Hi
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
which of these proteins is most likely to be involved in the second step of secondary active transport
Symporter
how do intracellular signaling molecules, defer chemically to extracellular signals?
Small nonpolar (or polar : H2O) molecules that can diffuse across the membrane
select the correct end into the statement signal peptide sequences are _____
Remove removed from the mature polypeptide
in eukaryotes ribosomes associate with endoplasmic reticulum membranes when
A signal sequence on the protein being synthesized causes translation to stop in the ribosome to attached to the ER membrane
when a G protein is activated in a signal transduction pathway,
GDP is released from the G-protein, And GDP occupies the nucleotide binding site
what is a possible response of a cell that signals to cytoskeletal effector protein?
A change in cell shape
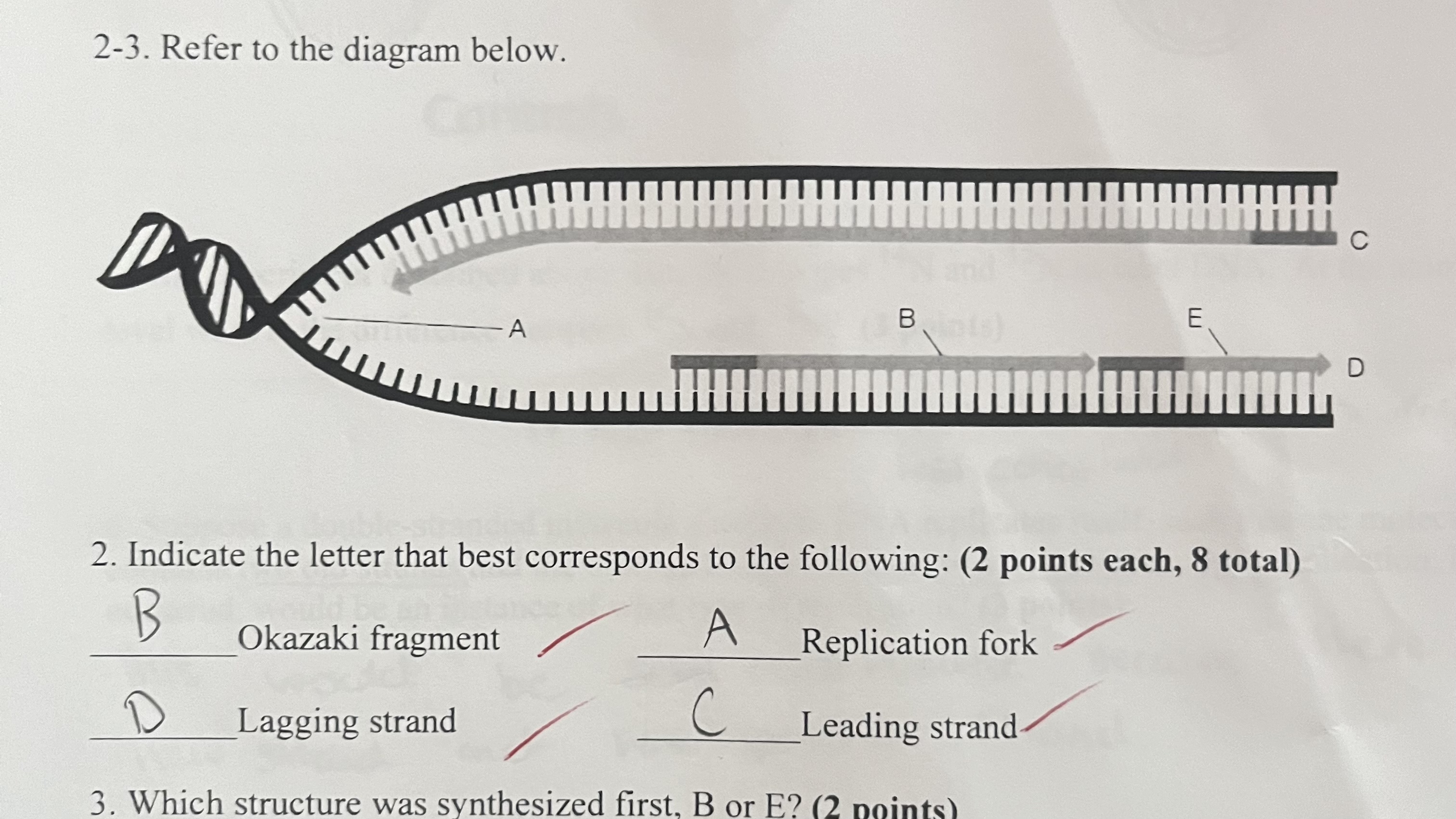
E
STOP CODONS, dna and rna
UAA, UGA, UAG
TAA, TGA, TAG
which of the following statements is true
a. DNA is completely replicated, but only partially transcribed
b. DNA is partially replicated but completely transcribed.
c. RNA is completely replicated but only partially translated do
d. DNA is completely replicated and completely translated.
e. DNA is partially replicated or completely translated.
a. DNA is completely replicated, but only partially transcribed
in eukaryotic cells, translation occurs in the ____ transcription occurs _____
a. nucleus; in the nucleus
b. nucleus; in the cytoplasm
c. cytoplasm; in the nucleus
d. nucleus; outside of the cell
e. cytoplasm; outside of the cell
b. nucleus; in the cytoplasm
which of the following is not required for transcription
A DNA template
B a primer
C ribonucleotide triphosphate
D RNA polymerase
E all of them are required for transcription
B a primer
inhibitors
regulate enzymes
exergonic and
catabolism
endergonic and
anabolism
reactants are called substates. they bind to the
active site of the enzyme
what mechanisms do enzymes use
orient substrates, induce strain in substrate
different types of reversible inhibitors
non competitive (bind to enzyme at different site) and competitive
allosteric regulation
effector binds to enzyme at a different site, changing its shape