Exercise 8. Monolayer of surface active substance - a study model of the specific features of lipid aggregrates in aqueous medium. Spatial characteristics and density of the monolayer molecules in different conditions resembling membrane phase transitions.
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
288. What drives phospholipid molecules, contained water environment, to self-assemble into bilayer structures?
a) the amphiphilic properties of the phospholipid molecules;
b) the electrostatic attraction between the polar heads of the lipid molecules;
c) the repulsive forces between the lipid heads and the water molecules.
a) the amphiphilic properties of the phospholipid molecules;
289. What is the approximate shape of the phospholipid molecules building the biological membranes?
a) conical shape: small heads and relatively large volumed tails;
b) inverse cone: large heads and relatively narrow tails;
c) cylindrical: the cross-sectional area of the head and the tails is similar.
c) cylindrical: the cross-sectional area of the head and the tails is similar.
290. Which surface of the phospholipid molecule interacts with the water molecules?
a) the hydrophobic surface;
b) the hydrophilic surface;
c) in the multilayer complex both surfaces interact with water.
b) the hydrophilic surface;
291. The following phase state is attributed to the lipid bilayers of biological membranes:
a) dimeric – crystalstate;
b) liquid – gel (crystal) state;
c) liquid – gasstate.
b) liquid – gel (crystal) state;
292. Phospholipid molecules are generally build of:
a) hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails;
b) hydrophilic head and one hydrophobic tail;
c) hydrophobic head and two hydrophilic heads.
a) hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails;
293. When placed water, phospholipids form:
a) ion channels;
b) micelles;
c) two dimensional solid crystal lattice.
b) micelles;
294. The so called “flip – flop” motion of the phospholipids in the membrane is:
a) the transverse migration of phospholipid molecules form one layer into the other;
b) the lateral migration of the phospholipid molecules within the same layer;
c) the rotational motion of the hydrocarbon tails, without change of position or layers.
a) the transverse migration of phospholipid molecules form one layer into the other;
295. Phospholipids of the membrane double layer are:
a) synthesized in the extracellular space;
b) gathered from food;
c) synthesized in the cytosol.
c) synthesized in the cytosol.
296. The molecules of the membrane lipid bi-layer:
a) participate directly in the ion transport;
b) have a long double chain fatty acid tails;
c) are part of the peripheral protein complexes.
b) have a long double chain fatty acid tails;
297. Membrane proteins:
a) have transport functions;
b) build the glycocalyx of the cell;
c) contribute to the formation of membrane kinks.
a) have transport functions;
glycocalyx- glycoprotein and glycolipid covering that surrounds that cell membranes
298. Phospholipid molecules placed in the air-water interface will form:
a) monolayer;
b) bilayer;
c) micelles.
a) monolayer;
299. “Phase transition” of the lipid membrane is when:
a) the lipid bilayer transforms between liquid and crystal-like (gel) states;
b) the membrane proteins change conformational states;
c) the membrane ion permeability changes due to rapid depolarization.
a) the lipid bilayer transforms between liquid and crystal-like (gel) states;
300. Viscosity of biological membranes is:
a) an electrical property;
b) a mechanical property;
c) chemical property.
b) a mechanical property;
301. The bending (kink) in one of the hydrocarbon tails of the phospholipid molecule, due to a double carbon bond, has the following implications:
a) it aids the rotational motion of the phospholipid heads;
b) it eases the transmembrane diffusion of gases and small molecules;
c) it facilitates the motion of segments of the molecule.
b) it eases the transmembrane diffusion of gases and small molecules;
302. What is the approximate thickness of the cellular membrane?
a) 6 – 10 nm;
b) 6 – 10 μm;
c) 60 – 100 nm.
a) 6 – 10 nm;
303. Lipids are not soluble in:
a) water;
b) ethyl alcohol;
c) benzene.
a) water;
304. The amphiphilic lipids of the plasma membrane have:
a) certain fixed positions at the membrane;
b) lateral and rotational mobility within their layers;
c) have lateral, rotational, and trans-layer mobility.
c) have lateral, rotational, and trans-layer mobility.
1. Sketch and label the general structure of the phospholipid molecule:
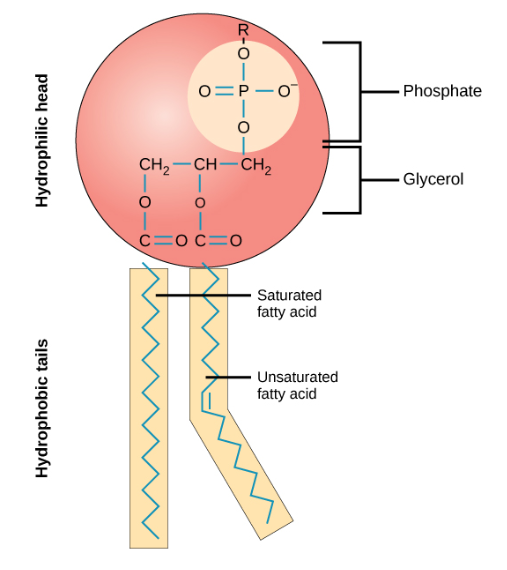
2. What is the meaning of the term liquid-crystal (liquid-gel) state of the membrane?
Liquid crystals = a state of matter which has properties b/w that of (l) and (s)
A measure of the lipid bi-layer
The lipid tails are fully random and unhindered to take any orientation in the bilayer
If the bilayer shows a preferred orientation (e.g.at low temperatures), it’s considered to be in a gel state
3. What characterizes the lipid bilayer as the basic structural element of the membrane?
The phospholipids which form the double layer characterize the lipid bilayer.
*When phospholipids interact w/ water they spontaneously rearrange themselves to form the lowest free-energy configuration:
hydrophobic tails arrange away from water
hydrophilic heads arrange facing water,
resulting in the lipid bilayer.
4. Sketch a monolayer of lipid molecules in liquid and gel (crystal) states.
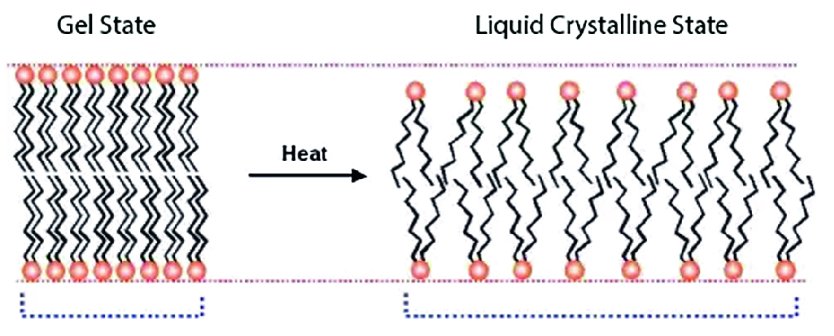
5. List the three basic types of mobility of the phospholipids in the membrane, and order them according to their statistical likelihood (time constant):
a. very likely (very short time):
b. probable (short time):
c. low probability (long time):
a. Rotation (faster: 10-9s)
around their long axes
b. Lateral mobility (relatively rapid: 10-6s)
mvmt within the plane of a membrane
c. Transverse (flip-flop) diffusion (slow: hours, days r> 105s)
from one half of the bilayer to the other