ap psych unit 5 vocab
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, & communicating
concepts
mental groupings of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
formed by prototypes
ex. the idea of a chair
prototypes
a mental image or best example of a category. new items can be matched to this example to easily categorize them
ex. comparing feathered creatures to a classic bird
metacognition
an awareness of your own thought processes and the patterns behind them
algorithm
methodical, logical rule that guarantees a solution to a problem
can take a very long time and a lot of effort
will not make any errors though
heuristics
a simple thinking strategy that allows us to make judgements and solve problems efficiently
speedier than an algorithm but also more error-prone
insight
a sudden realization of a problem’s solution
confirmation bias
a tendency to seek information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence
we also don’t look for evidence that disproves our assumptions!
fixation
an inability to see a problem from a new perspective once we’ve formed our belief
caused by confirmation bias
mental set
our tendency to approach a problem in a particular way that has been successful in the past
perceptual set vibes
schema
a mental framework or concept that helps organize + interpret information
a pattern of thought and behavior that represents our unique knowledge, beliefs, and expectations
assimilation
the process of incorporating new information into existing schemas
accomodation
the process of modifying schemas or creating new ones to incorporate new information
functional fixedness
cognitive bias limiting us to use objects only in the way they’re traditionally used
executive function
a set of cognitive processes that allow us to plan, organize, and regulate behavior
ex. problem-solving, impulse control
intuition
effortless, immediate, automatic thought
representativeness heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on how well they match particular prototypes
may lead us to ignore relevant information
ex. how after 9/11 young arab men were seen as terrorists (even though they were regular people)
availability heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory
we perceive events as common when they come easily to mind
ex. wins are loud but losses are quiet in casinos, so we think that we win more than we do
priming
unconscious activation of associations, predisposing one’s memory/perception/response
nudge
an attempt to influence the behavior, choices, judgements, or feelings of an individual/group in a predictable way without forbidding options or changing incentives
subtly influences behavior in ways that are easily avoidable
ex. putting fruit at eye level in the cafeteria
gambler’s fallacy
belief that the probability of a random event occurring in the future is influenced by previous instances of that type of event
ex. believing that a coin must land on tails next after landing on heads 3x
sunk-cost fallacy
when someone refuses or is reluctant to abandon a strategy/course of action because they’ve invested a lot into it… even though abandonment would be more beneficial!
overconfidence
our tendency to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgements
belief perseverance
clinging to one’s initial conceptions after they’ve been discredited or disproved
framing
the way an issue is posed
significantly effects our stances and judgements
ex. “pro-life” vs. “anti-abortion”
creativity
the ability to produce novel, valuable ideas
convergent thinking
narrowing down available solutions to find the single best one
used on standardized multiple-choice test
requires aptitude
divergent thinking
expanding the number of possible solutions
creative thinking does this
language
our spoken/written/signed words and the ways we put them together to form meaning
phonemes
smallest distinctive units of sound in a language
not syllables! literal sounds like b, a, and t in ‘bat’
morphemes
smallest units of language that have meaning.
ex. prefixes like re- and pre-, and short words like bat or gentle
grammar
a language’s set of rules that enable people to communicate and understand each other
semantics
the set of rules for deriving meaning from sounds
literally about what words, phrases, and sentences mean
syntax
the set of rules for combining words into grammatically compliant or sensible sentences
universal grammar
a universal human predisposition to know or easily learn grammar rules
all languages have similar building blocks
receptive language
the ability to understand and process language
starts developing when you’re a baby! you will be especially good at it during that time
productive language
the ability to produce words
cooing
production of soft vowel-like sounds (e.g. ‘coo’ or ‘goo’) between 6-8 weeks
babbling
infant utters various sounds unrelated to the household language. begins ~4 months, at ~10 months will sound like home language
usually sounds that are easy to form
babies will lose their ability to discriminate between tones if they aren’t exposed to them
one-word stage
child speaks mostly in single words 1-2 years old
will begin to use sounds to communicate meaning
learn way more words by 1.5 y/o
two-word stage
child speaks mostly in 2-word statements ~2 years old
starts using telegraphic speech
starts following syntax rules of language
after 2 years, speech rapidly develops into full sentences
telegraphic speech
pattern of speech used by little kids that literally sounds like a telegram, using mostly just verbs and nouns
ex. “go car”, “want juice”
critical period
specific time during childhood development when certain aspects of language can most readily be mastered
closes gradually, and if you get too old without learning language, you won’t be able to
overgeneralization
when the rules of grammar are applied too broadly, beyond exceptions. often done by children while learning language
ex. “I goed” vs. “I went”, “I rided” vs. “I rode”
linguistic determinism
Whorf’s hypothesis that language determine the way we think
but we can think about things we have no words for… + we can think about images… so not really true
linguistic relativism
more chill version of linguistic determinism, says that language influences worldview and cognition
lots of evidence supporting this one!
intelligence
the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
general intelligence (g)
Spearman’s idea that we have one intelligence that underlies all mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence task
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of test items that reflect a particular trait
Spearman used it to build his theory of general intelligence, because he saw that people who were particularly great in one area were also above average in other areas
savant syndrome
condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability is exceptional at a specific skill (such as art, memory)
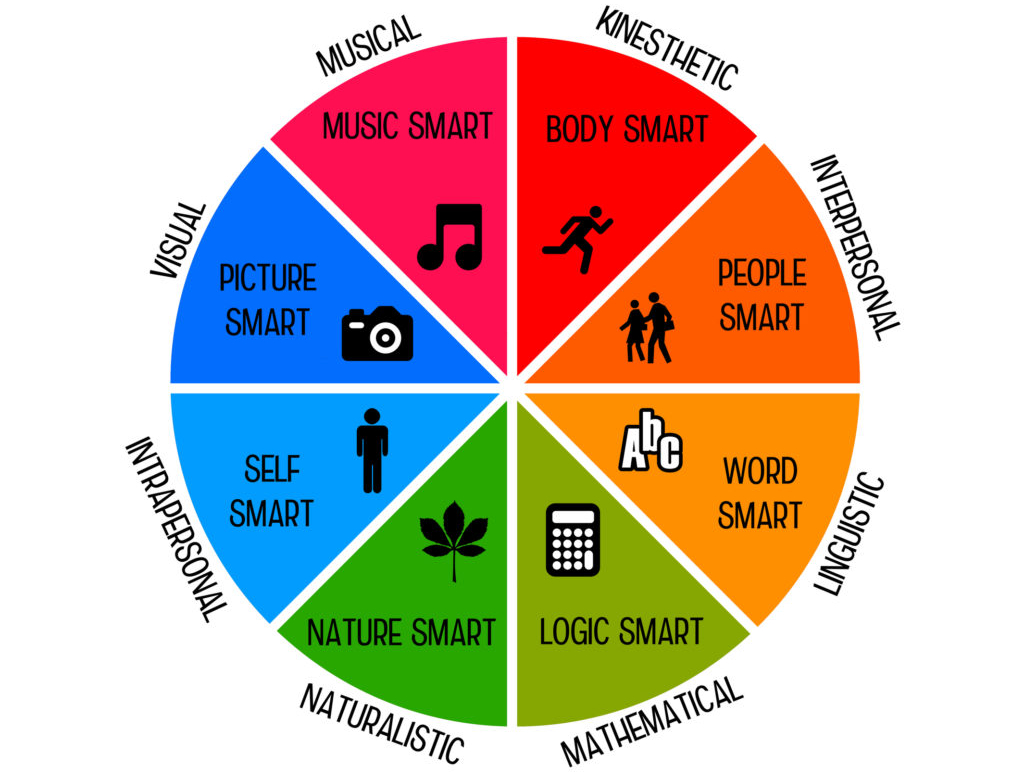
multiple intelligences
Gardner’s theory that our abilities are best classified into 8/9 independent intelligences, including a broad range of skills outside of school smarts
triarchic theory
Sternberg’s theory of intelligence, proposes that we have 3 intelligences: analytical (well-defined problems, things with 1 right answer), creative (innovation, adaptation), and practical intelligence (everyday poorly defined tasks w/ many solutions)
emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
intelligence test
method for assessing and comparing individuals’ mental aptitudes using numerical scores
achievement tests
designed to assess what you’ve learned
aptitude tests
designed to predict your future performance and show your capacity to learn (ex. SAT, ACT)
alfred binet
French psychologist who designed the first intelligence test. did it for an assignment to determine the learning potential of Parisian schoolchildren, and he chose to measure the kids’ mental age
mental age
the level performance typical of children of a certain age
lewis terman
stanford guy who revised Binet’s mental age test and made the Stanford-Binet intelligence test
stanford-binet intelligence test
version of Binet’s intelligence edited by Stanford
intelligence quotient
term derived from Binet/Stanford tests, originally an actual quotientbut now a derivation from the average performance at a certain age. the average is 100
wechsler adult intelligence scale (WAIS)
the most commonly used intelligence test
contains verbal and nonverbal/performance subtests
psychometrics
the field of psychology that focuses on measuring psychological attributes (intelligence, personality, attitudes) using standardized tests and statistics
longitudinal study
research design where data gathering happens over an extended period with just one group
cross-sectional study
observational research analyzing data from a population at a specific point in time. like a snapshot of the population
standardization
defining uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison with the performance of a pretested group
normal curve
symmetrical curve describing the distribution of many types of data. most scores fall around the mean and few fall around the extremes
Flynn effect
worldwide phenomenon where IQ scores are improving over time
Flynn says it’s due to our modern world requiring more mental skills
reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results
split-half reliability
splitting the test into two and comparing how a person does on one half of a test and on the other half to measure how reliable the test is
test-retest reliability
testing someone, then testing them again later to measure how reliable the test is
validity
the extent to which a test measures or predicts what it’s supposed to
content validity
describes how well a test samples the behavior it’s interested in
predictive validity
the success with which a test predicts the behavior it’s designed to predict. tests should predict the criterion (standard) of future performance
construct validity
the extent to which a test represents the concept/construct it’s trying to measure
cohort
a group of people sharing a common characteristic
intelligence remains stable in the same cohort until late in life, but cross-sectional studies show a decline in intelligence for older folks
crystallized intelligence (gc)
our accumulated knowledge + verbal skills
increases with age
fluid intelligence (gf)
our ability to reason speedily and abstractly
tends to decrease with age
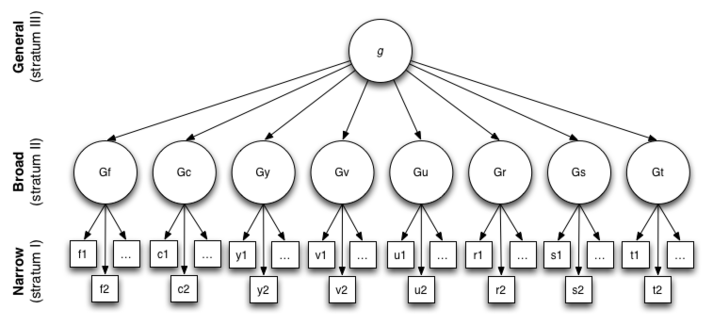
Cattel-Horn-Carroll Theory
comprehensive theory of intelligence, combining the theory of fluid intelligence, crystallized intelligence, and three-stratum theory which describes intelligence as having 3 levels that go from specific to very broad
intellectual disability
condition of limited mental ability, indicated by an IQ score of less than or equal to 70 and difficulty adapting to the demands of life
gifted
a child who does very well on aptitude tests
they tend to be very successful later in life
heritability
the proportion of variation among people in a group that can be attributed to genes. depends on the range of populations and environments studied
heritability of intelligence
it’s ~50-80% heritable
identical twins have very similar intelligence and other talents
polygenic trait
environment has a modest influence on intelligence
growth mindset
a focus on learning and growing. helps kids become more motivated and hard-working so that they can become successful!
fixed mindset
viewing one’s own level of ability as unchanging
stereotype threat
self-affirming concern that one will be evaluated based on a negative stereotype
ex. someone will do worse on a reading test if you tell them right before that people like them are bad at reading
stereotype lift
increase in a group’s test performance due to not being part of a negative stereotype
ex. men do better on a math test after being told that men are better than women at math