CH 28 Protists
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Protists
Diverse eukaryotic organisms not classified as fungi, plants, or animals.
(classified via exclusion)
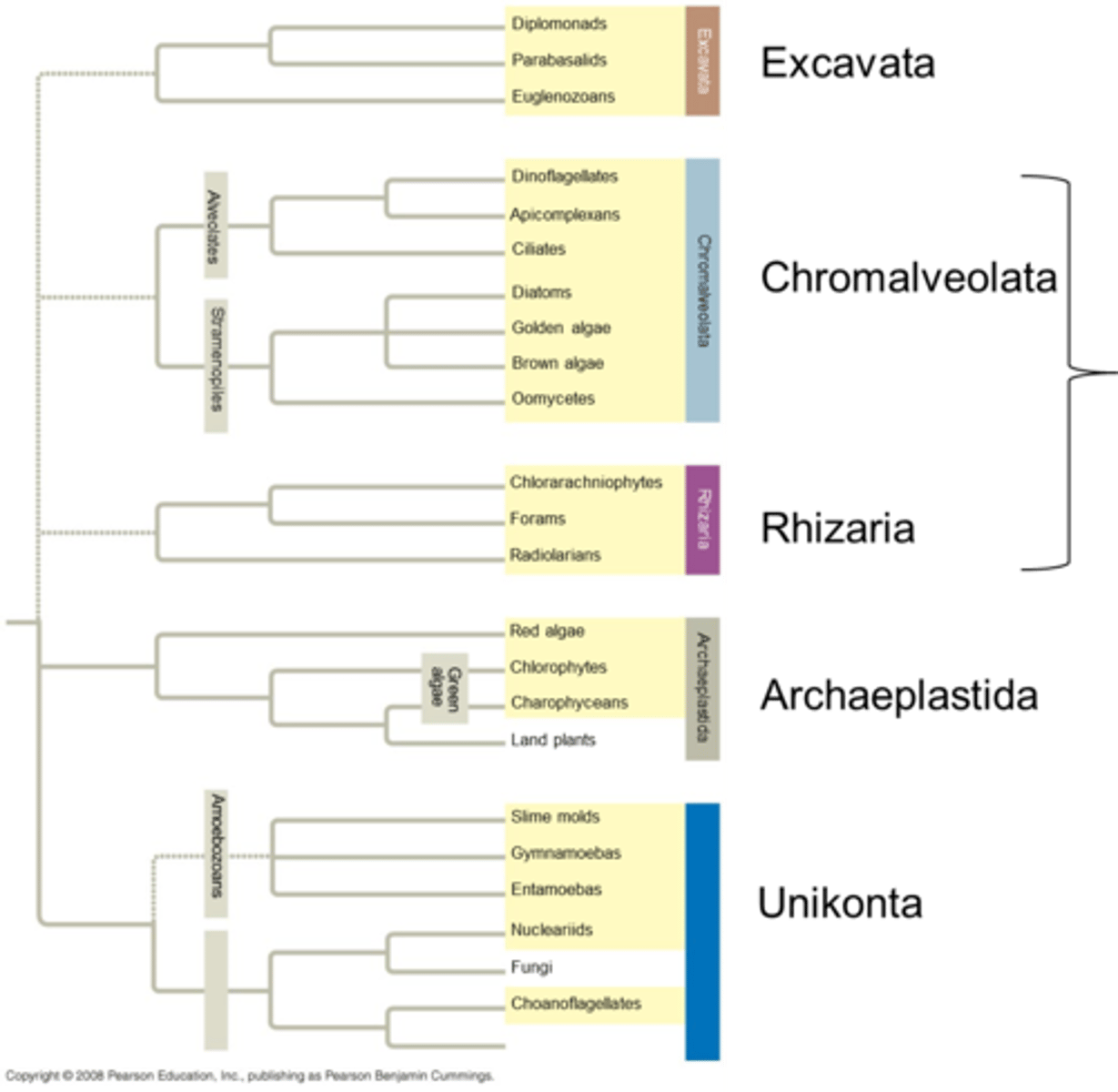
Supergroups of Protists (5)
Major classifications of protists: Excavata, SAR, Archaeplastida, Amoebozoa, Opisthokonta.
Eukaryotes vs Prokaryotes
presence of complex cytoskeleton
compartmentalization (nucleus & organelles)
Proks 3.5BYA, Euks 1.5BYA
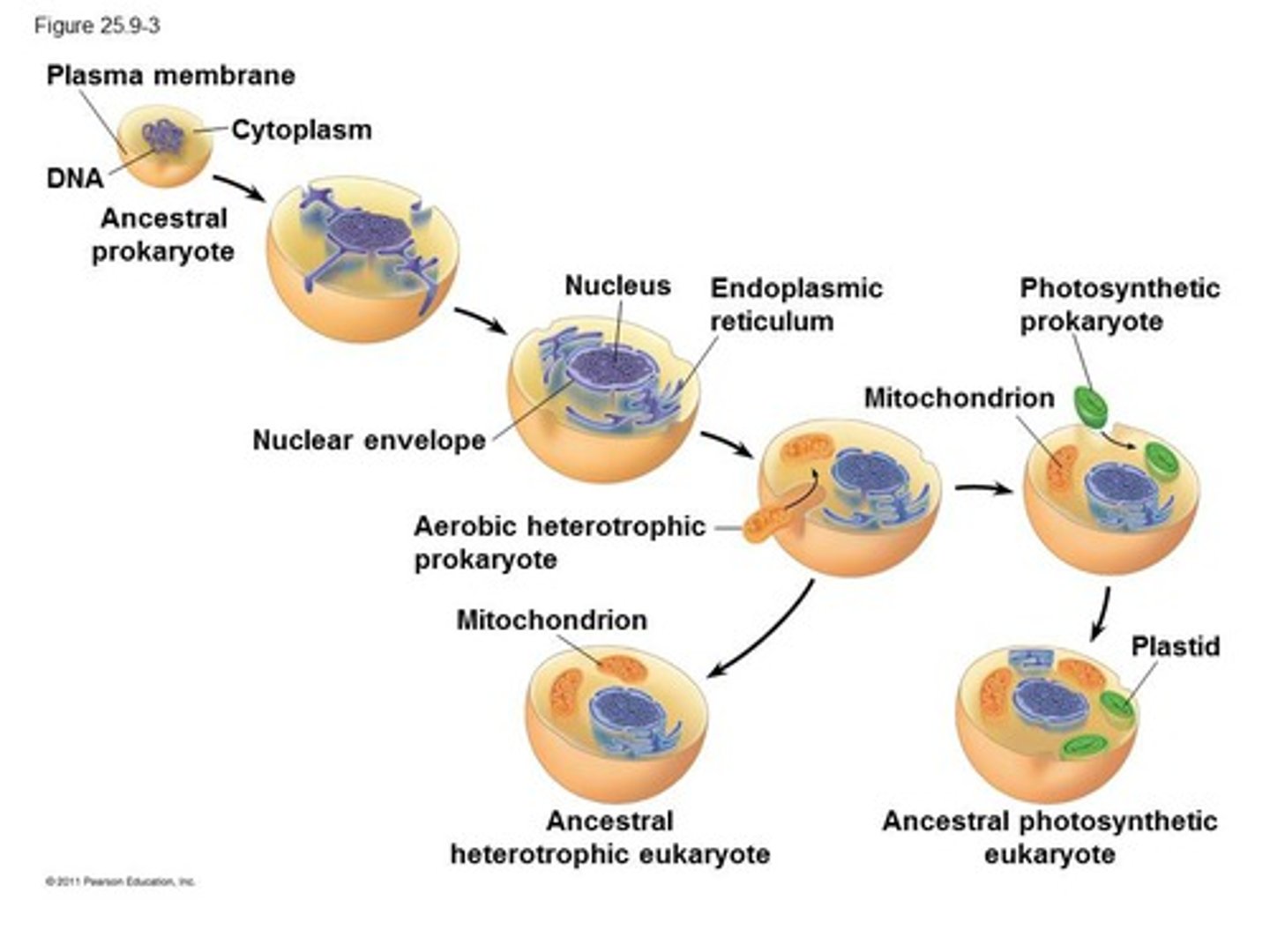
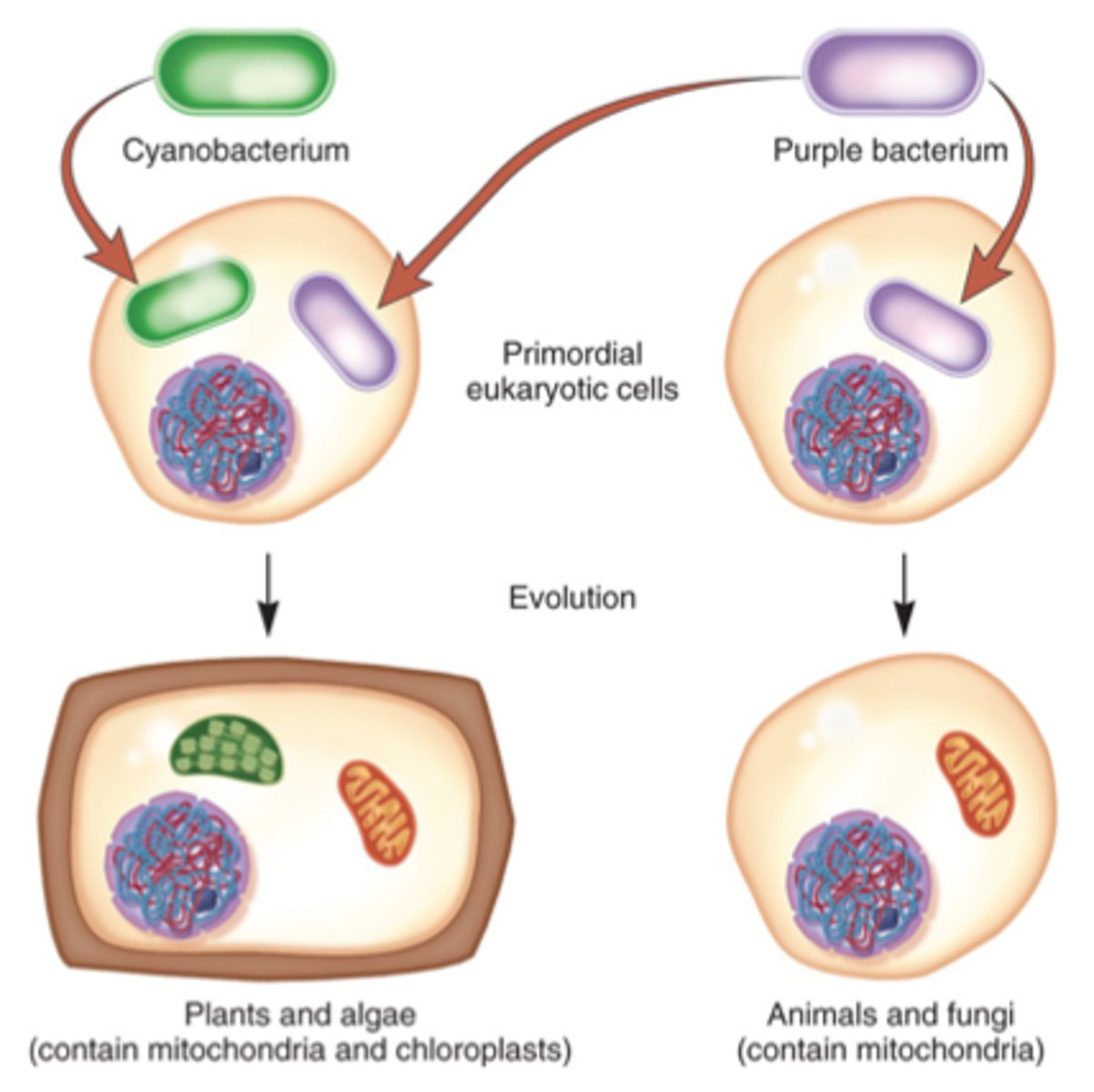
ER, nucleus & Endosymbiosis (1st & 2nd)
ER & nucleus arose from infoldings in prok. cell membrane
1st endosymbiosis: Big bacteria engulfed anaerobic bacteria (mitochondria)
2nd endosymbiosis: already developed Euk. engulfed green bacteria for plants
Evidence for Endosymbiosis
DNA inside mitochondria & chloroplasts (circular DNA, similar to bacteria in size & character)
Ribosomes inside mitochondria similar to bacterial ribosomes & vulnerable to antibiotics
Chloroplast & mitochondria replicate by binary fission not mitosis (mitosis evolved in eukaryotes)
How do protists vary?
Unicellular, colonial & multicellular groups
Most are microscopic but some are huge
Many forms & symmetries
All types of nutrition
Cell Surface of Protists contain?
Protist have varied array of cell surfaces
Plasma membrane
Extracellular matrix (ECM) in some
Diatoms & foraminifera-> silica shells
Cysts
Dormant cells with resistant outer covering (analogous to endospores in proks)
Used for disease transmission
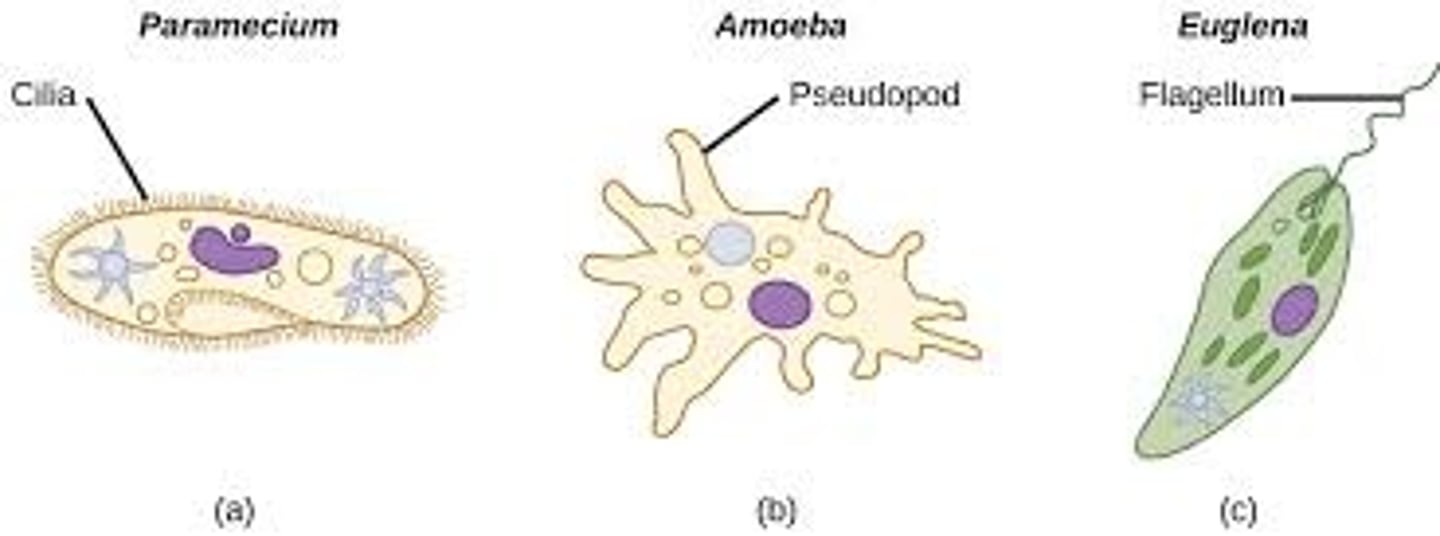
Locomotion of protists via...?
Flagella; one or more
Cilia; shorter & more numerous than flagella
Pseudopodia ("false feet"); chief means of locomotion for amoebas; used by other protist as well
Nutrition of Protists (3)
Autotrophs
- Some photosynthetic
- Some chemoautotrophic
Heterotrophs
- Chemoorganotrophs
- Phagotrophs (ingest particulate food matter)
Mixotrophs (both phototrophic & heterotrophic)
Reproduction of Protists
Asexual Repro; typical mode, but under stress can be diff.
- mitosis, budding, schizogony
Sexual Repro; under stress (major Euk. innovation)
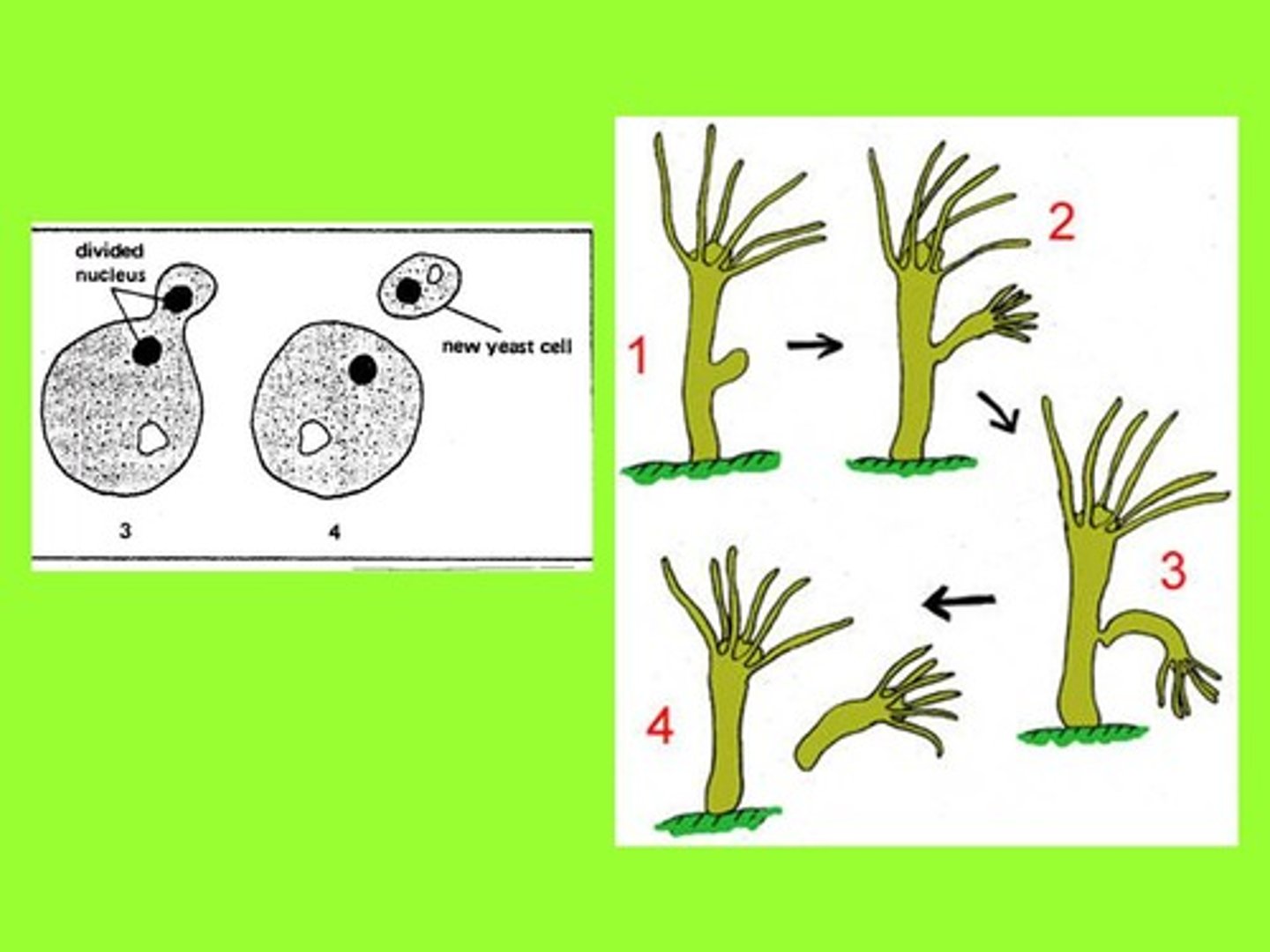
Budding
Asexual reproduction producing one smaller daughter cell.
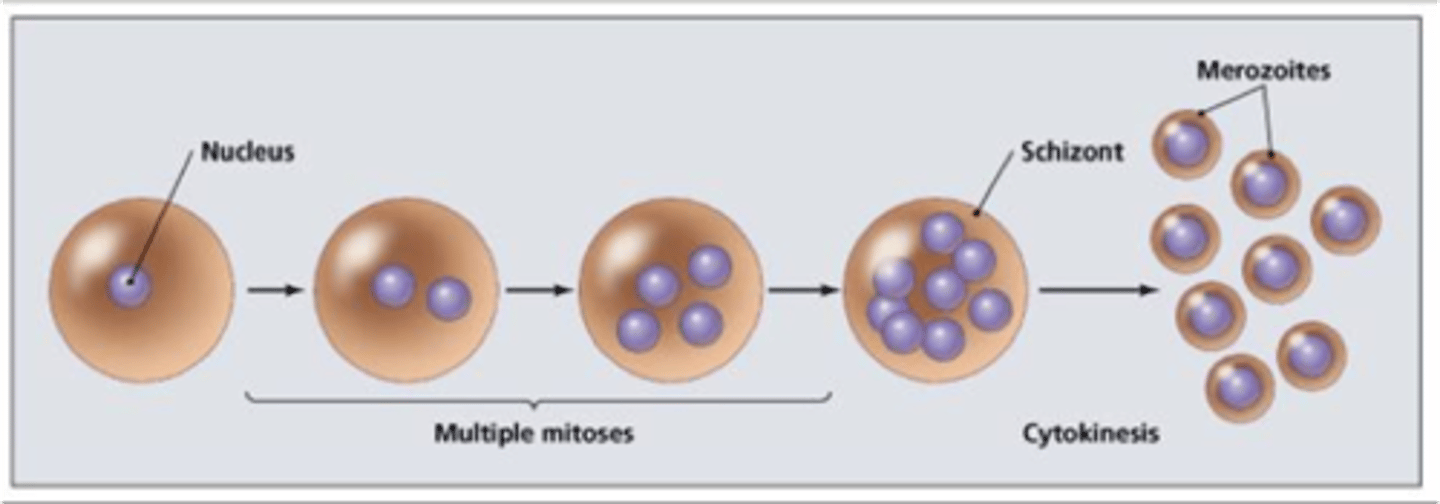
Schizogony
Multiple nuclear divisions before cell division, producing many cells.
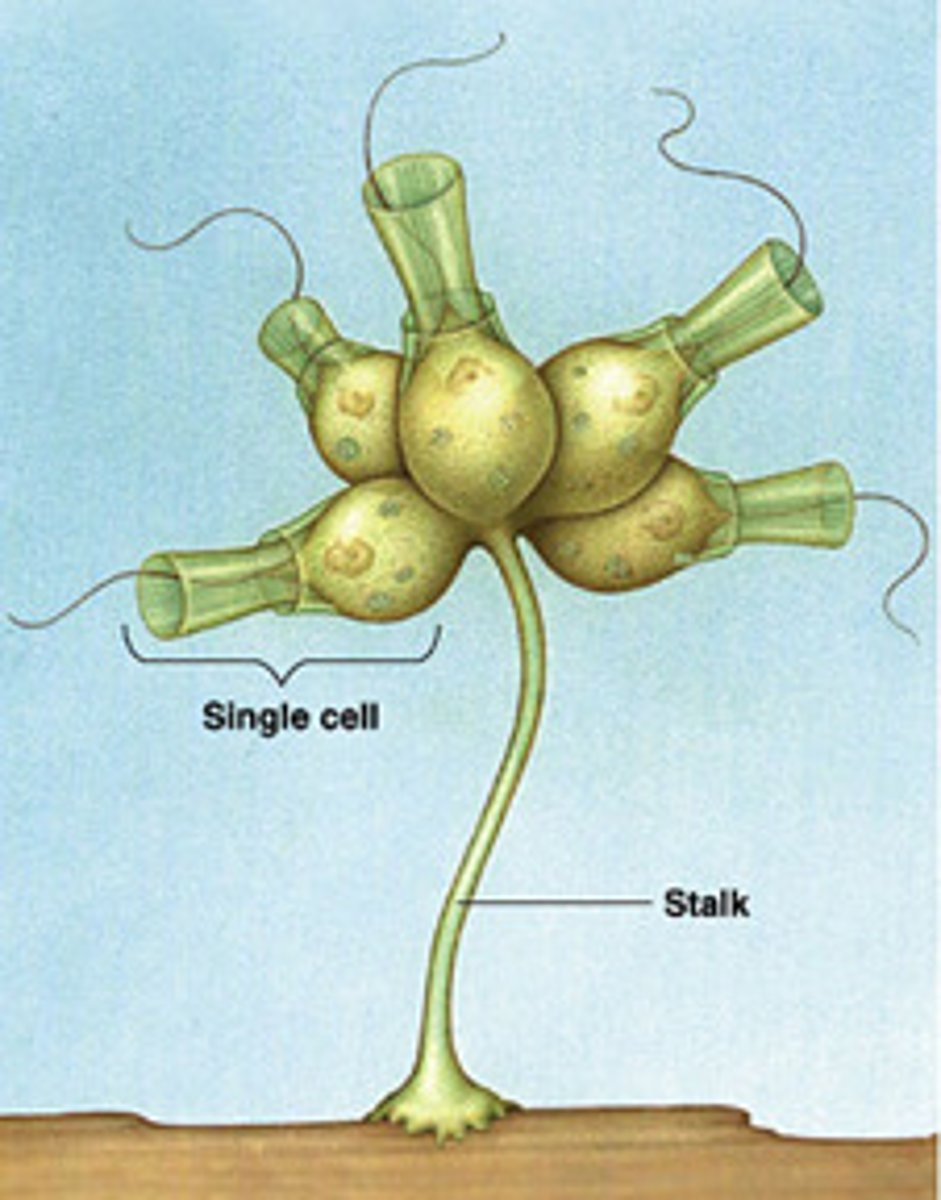
How are protist a bridge to multicellularity?
Single cells-> colonies-> true multicellularity
- Allows for specialization
(Few innovation have had as great an influence on history of life)
Excavata (supergroup)
Asymmetrical appearance w/ feeding groove "excavated" from one side
- includes phylum Diplomonads (ex. Gardia) & Euglenozoa (ex. Euglenids) & parabaslids
Gardia (of super group & phylum?)
- unicellular & 2 haploid nuclei
- lack functional mitochondria
- use cytosolic pathway (reparation genes) via horizontal gene transfer from bacteria
Protist - Excavata - Diplomonads
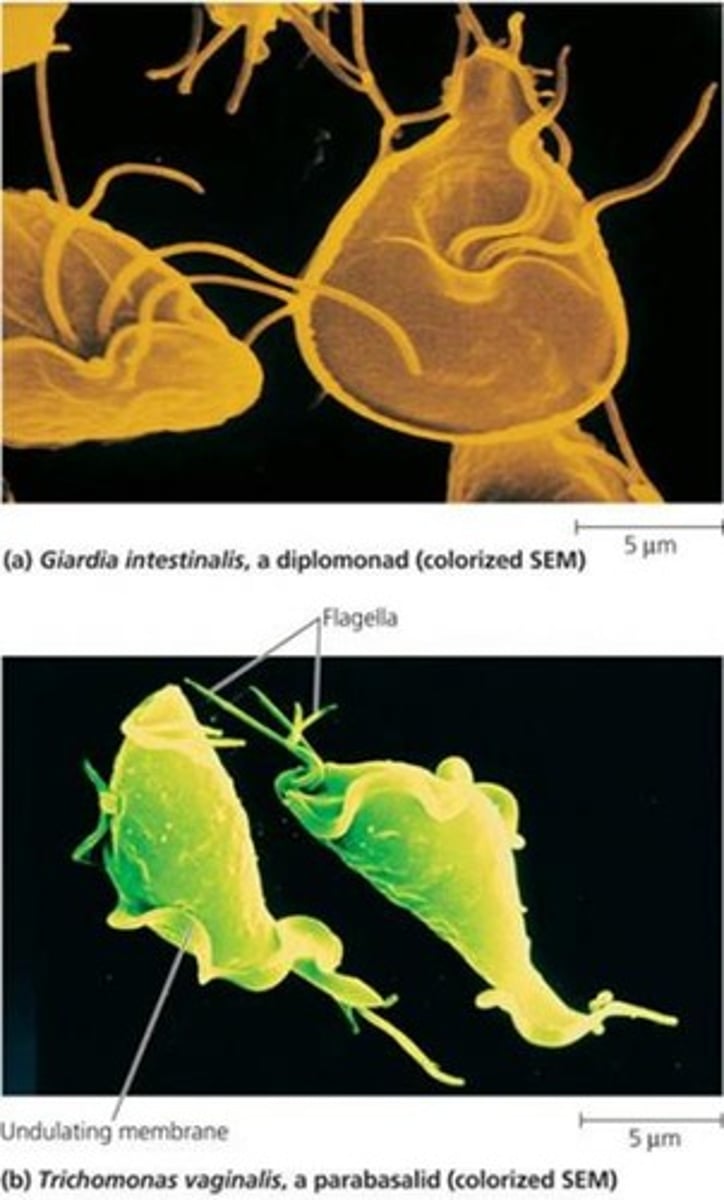
Diplomonads (of supergroup?)
phylum of excavata supergroup
unicellular with multiple flagella
include ex. Gardia
Lack functional mitochondria; use pathway derived from horizontal gene transfer from bacteria
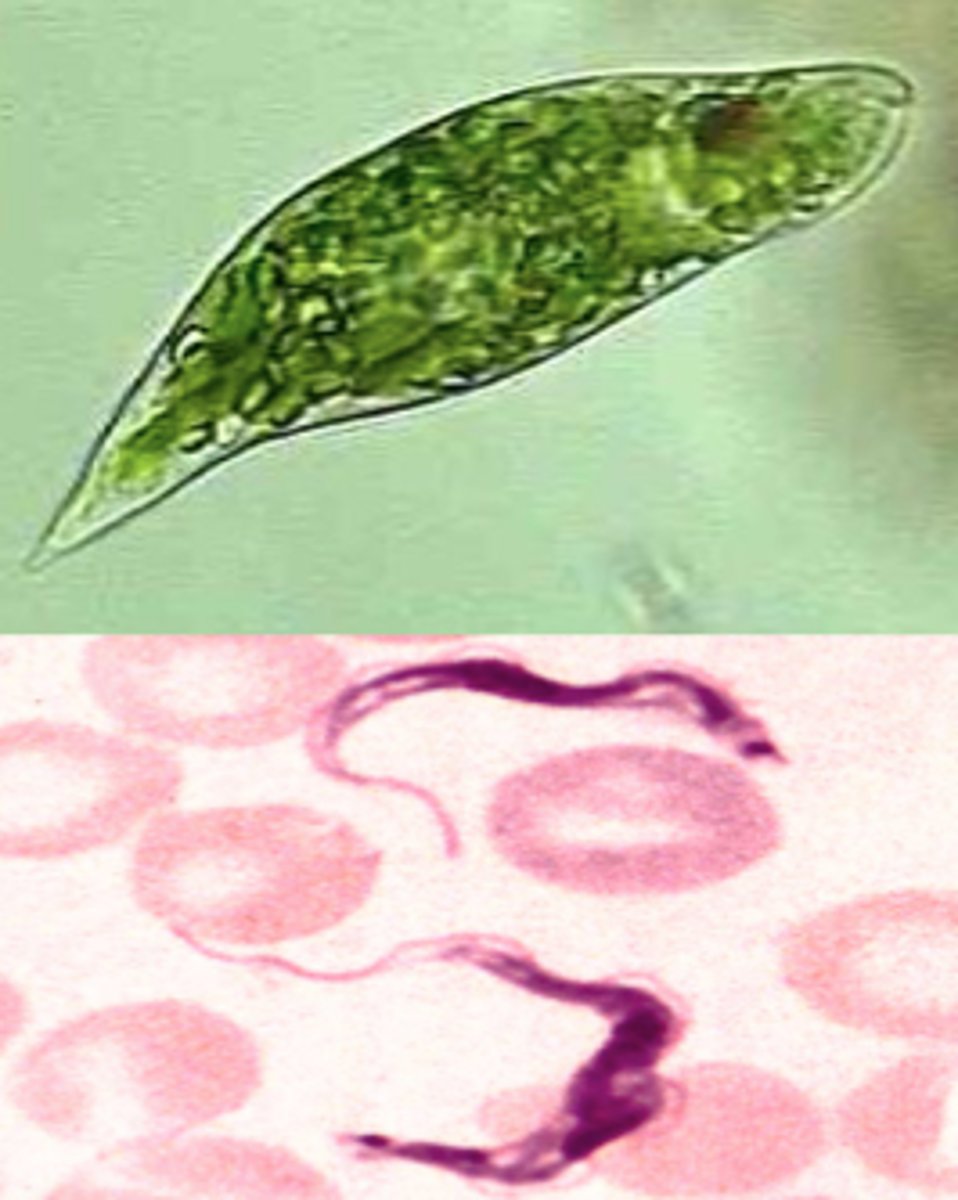
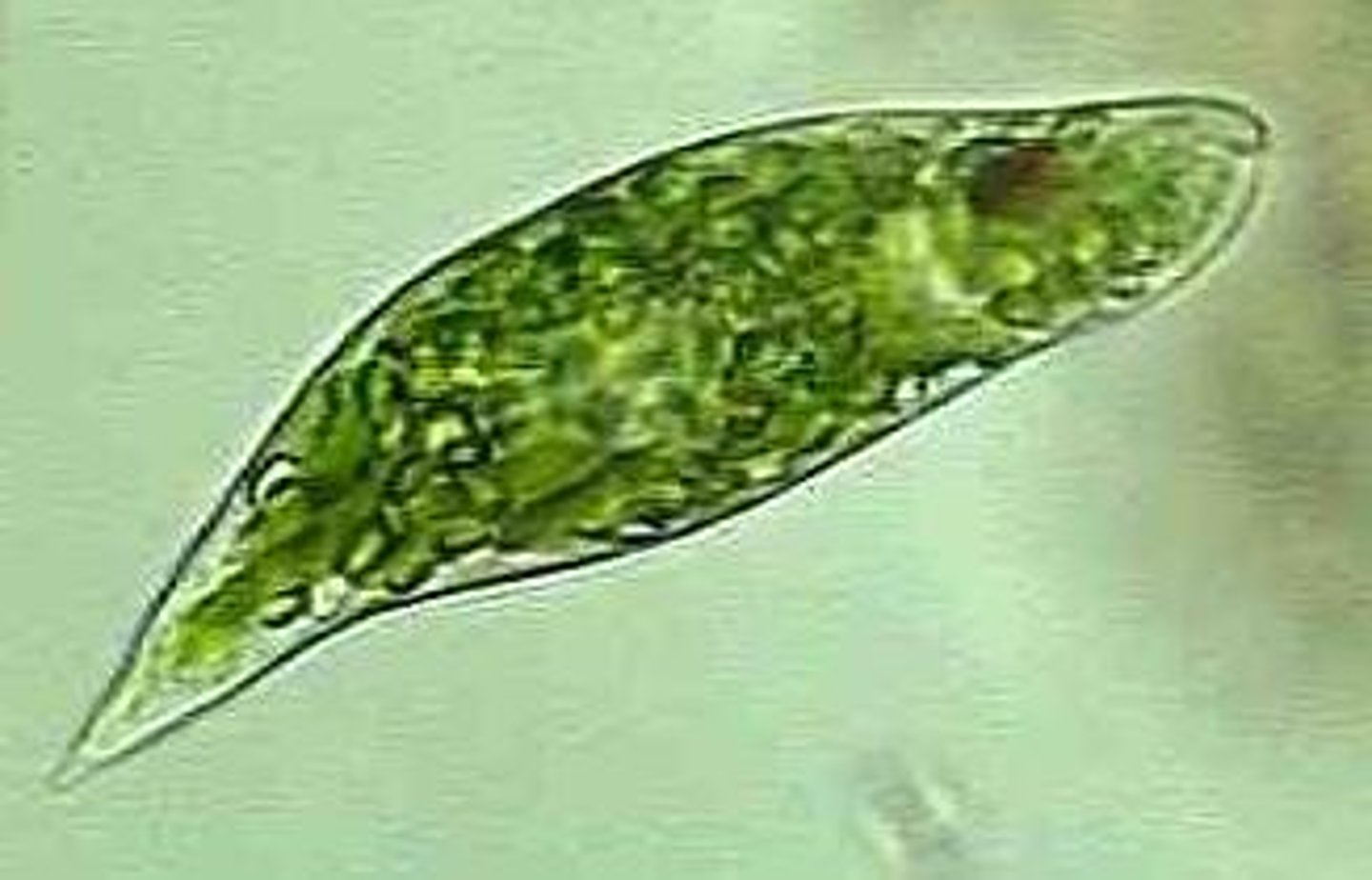
Euglenozoa (of supergroup?)
phylum of excavata supergroup
cells change shape while swimming
Asexual
include ex. Euglenids (1/3 have chloroplasts & autotrophic)
Include ex. Euglean (2 unequal flagella & stigma for light detection)
Protist - Excavata
Euglenids (of supergroup & phylum?)
- have flagella
-contractile vacuoles & stigma
- chloroplasts & mitochondria
Protist - Excavata - Euglenozoa
SAR (supergroup)
- containts superphylums Stramenopila, Alveolata, Rhizaria
SAR: Stramenopila (of supergroup?)
Mostly single-celled, but some multicellular + very fine hairs on flagella (some species have lost hair via evolution)
include Diatoms, Brown algae & Oomyce
Protists - SARs supergroup
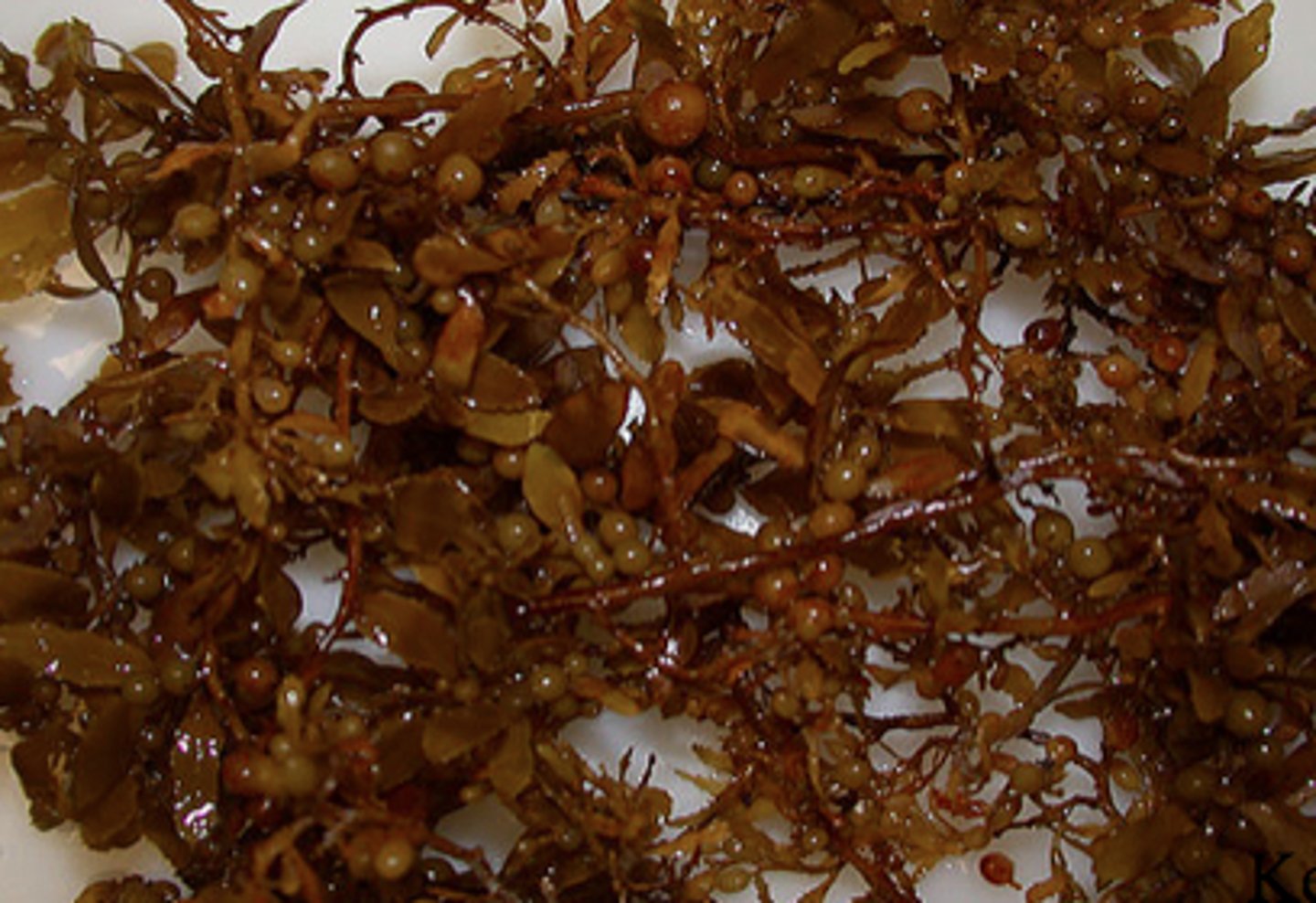
Brown Algae (of supergroup & superphylum)
Conspicuous seaweeds
multicellular & photosynthetic
Haplodiplontic life cycle (sporophytes & gametophytes)
protist - SAR - stremenophila

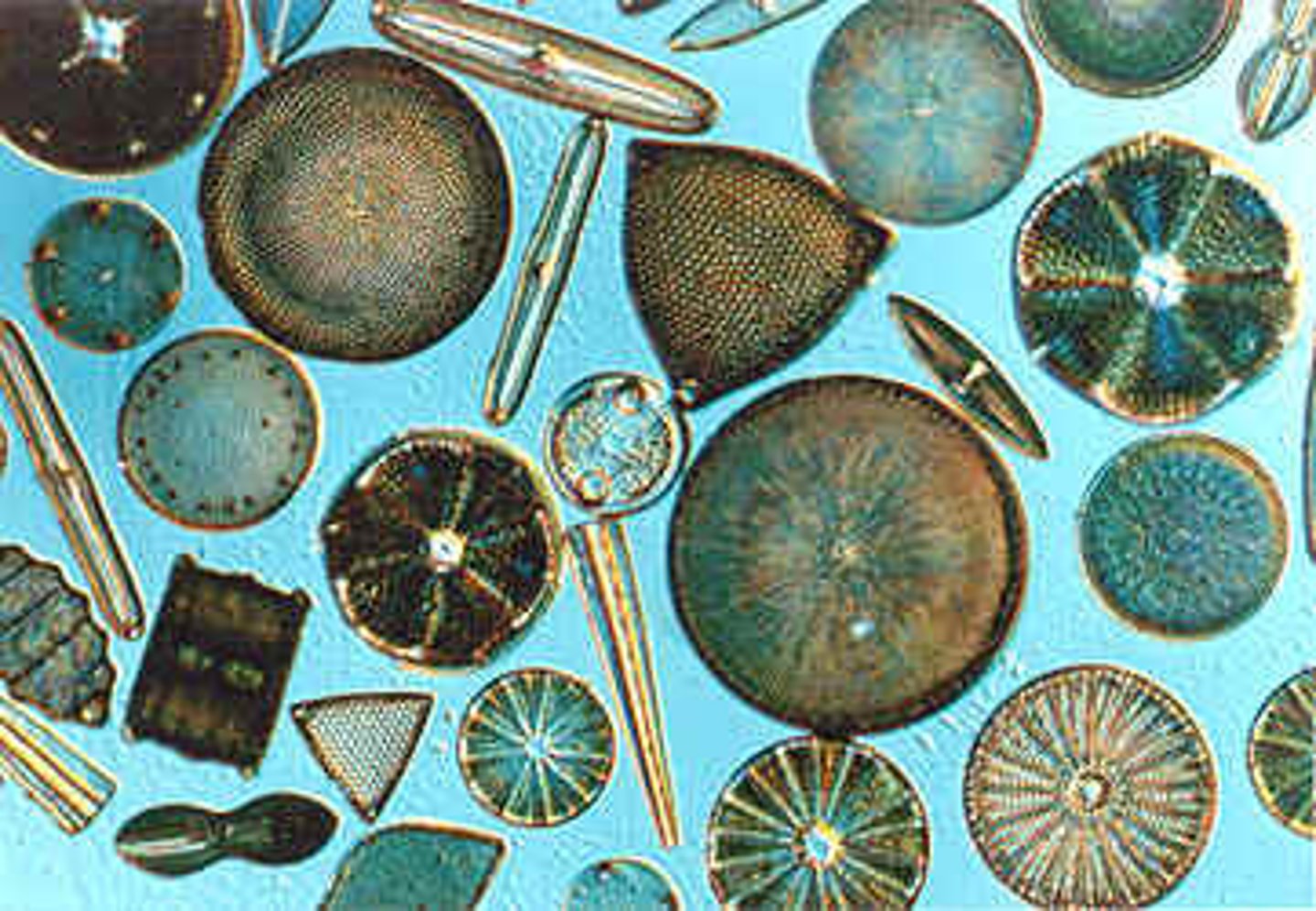
Diatoms (of supergroup & superphylum)
Photosynthetic unicellular
unique double silica shells.

Oomycetes (of supergroup & superphylum)
Water Molds (not fungi)
parasites/ saprobes [eat decayed matter]
(caused the Irish potato famine)
Protist- SARs - Stramenopiles
![<p>Water Molds (not fungi)</p><ul><li><p>parasites/ saprobes [eat decayed matter]</p><p></p></li></ul><p></p><p>(caused the Irish potato famine)</p><p>Protist- SARs - Stramenopiles</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c5373dce-b7f9-4632-b178-ce5ec9146c85.jpg)
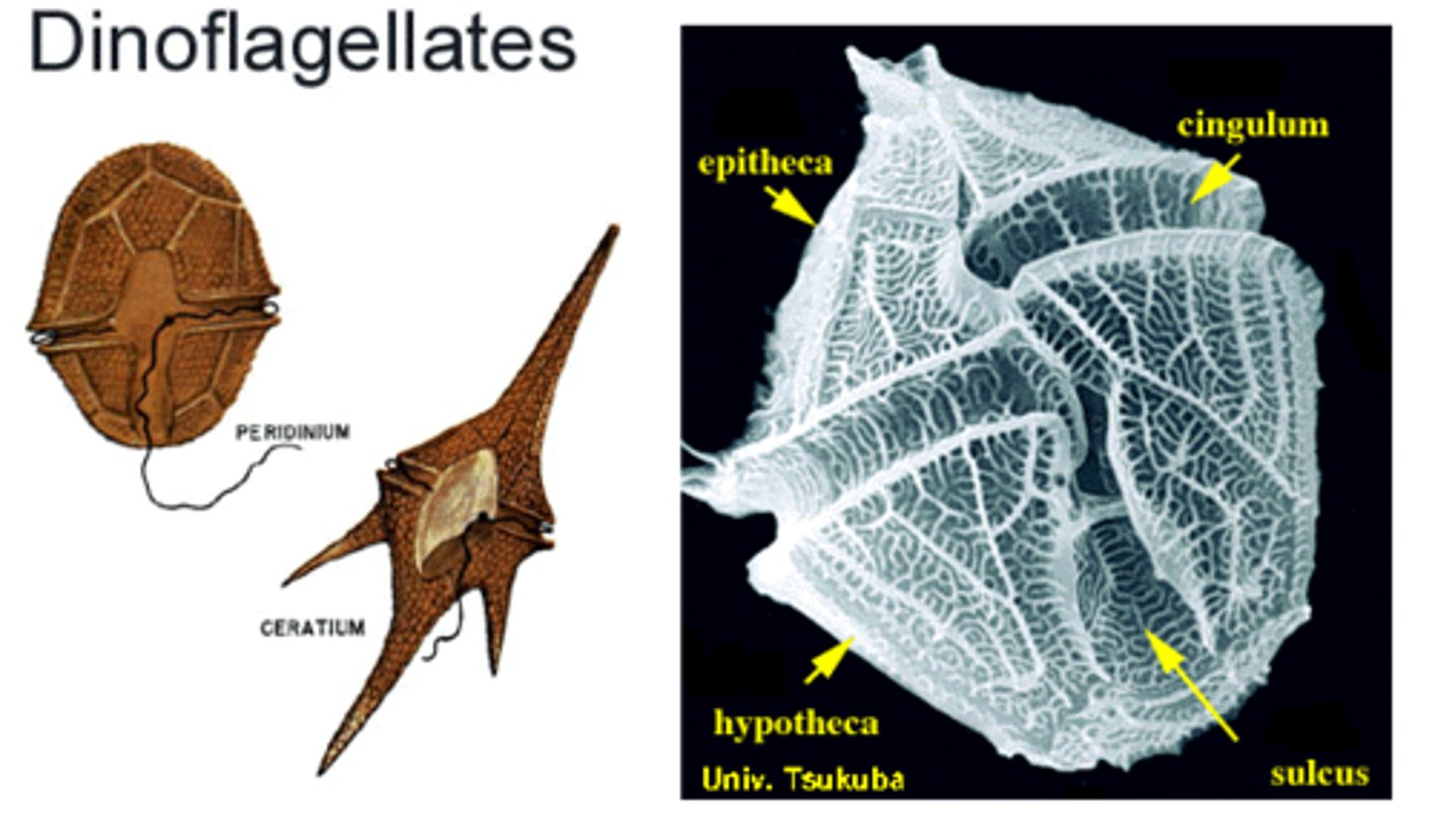
SAR: Alveolata (of supergroup?)
flattened vesicles called alveoli, may have apical complex (helps infect other cells)
contains Dinoflagellates, Apicomplexans (ex. gondii), & Ciliates
Protists - SARs
Dinoflagellates (of supergroup & superphylum?)
unicellular & photosynthetic
Flagella (two that whirl around)
bioluminescent sometimes
(red tide→ red pigmented dinoflagellates with toxins that are deadly)
protists- SAR - Alveolates
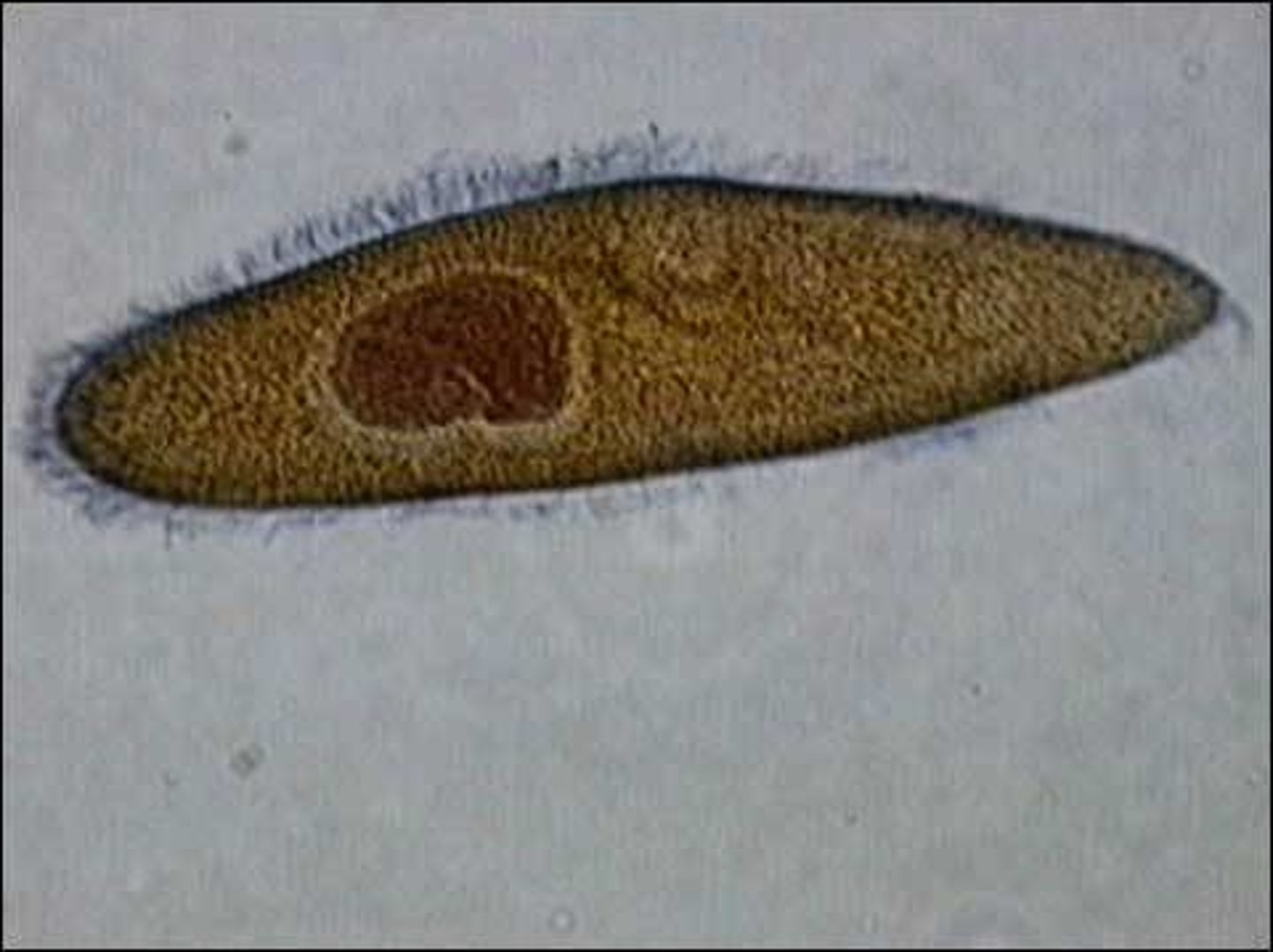
Apicomplexans (of supergroup & superphylum?)
Apical complex is a unique arrangement of organelles at one end of the cell (enables cell to invade host)
parasites
Plasmodium→ causes malaria; common in mosquito vector
protists- SAR - Alveolates
Ciliates (of supergroup & superphylum?)
Have large numbers of cilia in longitudinal rows or spirals around cell
2 nuclei (micronucleus/germline & macronucleus/function)
2 vacuoles (food & contractile for water)
protists- SAR - Alveolates
SAR: Rhizatia (of supergroup?)
silica shells
contain Foraminnifera & Radiolarians
protist- SARs
Radiolarians (of supergroup & superphylum)
Glassy exoskeletons made of silica, needle-like pseudopods.
protists- SAR - Rhizaria
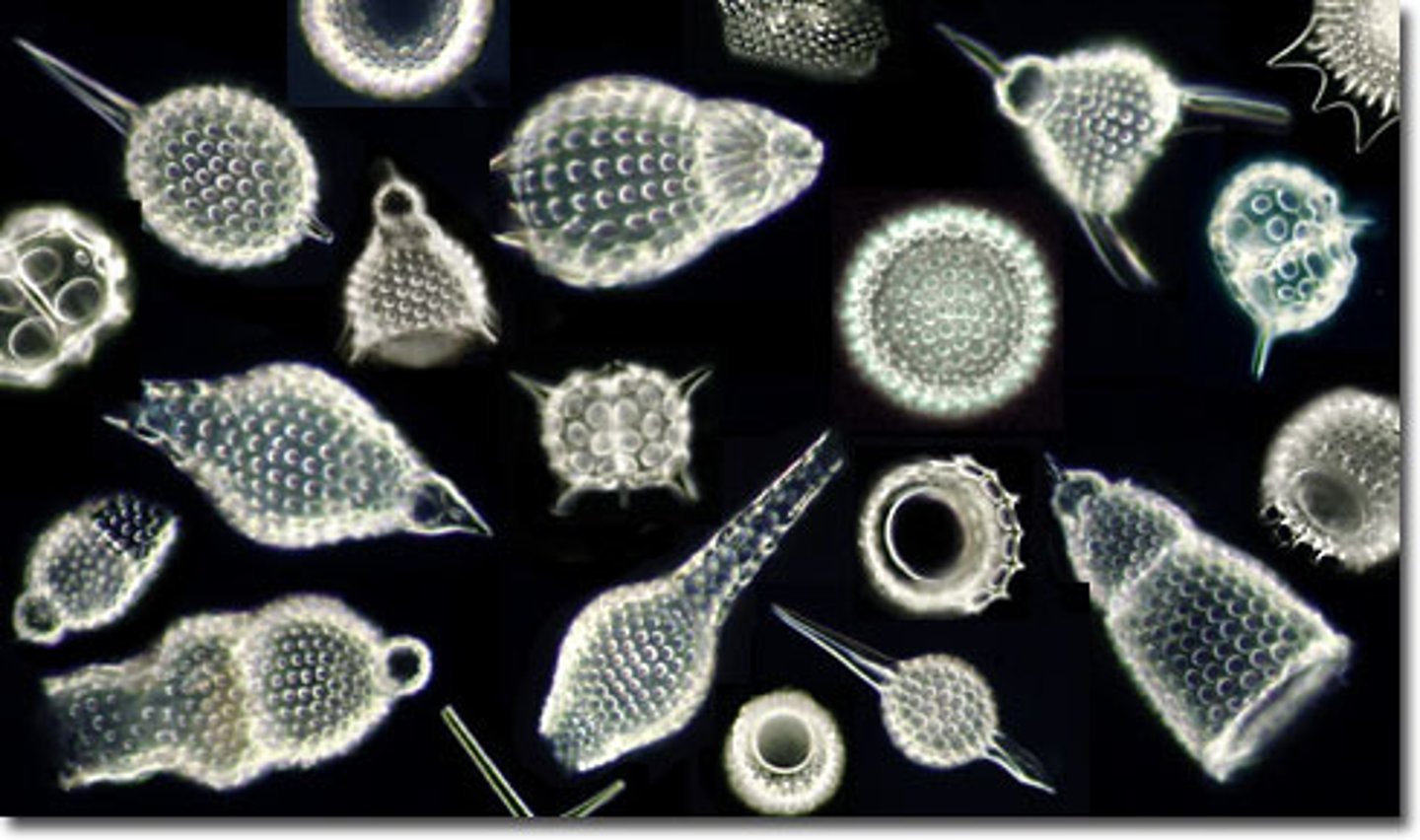
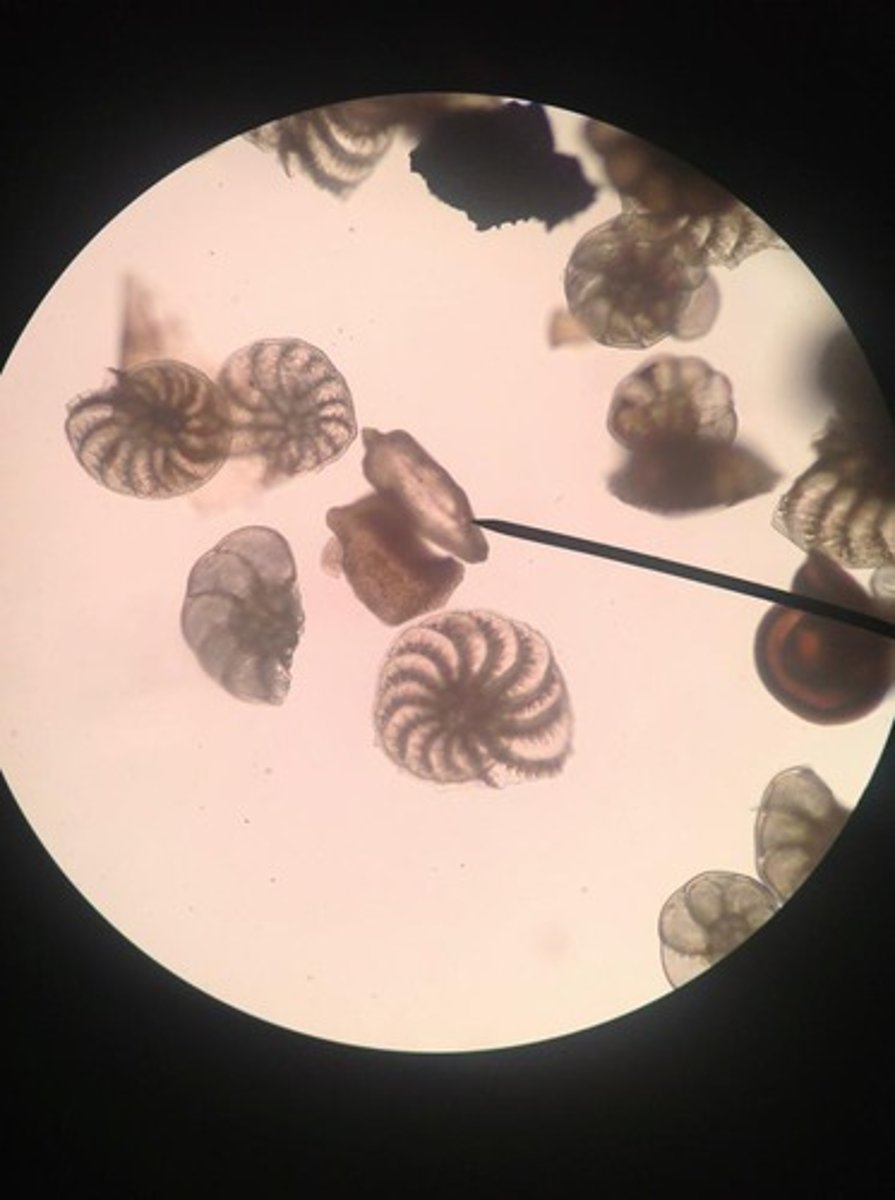
Foraminifera (of supergroup & superphylum?)
Marine protists with pore-studded calcium carbonate tests.
contribute to limestone formation
protists- SAR - Rhizaria

Archaeplastida (supergroup)
include red & green algae
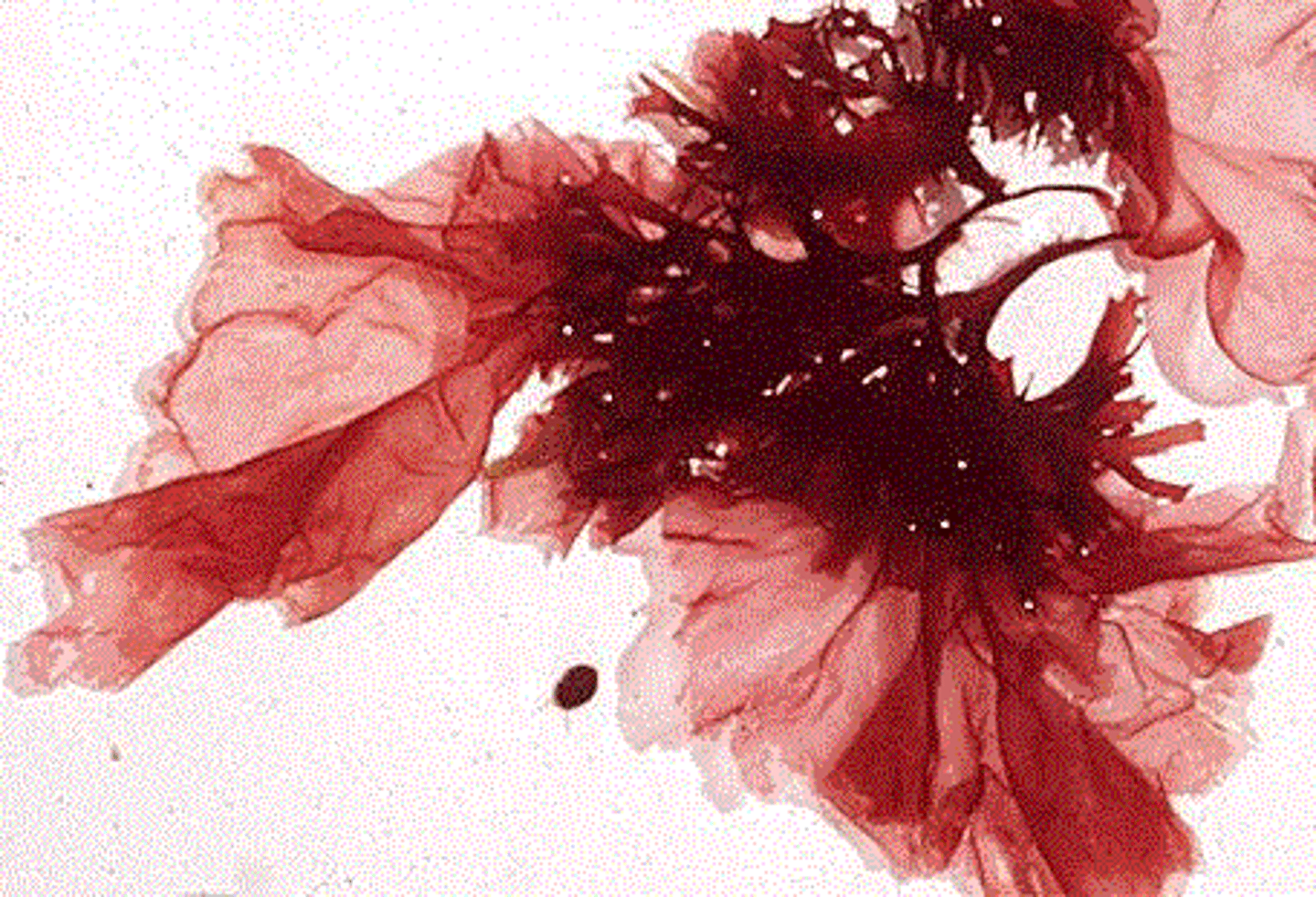
Red Algar (of supergroup & phylum?)
Red algae (have accessory pigments)
lack flagella
range from microscopic single celled to very large multicellular
protists - arceplastida

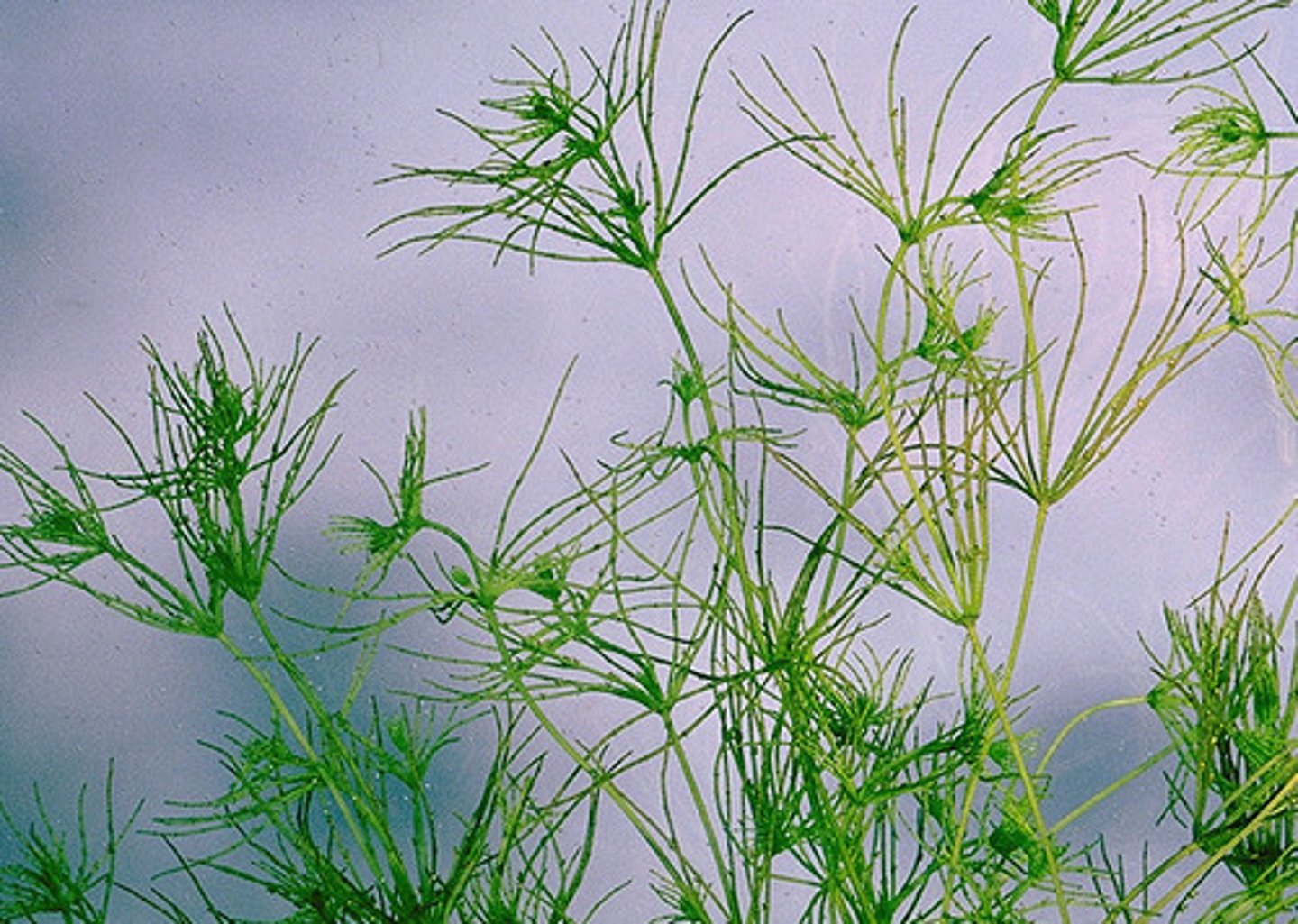
Green Algae (of supergroup?)
Has 2 lineages
Chlorophyta (unusual diversity and specialization)
charophytes (gave rise to land plants)
Protists - archaeplastida
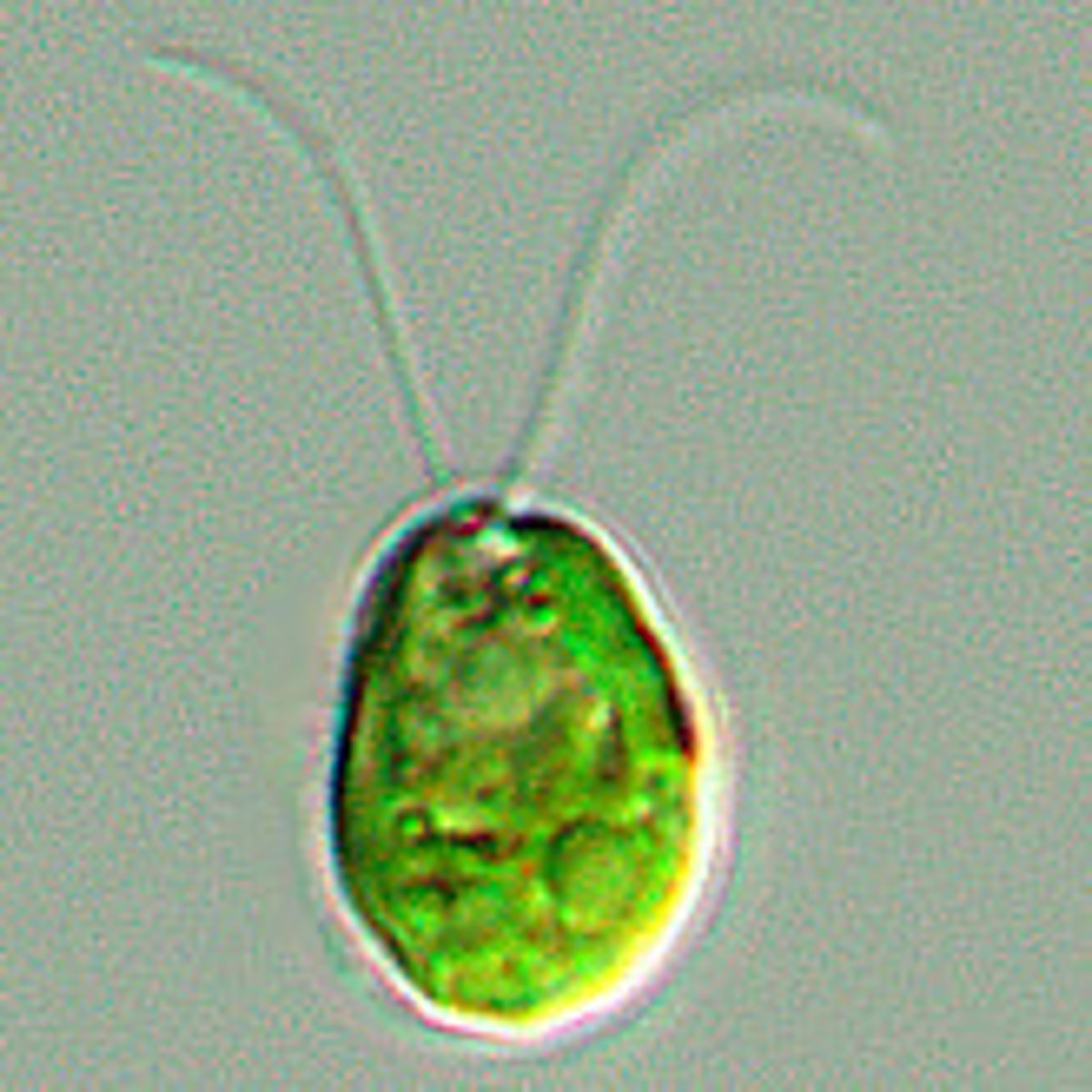
Chlorophyta (Of supergroup & phylum?)
unusual diversity and specialization leading to multicellularity
Protists - archaeplastida - green algae
Charophytes (of supergroup & superphylum?)
Green algae lineage that gave rise to land plants.
closest ancestor to land plants
Protists - archaeplastida - green algae

Amoebozoa (supergroup & phylum)
Move via pseudopods
used to push organism forward & intake food
Amoeba (of supergroup & phylum?)
Free living (found in soil & fresh water)
some parasitic
(brain eating amoeba can cross blood-brain barrier causing inflammation and death)
Protists - amoebozoa
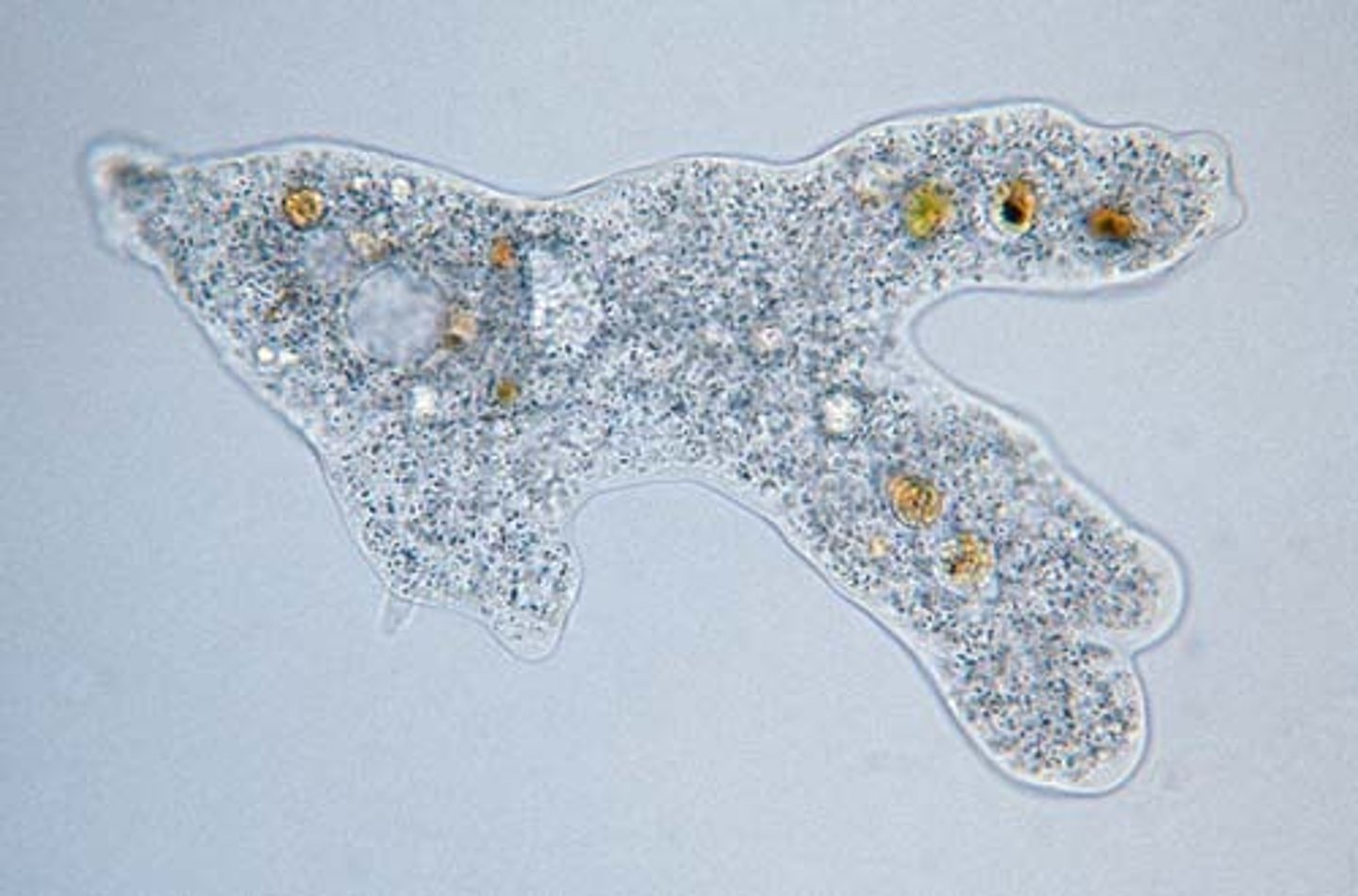
Opisthokonta (supergroup)
contain choanoflagellates (closest living relatives to animals and fungi)
Chanoflagellates (of supergroup?)
closest ancestor to animals & fungi (have matching structures to sponges)
flagellum surrounded by funnel-shaped collar (feature in sponges)
Protists- Opisthokonta