Spinal Cord Anatomy
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
What is the Spinomedullary Junction?
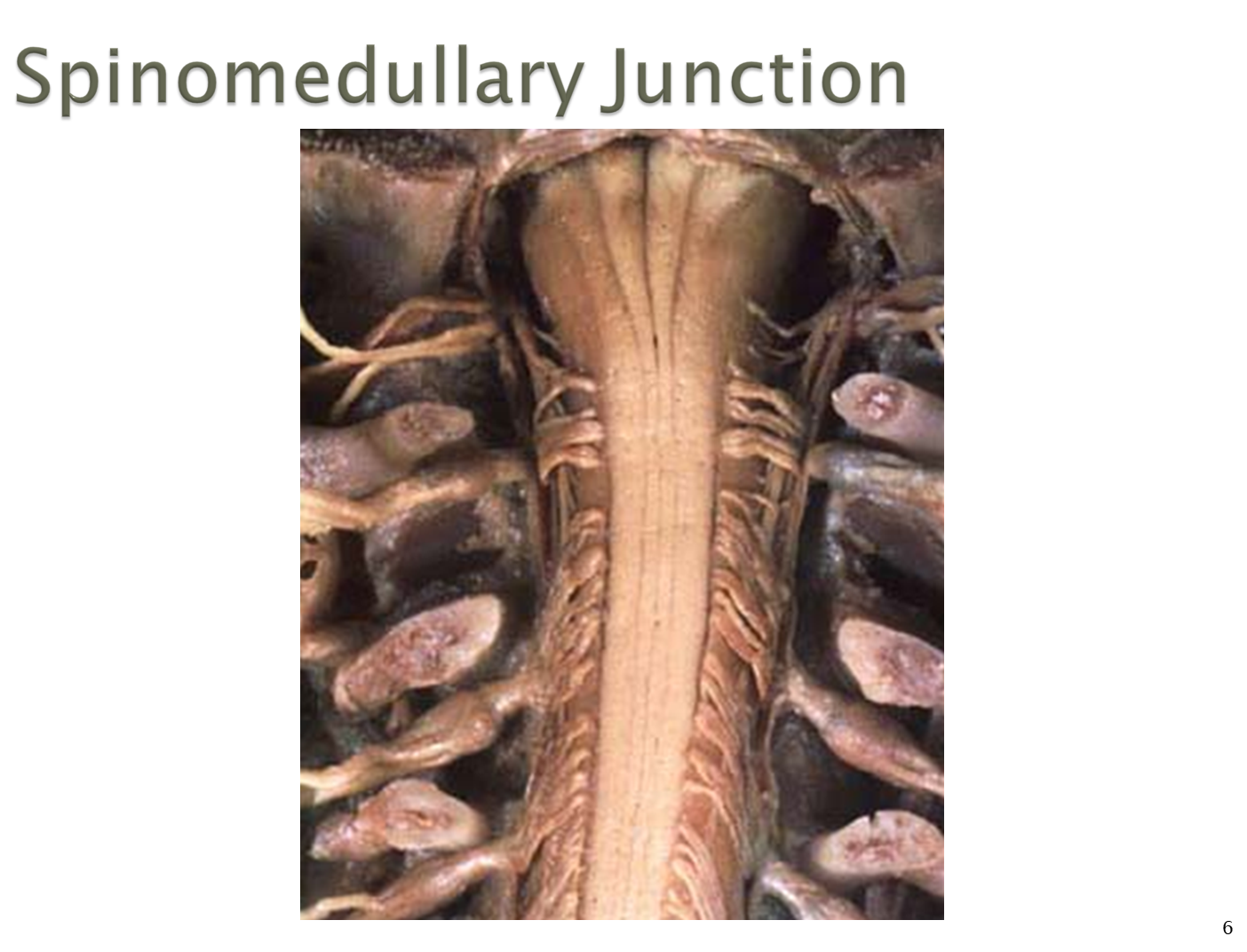
The spinomedullary junction is the portion of the spinal cord that is connected to the most inferior portion of the brain, the medulla oblongota
What is the structure of the spinal cord?
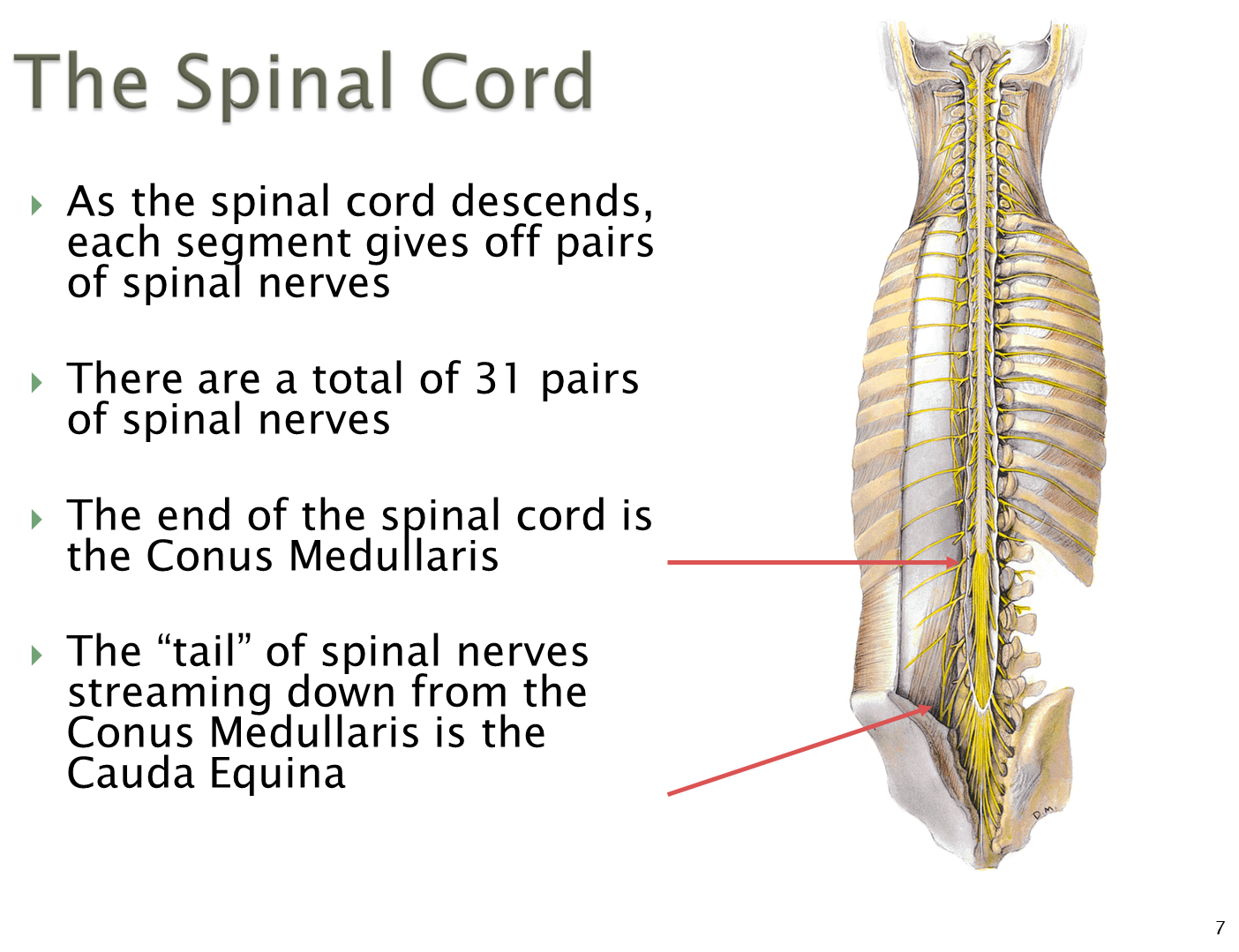
The spinal cord creates 31 pairs of spinal nerves as it descends down the body. The denticulate ligaments formed from the pia mater will help to tether the cord within the spinal canal
1) each spinal nerve is formed by dorsal and ventral rootlets with dorsal roots containing sensory nerves and ventral rootlets containing motor function
→ these nerves will descend through the spinal foramen/vertebral canal where they will then project outward from the intervertebral foramen formed from superior and inferior notches of vertebrae
2) the inferior portion of the spinal cord forms a tail known as the conus medullaris which has nerves breaking off known as the cauda equina
→ there is a thin cord known as the filum terminale formed from the pia which tethers the cord to the bottom of the sacrum
What are the major divisions of the spinal cord? How are spinal nerves named
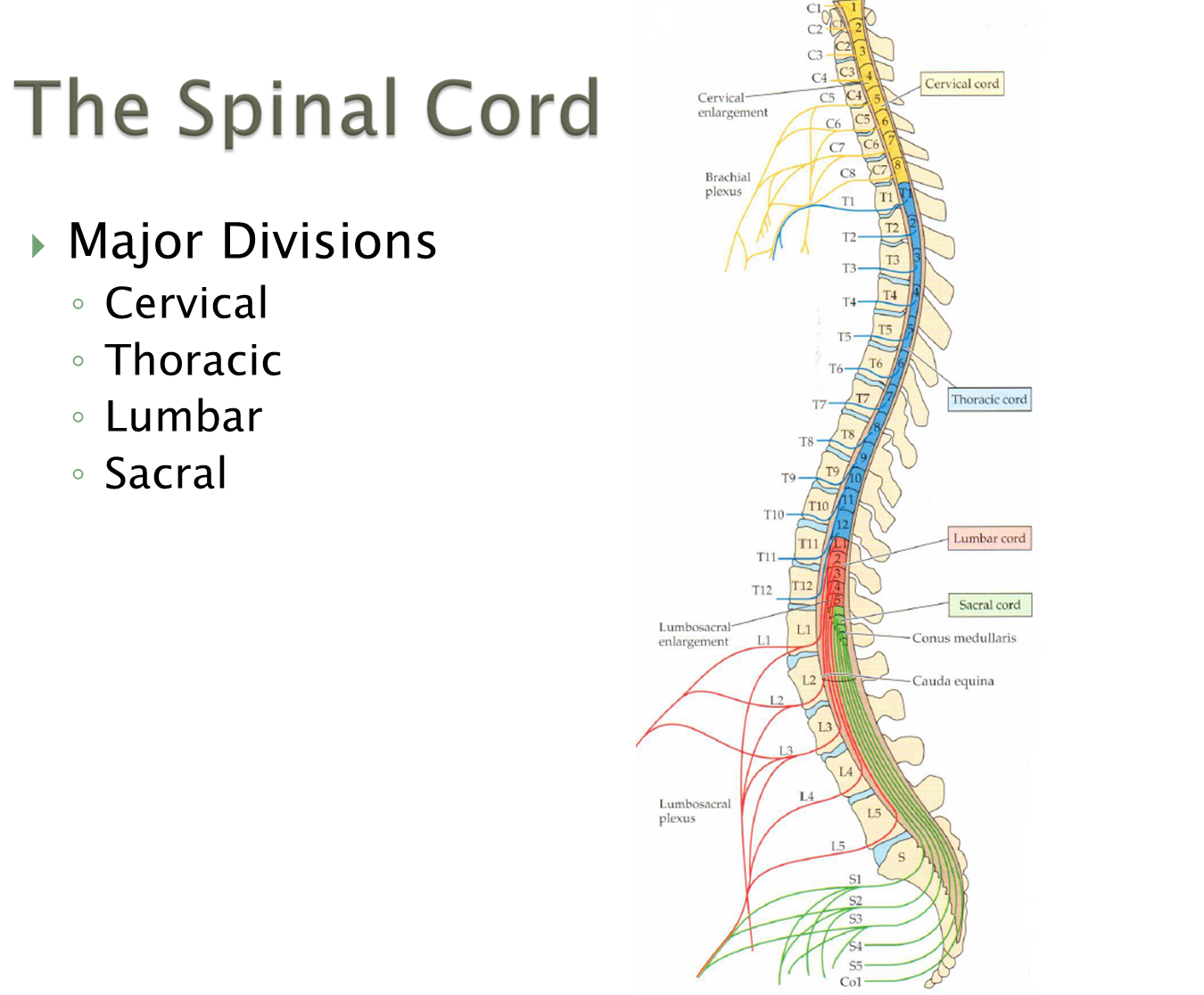
There are four major divisions of the spinal cord with one additional nerve exiting from the coccyx intervertebral foramina
Cervical - 8
Thoracic - 12
Lumbar - 5
Sacral - 5
Coccygeal - 1
The spinal nerves are then named based on the intervertebral foramen they exit from
→ C1-C7 exit above their corresponding vertebrae
→ C8 exits between C7 and T1
→ Starting with T1 after, all nerves exit below their corresponding vertebrae
How is the gray matter and white matter organized in the spinal cord
Opposite to the brain’s organization, the gray matter of the spinal cord is on the inside whereas the white matter tracts are exterior
How is the Gray Matter organized in the spinal cord
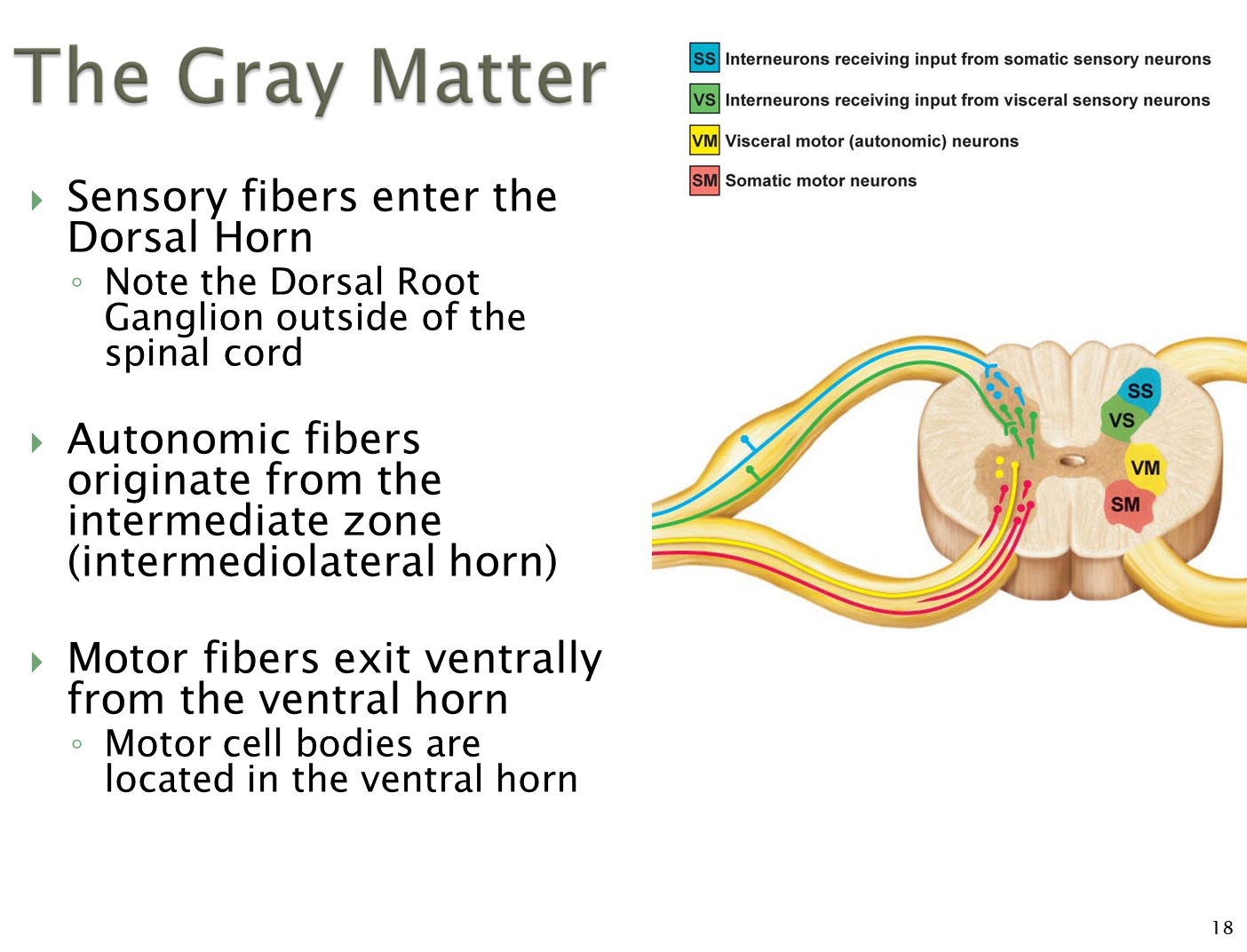
Gray matter is differentiated into a dorsal horn and a ventral horn
1) Dorsal Horn is where the sensory information is integrated
→ dorsal root ganglion will be located immediately outside the spinal cord
2) Ventral Horn is where motor fibers exit the spinal cord
→ motor cell bodies are located within the ventral horn, with medial motor neurons innervating axial muscles and lateral motor neurons innervating the arms and legs
What are the White Matter Columns?

Large white matter columns or funiculi are responsible for longitudinal communication up and down the spinal cord. Subdivided into three funiculus
1) Dorsal Funiculus - sensory information up to the brain
2) Lateral Funiculus - motor information down into the spinal cord
3) Ventral Funiculus - mixture of motor and sensory activity for pain and temperature
What is the Vascular Supply to the Spinal Cord?
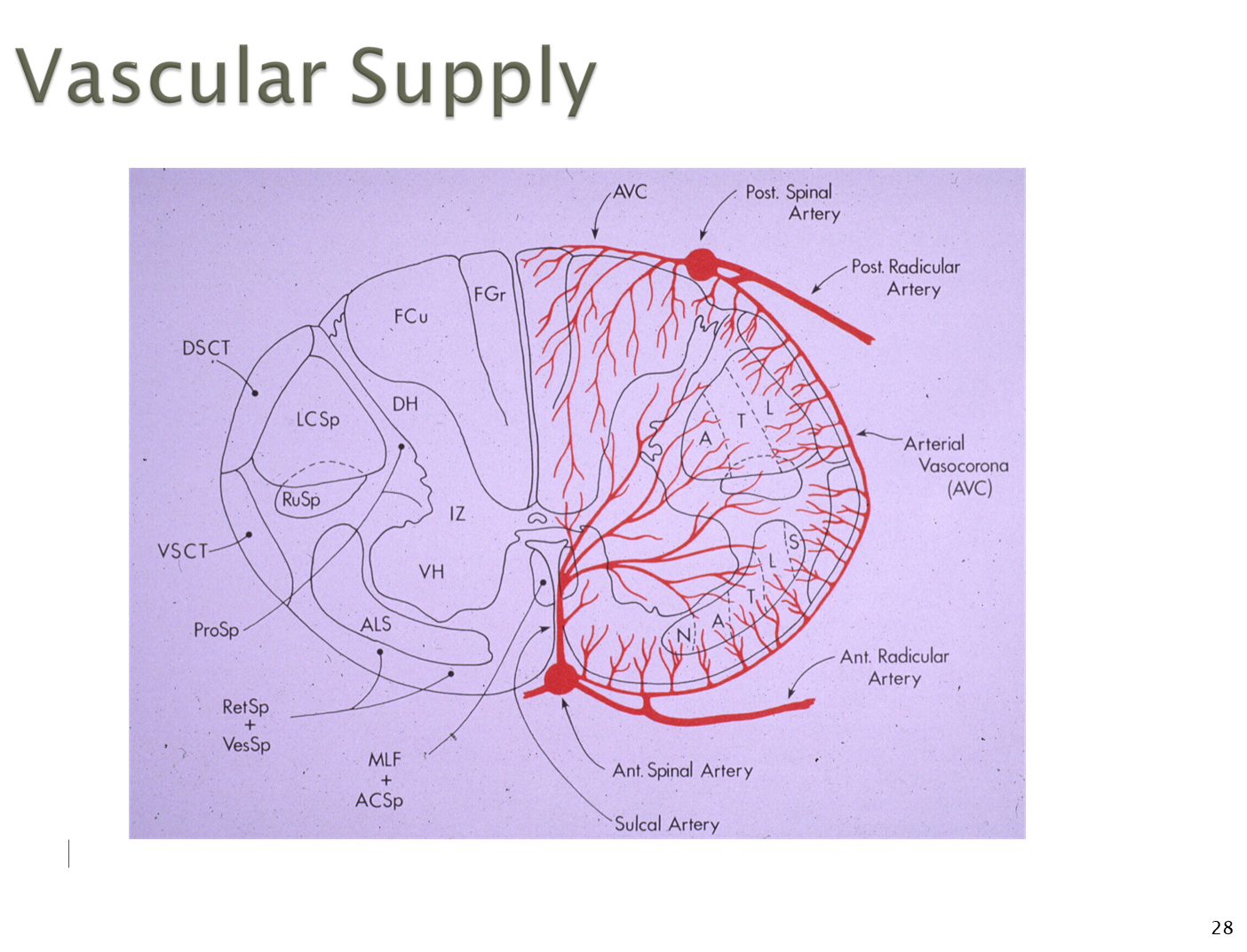
The vascular supply to the spinal cord is done via one anterior spinal artery and two posterior spinal arteries
1) Anterior Spinal Artery
→ before the formation of the basilar artery from the vertebral arteries, the vertebral artery will branch off into the anterior
→ Anterior artery is continually supplied by radicular arteries which provide anastomotic blood flow
→ anterior provides to everything but the dorsal portion
2) Posterior Spinal Arteries
→ arise from the vertebral arteries or posterior inferior cerebellar artery that also receives contributions from radicular arteries
How does the cross sectional anatomy differ depending on location in the spinal cord
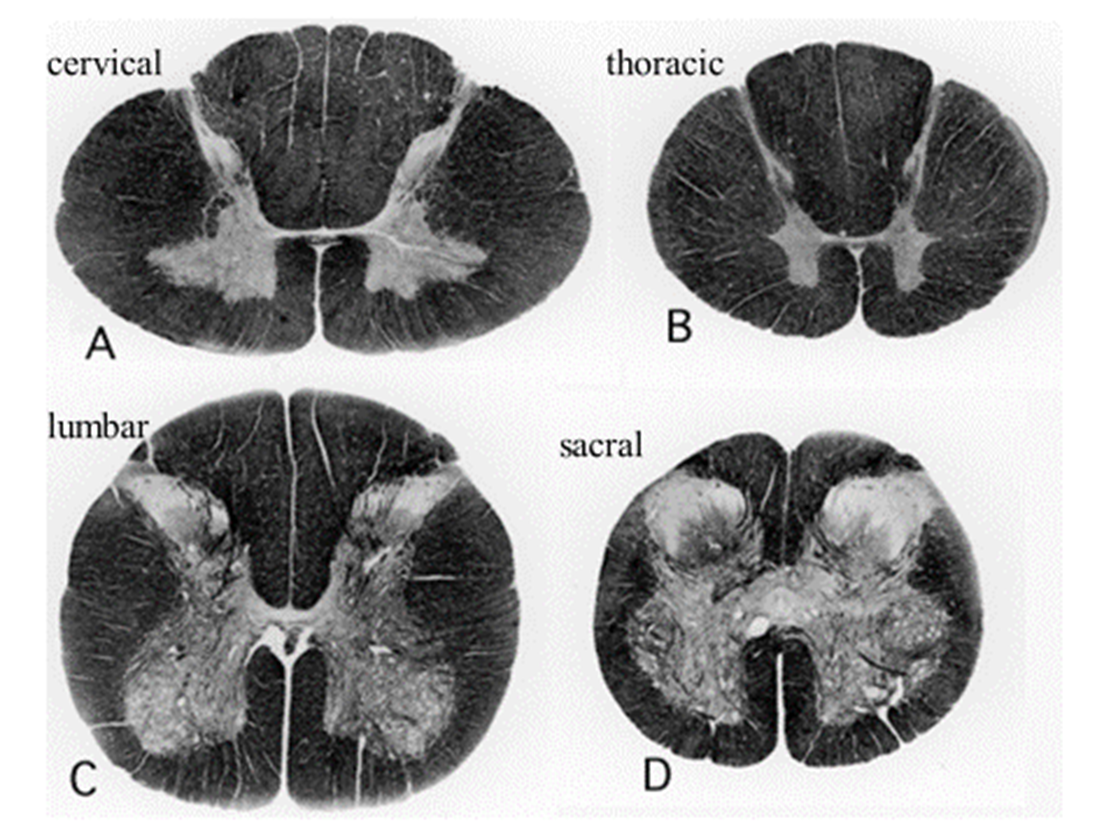
Cervical and thoracic have small gray matter tracts
→ lumbar and sacral are huge