Bio 251 Final Exam
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
What is genetics used for
Disease study and Transmission
Increase agricultural output
Pharmaceutical
Medicine
Crime Scene analysis
Environmental DNA
Branches of Genetics-Transmission
Basic principles of heredity and how traits are passed from one generation to the next
Branches of Genetics-Transmission Example
Disease
Breeding → Animals
Branches of Genetics- Molecular
chemical nature of the gene itself; how genetic info is encoded, replicated, and expressed
Branches of Genetics- Population
Genetic composition of populations and how that composition changes geographically and with the passage of time
How do we study genetics
By using model organism
Model organisms characteristics
reproduce quickly
easy to maintain in lab
observable over entire lifespan
many offspring
know DNA sequences
How long have humans been interested in genetics
12,500
domestication of plants and animals
4,000 years ago
artificial selection via selective breeding
History of Human Genetics- Pangenesis
each part of the body contains genetic information for that body
History of Human Genetics- Preformationism (1665)
inside the egg/sperm there exists a fully formed mino adult which simply enlarges
History of Human Genetics- Germ plasm Theory (1800s
cells in reproduce organs carry a complete set of genetic info that is passed to egg and sperm
Gene
Inherited genetic material or DNA sequence that codes for a protein and trait
What are the units of heredity
Gene
Allele
Alternate forms of a gene
Phenotype
physical trait
Genotype
set of alleles that determines a trait
Prokaryotes characteristics
Nucleus: No nucleus
Cell Diameter: relatively small
Genome DNA: circular DNA
Amount of DNA: one chromosome
Membrane bound organelles: none (typically)
Eukaryotes characteristics
Nucleus: Has a nucleus
Cell Diameter: relatively big
Genome DNA: linear DNA
Amount of DNA: multiple chromosome
Membrane bound organelles: has membrane bound organelles
Types of prokaryotes
Bacteria and Archaea
Types of Eukaryotes
Fungi, Plant, Animals, and Protists
Prokaryotes
DNA does not exist in the highly ordered/ packed arrangement (nucleoid location)
single origin of replication
Eukaryotes
Genetic material is surrounded in a nuclear envelope
DNA is closely associated with histones to form tightly packed chromosomes
Multiple origins of replication
What is Prokaryotic Cell Division called
Binary Fission
Binary Fission Steps
Replication Begins at origin of replication
chromosome duplicated
two origins of replication move to opposite sides of cell
SMC (Structural Maintenance Chromosome) complexes prevent tangling
New cell wall forms Can take as little as 20 mins
Over 2 billion cells in 24 hours
Homologous Chromosomes
chromosomes that are similar in size and structure
carries genetic information for the same sett of characteristics
one set of chromosomes from each parent
Centromere
Attachment point fro spindle microtubules
Telomeres
at the tips of a linear chromosome
gets shorter at each cell replication
if they get too short it can cause cell death
Origins of replication
Location where DNA synthesis begins (replication)
Sister chromatids
two copies of a chromosome that are held together at the centromere
How to find the number of chromosomes in a cell
count the number of chromatid
Cohesion
protein that holds the chromatids together
warps around the chromatids
Shugoshin
protects cohesin so chromatids stay together
Chromatid
one DNA molecule
Mitosis
separation of sister chromatids
Mitosis phases
Interphase
Prophase
Prometaphase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Cytokinesis
Eukaryotic Cell Division: Interphase- G1/S
regulated decision point
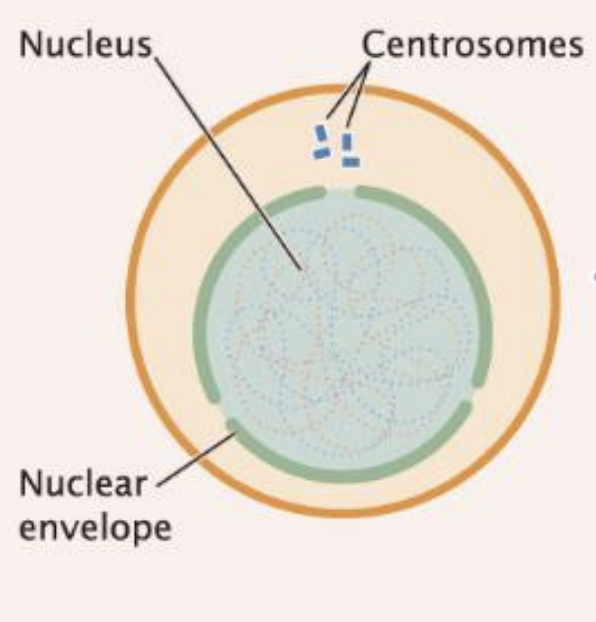
What does G1 do in interphase
Cells grows
Eukaryotic Cell Division: Interphase- G1
G1: growth and proteins for cell division synthesized
Eukaryotic Cell Division: Interphase- G0
damage cells may enter G0 which is a non-dividing phase which creates cell death
Eukaryotic Cell Division: Interphase- G1/S checkpoint
determines if the cell has internal and external conditions to see if they have the necessary resources, growth signals, and DNA integrity to continue the cell cycle
what happens to the cell after the G1/S checkpoint
the cell is committed to dividing
Eukaryotic Cell Division: Interphase- S phase
The DNA duplicates
Eukaryotic Cell Division: Interphase- G2 phase
helps prepares the cell for mitosis
Eukaryotic Cell Division: Interphase- G2/M checkpoint
only allows the cell to passed if DNA is completely replicated and undamaged
Prophase
chromosomes are condense to form two chromatids
mitotic spindles form
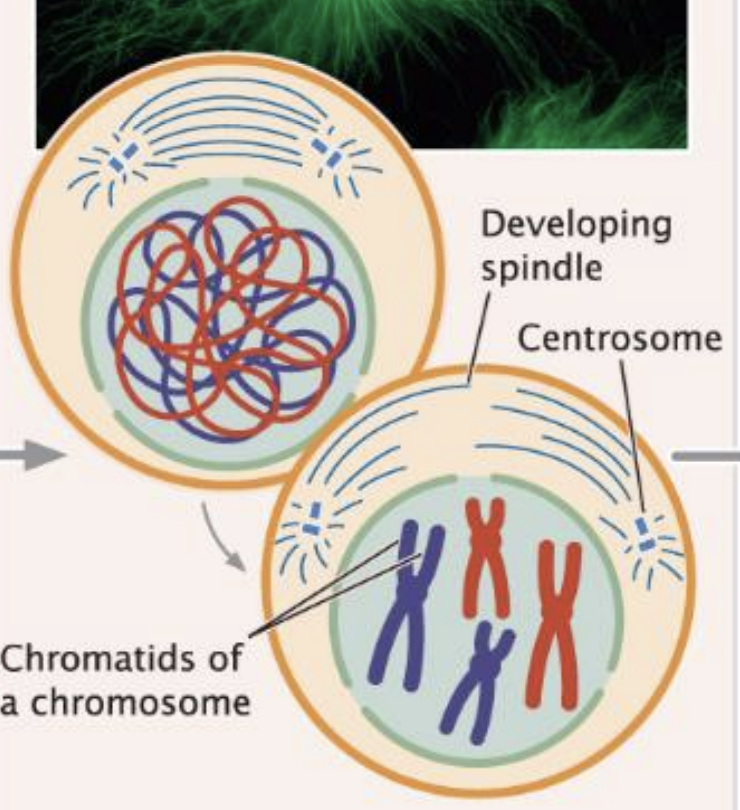
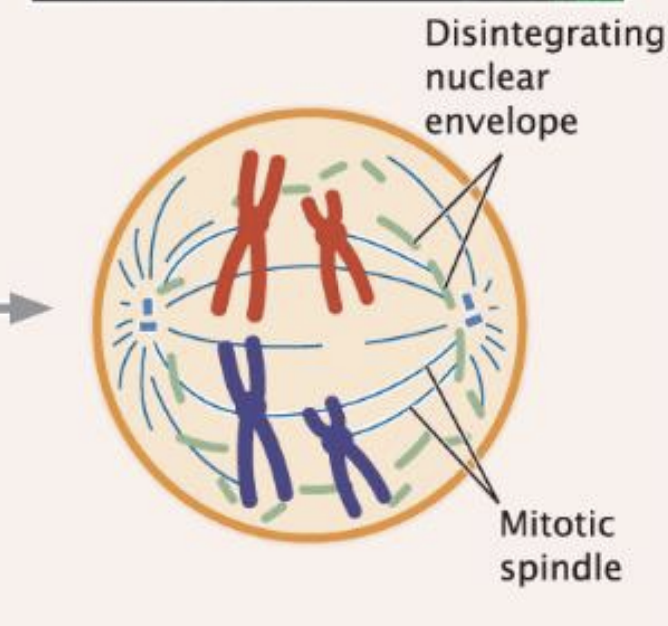
Prometaphase
nuclear membrane breaks down
spindles attach the chromosome at kinetochore
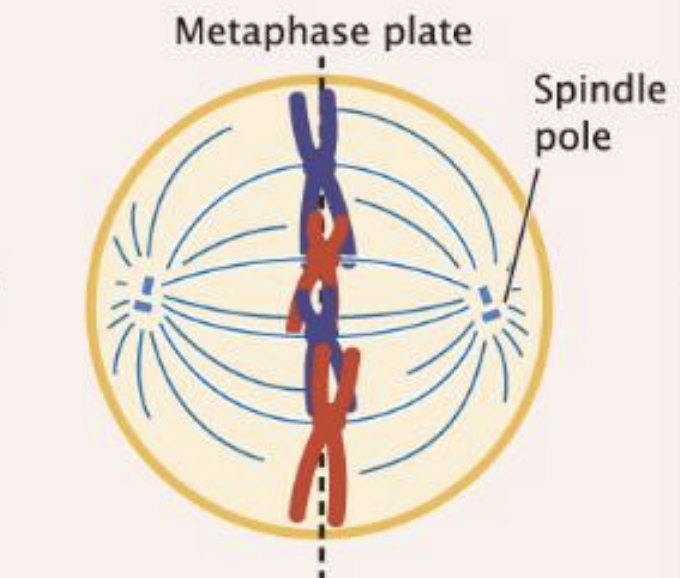
Metaphase
Chromosomes align in center of cell
cohesion begins to break down
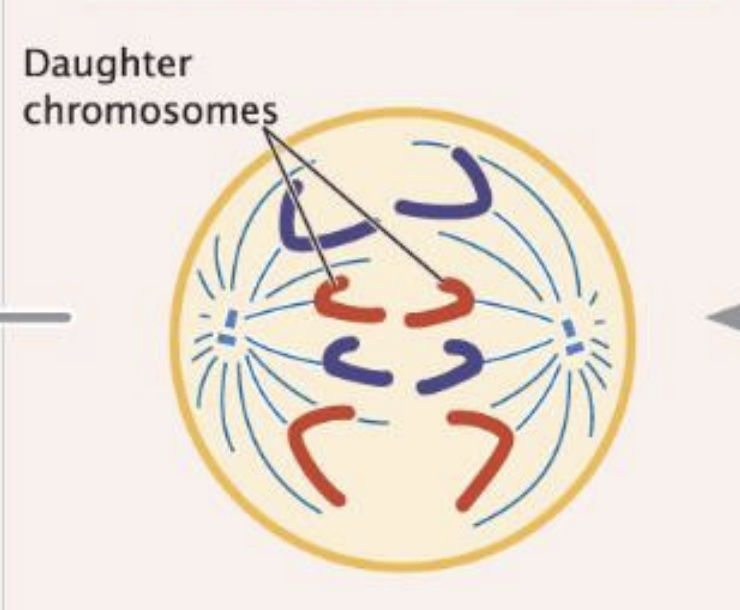
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate move to poles
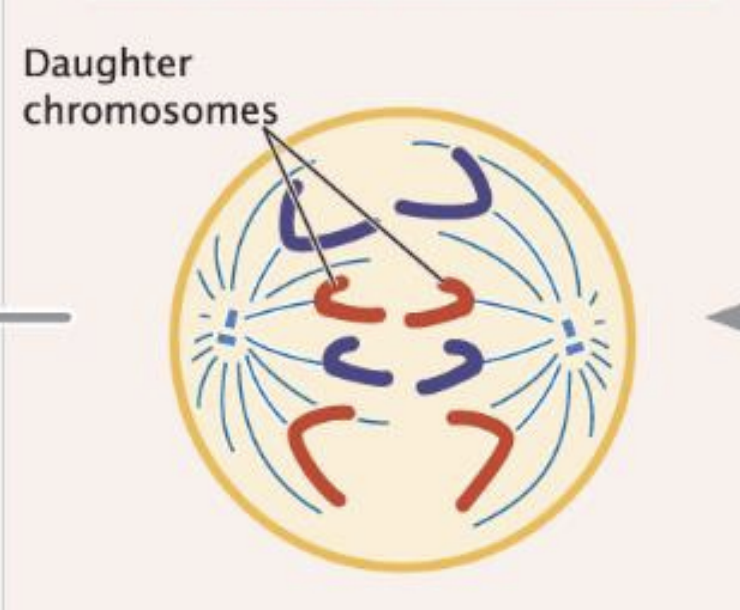
Telophase
nuclear membrne reforms and chromosome decondense
Cytokinesis
separation of cytoplasm
results of Mitosis
Two genetically identical cells that are identical to parent cell
cells have full compliment of chromosomes
each daughter cell has half of cytoplasm and organelle content
Synapsis
Close pairing of homologous chromosomes
Tetrad
Closely associated four sister chromatids of two homologous chromsomes`
Crossing Over
when chromosome segments from sister chromatids of one chromosome to the sister chromatid cross over of the synapsed chromosome
Where does crossing over happen
happens in prophase one of meiosis
Meiosis
production of haploid gametes that creates genetic variation
Meiosis Stages
Interphase
Prophase 1
Metaphase 1
Anaphase 1
Telophase 1
Interkinesis
Prophase 2
Metaphase 2
Anaphase 2
Telophase 2
Cytokinesis 2
Prophase One
nuclear membrane breaks down
crossing over occurs following condensation of chromosomes and homologous chromosome pairing
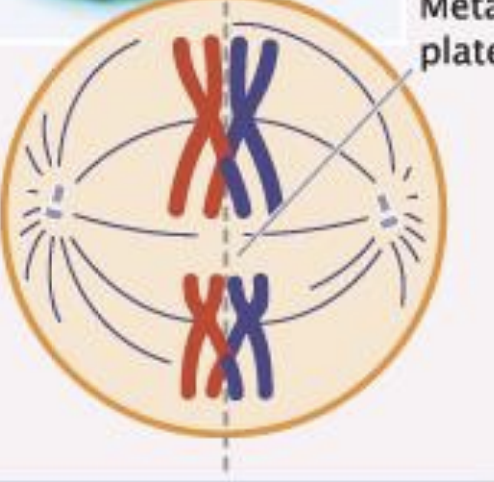
Metaphase One
homologous pairs randomly align of center of cell
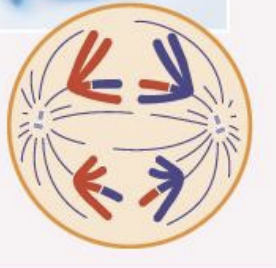
Anaphase One
shugoshin protects cohesion
Homologous chromosomes separate
Move towards poles
Telophase One
cytoplasm separates after chromosomes move to poles
nuclear membrane begins to form
chromosomes decondense
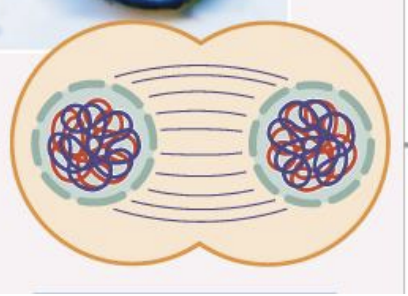
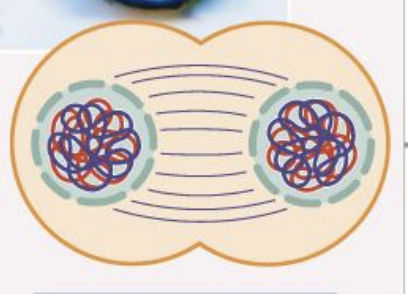
Meiosis Two- Interkinesis
Nuclear membrane reforms and decondense
Prophase two
nuclear membrane breaks down
chromosomes re-condense
spindle fibers begin to form
Metaphase two
spindle fibers attach
individual chromosomes align at center cell
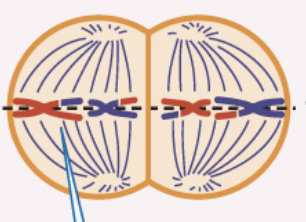
Anaphase two
shugoshin breaks down
cohesin breaks down
sister chromatids separate
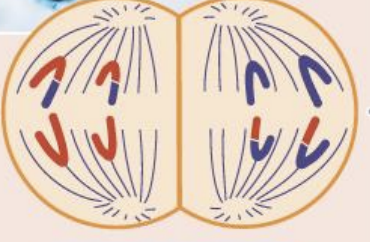
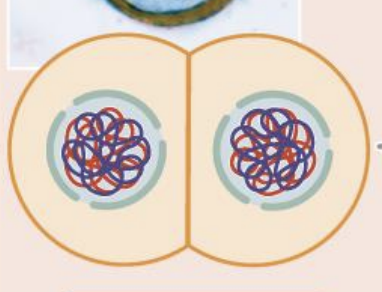
telophase two
chromosomes move to poles
nuclear membrane forms
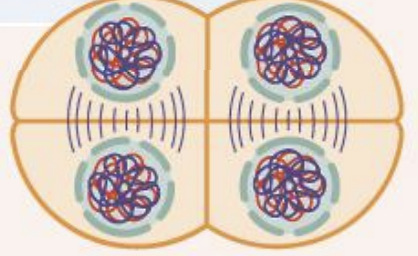
Meiosis two results
4 daughter cells from one parent cell n
number of chromosomes in daughter cells is half of parent cell
each daughter cell is genetically unique
Five characteristics of model organisms
easy to use in lab
Fast lifecycle
Genetic background known
genetically diverse
lots of offspring
Medel’s Model Organisms Study approach
pea plants studying seven characteristics
binary characteristics
conducted crosses of plants for seven years
hypothesis based testing
Locus
location on a chromosome
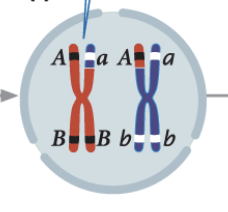
heterozygous genes
two different alleles (Bb)
Homozygous genes
two copies of the same allel (BB/bb)
what do alleles contain
Alleles contains DNA squence
Monohybrid
organisms differ in one trait
Dihybrid
organisms differ in two traits
Principle of Segregation
each individual diploid organism possesses two alleles for a characteristic
two alleles segregate when gametes are formed
one allele goes into each gamete
Where does Principle of Segregation happen
happens in anaphase
Concept of Dominance
when two different alleles are present in genotype
only the trait encoded by one of them is observed in the phenotype
Dihybrid cross
parents differ in two traits
Principle of Independent Assortment
genes that don’t influence each other during sorting of alleles into gametes
every possible combination of alleles for every gene is equally likely to occur
Probablity
likelihood of the occurrence of a particular even
cN be used to predict outcomes of crosses
Multiplication rule
Probability of two or more independent events taking place together
multiply independent probabilities
Example of multiplication rule
1/6 × 1/6 = 1/36
Addition rule
probability of any of two or more mutually exclusive events
calculated by adding the probabilities of events
Example of Addition Rule
¼ + 1/2 = ¼ + 2/4 = 3/4
Binomial expansion
Formula: (p+q)^n
p= probability of having the recessive trait
q= probability of having the dominant trait
n= number of offspring
Chi- square test
compares the observed and expected values based on phenotype using null hypothesis
Chi- Square Test Formula
χ² = Σ(O - E)²/E
Σ: sum your terms
O: observed count from cross
E: expected count based on punnett square
Null Hypothesis
there is no significant difference between the observed and expected numbers of difference of the values
Degrees of Freedom
number of independent random variables involved
formula: n-1
What do you do is the p-value is more than 0.05
accept the null hypothesis
What do you do is the p-value is less than 0.05
reject the null hypothesis