hello can you please be seen - astronomy (copy)
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
aaaahhhh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
(1) The Universe is around 1.3×10^10 years old. This can also be said as:
13 Billion Years Old
(1) A collection of dangerous particles bursts of the Sun at 20,500 m/s. In scientific notation, this would be written as:
2.05 × 10^4 m/s
(2) Which color light has the highest frequency (out of these choices)
Blue
(2)Which color light has the longest wavelength (out of these choices)
Red
(2) Which color light travels the fastest in a vacuum (empty space)
They all travel at the same speed
(2) Which everyday word corresponds the best with the amplitude of a light wave?
Brightness
(2) Which of these have the shortest wavelength?
X-Rays
(2) Which of these have the highest energy photons?
X-Rays
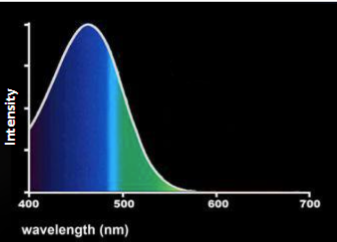
(3.1) The image shows the spectrum of a lightbulb. What does the bulb look like?
Mostly Blue
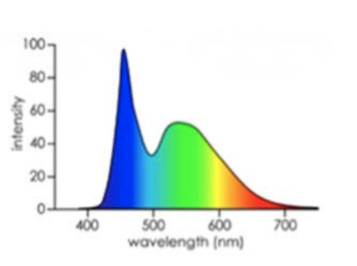
(3.1) The image shows the spectrum of a lightbulb. What does the bulb look like?
White with an extra hint of blue
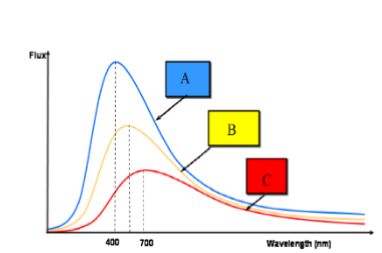
(3.1) Three blackbody curves are shown of three different objects with different temperatures. Which is the coldest of the three objects?
C

(3.1) Three blackbody curves are shown of three different objects with different temperatures. Which is the brightest of the three objects?
A
(3.2) Which of the following are found in the nucleus of an atom
Protons & Neutrons
(3.2) Most of the mass of an atom is located:
In the Nucleus

(3.2) The Hydrogen Series of emission lines happens whenever an electron drops to Shell number 2 of the hydrogen atom. Hydrogen alpha refers to which of these transitions:
C
(4.3) Your friend tells you to look directly west and then tilt your head up by 45 degrees. This is a clear usage of the”
The Horizontal Coordinate system (Altitude and Azimuth)
(4.3) Which coordinate system is “glued: to the sky and rotates with it?
The Equatorial Coordinate System (Right Ascension and Declination)
(4.3) What is the altitude angle for something directly above your head
90
(4.3) What is the altitude angle for something at the horizon?
0
(4.3) Your friend asks you to look at something in the night sky at an altitude of 45* and an azimuth of 180*. You Should:
Face South and look halfway between the horizon and above your head
(4.3) You land on an alien planet, where the strange atmosphere lets through shorter visible wavelengths, and scatters longer visible wavelengths. Assuming the star in this system gives off white light, on this planet, during daytime, the sky will look:
Red
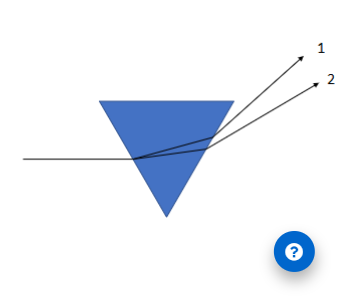
(5.1) The diagram shows a beam of light that split up into two distinct rays
after going through a prism. This tells us that:
1 has a shorter wavelength than 2
(5.1) A larger aperture leads to:
More light = Sharper & Brighter Image by the telescope
(5.2) For a refracting telescope, which part correctly identifies the structure
that gathers and concentrates light?
Objective Lens
(5.2) I used to have a telescope with a front opening (aperture) of 2 inches.
Now I bought a new one with an aperture of 8 inches. What is going
to happen to my images? (choose all that are correct)
My images will be 16x brighter and will be more detailed
(6.1) Kepler’s 3rd Law described quantitatively how (choose multiple)
Saturn takes longer to go around the Sun than the Earth. And how the Earth takes longer to go around the Sun than Mercury.
(6.1) Your friend has been taking photos of Jupiter in the night sky for quite a while. For many months Jupiter has been moving relative to the background stars in one direction. And then suddenly, for about 4 months, it starts to drift “backwards” relative to the stars, and then after 4 months, goes back to its original drift. This is explained by:
This happens due to the relative motions of Earth and Jupiter
(6.1) The eccentricity of Earth’s orbit is 0.0167. This means that (choose multiple):
Earth’s orbit is almost like a circle, but just a little bit stretched out.
And Earth’s orbit brings it slightly closer than average to the Sun and slightly farther than average to the Sun. The time between the farthest and closest points is 6 months.
(6.1) In January the Earth is its closest distance of 91 million miles from the Sun and in July the Earth is its farthest distance of 94 million miles from the Sun. The Earth is moving the fastest around the Sun in:
January
(6.2) To make something move in a circle you must:
Push on the object inward (towards the center of the circle)
(6.2) Why are planets going in a circle around the sun and not in a straight line?
Planets move in circles because the Sun is pulling on them with the gravitational force
(6.2) If I wanted to find the mass of Mars, I should figure out two things:
The distance of Deimos (a moon of Mars) from Mars. And The time Deimos (a moon of Mars) takes to go around Mars
(7.1) The temperature keeps dropping as you go higher away from the surface of the Earth
False
(7.2) When is the signal delay from Earth to Mars the longest?
When Earth and Mars are on opposite sides of the Sun

(8.1) The image shows an visible wavelength picture of Saturn. Notice the glowing lights at the North Pole. This indicates that:
Saturn has a magnetic field

(8.1) The pictures on the right show renditions of the Cassini Spacecraft. What can we infer about its energy source?
Cassini is powered by a nuclear battery
(8.2) When Pluto blocks out the light of a distant star, instead of the light disappearing in an instant when Pluto covers it and coming back in an instant when Pluto moves away, the light gradually dips and then gradually comes back to full brightness. This means that:
Pluto has an atmosphere
(8.2) To be considered as a planet in our Solar System, a celestial body has to fulfill a set of 3 criteria listed below. Which of these criteria is not fulfilled by pluto?
Has cleared its orbit of debris
(8.2) You are staring at the night sky and you see streak of light zoom by and disappear within a few seconds. What you most likely saw was:
Meteor
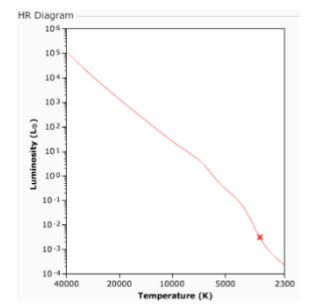
(9.2) In the HR diagram, we see a star marked with an X on the Main Sequence. This star is:
Cooler than the Sun
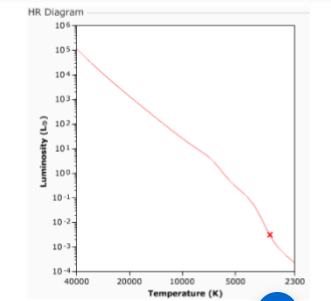
(9.2) In the HR diagram, we see a star marked with an X on the Main Sequence. This star is:
Smaller than the Sun
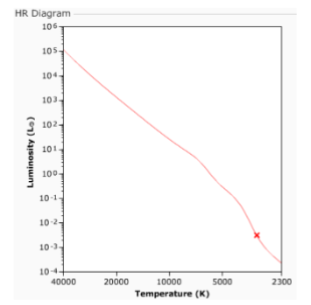
(9.2) In the HR diagram, we see a star marked with an X on the Main Sequence. This star is:
Intrinsically dimmer than the
Sun
(9.2) You know the apparent brightness of a star by observing it with a telescope. What other piece of information would you need to find the distance to that star?
Its true or intrinsic brightness
(10.1) Why are most nebulas mostly red?
They are mainly made of hydrogen
(10.1) What is the main way stars produce energy?
By fusing hydrogen nuclei to make helium
(10.1) A planetary nebula is
When a star dies and gently releases its outer layers
(10.2) What opposes the force of gravity that is constantly trying to squeeze a white darf to an even smaller size?
Outward force from electron degeneracy pressure (electrons cannot
come closer to each other than a certain limit)
(10.2) What opposes the force of gravity that is constantly trying to squeeze a neutron star to an even smaller size?
Outward force from neutron degeneracy pressure (neutrons cannot come closer to each other than a certain limit)

(11.1) What kind of nebula is this that is glowing because it is made of hot gas?
Emission Nebula

(11.1) What kind of nebula is this that is lit up by a nearby star?
Reflection Nebula

(11.) What is the most likely classification of this galaxy?
Elliptical

(11.1) What is the most likely classification of this galaxy?
Irregular

(11.1) What is the most likely classification of this galaxy (the large one)?
Spiral
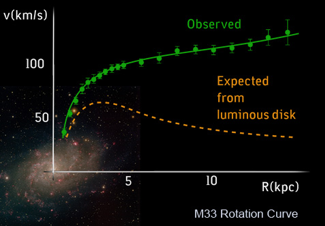
(11.2) The observed stars are rotating faster than predicted in the galaxy. This means that inside a given radius, there is _______ matter compared to what can be observed using light
More
(11.2) Which of these is not evidence of dark matter?
Star rotate around the center of galaxies slower than expected
(11.2) Choose the correct properties of dark matter
It interacts with Gravity. It comes in compact, dense lumps
(12.1) Hubble’s constant is about 70 km/s per Mpc. You take a picture of a distant galaxy about 20 Mpc away from us (as a comparison, Andromeda is less than 1Mpc away from us). How fast is that galaxy receding from us?
1400 km/s
(12.1) When heated up, oxygen emits light at the 500nm wavelength in laboratory conditions. When analyzing the spectrum of a distant galaxy at redshift 2, what will be the wavelength of light you receive from hot oxygen in that galaxy?
1500 nm
(12.2) Which of these statements is correct?
The space between galaxies is expanding
(12.2) What is the part of the Universe that interacts with other things gravitationally and can also interact (absorb, emit, reflect) light?
Baryonic matter
(12.2) What is the part of the Universe that causes space to expand on large scales?
Dark Energy