ap chem ch. 7
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:55 PM on 4/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
1
New cards
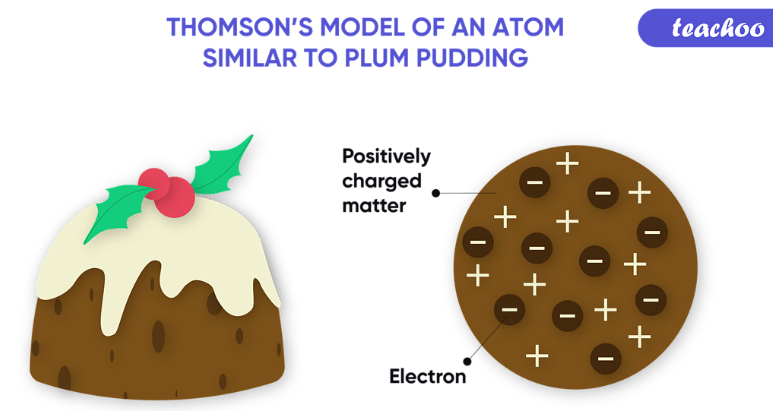
thompson
plum pudding model
2
New cards
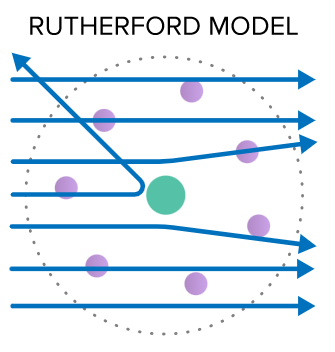
rutherford
sea of electrons
3
New cards
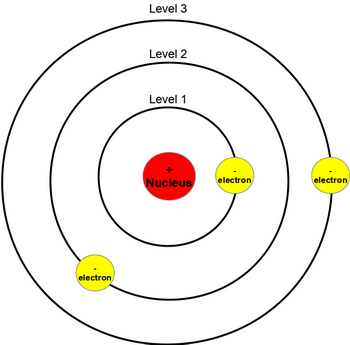
bohr
planetary model
4
New cards
wave velocity =
frequency*wavelength
5
New cards
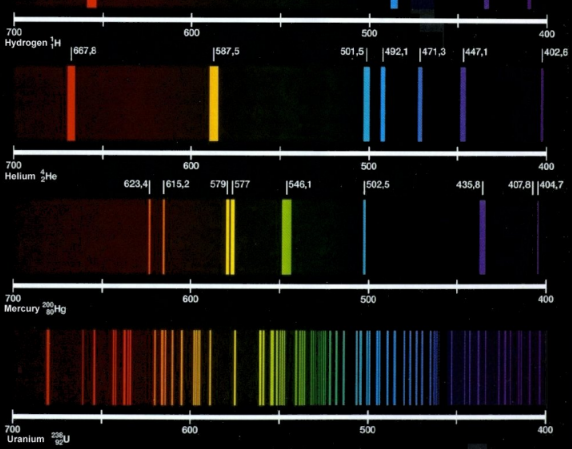
emission line spectrum
shows how many times an electron transitioned from a higher to lower energy state; more lines means more energy
6
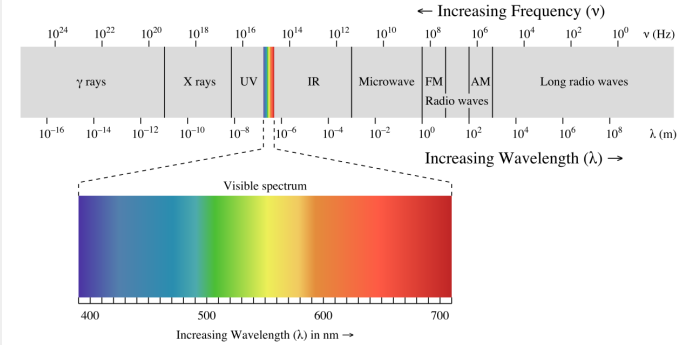
New cards
electromagnetic spectrum
7
New cards
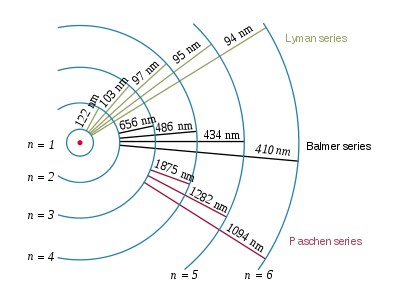
balmer series
shows visible light
8
New cards
s sublevel
sphere shaped, 1 orbital
9
New cards
p sublevel
dumbbell shaped, 3 orbitals (px, py, pz), all the dumbbells together form a sphere
10
New cards
d sublevel
clover shaped, 5 orbitals, all the clovers together forms a sphere
11
New cards
f sublevel
flower shaped, 7 orbitals, all the flower
12
New cards
hund's rule
electrons fill unoccupied degenerate orbitals before pairing
13
New cards
pauli's exclusion principle
no two electrons can have the same 4 quantum numbers
14
New cards
plank's hypothesis
worked with electromagnetic waves; E = hv = plank's constant * frequency
15
New cards
plank's constant
6.626x10^-34
16
New cards
atomic spectra
produced when an electron moves from a higher to lower energy level, giving off light in the process; delta E = Ehi - Elo = hv = h*c/λ
17
New cards
bohr model
electrons move around the nucleus with a fixed radius, they absorb energy as as they get farther from the nucleus, and gives off energy yas it gets closer to the nucleus. this resulted in the emission spectra, which only happens as certain visible wavelengths.
18
New cards
wave/particle duality
- plank said waves can act like particles
- de broglie said E = hv = mc^2
- experiments can only demonstrate one of these particles at a time
- hiesnburg uncertainty principle: the momentum & position of a particle cannot be known at the same exact time. therefore, we can only refer to the probability of finding an electron in a region; we cannot specify the path
- de broglie said E = hv = mc^2
- experiments can only demonstrate one of these particles at a time
- hiesnburg uncertainty principle: the momentum & position of a particle cannot be known at the same exact time. therefore, we can only refer to the probability of finding an electron in a region; we cannot specify the path
19
New cards
schrodinger
wave equations (ψ2) can be used to predict the region of probability for locating an electron
20
New cards
particle behavior
photoelectric effect (solar powered calculator)
21
New cards
wave behavior
refraction (changes speed in different media), defraction (bends around barriers), reflection
22
New cards
exceptions to the auf bau
electron promotion; an electron can be promoted from the s sublevel to the d sublevel for stability (half or full)
23
New cards
elements in the same group have
similar chemical properties & outer electron config
24
New cards
elements in the same period have
similar physical properties
25
New cards
coulombs law
strength of a bond
26
New cards
types of bonds
strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic, gravitational
27
New cards
periodic trends
explained by Z effective force (how strong the nucleus is); represented by the numerator (q1 * q2)
28
New cards
groups trends
explained by quantum energy & shielding effect - electron penetration; represented by the denominator (r^2)
29
New cards
trends of the periodic table
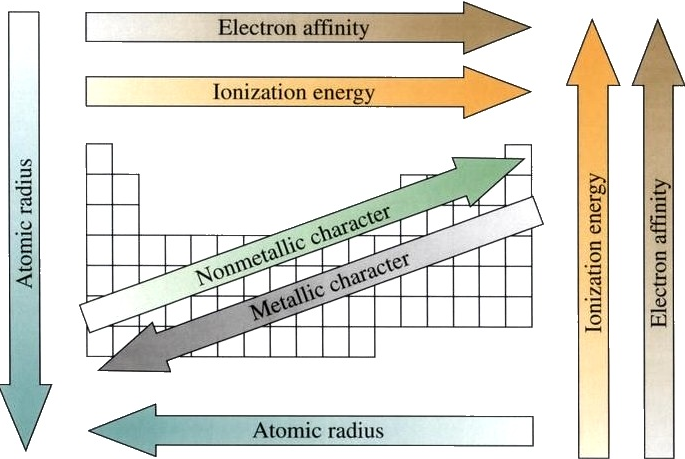
30
New cards
shielding effect
the attraction between outer electrons and the nucleus decreases as the number of electrons between them and the nucleus increases, causing bonding situations
31
New cards
Z effective force
how strong a nucleus is; # of protons - # core electrons
32
New cards
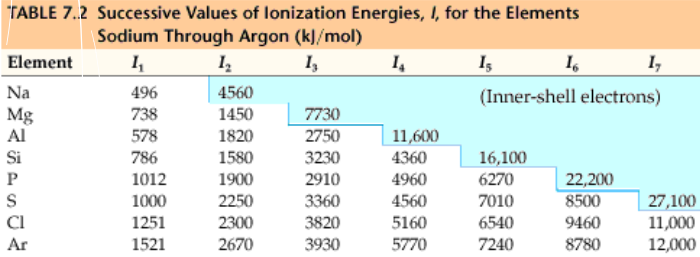
ionization energy
the energy required to remove one electron from one gaseous atom
33
New cards
electron affinity
atoms ability to attract additional electrons; metals have a high electron affinty, non-metals have a low electron affinty
34
New cards
multiple ionization energies
looking at the table - remove valence electrons take less energy and removing core electrons take a lot more energy, as they are more stable. 2nd and 3rd ionization energys can give clues as to the atomic structure