physics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
A description of a rule of nature is
scientific law
In the metric system (SI) what is the base unit for length
meter
SI units biggest to smallest
Tera (12), Giga (9), Mega (6), Kilo (3), Hecto (2), Deka (1), Base Unit, Deci (-1), Centi (-2), Milli (-3), Micro (-6), Nano (-9), Pico (-12), Femto (-15)
What is the base unit for mass
Kilograms
Which prefix denotes the smallest amount
Femto or Pico
A hypothesis can best be defined as a..
prediction
A device with very small divisions on its scale can measure with high …..
precision
A ____ relationship exists when one variable relies on the square of another
quadratic
The equation y = ax² + bx + c, illustrates what kind of relationship?
quadratic
What should a scientist do if his conclusion does not match his original hypothesis
revise the original hypothesis
Explain the difference between a scientific law and a scientific theory
A theory is an explanation and a law is a statement of what will occur under specific conditions
Describe the scientific method
The process of objectively establishing facts through testing and experimentation. Ask the question, conduct research, develop your hypothesis, test your hypothesis with experiment(s), record observations, examine results, draw conclusions, and share your findings.
What is more precise, a beaker or graduated cylinder?
Graduated cylinder
What axis does the independent variable use?
X-axis
What axis does the dependent variable use?
y axis
Why are significant digits important to science?
They show how precise a number is
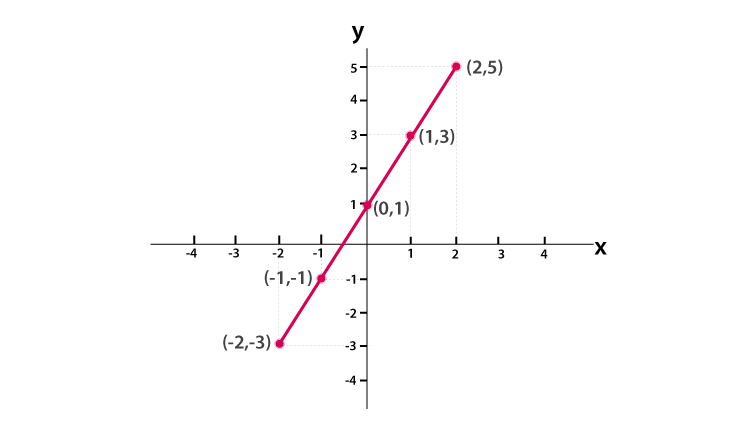
What type of graph is this?
Linear
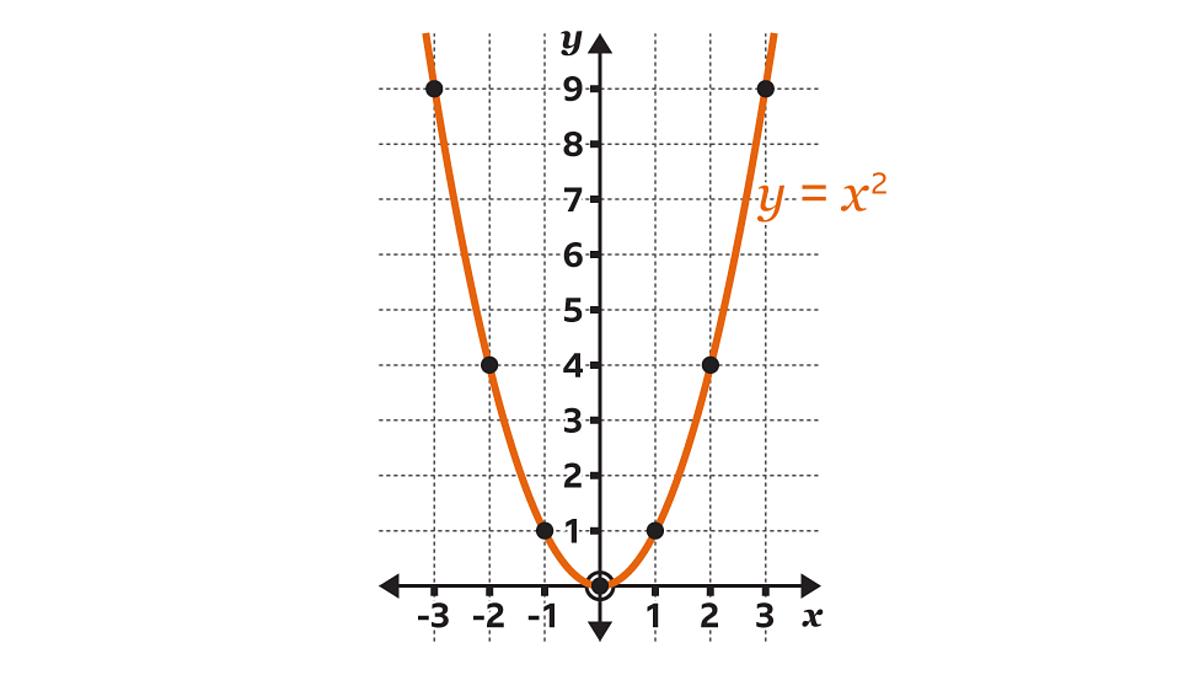
What type of graph is this?
Quadratic
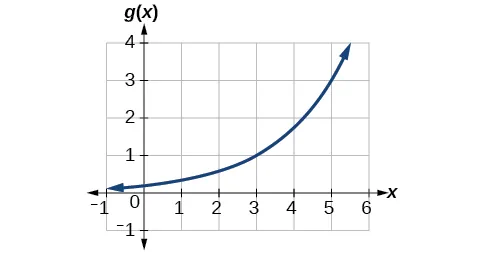
What type of graph is this?
Inverse
What is the general equation for linear graphs?
y = mx + b
What is the general equation for quadratic graphs?
f(x)=ax2+bx+c
What is the general equation for inverse graphs?
y = a/x
Scientific theory
A broad explanation that is widely accepted because it is supported by a great deal of evidence
Scientific Law
Statements based on repeated experiments or observations that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena.
precision
How close measurements of the same item are to each other. The degree of the exactness of a measurement .
accuracy
how close a measurement is to the “true” or “Accepted” value
scalar
a quantity that is just a number without any direction. Ex: distance, time, or temperature.
vector
a quantity that has both magnitude and direction
Ex: velocity, momentum, and force
temperature scale of most lab thermometers
celsius
SI unit of temperature
Kelvin