PHYSICS IGCSE CIE EXAM Q
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
SCALAR QUANTITIES INVOLVE MAGNITUDE
Temperature
Speed
Mass
Distance
VECTOR QUANTITIES INVOLVE MAGNITUDE AND DIRECTION
Gravitational field strength
Force
Weight
Velocity
WHAT IS SPECIFIC HEAT CAPACITY
The amount of heat needed per 1KG of mass to increase temperature by 1*C
WHAT IS SPECIFIC LATENT CAPACITY
The amount of heat needed per 1KG of mass to change state
PROPERTIES OF A THERMOMETER
→ Can only measure 100*C
→ Mercury expands when heated up
→ Additional volume increases accuracy of temperature measurement
PROCESS OF CONDENSATION
Liquid particles gain energy and move faster and break free from the liquid into the air. In boiling, they escape in forms of bubbles.
PROCESS OF CONDUCTION
Solid particles are close together, and when heated vibrate in place and gain more energy. This energetic particle then vibrates against neighbouring particles which then spreads throughout the whole solid.
WHAT IS THE CONVECTION CURRENT
Warmer fluid is less dense and rises
Cooler fluid is denser and sinks
Distributing heat through the fluid
THERMAL EXPANSION EG.
→ Railway lines
→ Thermometers
→ Power lines
PROCESS OF LIQUID EXPANSION
When a liquid is heated, its particles gain energy and move faster. This increased movement causes the particles to spread out and take up more space, making the liquid expand.
PROPERTIES OF TRANSVERSE WAVE
→ Seismic s-wave
→ Vibration is 90* to propagation
→ Electromagnetic wave
PROPERTIES OF LONGITUDINAL WAVE
→ Seismic P-wave
→ Vibration is parallel to propagation
→ Sound wave
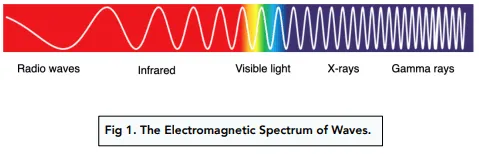
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
Red has the longest wavelength and the lowest frequency
Violet has the shortest wavelength and the highest frequency
SPEED OF LIGHT IN: AIR, WATER, GLASS
Air: 3.0×10^8
Water: 2.25×10^8
Glass: 2.0×10^8
USES OF ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM
Radio waves: radio and television transmissions & RFID
Microwaves: satellite television, mobile phones, microwave oven
Infrared: short range communications, intruder alarms, thermal imaging, optical fibres
Visible light: vision, photography, illumination
Ultraviolet: security marking, detecting fake bank notes, sterilising water
X-rays: medical scanning, security scanners
Gamma rays: sterilising food & medical equipment, detection & treatment of cancer
HOW DOES AN OPTICAL FIBRE WORK
It uses the principle of total internal reflection to transmit data efficiently through light signals, typically using infrared light.
PROPERTIES OF DISCRETE SIGNALS
→ Binary
→ Higher transmission rates
→ Digital data, internet signals, computer memory
PROPERTIES OF ANALOG SIGNALS
→ Continuous
→ Limited by signal degradation over distance
→ Audio, television, older telephone systems
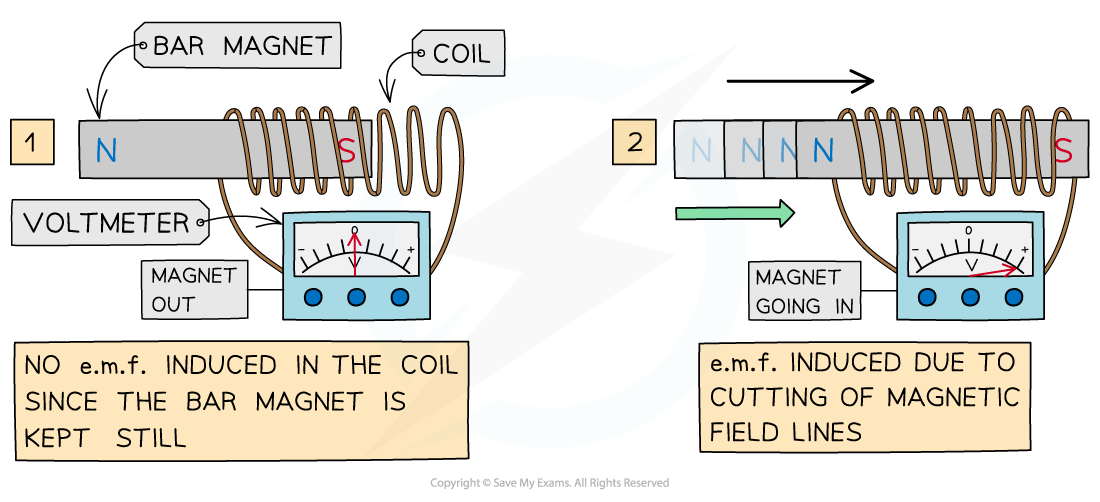
LENZ’S LAW
The direction of the induced current opposes the change of the flux that creates it
HOW IS CURRENT PRODUCED IN THE SECONDARY COIL IN A TRANSFORMER
When a.c flows through the primary coil, it creates an alternating magnetic field; this then induces a current in the secondary coil through electromagnetic induction.
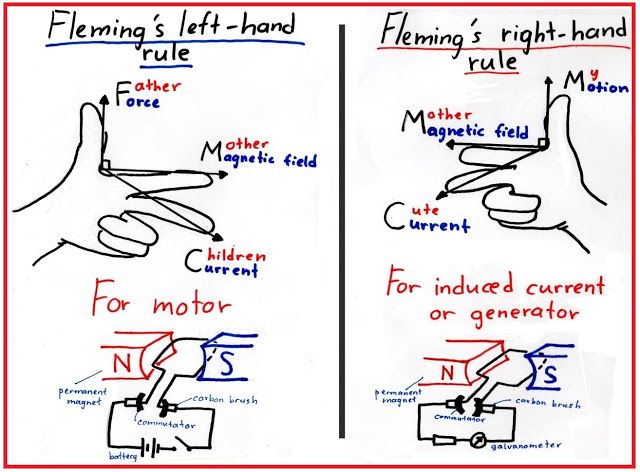
FLEMING LEFT HAND AND RIGHT HAND RULE
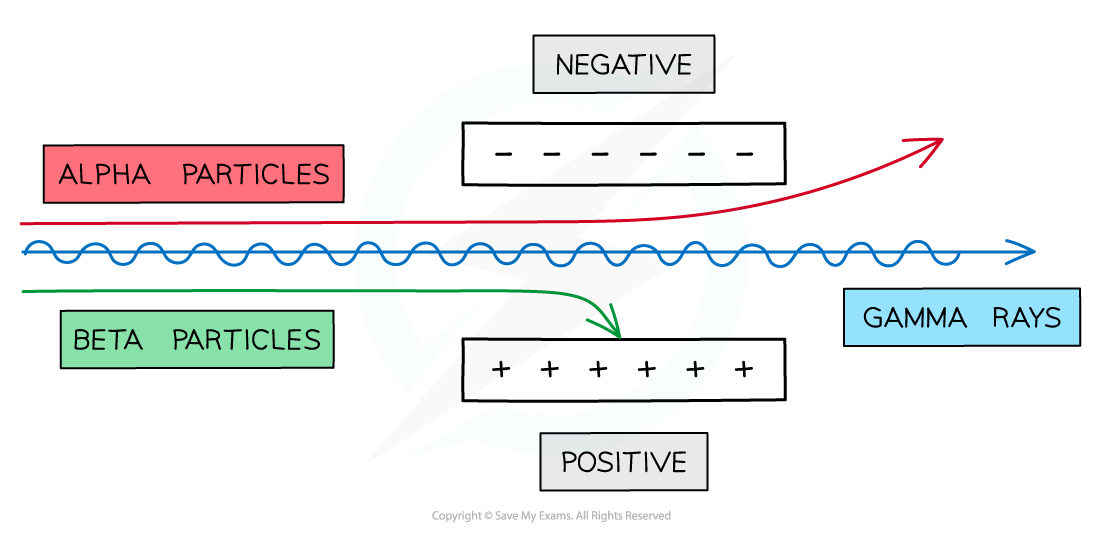
IONISING & PENETRATING POWER OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE
a-particle: very strong & very weak (paper block)
b-particle: medium & medium (aluminium foil block)
y-radiation: very weak & very strong (lead block)
USES OF ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVE
a-particles:
→ smoke detectors, able to ionise the air—making smoke flow slower than usual which triggers the alarm
→ less dangerous unless source is inhaled or ingested
b-particles:
→ used to measure thickness of material
y-rays:
→ high penetrating power allows killing of bacteria and harmful cells
LIFE CYCLE OF A STAR
1) A star is formed from interstellar clouds of gas and dust that contain hydrogen
2) A protostar is an interstellar cloud collapsing and increasing in temperature as a result of its internal gravitational attraction
3) A protostar becomes a stable star when the inward force of gravitational attraction is balanced by an outward force due to the high temperature in the centre of the star
4) Most stars expand to form red giants & massive stars expand to form red supergiants when most of the hydrogen in the centre of the star → to helium
5) A red giant from a less massive star forms a planetary nebula with a white dwarf star at its centre
6) A red supergiant explodes as a supernova, forming a nebula containing hydrogen + new heavier elements, leaving behind a neutron star or a black hole at its centre
7) The nebula from a supernova may form new stars with orbiting planets
DEFINITION OF REDSHIFT
An increase in the observed wavelength of electromagnetic radiation emitted from receding stars and galaxies
DEFINITION OF HUBBLE CONSTANT
The ratio of the speed at which the galaxy is moving away from the Earth to its distance from the Earth
H = v/d & 2.2 × 10^–18 per second
This is evidence for the idea that all the matter in the Universe was present at a single point