Population/Demographic Change Test
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
1
New cards
What is demography?
the study of human populations and the implications of changes in population size and composition
2
New cards
What is a birth rate?
the number of live births per thousand of population per year
3
New cards
What is a death rate?
the number of people per thousand who die in a particular area per year
4
New cards
What is an immigration rate?
the number of people immigrating to a country per thousand in a population per year
5
New cards
What is an emigration rate?
the number of people emigrating from a country per thousand in a population per year
6
New cards
What is a dependency load?
the population of people 15 and under and 65 and over who need to be supported by the independent, working population
7
New cards
What is an infant mortality rate?
the number of infants who die per thousand in a population
8
New cards
What is a natural increase rate?
the difference between a country’s birth rate and death rate
9
New cards
What is a fertility rate?
the number of babies born to a woman during her life-time
10
New cards
What is a replacement rate?
the number of births needed to sustain a population’s numbers
11
New cards
When did the world’s population explosion begin and what are some reasons why?
when: latter half of the 1600’s and onward, accelerated through the 1900s
why:
* The Industrial Revolution (1760 to 1840)
* World War II / The Baby Boom (1946–1964)
* Significant agricultural advancements including technology
* Developments in modern medicine and healthcare
* \
why:
* The Industrial Revolution (1760 to 1840)
* World War II / The Baby Boom (1946–1964)
* Significant agricultural advancements including technology
* Developments in modern medicine and healthcare
* \
12
New cards
What is the Demographic Transition Model?
a chart that tracks the phenomenon of high birth and death rates changing to low birth and death rates over time as a population fluctuates
13
New cards
What are population pyramids?
a graph used to make comparisons between men and women in the same age group or between young people and older people
14
New cards
What are the defining factors of a stage 1 population pyramid?
* High birth rates
* High death rates
* Stable but small population, slow natural increase
* Wide, thin bottom that curves upwards to a narrow peak
* High fertility rate
* Low life expectancy
* Poor access to medicine
Ex: Canada in 1750 or Chad today
* High death rates
* Stable but small population, slow natural increase
* Wide, thin bottom that curves upwards to a narrow peak
* High fertility rate
* Low life expectancy
* Poor access to medicine
Ex: Canada in 1750 or Chad today
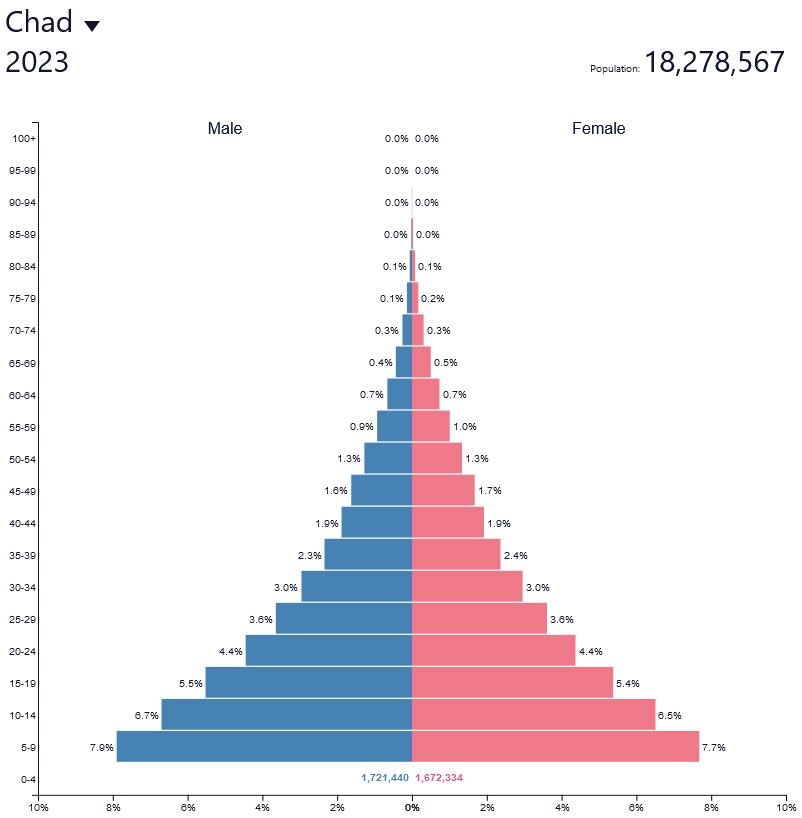
15
New cards
What are the defining factors of a stage 2 population pyramid?
* High birth rates
* Rapidly falling death rate
* Very rapid natural increase
* Dramatic decline in the death rate due to better sanitary conditions, access to medicine or better food supply.
* Life expectancy increases so the population pyramid gets wider in the lower half
* Straight sides, pyramid shape
Ex: Palestine
* Rapidly falling death rate
* Very rapid natural increase
* Dramatic decline in the death rate due to better sanitary conditions, access to medicine or better food supply.
* Life expectancy increases so the population pyramid gets wider in the lower half
* Straight sides, pyramid shape
Ex: Palestine
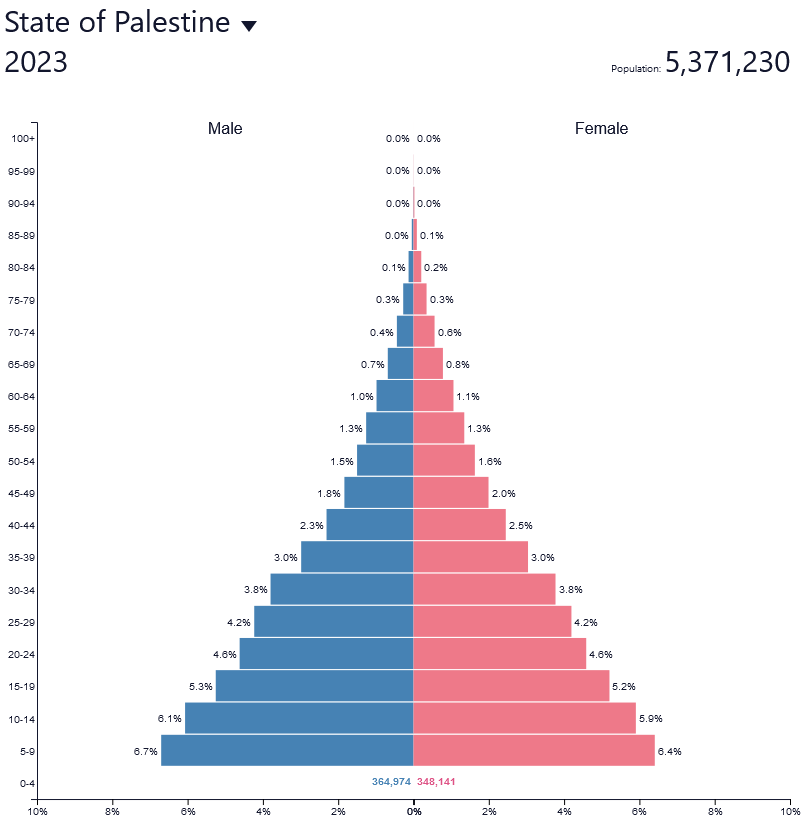
16
New cards
What are the defining factors of a stage 3 population pyramid?
* Falling birth rate (people may choose to have fewer children due to low infant mortality rates and access to birth control)
* Falling death rate, more slowly
* Natural increase slows down
* Typically women are entering the work force in larger numbers
* Pyramid shape lifted onto a rectangular base
Ex: Mexico
* Falling death rate, more slowly
* Natural increase slows down
* Typically women are entering the work force in larger numbers
* Pyramid shape lifted onto a rectangular base
Ex: Mexico
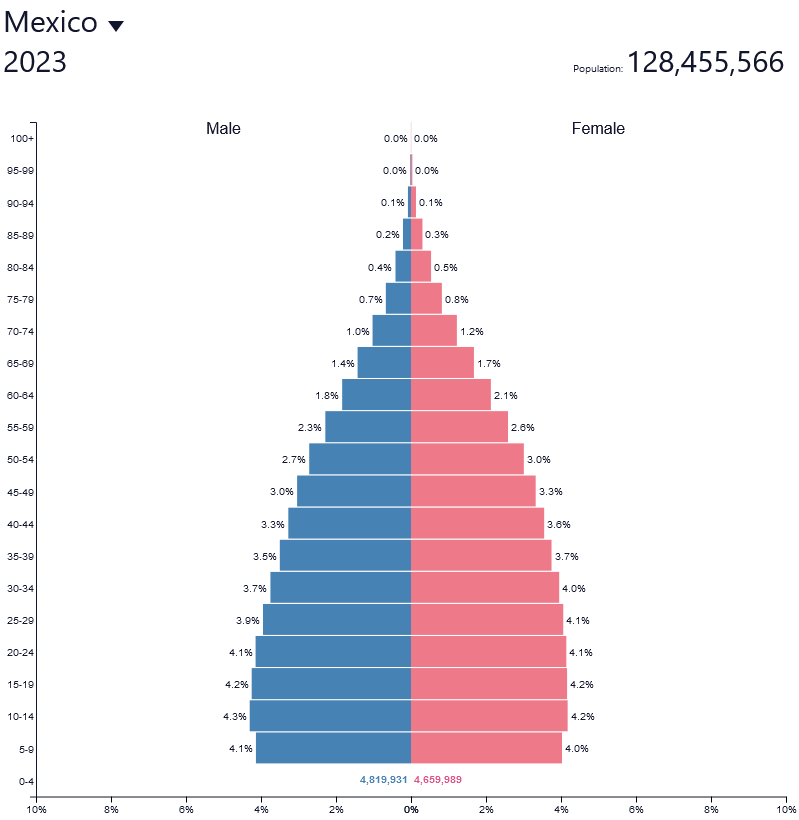
17
New cards
What are the defining factors of a stage 4 population pyramid?
* Low birth rate
* Low death rate
* Falling natural increase that eventually stabilizes
* Highly urbanized societies
* High life expectancy rate
* Population growth typically happens due to immigration instead of natural increase
* Curved shape, arching at a rounded top
Ex: Australia
* Low death rate
* Falling natural increase that eventually stabilizes
* Highly urbanized societies
* High life expectancy rate
* Population growth typically happens due to immigration instead of natural increase
* Curved shape, arching at a rounded top
Ex: Australia
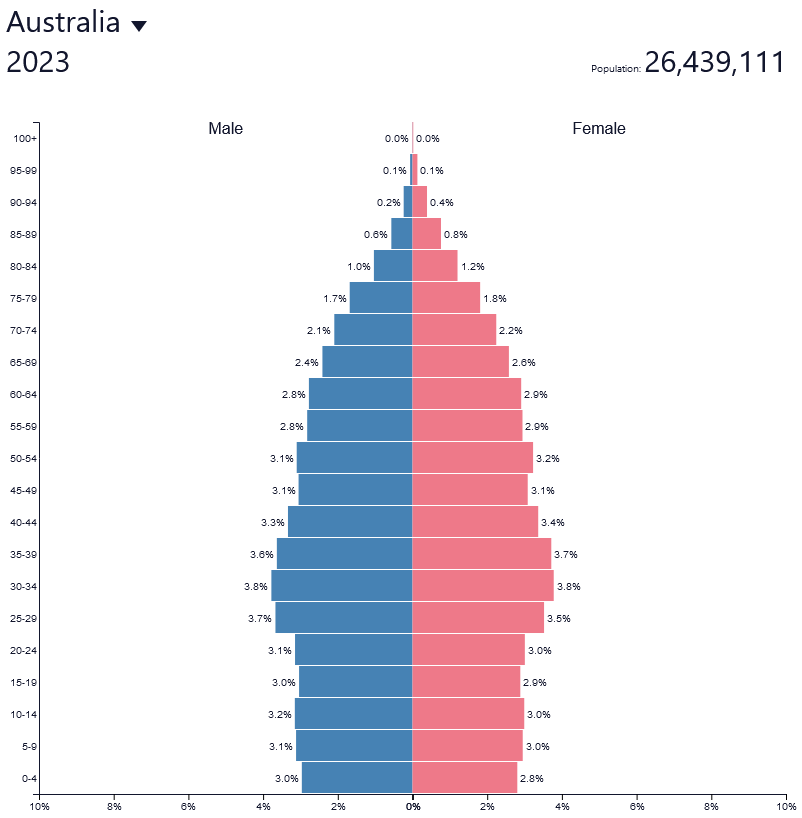
18
New cards
What are the defining factors of a stage 5 population pyramid?
* Birth rate begins to rise again
* Low death rate
* Stable or slow natural increase
* Maintains its rounded tip but begins to expand outward at the base
Ex: Ukraine
* Low death rate
* Stable or slow natural increase
* Maintains its rounded tip but begins to expand outward at the base
Ex: Ukraine
19
New cards
What factors affect the way populations change?
* Cost of education/education opportunities
* Quality of/access to healthcare
* Stability of society
* Government
* Economic growth
* Competition for resources
* Mass death (disease, war, etc.)
* Access to necessities (food, water, shelter, etc.)
* Quality of/access to healthcare
* Stability of society
* Government
* Economic growth
* Competition for resources
* Mass death (disease, war, etc.)
* Access to necessities (food, water, shelter, etc.)
20
New cards
What is China’s One Child Policy? What were some of its benefits/consequences?
a population planning initiative in China implemented between 1980 and 2015 to curb the country's population growth by restricting many families to a single child.
Benefits:
* Women are now valued more than before as there is a “shortage” of them
* Efforts to rectify the educational imbalance between men and women are being made
* Successfully reduced birth/fertility rate to improve quality of life for families (allow for resources to be distributed better between families)
Consequences:
* Millions of Chinese men are unable to marry due to there being not enough women
* Labour shortage
* Higher dependency load
Benefits:
* Women are now valued more than before as there is a “shortage” of them
* Efforts to rectify the educational imbalance between men and women are being made
* Successfully reduced birth/fertility rate to improve quality of life for families (allow for resources to be distributed better between families)
Consequences:
* Millions of Chinese men are unable to marry due to there being not enough women
* Labour shortage
* Higher dependency load
21
New cards
What are the causes and consequences of the gender gap in India and China?
Causes:
* abnormally high ratio of male births to female births
* sex-selective abortions to prioritize having male children
* many families in India prefer to have male children as they remain in the home after marriage and can provide care for aging family members
* boys supply manual/farm labour and run family businesses
* boys carry on the family name
Consequences:
* men have to travel to find women to marry due to a shortage of women
* men may have to marry outside of their socioeconomic groups or outside of their country
* poor families may sell their daughters into arranged marriages
* abnormally high ratio of male births to female births
* sex-selective abortions to prioritize having male children
* many families in India prefer to have male children as they remain in the home after marriage and can provide care for aging family members
* boys supply manual/farm labour and run family businesses
* boys carry on the family name
Consequences:
* men have to travel to find women to marry due to a shortage of women
* men may have to marry outside of their socioeconomic groups or outside of their country
* poor families may sell their daughters into arranged marriages
22
New cards
Why will working until an older age be common in the future in North America and Europe?
* Due to the baby boom, society has been largely dominated by a younger population of roughly the same age group, though, as time passes, this population will age and society will become overwhelmed with a majority elderly population, meaning more money and resources will need to go into supporting the older population of the dependency load and there will be less active workers in the labour force.
* In order to accommodate for the volume of elderly citizens, alterations may be made to pensions and benefits that will give less money to people in need, causing people to need to work for longer to be able to afford retirement.
* In order to accommodate for the volume of elderly citizens, alterations may be made to pensions and benefits that will give less money to people in need, causing people to need to work for longer to be able to afford retirement.
23
New cards
What is a push factor?
certain conditions cause people to leave the places where they live.
These may include:
* High crime rates
* Lack of economic opportunity
* Shortages of food
* Wartime conditions
* Low wages, underemployment and unemployment
* Persecution
These may include:
* High crime rates
* Lack of economic opportunity
* Shortages of food
* Wartime conditions
* Low wages, underemployment and unemployment
* Persecution
24
New cards
What is a pull factor?
other conditions attract people to new places to live
These may include:
* Educational opportunities
* High standards of living
* Safe from religious and political persecution
* Plentiful resources such as fresh water, forests, wildlife or agricultural land
These may include:
* Educational opportunities
* High standards of living
* Safe from religious and political persecution
* Plentiful resources such as fresh water, forests, wildlife or agricultural land
25
New cards
What is a refugee?
involuntary migrants who move to other countries to seek safety and/or protection
26
New cards
What is illegal migration?
the migration of people into a country in violation of the immigration laws of that country or the continued residence without the legal right to live in that country
27
New cards
What is legal migration?
migrants following the laws and regulations set by countries accepting immigrants and refugees and obtain citizenship legally
28
New cards
What is remittance?
* funds transferred from migrants to their home country
* they are the private savings of workers and families that are spent in the home country for food, clothing, and other expenditures, and which drive the home economy
* they are the private savings of workers and families that are spent in the home country for food, clothing, and other expenditures, and which drive the home economy
29
New cards
What are internally displaced persons (IDPs?)
people who have to move *within* a country
30
New cards
What is urbanization?
the increase in the proportion of people living in towns and cities
31
New cards
What is gentrification?
* the transformation of a city neighborhood from low value to high value
* also viewed as a process of urban development in which a neighborhood or portion of a city develops rapidly in a short period of time, often as a result of urban-renewal programs
* this process is often marked by inflated home prices and displacement of a neighborhood's previous residents
* also viewed as a process of urban development in which a neighborhood or portion of a city develops rapidly in a short period of time, often as a result of urban-renewal programs
* this process is often marked by inflated home prices and displacement of a neighborhood's previous residents
32
New cards
What are megacities?
a city with a population of 10 million or more
33
New cards
What is urban sprawl?
the spreading of urban developments on undeveloped land near a city
34
New cards
What are some positive and negative factors of rural to urban migration?
Positive:
* better job opportunities
* closer to goods and services (food, stores, etc.)
* closer to other people, potentially including family
* less need to be self-sustaining/self-reliant (access to services)
Negative:
* higher cost of living (especially housing)
* higher crime rates
* less people working with agriculture
* overpopulation
* trouble finding work/housing
* more pollution
* urban sprawl
* better job opportunities
* closer to goods and services (food, stores, etc.)
* closer to other people, potentially including family
* less need to be self-sustaining/self-reliant (access to services)
Negative:
* higher cost of living (especially housing)
* higher crime rates
* less people working with agriculture
* overpopulation
* trouble finding work/housing
* more pollution
* urban sprawl
35
New cards
What is voluntary migration? Give an example.
the movement of people from one place to another completely willingly and of their own accord
Ex:
* Between 1800 and 1914, approximately 70 million people left Europe and migrated, by choice, to Canada, the U.S., Australia, Argentina and other countries.
Ex:
* Between 1800 and 1914, approximately 70 million people left Europe and migrated, by choice, to Canada, the U.S., Australia, Argentina and other countries.
36
New cards
What is involuntary migration? Give an example.
the movement of people, against their will, to a different location
Ex: human trafficking
* Between the year 1500 and 1900, between 11 and 15 million people were forcefully taken out of Africa to be sold as slaves in America
Ex: human trafficking
* Between the year 1500 and 1900, between 11 and 15 million people were forcefully taken out of Africa to be sold as slaves in America
37
New cards
How is Canadian immigration different now than it was in 1921?
In the 1920’s, Canada was very selective of who they allowed to immigrate to the country, most, if not all, coming from Europe, specifically French, British, Belgian, Swiss, etc. The Immigration Act was amended in 1919 to be more restrictive of who was allowed in the country. Nowadays, Canada is far more accepting and tolerant of immigrants and refugees from countries all around the globe.
38
New cards
What impact does illegal migration have on its host country? Ex: Roxham Road
* countries do not have control of who is being let into their country, allowing potentially dangerous or harmful individuals to seek refuge
* individuals require resources, but may not be an active member of the workforce or society in order to contribute to the country’s well-being
* individuals require resources, but may not be an active member of the workforce or society in order to contribute to the country’s well-being
39
New cards
What are some major priorities to improve urban life in MEDCs in the future?
* sustainability
* preserving the environment
* being able to provide/accommodate for lower income families or people in poverty
* preserving the environment
* being able to provide/accommodate for lower income families or people in poverty