11. large animal med- pathophys/diagnosis of liver disease in LA
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
what is the flow of bile in horses and camelids?
bile--> canaliculi and bile ducts--> **cystic bile duct and gall bladder --> common bile duct --> small intestine
**horses and camelids lack a gallbladder

what is enterohepatic cycling?
substances excreted in bile is resorbed from gut and re-circulates in portal blood to the liver, re-excreted
normal for bile acids, bilirubin, and urobilinogen
what do kupffer cells do?
clear particulate matter, bacteria, aged RBCs, etc (macropahges of liver)
compromised liver=antigen escape=high globulin
what is total plasma bilirubin made up of?
total plasma bilirubin= unconjugated bilirubin + small amount of conjugated bilirubin
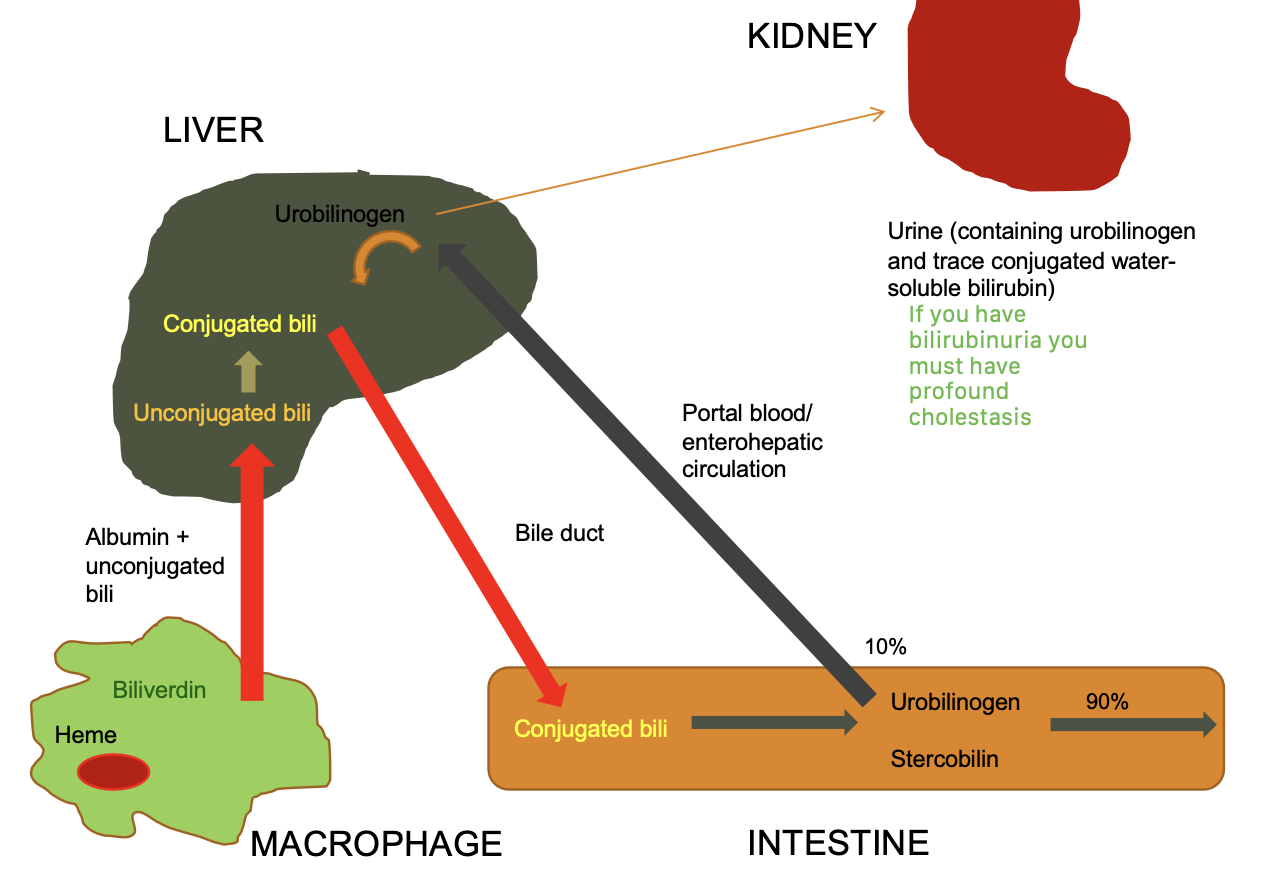
what are causes of increased unconjugated bilirubin?
-excess production (hemolysis)
-decreased uptake into hepatocytes
-disturbed intracellular protein binding or conjugation
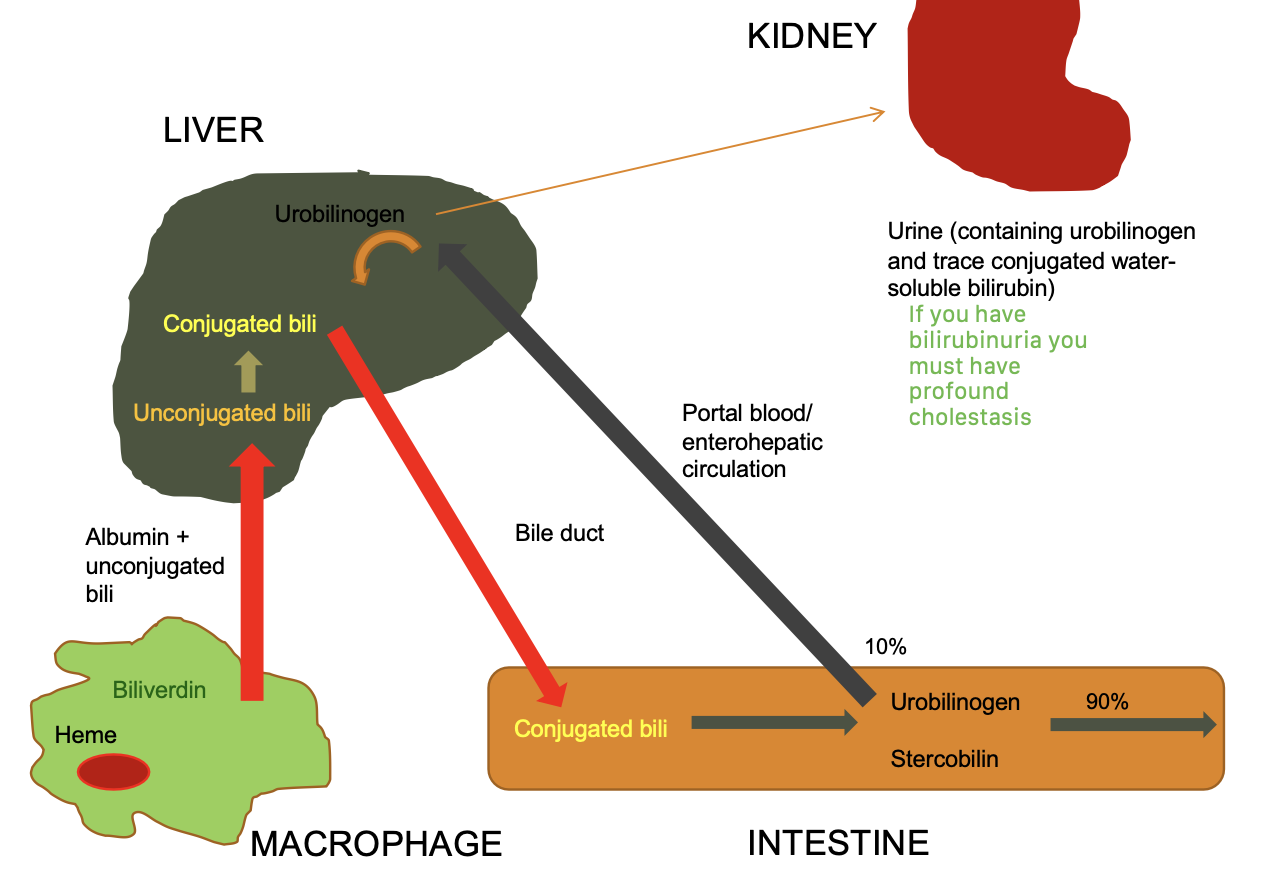
what are causes of increased conjugated bilirubin?
regurgitation into blood:
-disturbed secretion of conjugated bilirubin into canaliculi
-intra or extra hepatic bile obstruction
what are the main functions of the liver?
protein synthesis
fat metabolism
blood glucose control
bile acid synthesis and excretion
immune protect - kuppfer cells
detoxification
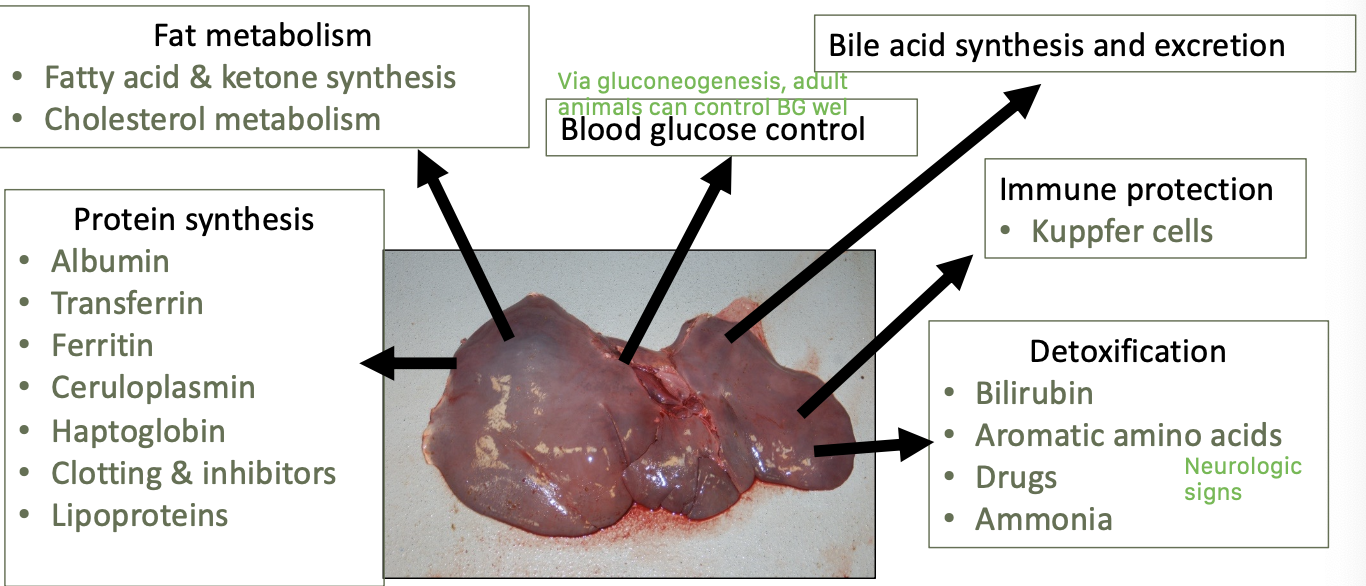
what proteins are synthesized in the liver?
albumin
transferrin
ferritin
ceruloplasmin
haptoglobin
clotting and inhibitors
lipoproteins
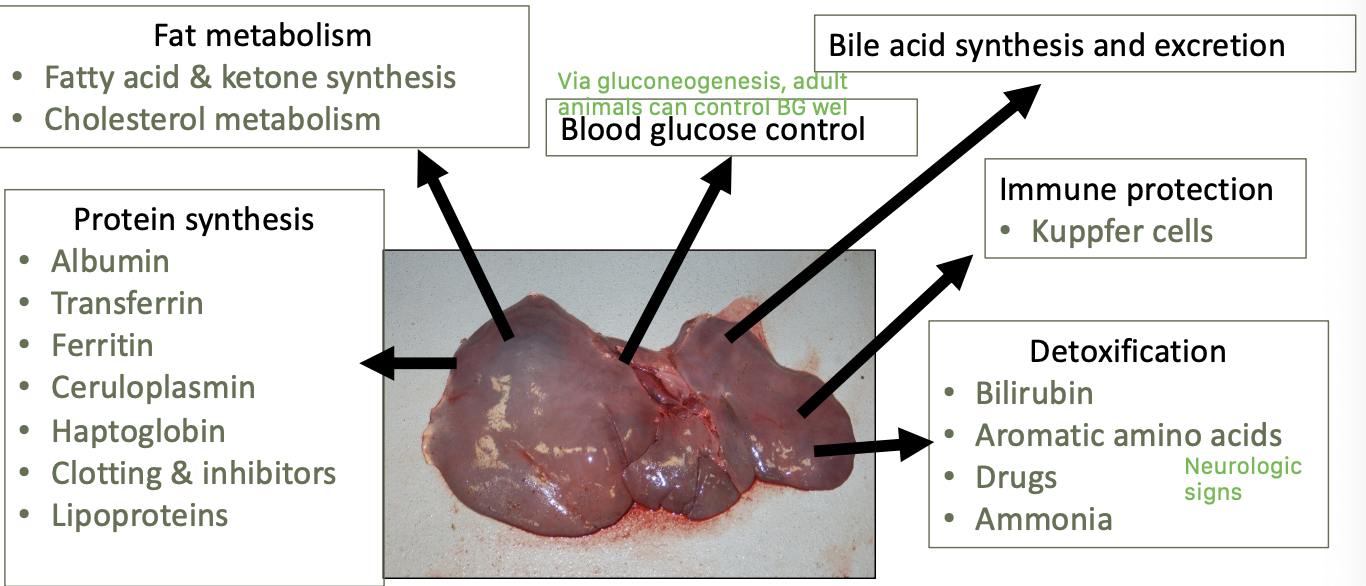
what does the liver detoxify?
bilirubin
aromatic amino acids
drugs
ammonia
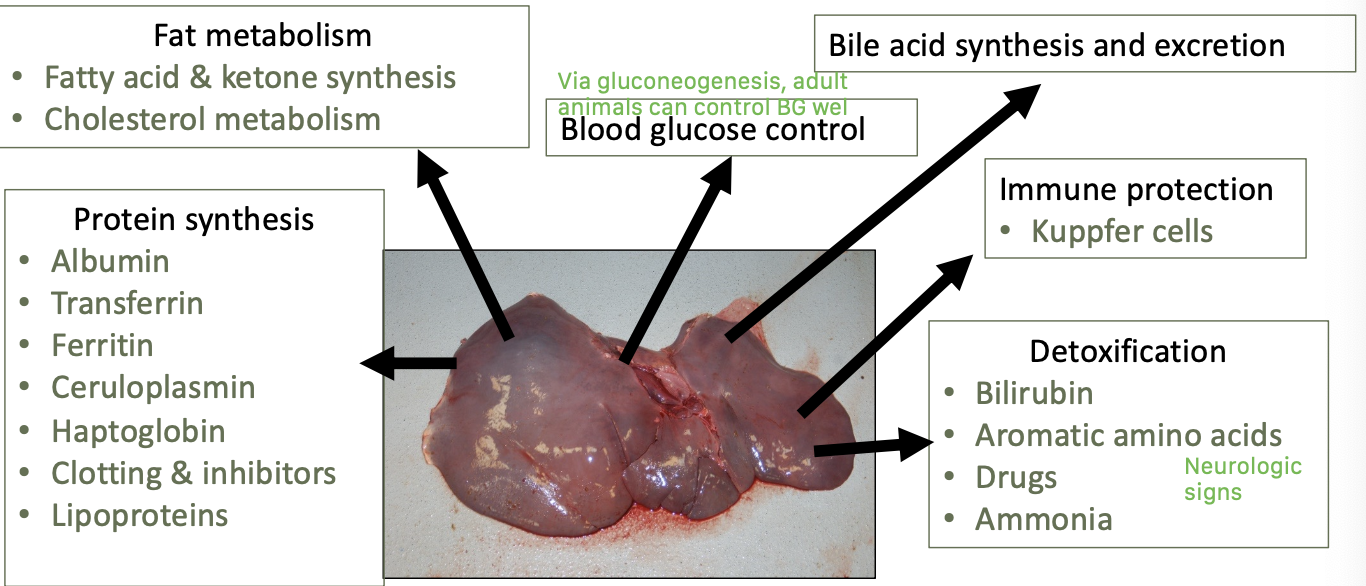
what fatty metabolism processes occur in the liver?
fatty acid and ketone synthesis
cholesterol metabolism
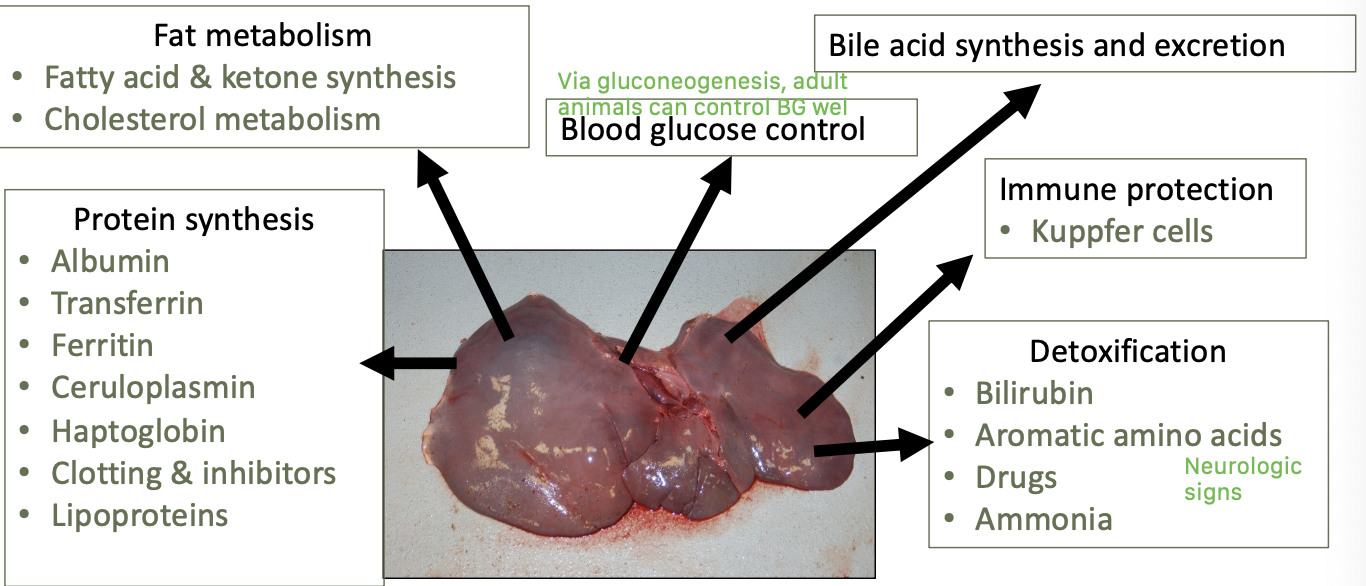
how much hepatic function is lost once signs of hepatic insufficiency is seen?
~75%
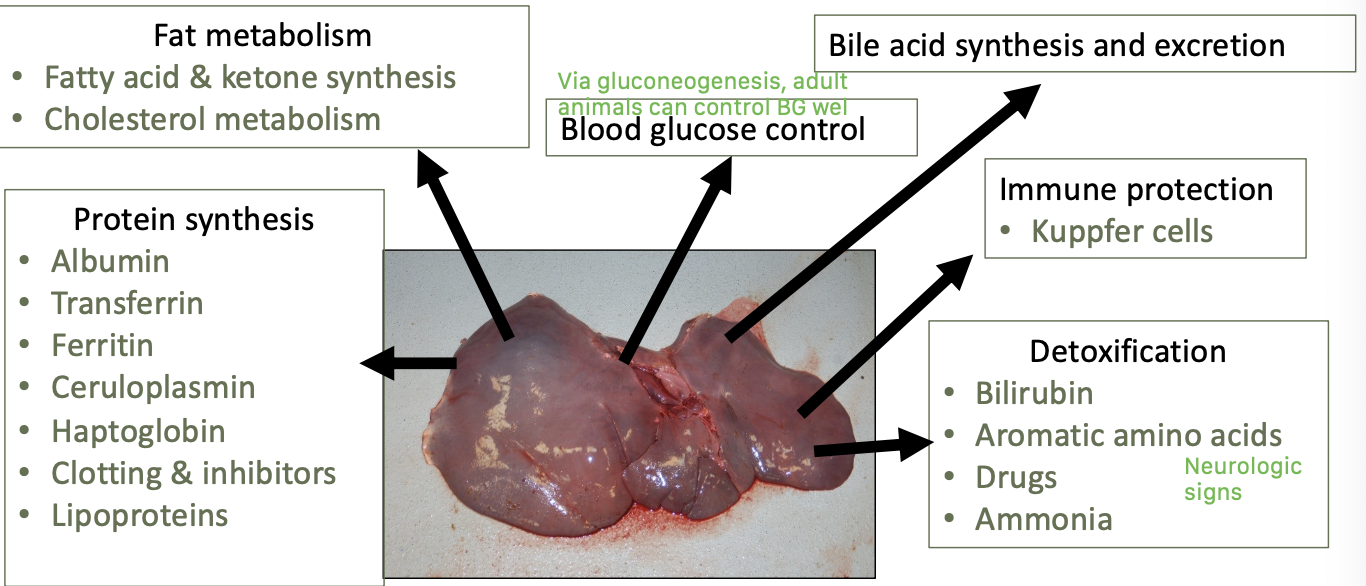
Signs of liver disease reflect liver ____. Primarily ___, ___, ___ but signs can also be subtle and non-specific.
duties,
jaundice, CNS disturbance, photosensitization
e.g. weight loss, colic, anorexia, pruritis, ventral edema, hemorrhage, diarrhe,a fever, hemolysis, PD, laryngeal paralysis, polycythemia, dermatitis

what lab/clin path changes may reflect hepatic insufficiency?
-hypoglycemia
-high bilirubin
-high bile acids
-high ammonia
-clotting anomalies
-protein changes (decreased albumin, increased globulin)
what is high unconjugated vs high conjugated bilirubin indicative of?
unconjugated: hepatocellular disease
conjugated (in urine): severe cholestasis
true or false? Normal horses will not have bilirubin in urine.
true
what should the history of suspected liver dz patients include questions about?
-vaccination or transfusion with blood or plasma
-exposure to plant or chemical toxins
-fever, colic, weight loss
-# of affected or exposed animals
-any prior lab work or treatment

what may be found on physical exam of patients with liver disease?
PE often unremarkable
-hepatic injury often reflected only in biochemistry
hepatic disease w/o insufficiency causes few signs
what are the common clinical signs of hepatic disease?
1. icterus
2. hepatic encephalopathy
3. weight loss (esp. in chronic dz)
4. colic
5. depression and anorexia
is icterus more prominent with elevated conjugated or unconjugated bilirubin?
conjugated bilirubin will cause more prominent icterus

will anorexic horses have elevated conjugated or unconjugated bilirubin?
increased unconjugated bilirubin
what is hepatic encephalopathy?
CNS dysfunction from hepatic failure
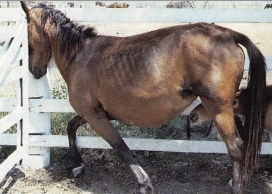
what are signs of hepatic encephalopathy in horses?
depression, head pressing, walking, circling, ataxia, yawning
what is important to remember about hepatic encephalopathy in large animals?
dangerous!!! AND unpredictable with sedation
what are differentials for hepatic encephalopathy in horses?
1. GI associated hyperammonemia (colic, colitis)
2. trauma
3. viral encephalomyelitis (rabies)
4. leukoencephalomalacia
5. brain abscess
6. EPM (equine protozoal myelitis)
7. botulism
8. heavy metal toxicity

what colic signs are seen with liver disease in horses?
-usually subacute
-hepatic swelling, biliary obstruction
-gastric impaction (esp in donkeys and minis)

what are less common clinical signs of hepatic disease?
1. pruritus
2. ventral edema/ascites (hypoalbuminemia- uncommon in horses)
3. hemorrhage/DIC (impaired factor production and vit.K absorption)
4. diarrhea (esp in cattle)
5. photosensitization
6. other (fever, PD, steatorrhea, dermatitis, laryngeal hemiplegia)
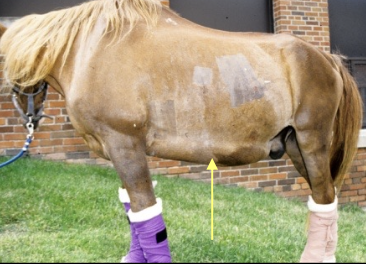
what causes ventral edema/ascites in patients with liver disease?
increased portal pressure from hepatic fibrosis
what causes diarrhea in patients with liver disease?
portal hypertension + increased hydrostatic pressure
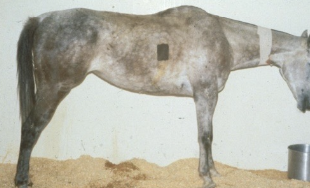
what is photosensitization?
seen with chronic hepatic dz:
-erythema and crusting of non-pigmented skin (accumulated phylloerythrin reacts with light)
-can be non-hepatic origin (via ingestion of plant toxins)

what is the appropriate bloodwork to run on patients with suspected liver disease?
-all relevant enzymes (liver, muscle)
-non-specific tests of function
-specific testing (bile acids) if indicated - BA and ammonia not on routine chemistry, triglycerides variable

what is the goal of evaluation of PE, blood work, and ultrasound in patients with hepatic disease?
to determine:
-acute vs chronic
-likely cause
-likely prognosis
-appropriate treatment
what are hepatic enzymes useful indicators of?
useful indicators of presence of disease (fairly sensitive to any disorder)
are hepatic enzymes indicators of function?
no, hepatic enzymes are not indicators of hepatic function:
-degree of increase does not reflect severity
-enzymes are best evaluated over time and with other diagnostics
what do hepatic leakage enzymes increase/decrease with?
cell damage increases serum activity
enzymes decline with improvement or decreased hepatic mass
what are the leakage enzymes?
AST (aspartate transaminase) and SDH (sorbitol dehydrogenase)
how is AST evaluated?
interpret with GGT and CK to confirm liver vs muscle origin (if AST>4000U/L, likely from muscle)
-sensitive and stable
-peaks 24-48hrs, lasts up to 2 weeks
-can normalize with chronic dz
what is SDH?
- specific for acute hepatocellular damage
-shorter half-life (values normalize in 3-5 days)
-continued increase=continued dz
-not stable, process quickly
what are increases in SDH commonly seen with?
increases in SDH commonly occur with GI disease such as enteritis (still liver origin)
what is GGT?
gamma glutamyltransferase (GGT)
induced enzyme, liver specific indicator of biliary dz (cholestasis, biliary proliferation)
-peaks in 7 days, can last weeks
-increases can reflect colostrum, large (right dorsal) colon displacement, heavy training

what are the non-specific indicators of hepatic function?
-increased total bilirubin
-decreased BUN
-decreased glucose
-decreased albumin (requires 80% loss for 3 weeks)
-increased globulins (suggests chronicity)

what are the specific indicators of hepatic function?
1. serum bile acids
2. blood ammonia
how can increased serum bile acids be an indicator of hepatic dysfunction?
95% of bile acids are resorbed from ileum into portal vein, extracted by the liver, and excreted into bile
-the diseased liver will continue to produce
increased BA in serum indicates impaired blood flow, uptake, or excretion

how are bile acids ran in horses?
dont need to fast, >20umol/L sensitive for equine liver disease
-single sample is adequate
-sample is stable
-poor discrimination of cause
- increases if anorexic for more than 3 days
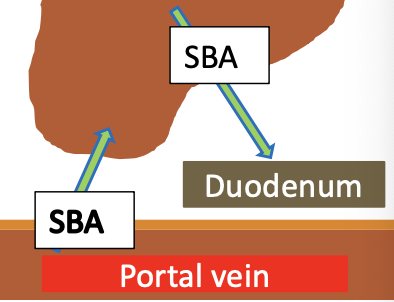
what does increased blood ammonia suggest?
increased ammonia suggests diffuse hepatic disease, >60% function loss
be aware of gut associated hyperammonemia!
What sample should you collect for blood ammonia?
EDTA sample, chill and run in 6h or freeze
what other diagnostic can strongly support presence of hepatic disease?
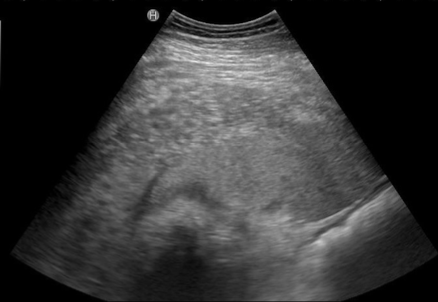
ultrasound
must know normals! (architecture, expected size, comparison to spleen)
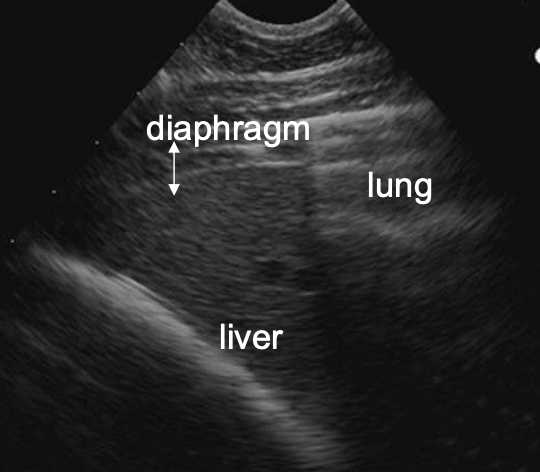
where is the liver located on the right side of the horse?
6th-15th intercostal space
ventral to lung (usually ends at costochondral junction)
may not be visible in geriatric horses (right lobes atrophy as horses age)
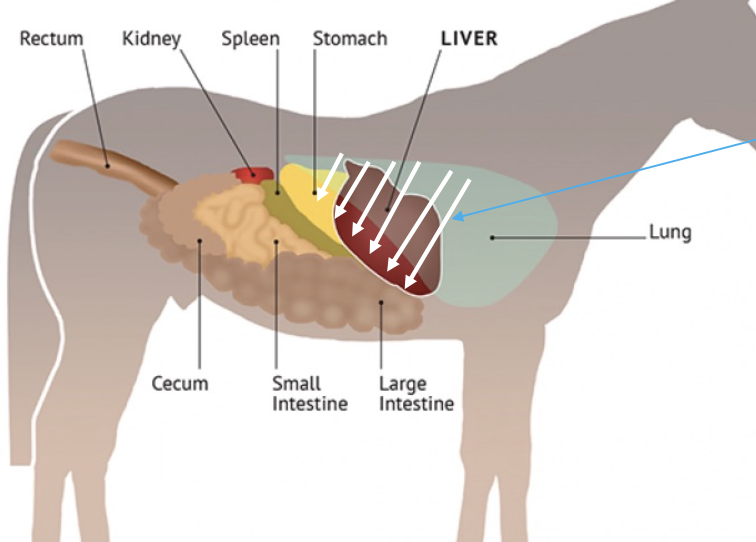
where is the liver located on the left side of the horse?
7th-9th intercostal space
ventral to lung, next to spleen (usually ends at costochondral junction)
stable with age (unlike the right side)
what is the normal appearance of the liver on ultrasound?
-uniform
-sharp edges
-darker than spleen (left side)
-ends at or before costochondral junction (dont confuse with peritoneal fat)
-anechoic vessels visible
-no obvious biliary channels
-no shadowing structures
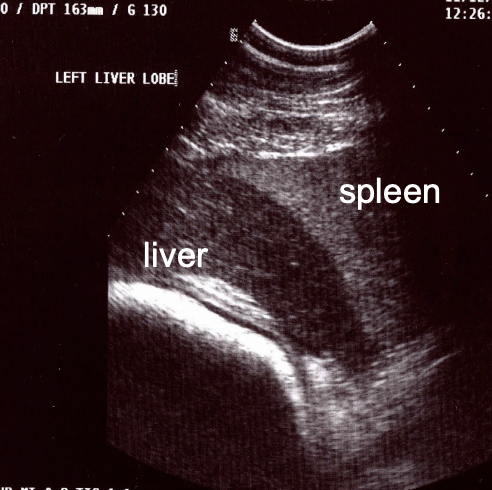
where is the liver located in cattle?
right side: from 8th-12th intercostal space
rumen prevents visualization on left side
gallbladder at ventral border in 9th-12th intercostal space
where is the liver located in sheep?
7th-12th intercostal space on the right side

where is the liver located in goats?
7th to last rib on right side
gallbladder extends below ventral border
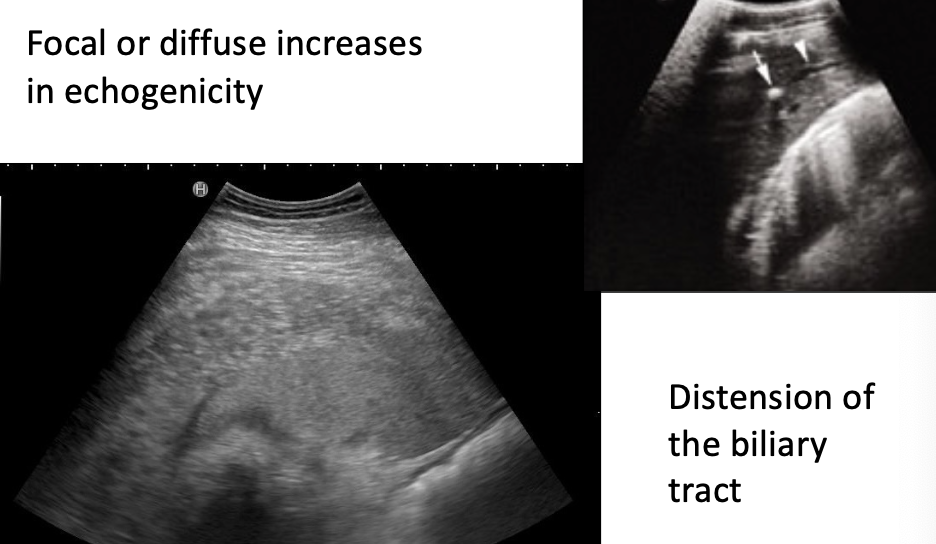
what abnormal findings may be seen on ultrasound?
-focal or diffuse increases in echogenicity
-distension of biliary tract
-focally, multifocally, or diffusely disturbed architecture
-changes in size, rounded or abnormal edges
when are liver biopsies indicated?
-persistent increases in liver enzymes, chronic dz, poor treatment response, or suspect toxicity
-increased bile acids
-masses, infiltrate, abnormal size on ultrasound (except abscesses)
when should you not do a liver biopsy?
Do not use to confirm reliable clinical diagnosis (e.g. lipidosis, Theiler’s)
Less invasive tests first ( e.g. belly tap for suspected lymphoma)
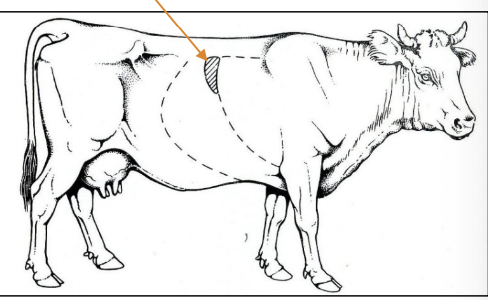
where are liver biopsies performed in horses?
use ultrasound to select site:
-need adequate liver depth (3cm)
-avoid vessels, over structures
-usually on right side between 12th-14th ICS
-use first sample for culture if needed
or via laparoscopy or surgical collection

what are poor prognostic indicators of hepatic disease?
-albumin <2.5g/dL
-increased globulin
-30% increase in prothrombin time
-increased GGT/ALP with normal or low AST/SDH
-marked fibrosis
-encephalopathy or hemolysis
-bile acids >50umol/L
