BOH4M1 Exam Review
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
OCEAN: What does ‘O’ stand for? What does it mean? What’s the opposite?
Openness: Open to change and new ideas
Opposite: Narrow-mindedness
OCEAN: What does ‘C’ stand for? What does it mean? What’s the opposite?
Conscientious: Responsible, dependable
Opposite: Careless
OCEAN: What does ‘E’ stand for? What does it mean? What’s the opposite?
Extraversion: Ability to be social, outgoing, create large # of relationships
Opposite: Introversion
OCEAN: What does ‘A’ stand for? What does it mean? What’s the opposite?
Agreeableness: Cooperative, good-natured
Opposite: Disagreeable (source of conflict)
OCEAN: What does ‘N’ stand for? What does it mean? What’s the opposite?
Neuroticism: Emotionally stable, calm or confident
Opposite: Lacks emotion regulation
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: List from bottom to top
Physiological needs, safety, love and belonging, self-esteem, self actualization
6 Steps of Communication Process
Sender
Message
Method/Medium
Noise
Receiver
Feedback
Types of Barriers
Process Barrier
Physical Barrier
Semantic Barrier
Perception Barrier
Process Barrier: Definition and Example
Blocked or broken step in communication process (Filtering, Emotional disconnect, Gossip)
Ex: Alice can’t share her ideas because she’s afraid of criticism (eg. emotional barrier)
Physical Barrier: Definition
Any form of physical distraction
Eg. Wall, poor cellphone reception
Semantic Barrier: Definition and Example
Distorted words to convey message
Eg. Person doesn’t understand technical jargon
Perception Barrier: Definition
The way people receive and interpret messages (Stereotypes, preconceived notions, etc.)
4 Types of Perceptual Distortions
Stereotypes
Stereotype Threat: When stereotypes are internalized → into realityHalo Effect
Draw conclusion based on visual characteristicsSelective Perception
Define one’s problem based on one’s perspectiveProjection
Project oneself onto someone else
3 Levels of Management: Definitions and Examples
Top
Responsible for organization’s performance as a whole
eg. CEOMiddle
Oversee work of large divisions and reports to top managers
eg. HRTeam Leaders/Supervisors
Someone in charge of a small work group
eg. someone who looks over team
4 Functions of Management
Planning
Organizing
Leading
Controlling
3 Types of Position Power
Reward Power: Ability to offer something to others
Legitimate Power: Ability to influence with status
Coercive Power: Ability to influence with punishment
2 Types of Personal Power
Expert Power: Ability to influence based on expertise
Referent Power: Ability to influence based on admiration
5 Stages of Team Development
Forming: Establish ground rules
Storming: Communicate feelings but still hostile
Norming: Start becoming a team
Performing: Team performs working together
Adjourning: Assess and give feedback
of 7. Scientific Management
Father of Scientific Management: Frederick Taylor
Efficiency, productivity
Workers assigned tasks they’re naturally good at
Doesn’t care for worker wellbeing
Based on time studies
of 7. Administrative Theory
Father of Management: Henry Fayol
14 principles of management
Planning, controlling, organizing, etc.
Vertical structure (hierarchy)
of 7. Bureaucratic Theory
Max Weber
Efficiency based on logic, authority, and organization
Still doesn’t consider well being
of 7. Hawthorne Studies
Father of Human Relations: Elton Mayo
People work differently when they know they’re being watched
Employees motivated by relational factors
of 7. Theory Z
William Ouchi
Combo of American + Japanese management
Generalists — Continuous learning = well-rounded employees
Lifers: Loyal employees who stick to the company
and 6. of 7. Theory X and Y
Douglas McGregor
Theory X: Workers don’t like to work = need +supervising and micromanaging
Theory Y: Workers like to work = self-control
of 7 Behavioural Theory
Frederick Herzberg
Hygiene (external factors): Salary, work conditions, etc.
Motivation (internal factors): Recognition, achievement, etc.
3 Leadership Styles
Autocratic
Laissez-Faire
Democratic
3 Leadership Styles: Autocratic (Definition and When It’s Effective)
Strict — exactly what to do, doesn’t consider opinions
Used when: Limited time, lack of skill/knowledge/teamwork
3 Leadership Styles: Laissez-Faire (Definition and When It’s Effective)
Laid-back — little to no direction, self-led
Used when: Existing skill and teamwork
3 Leadership Styles: Democratic (Definition and When It’s Effective)
Takes opinions into consideration, promotes collaboration
Used when: Available time, members are motivated and cooperative
Internal Control vs. External Control
Internal: Ability to control yourself (self-control)
External: Managers control workers (supervision)
SMART GOALS Definition
A good goal fits this criteria:
Specific
Manageable
Attainable
Realistic
Timely
SWOT
Strengths/Weaknesses = internal
Opportunities/Threats = external
Mission
What the company’s goal is right now
Vision
What the company’s goal is for the future
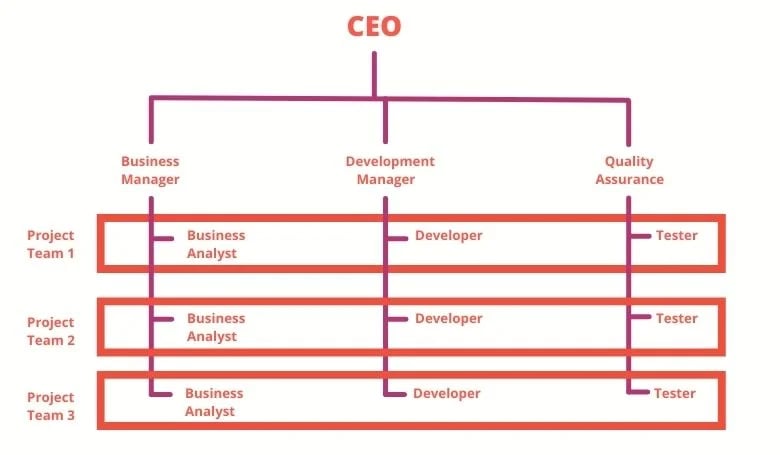
3 (Main) Types of Organizational Structures: Functional
People of similar skills work together
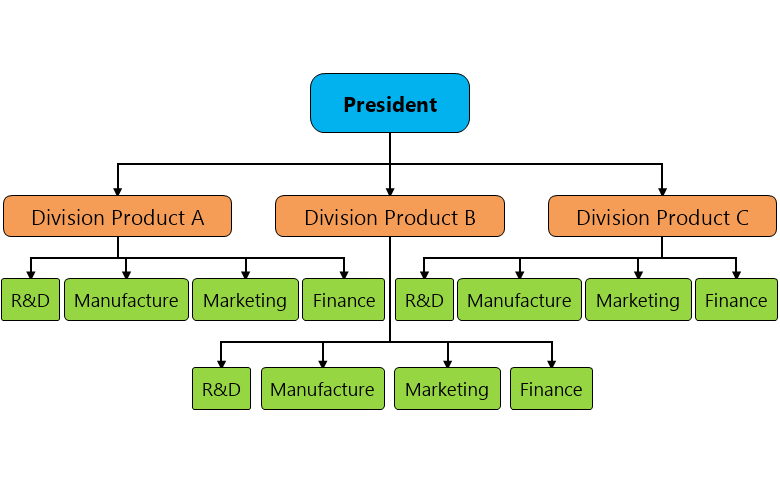
3 (Main) Types of Organizational Structures: Divisional
People grouped based on either:
Product
Geography
Customer
Process
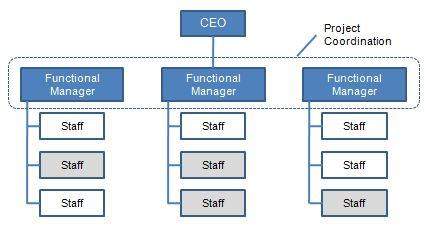
3 (Main) Types of Organizational Structures: Matrix
Combo of functional and divisional structure
Employees have both functional and divisional managers
3 Trends in Organizational Structures We’re Seeing More of Today
Decentralization (Shorter chain of command, wider spread of control)
Hybrid (digital work)
AI
4 Social Responsibility Strategies: Definitions
Obstructionist: Know they’re violating ethics but don’t care
Defensive: Stay within the law but don’t attempt social responsibility
Accommodating: Realize need for social responsibility
Proactive: Above and beyond
Network Organization: Definition, Example, 3 Pros and Cons
Individual employees teamed based on specialization + relationships and network amongst each other.
Pros: Exchange ideas, increased knowledge in particular field
Cons: Lack of secrecy, lack of control
Ex: H&M — Distributes functions for different companies across different countries
4 Steps in Human Resource Process
HR Planning
Analyze needs
Attracting Employees
Typical process:
Application Review
Interview
Testing
Reference Checks
Comparison
Developing Employees
Orientation/Training (on/off job)
Retaining Employees
Diversity + labour management
4 Views of Ethical Behaviour
Utilitarianism
Individualism: Long-term self interests
Moral rights
Justice
Procedural: Follow policies + rules
Distributive: Unbiased respect
4 Planning Approaches
Contingency Planning: Plan for the worst/emergency
Forecasting: Examine trends + past experience
Strategy: Allocate resources to reach strategic goals
Benchmarking: Comparing results + performance with industry leaders
6 Methods of Group Decision Making
Lack of Response: Members throw ideas until 1 sticks, silence = lack of agreement, or no response
Authority Rule: 1 person decides after hearing opinions
Minority Rule: Minority group has higher power over others
Majority Rule: Majority has higher power
Consensus: Everyone ends up agreeing after discussion
Unanimity: Everyone agrees from the get-go
Channel Richness
Low-richness = impersonal (eg. text, memo, etc.)
High-richness = personal (eg. one-on-one, call)
Functional Chimney Problem
Employees report to higher ups without coordination or communication amongst divisions