EKG
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what does ekg stand for
electrocardiogram
what is the primary function of an EKG
to record and analyze the electrical activity in the heart
what are some indicators a EKG might be necessary
fast heart rate, heart palpitations, heart attack, chest pain
what is the significance of the p wave
shows the start of the cycle
what does the qrs complex represent in an EKG tracing
represents ventricular depolarization; triggers ventricle contraction
name the main components of the cardiac conduction system
sa node, av node, bundle of his, bundle branches, purkinje fibers
sa node
generates electrical signals, top part of atria, where it starts
av node
slows down electrical signals to allow the atria to contract before the ventricles
bundle of his
carries electrical signal from av node to interventricular septum, top of septum, branch off
bundle branches
2, left and right, bottom(apex) of heart
purkinje fibers
spread electrical signals through ventricular walls causing ventricles to contract, fish hook, loop around sides of heart
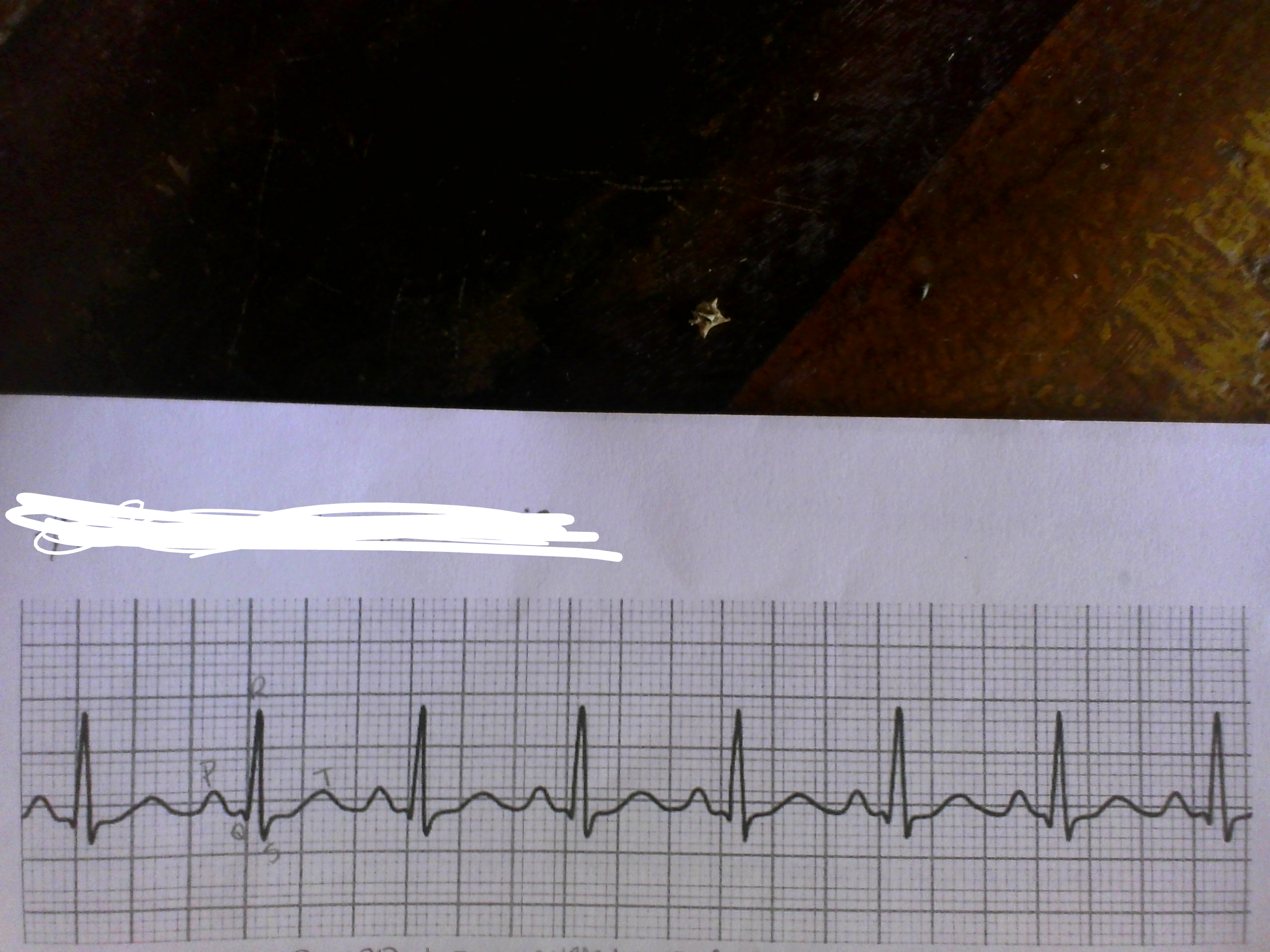
what is this
normal sinus(60-100bpm)
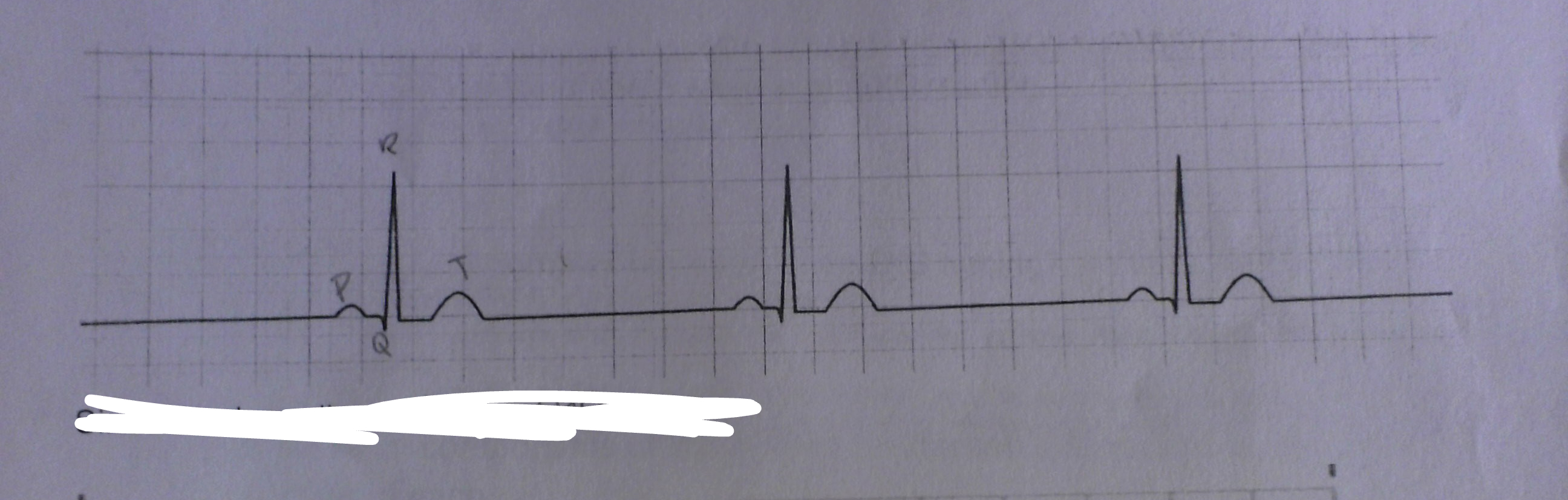
what is this
sinus bradycardia(slow, less than 60bpm)
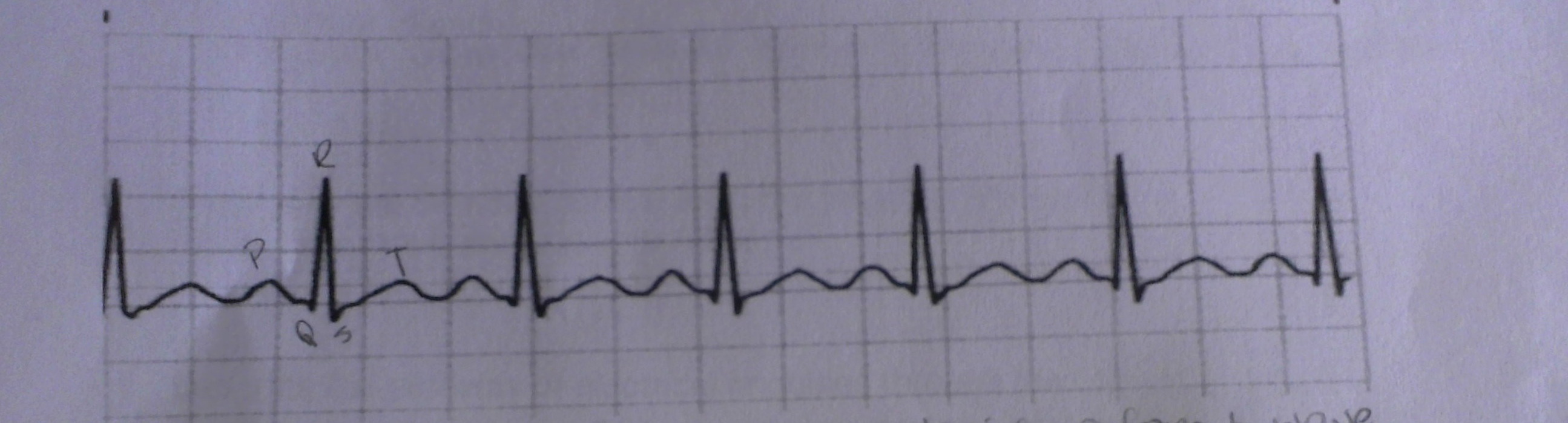
what is this
sinus tachycardia(fast, more than 100bpm)
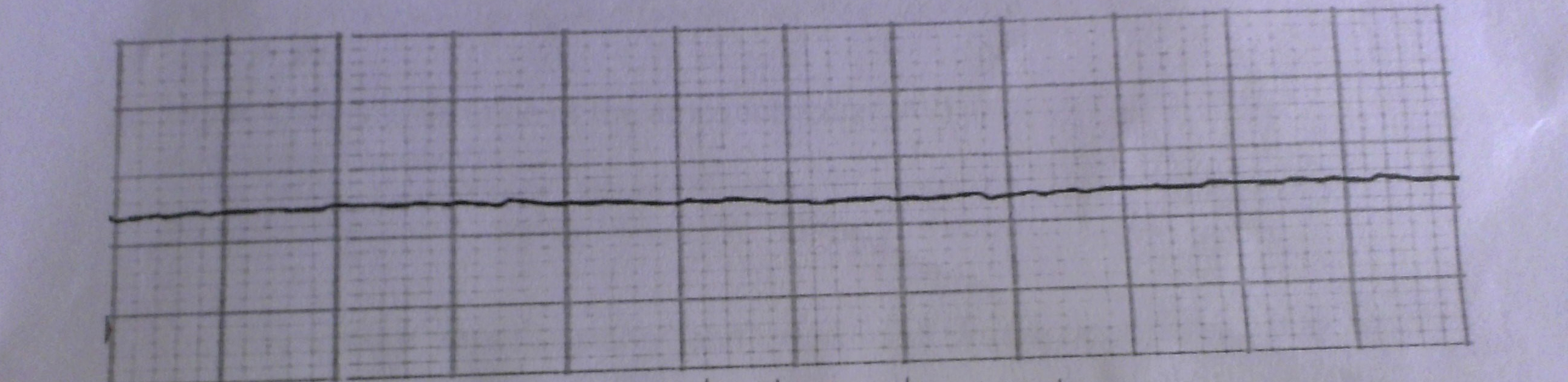
what is this
asystole(no electrical activity)
an EKG is an(description not what stands for)
electrical visual of the heart
at rest, the cells of the heart are
negatively charged
when the heart depolarizes, it becomes
positively charged
The size of the deflection (or curve) on the ECG reading corresponds to the size or magnitude of the dipole
in the direction (parallel to) of the dipole
In a standard ECG there are ____ electrodes
10
How many limb electrodes are in a standard ECG?
4
Do all leads produce the same ECG tracing/image?
yes