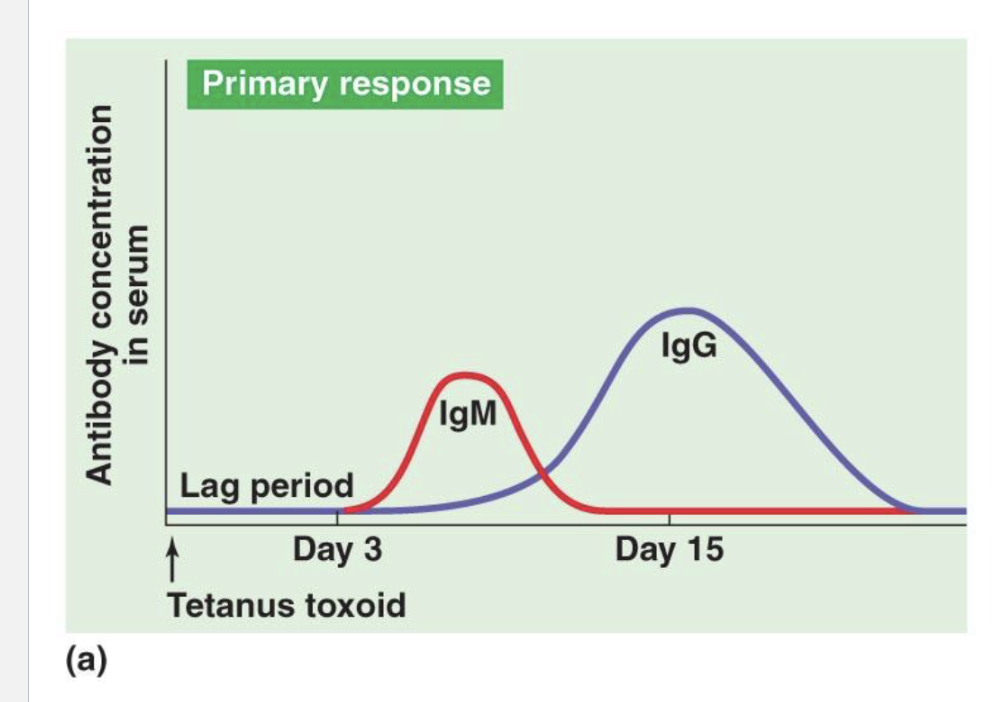
How does primary response work?
First exposure to antigen causes a lag period
Lag period is when B cell has to become antibody
The first antibodies are IgM that are short lived, the biggest antibody
The second antibody is IgG, the most abbundant
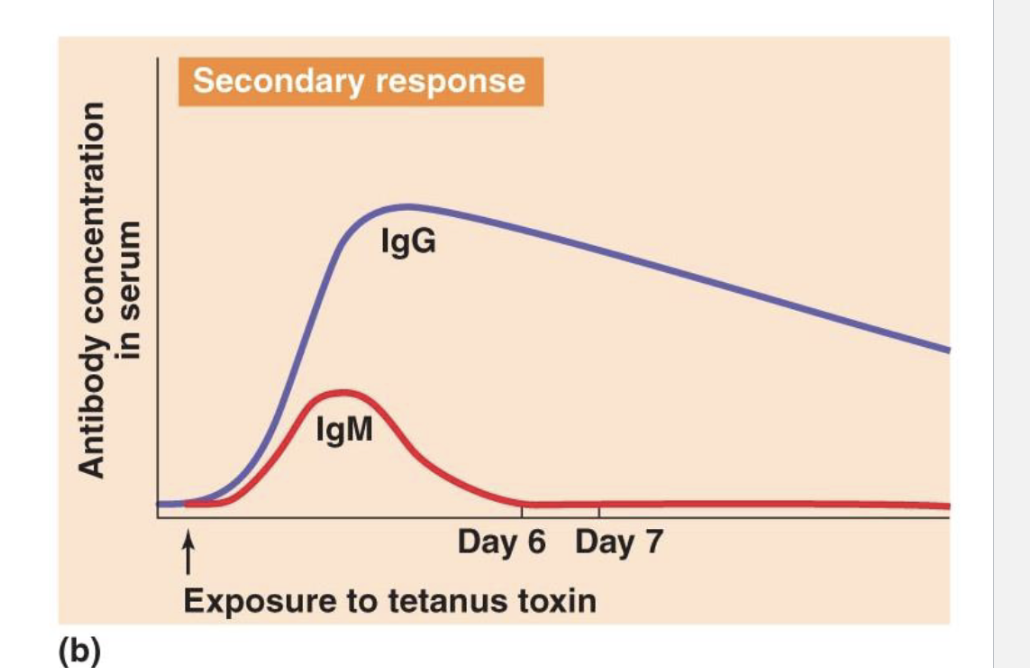
How does secondary response work?
•When exposed to perviously exposed antigen memory cells kick in, there is no lag time
•IgG antibodies are made quickly, while IgM goes slowly
What is naturally aquired immunity?
Gaining immunity by fighting off infection by oneself, antigens entered naturally and immune system responded.
In tern developing long term immunity
What is Passive Naturally Acquired immunity?
Gaining Antibodies from someone else
Mother to fetus via placetna
Or through mothers milk
What is Artificially Active Acquired immunity?
Vaccines, that contain weakened antigens
You make the antibodies
Work immediatly
What is is artificcialy Acquire passive Immunity?
Given antibodies
No Antigen exposure
Works immedialy no short term