Conflict resolution
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Types of conflict
Task: Parties focus on the issue, respect and understand the logic of the others POV
Relationship: Focus on personal characteristics (not issues) as the source of conflict
The conflict process model
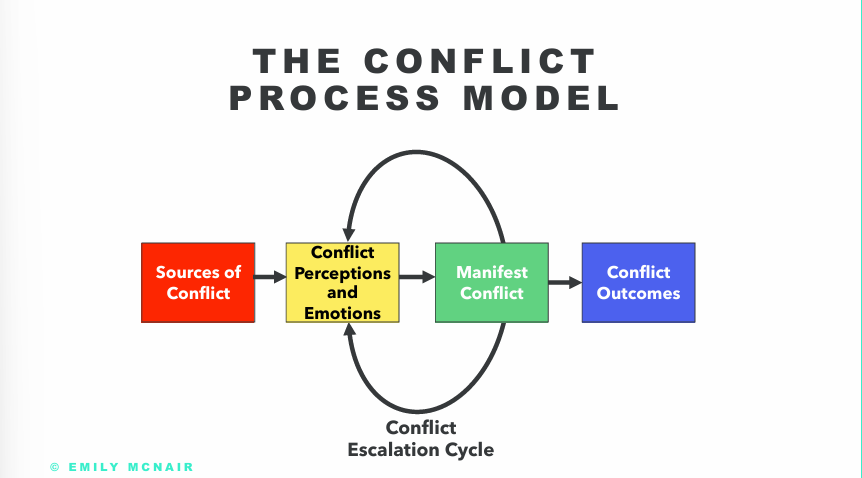
Sources of conflict

Conflict handling styles
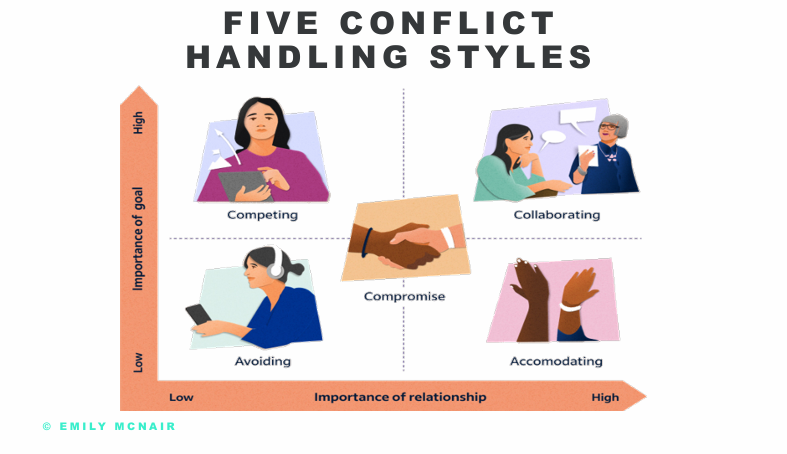
What allots differences in conflict styles
Culture: Cultural norms shape preferred conflict approaches and affect how outsiders should handle disputes.
Gender: Women often focus more on relationships, while men are generally more competitive with a short-term focus. (Note: These are generalizations, not true for everyone.)
approaches to conflict management
Focus on shared goals.
Reduce differences.
Improve communication.
Decrease reliance on each other.
Increase resources.
Clarify rules.
Third party conflict resolutions
Third party conflict resolution is any attempt by a relatively neutral person to help conflicting parties resolve their differences
Types of third party CR
Mediators have high control over the intervention process and interactions
Inquisitors control all discussion about the conflict
Arbitrators have high control over the final decision but low control over the process
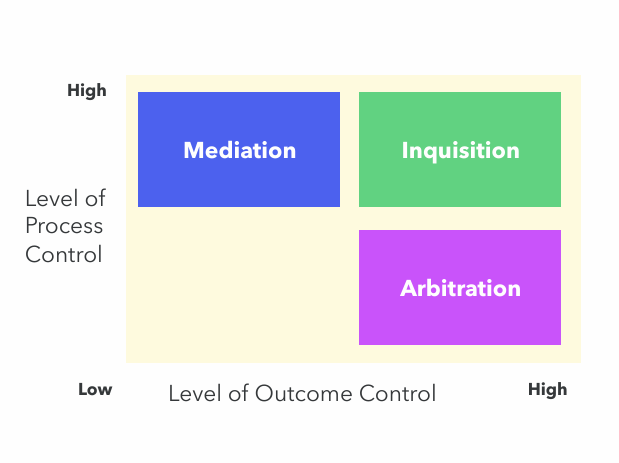
Mediation-Arbitration
it is a hybrid dispute resolution process.
positive: Parties are confident the dispute will be resolved.
Negative: Parties control what info is shared, but may be forced to answer follow-up questions.
Negotiation
Decision making situations in which two or more interdependent parties attempt to reach an agreement
Distribution
When the goals of two or more people are zero-sum so that one can gain only at the other’s expense
Integrative
When parties’ goals are linked, but not zero-sum, so that one person’s goal achievement does not block the goal achievement of another
Interest VS position
Interests are the underlying reasons for demands.
Positions are negotiable ways to satisfy interests. Giving a position may not satisfy the interest.
Situations influences on negotiations
Location: easier to negotiate on your own turf
Physical setting: seating arrangements, etc.
Audience: negotiators are more competitive, make fewer concessions when audience is watching
Crucial conversations are composed of

Silence VS Violence
S: Any action taken to withhold information from the pool of shared meaning
V: Any action taken to compel others to your point of view
S.T.A.T.E (when having crucial conversations)
Share the facts: What do you see/hear?
Tell your story: What were your expectations? Where's the gap?
Ask for other person’s perspective
Talk tentatively
Explore the other’s path