kidneys - cherry
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
oliguria
Decreased urine output
<400mL/day
anuria
absence of urine
<50mL/day
uremia
presence of urinary waste in the blood due to not excreting
azotemia
(excessive) urea and nitrogenous substances in the blood
diagnostic studies
- CT and MRI what you usually start with
- urinalysis / urine culture
- renal function tests
- ultrasonography
- POTASSIUM
BUN normal levels
7-20 mg/dL
CR
normal .7-1.4
renal function tests
Tests for diagnosing kidney disease
Evaluating their severity
Monitoring their progress
Determining renal clearance
Determining glomerular filtration rate;
BUN and Creatinine
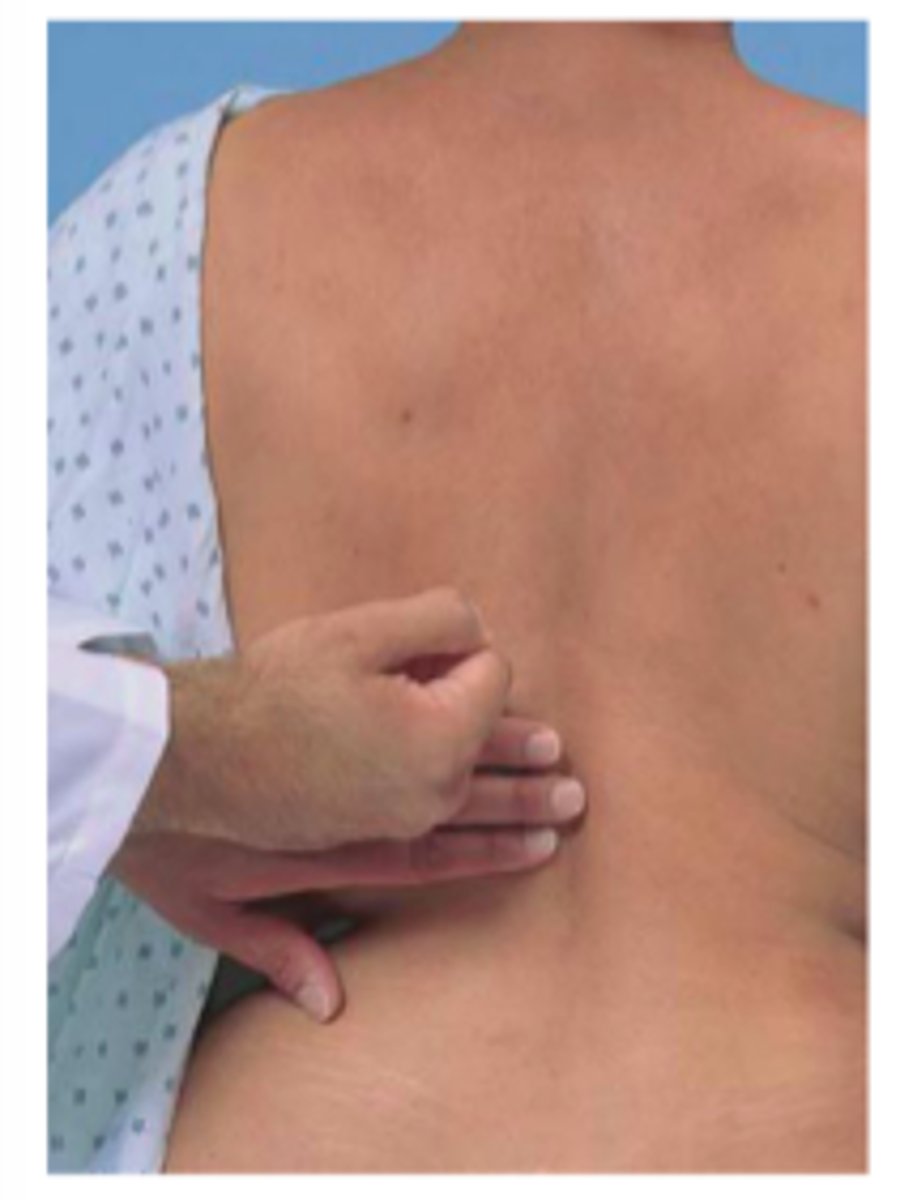
Palpation of kidney
The right kidney is easier to detect, because it is somewhat lower than the left one. In patients with obesity, palpation of the kidneys is more difficult.
Prone:
left kidney is palpated by reaching over to the patient's left side and placing the right hand beneath the patient's lower left rib. Push the hand on top forward as the patient inhales deeply.
Ca+ levels
8.5-10.5
Potassium
3.5-5.0
Monitoring ABGs for....
metabolic acidosis
monitor in fluid retention
- daily weight (MOST ACCURATE PREDICTOR); 1 KG weight gain is = 1 L of fluid
- I & Os
urinalysis
First morning void; needs to be examine within an hour
Creatinine Clearance
Collect 24 hour urine specimen, closely approximates GFR
- more accurate indicator of clearing out substances that are going in and ability to secrete
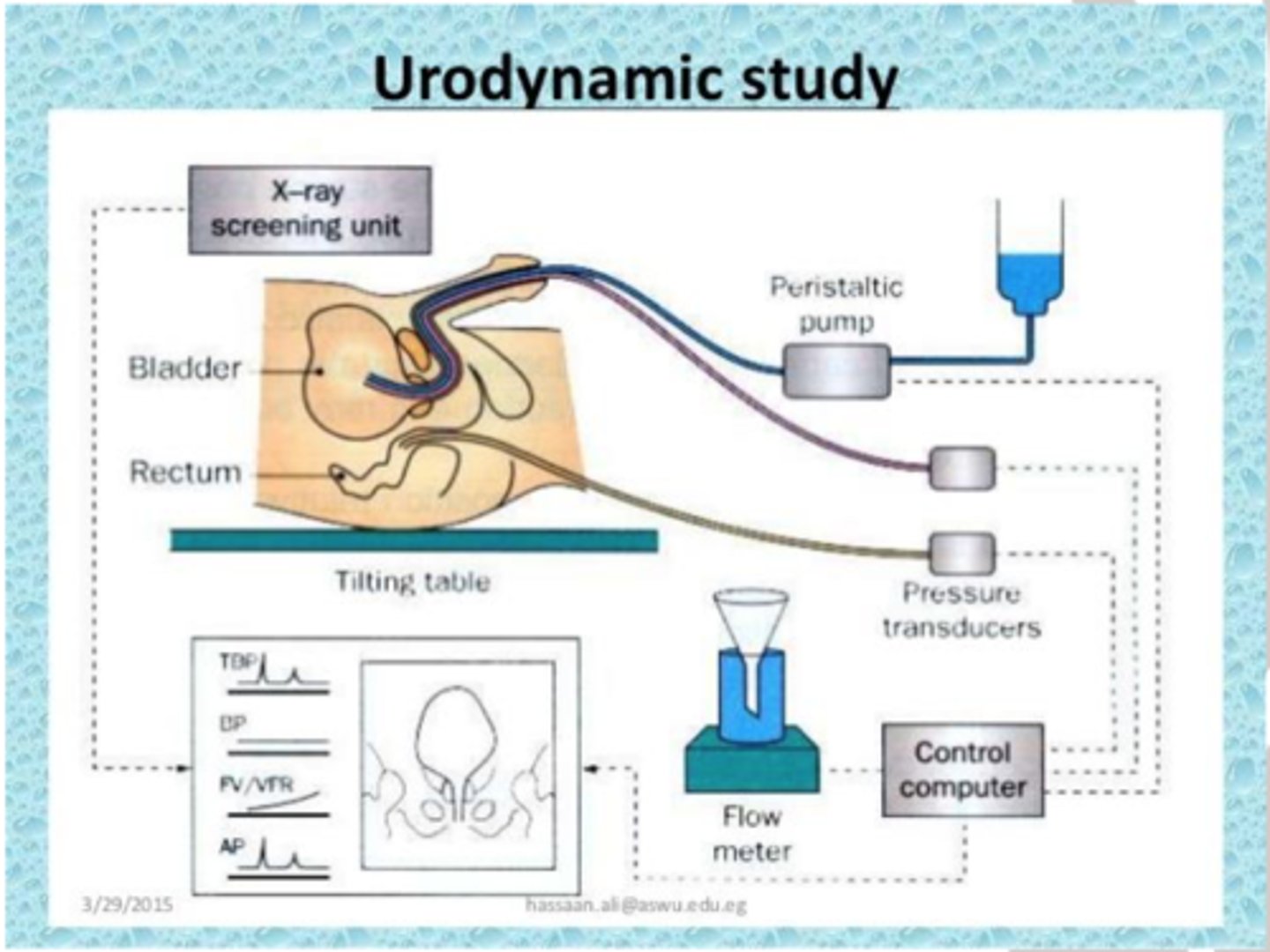
Urodynamics
diagnostic study of urine storage, bladder pressure, and urine flow throughout the urinary tract
CONTRAST INDUCED NEPHROPATHY
Contrast agents → nephrotoxic, major cause of hospital-acquired ARF
Risks:
- baseline Cr > 2.0 mg/dL
- diabetes
- metformin use
Prevention:
- hydrate pre-procedure
- consider ultrasound instead
- hold metformin 48 hrs before/after to decrease risk of lactic acidosis
Follow facility policy (guidelines vary)
acute renal issues
- lethargic
- ill
- dry skin & mucous membranes
- central nervous symptom s/s: confusion
- decreased GFR of sudden onset
(GFR - 1 25mL/min/1.73m2)
chronic renal issues
- progressive, irreversible loss of
function
- eventually affects other organ
systems leading to end-stage renal disease
(ESRD)
ACUTE KIDNEY INJURY
- Rapid loss of kidney function → ↑ Cr, ↓ urine output
- Normal Cr: 0.6-1.2 (M), 0.4-1.0 (F)
- Risks: hypovolemia, hypotension, HF, ↓ CO, HTN, DM, nephrotoxins, obstruction, infections, severe hypotension, toxins/metals, idiopathic
- Complications: metabolic acidosis, fluid/electrolyte imbalances (life-threatening)
Risks for AKI
- hypovolemia
- hypotension
- HF
- ↓ CO
- HTN
- DM
- nephrotoxins
- obstruction
- infections
- severe hypotension
- toxins/metals
- idiopathic
High creatinine =
impaired kidney function or kidney disease (kidneys not filtering waste effectively)
> 1.2 mg/dL
neprotoxic medications
- Aminoglycosides (gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin)
- [MICINs]
- Vancomycin
- NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin)
- ACE inhibitors / ARBs (lisinopril, losartan) - can worsen renal perfusion
- Amphotericin B
- Cisplatin (chemo)
- Radiographic contrast dye
- Cyclosporine, Tacrolimus (immunosuppressants)
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Kidney damage or ↓ GFR ≥ 3 months
Leads to ↓ quality of life, financial burden, ↑ mortality
Progresses to ESRD → uremia, dialysis or transplant needed
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) risks / causes
Risks:
- CVD
- DM
- HTN
- obesity
Causes:
- glomerulonephritis
- glomerulosclerosis
- PKD
- hereditary/congenital disorders
- renal cancers
- nephrosclerosis (arterial hardening from HTN)
Aging & Kidneys
- 30-90 yrs: kidney size/weight ↓ 20-30%
- By 70s: glomerular function ↓ 30-50%
- Atherosclerosis accelerates decline
- Prostate enlargement (males)
Age-Related Physiological Renal Changes
- ↓ elasticity & muscle support
- ↓ renal blood flow → ↓ GFR
- ↓ ability to concentrate urine (hormonal)
- Altered excretion of water, Na, K, acid
Gerontologic Considerations (Kidneys)
- Older adults = ↑ risk for AKI
- Risks:
- dehydration (polypharmacy → diuretics, laxatives)
- illness, immobility, hypotension, aminoglycosides, obstruction, surgery, infection
- Normal aging kidneys can maintain homeostasis, but sudden stressors (blood volume, acid load, insults) may overwhelm function
prerenal failure
Outside of kidney
Caused by shock, dehydration, burns, sepsis
An episode of ARF is pre renal only if it is reversed when the underlying cause of hypoperfusion is corrected
intrarenal failure
direct damage to the kidneys by inflammation, toxins, drugs, infection, or reduced blood supply
- Most common: Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
- Causes: ~30% meds (aminoglycosides, contrast, chemo) |
- 50% ischemia (↓ perfusion)
postrenal failure
sudden obstruction of urine flow due to enlarged prostate, kidney stones, bladder tumor, or injury
Pre-Renal AKI Causes
- Volume depletion → hemorrhage, diuretics overuse, GI losses (vomit/diarrhea), severe dehydration
- Impaired cardiac function → HF, MI, cardiogenic shock, valve disease, renal artery damage
- Vasodilation → meds, anaphylaxis, sepsis
Intra-Renal AKI Causes
- Prolonged ischemia → myoglobinuria (burns, trauma, muscle injury), hemoglobinuria
- Nephrotoxic agents → aminoglycosides, NSAIDs, contrast dye
- Infection → pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis (E. coli, bacteria, fungi, protozoa, viruses)
aminoglycosides antibiotics
Gentamicin,
Streptomycin,
Amikacin,
Neomycin,
Tobramycin,
Post-Renal AKI Causes
- Obstruction of urine flow (ureters → urethra)
- Urolithiasis (stones), clots, strictures
- Tumors: prostate, ovarian, cervical, colon
- Bladder dysfunction
- Obstructions: BPH, blocked catheter, ureteral blockage
Trauma
Obstruction to urine outflow
- GFR decreases
- hydronephrosis: kidney failure
- pressures interfere with function: cannot filter / remove waste
- obstruction: increased pressure
AKI phases / classifications
- Phases: oliguric → diuretic → recovery
If no recovery → may progress to CKD
RIFLE classification:
R = Risk
I = Injury
F = Failure
L = Loss
E = ESRD
Initiation period
begins with the initial insult and ends when oliguria develops
- Onset: 1-7 days after injury; lasts 10-14 days
- Most common sign: oliguria
- UA: casts, RBCs, WBCs
- Uremic s/s: weakness, fatigue, anorexia, weight loss, mental status changes, muscle cramps, visual changes, ↑ thirst, shallow respirations
Oliguric Phase
-Urine output decreases
-UO of 100-400 mL/24 hours
-This client is in fluid volume excess
-The potassium will be increased!
- Support renal fx
- keep client stable until injury heals/resolves
Diuretic Phase
increased urine (water, not wastes).
Kidney unable to conserve Na and H20. High BUN. Deficit of K, Na and H20. Azotemia
- volume may reach elevated values
- Hyponatremia
- Hypokalemia
- Dehydration
UREMIA S/S
- weakness
- fatigue
- anorexia
- weight loss
- mental status changes
- muscle cramps
- visual changes
- ↑ thirst, shallow respirations
hypermagnesium
flushing, drowsiness, ↓ reflexes, weakness, resp depression, cardiac arrest;
Tx: Ca gluconate, ventilation, dialysis
Hypocalcemia
→ cramps, tetany, Chvostek/Trousseau, tingling, ECG changes;
Tx: Ca replacement
therefore, HYPERPHOSTEMIA
Fluid volume excess
→ wt gain ≥5%, edema, crackles, JVD, ↓ Hct/BUN; Tx: restrict fluids/Na, diuretics, dialysis
Metabolic acidosis
→ HA, confusion, ↑ RR, warm skin; Tx: bicarb, dialysis
RECOVERY PHASE
•Lab values return to patient's normal level
- Recovery can take several months(up to a year)
- Goals: patient education (drink fluids unless CKD), followup, preventive measures
prevention of AKI/ARF
- Adequate hydration
- Prompt treatment: shock, hypotension, infection
- Meticulous catheter care
- Monitor/limit nephrotoxic meds & dosages
Medical Management of AKI/ARF
- Monitor/adjust nephrotoxic meds
- Weight loss, exercise
- ↓ Na & alcohol
- Smoking cessation, education, nephrology referral
- Control HTN (<130/80), treat hyperglycemia
- Manage anemia, manage CVD risk factors
Nutritional Education
- Maintain adequate caloric intake
- Restrict sodium
- Increase dietary fat
- Prevent/treat infections promptly
- Enteral nutrition
epoeitin
stim RBC production
Focused Renal Assessment
Physical exam: cardiopulmonary, renal, hemodynamic status
Hx: renal problems, nephrotoxic meds, heavy metals/solvents
Events: hypotension >25 min, tumors/clots, infection
Nursing Assessment
- Neuro: mental status, LOC
- Oral: mucosa hydration
- Pulmonary: lung sounds, circulatory overload
- Cardiac: rhythm, ↓ CO, S3 (HF)
- Labs/Diagnostics: review results