HUN2201 STUDY GUIDE EXAM 1
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
A good source of a nutrient has
10-19% DV per serving
A high or excellent source of a nutrient has
20% DV per serving
Nutrients one should limit should have DV of
5% or lower
Nutrients to limit
Saturated fat, cholesterol, and sodium
High Saturated fat leads to
raised blood cholesterol and heart disease
High Sodium leads to
raised blood pressure and cardiovascular risk
High Cholesterol leads to
heart disease
Limit added sugars to
<10% of daily calories
Reliable and accurate sources end in
.gov, .edu, .org
List 4 reliable and accurate sources
USDA, NIH, ACS, AHA
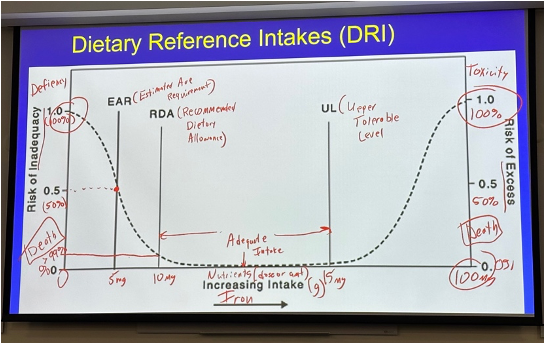
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI): EAR is the
Estimated Average Requirement (below this is deficiency & death)
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI): RDA is the
Recommended Dietary Allowance
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI): Between RDA and UL is the
Adequate Intake of a Nutrient
Dietary Reference Intakes (DRI): UL is the
Tolerable Upper Intake Level (above this is toxicity & death)
Draw the DRI graph.
The primary nutrient in dairy is
Calcium (but also Vitamin D)
The primary nutrient in protein is
B12
The primary nutrient in fruits and vegetables is
Vitamin C
Biggest sources of of Food and Nutrition Misinformation
Internet (70%) and media
Explain the development of dental caries.
1) Sugar enters the mouth.
2) Bacteria (Streptococcus mutans) feed on sugars and produce lactic acid.
3) Acids lower ph, demineralizing enamel.
4) If acid attacks continue, enamel breaks down → exposing dentin.
5) Continued demineralization creates a cavity (hole) in the tooth.
Sugar → Streptococcus mutans → acid → enamel erosion → dentin damage → cavity formation.
Gustation
the sensory process that allows us to perceive taste
Gustation works closely with —- to create the perception of flavor.
olfaction (smell)
5 basic tastes
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
How taste works (chemicals, receptors)
· Chemicals in food bind to receptors on your taste receptor cells in taste buds.
· Binding triggers a nerve signal to the brain → brain interprets as a specific taste (sweet, salty, etc.).
Sweet taste receptors detect
aldehydes/sugars
Sour taste receptors detect
H+ ions
Salty taste receptors
detect sodium ions (Na+)
Bitter taste receptors detect
alkaloids & nitrogenous compounds —> may signal toxins
Umami taste receptors
detect monosodium glutamate
Nutrient Density Formula
Nutrient density = Nutrient Content/Calories
Streptococcus mutans
Oral bacteria that form plaque and ferment sugars into acid
Helicobacter pylori
Bacteria that colonize the stomach lining; associated with gastritis and peptic ulcers
Lactobacillus acidophilus
Beneficial probiotic bacteria found in the gut and fermented foods; supports digestion and gut microbiome health.
Dysphagia
swallowing process is impaired → bolus of food enters the airway instead of the esophagus.
Results: choking, nasal regurgitation
Higher risk groups: infants, elderly
What does the epiglottis usually do when you swallow
closes to prevent bolus from entering the windpipe (trachea).
Mastication
Chewing food into smaller pieces, mixing with saliva to begin digestion
Deglutition
The process of swallowing, moving a bolus from the mouth → pharynx → esophagus → stomach.
Bolus
a soft mass of chewed food mixed with saliva, ready to swallow
Gastrin
stomach hormone that stimulates parietal cells to release HCl (gastric acid) and chief cells to release pepsinogen.
Pepsinogen
Inactive precursor secreted by chief cells in the stomach; converted by HCl into pepsin, which digests proteins.
Chyme
Semi-liquid mixture of partially digested food + gastric juices in the stomach.
Salivary amylase
Enzyme in saliva that begins chemical digestion of starch into maltose.
Mucous neck cells
secrete mucus + bicarbonate to protect stomach lining from acid.
Parietal cells
secrete HCl (lowers pH, kills microbes, activates pepsinogen) and intrinsic factor (essential for vitamin B12 absorption in the ileum).
Chief cells
secrete pepsinogen (inactive zymogen).
Pepsinogen + HCl →
pepsin
Pepsin
active enzyme that digests proteins into smaller polypeptides
G cells
secrete the hormone gastrin
CCK (Cholecystokinin)
hormone that slows gastric emptying (keeps food in stomach longer).
sends signals to the brain → satiety (feeling full).
Proteins (long chains of amino acids) are broken down by
pepsin into smaller polypeptides.
Gastroparesis
Delayed gastric emptying, often due to nerve damage (e.g., diabetes); causes nausea, vomiting, early satiety.
Aspiration
inhalation of food, liquid, or gastric contents into the airway/lungs
If the stomach’s protective mechanisms fail,
H. pylori infection or NSAIDs can damage mucosa → gastritis or peptic ulcers
What starts protein digestion in the stomach?
HCl denatures proteins and converts pepsinogen → pepsin; pepsin cleaves proteins into smaller polypeptides
Where does most protein digestion finish?
In the small intestine
Dysgeusia
Altered or distorted sense of taste.
Xerostomia
dry mouth; reduced or absent salivary secretion
Peptic Ulcer Disease
ulceration of gastric mucosa.
Mechanism: Breakdown of protective mucosal barriers due to Helicobacter pylori infection, NSAID use, or hyperacidity.
Gastroesophagul Reflux Disease / GERD
Chronic reflux of gastric contents into esophagus.
• LES fails to close properly → gastric acid refluxes into esophagus.
Steps in Protein Digestion
Food (bolus) enters the stomach → triggers gastric stretch receptors and presence of protein.
2. G cells → secrete the hormone gastrin → stimulates parietal cells to release HCl and chief cells to release pepsinogen (inactive zymogen).
HCl activates pepsinogen, turning it into pepsin.
Pepsin cleaves proteins into smaller polypeptides.
Vitamin B12 Absorption
1. Parietal cells also secrete intrinsic factor (IF).
2. Vitamin B12 from food binds to IF in the stomach.
3. This B12–IF complex travels to the ileum for absorption.
Nutrition-related contributors of GERD:
High fat diet, obesity
Nutrition-related contributors of PUD (ulcer):
Alcohol, NSAIDs, high salt, low antioxidants
Dysgeusia impact on nutrition
decreased appetite and food intake, weight loss, nutrient deficiencies
Xerostomia impact on digestion/absoption
harder to chew and swallow; less starch breakdown
(Salivary amylase activity decreases → slows starch digestion)
Dental caries impact on nutrition
Painful chewing, avoidance of hard/nutrient-dense foods
Anorexia impact on nutrition
low calorie and nutrient intake
Dysphagia impact on nutrition
Risk of aspiration and choking, Reduced solid/liquid intake
Gastroparesis
Stomach empties food into small intestine more slowly
Gastroparesis impact on nutrition
Early satiety + nausea → reduced food intake, nutrient loss
Type of study that found that high saturated fat and blood cholesterol associated with heart disease.
cohort study
Compare the nutritional value of whole grains to refined (processed) grains.
Whole grains have more fiber.
1 ATP is equivalent to
7 calories
What are the 3 classes of nutrients used to make ATP or energy?
carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins
What are the 6 classes of nutrients?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, vitamins, minerals, water
The primary nutrients in grains are
B vitamins, fiber
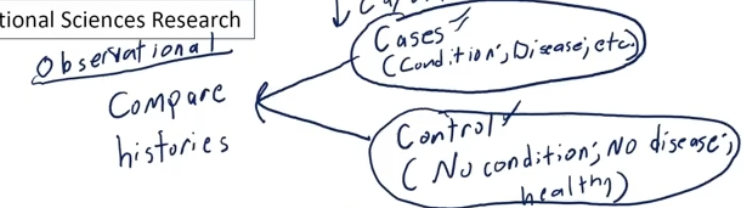
Observational Studies
no intervention
Case Control Study
group with condition/disease and group without (control group) - go back in time to compare histories.
ex: comparing history of a group of kids with broken bones and group of kids who are healthy to see what caused this difference
Type of study that led to fortification of iodide.
case control
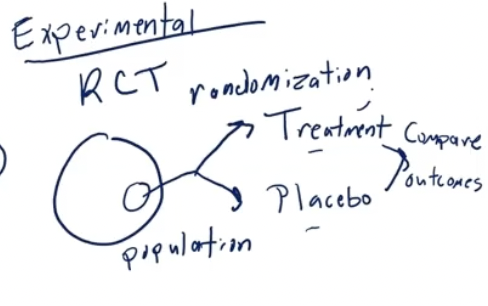
Experimental
have intervention
Randomized Control trial
sample of population, randomly assign to different groups. one receives treatment and one receives placebo. compare outcome
To establish guidelines,
a lot of research studies will be used. best: systematic reviews & meta analysis.
Epithelial cells
type of mucous cell
building blocks of atp: fatty acids, carb, and ??
cariogenic meaning
what step does chyme dump into small intestine during protein digestion
law made for supplements