AP Psych 3.1-3.6 Early Development Quiz Terms
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Teratogens
Agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm.
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS):
Physical and cognitive function deficits in children caused by their birth mother’s heavy drinking during pregnancy. Symptoms include a small, out of proportion head and distinct facial features. Alcohol has an epigenetic effect, meaning it leaves chemical marks on DNA that switches genes abnormally.
Habituation:
Decreasing responsiveness with repetition. As infants gain familiarity with repeated exposure to a stimulus, their interest decreases and they look away sooner.
Examples: Wearing a perfume everyday for several weeks that you no longer notice the smell.
Maturation:
Biological growth (nature) processes that enable orderly changes in behavior, relatively uninfluenced by experience. Genes and scenes interact.
Adolescence:
The transition period from childhood to adulthood, extending from puberty to independence.
Puberty:
A period of sexual maturation, during which a person becomes capable of reproducing.
Menopause
The time of natural cessation of menstruation. This is when a woman’s ability to reproduce declines.
Intersex:
Processing male and female biological sexual characteristics at birth.
23 chromosomes from mom and 23 from dad= 46 Total
Relational Aggression:
An act of aggression (physical or verbal) intended to harm a person’s relationship or social standing.
Women are more likely to do this (Girl bullying).
Spermarche
First ejaculation… at age 14…
Menarche:
The first menstrual period.
Gender Roles:
A set of expected behaviors and traits for men and women.
Gender Identity:
One’s sense of gender: being male, female, or neither regardless of whether this identity matches our sex assigned at birth.
Gender Typing:
The acquisition of a traditional masculine or feminine role. Culture’s also differ in their conceptualizations of gender.
Examples: When a girl wears pink because she’s a girl or when a boy attributes himself to the male identity by playing with trucks and avoids girly dolls.

Androgyny:
Blending traditionally masculine and traditionally feminine physiological traits. These people are more flexible with their actions and career choice, resillient, accepting, and adaptable.
Asexual:
Having no sexual attraction to others (Only 1% are this).
Sexual Orientation:
Sexual attraction to another person
Straight/ Heterosexual
Pan
Jimbo
Alexa
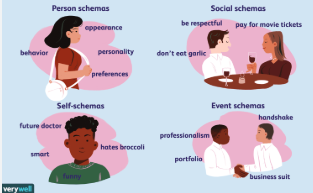
Schema:
A concept or mental mold that organizes information and experiences.
Ex: We have schemas for everything from simple objects: desk and cat, to complex concepts like love and friendship.
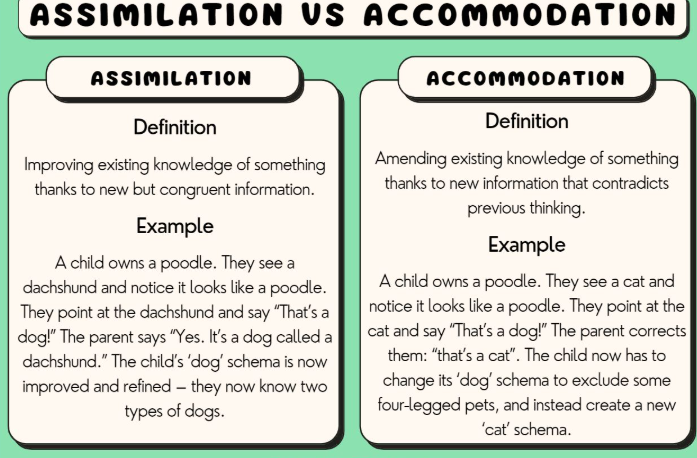
Assimilation:
Incorporating our new experiences into our existing schemas. Making things the same.
Ex: A child with a dog at home referring to a horse as a “dog.”
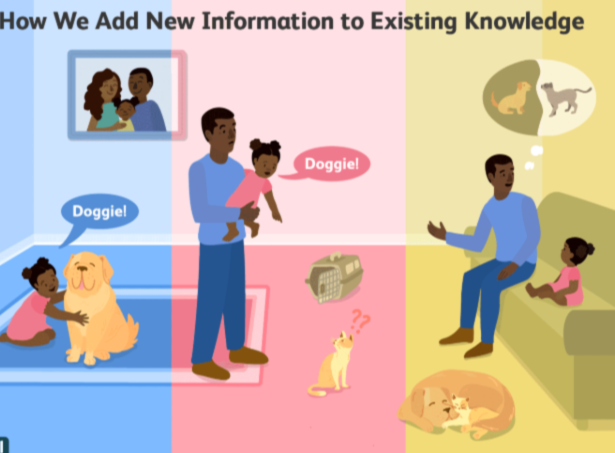
Accommodation:
Correcting our current schemas/ understandings to make room for new information.
Ex: A child learning that a horse is different than a dog.
Theory of Mind:
People’s ideas about their own and other’s mental states— about their feelings, perceptions, and behaviors these might predict.
Example: A preschooler understand what made a playmate angry, what might make their parents buy a toy, and how they make others feel.
Linguistic Determinism (Whorf):
Whorf’s extreme hypothesis that language governs the way a person’s cognitive processes and thinking.
Ex: People who use languages with no past tense cannot readily think about the past. Thinking about a shade of blue that someone cannot name.
Linguistic Relativism:
The idea that language influences the way a person sees the world.
Examples: Your mom speaks Japanese when she’s angry, and Cantonese when she’s even more angry.
Attachment:
An emotional tie with other people which is shown in young children seeking closeness with their caregivers.
Imprinting:
The process by which certain animals or infants form strong attachments during early life.
EX: A duckling saw their mom as the first moving object and therefore followed her everywhere.
Basic Trust:
A sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy; It is said to be formed during infancy with responsive caregivers.
Self-Concept:
All our thoughts and feelings about ourselves.
Question: “Who am I?”
Temperament:
A person’s emotional reactivity and intensity.
Ex: A baby who is difficult, cries, and is intense compared to a calm cheerful one.
Social Identity:
The “we” aspect of our self concept; the part of our answer to “Who am I"? that comes from our group memberships.
Example: I am a jock. I am FGLI.