Metric Systems , Gas Laws , Ideal Gas Law, & Combined Gas Law
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry Quiz #1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
1m =
100 cm & 1000 mm
1km =
1000m
1g =
100 cg & 1000 mg
1kg =
1000 g
1L =
100 cL , 1000 mL
1s =
1000 ms
5.2 cm to meters

2.48 × 10.3
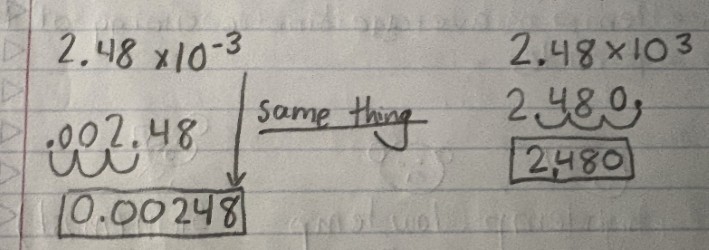
Assume that 1 atmosphere gas
0 degrees C
Equation for Boyle’s Law
Volume decreases, pressure increases (temp remains constant)
Volume increases, pressure decreases (temp remains the same)

Equation for Charle’s Law
Temperature increases particles move faster, volume increases (pressure remains constant)
Temperature decreases move more slowly, volume decreases (pressure remains constant)
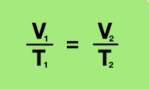
How do you convert Celsius to Kalvin?
K = C + 273
Equation Gay- Lussac’s Law
Pressure increases, temperature increases, particles move faster (volume constant)
Pressure decreases, temperature decreases, move slower (volume constant)
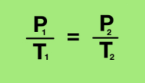
Quanity
of gas
Volume
gas which describes the amount of space the gas occupies
Temperature
gas which describes the average kinetic energy of the particles
Pressure
gas which describes the force and number of collisions of gas particles against the walls of its container.
1 kL
1000 L
Kinetic Molecular theory
Particles far away from each other
Constant random motion
No energy loss (elastic collision)
No attraction or repulsion
Temp proportional to average kinetic energy
STP
Standard Temperature and Pressure, defined as 0°C (273.15 K) and 1 atm pressure, used for gas calculations.
Chemical Reactions
Processes where reactants transform into products, involving breaking and forming of bonds.
Combined Gas Laws
The relationship between the pressure, volume, and temperature of a fixed amount of gas, combined from Boyle's, Charles's, and Avogadro's laws.
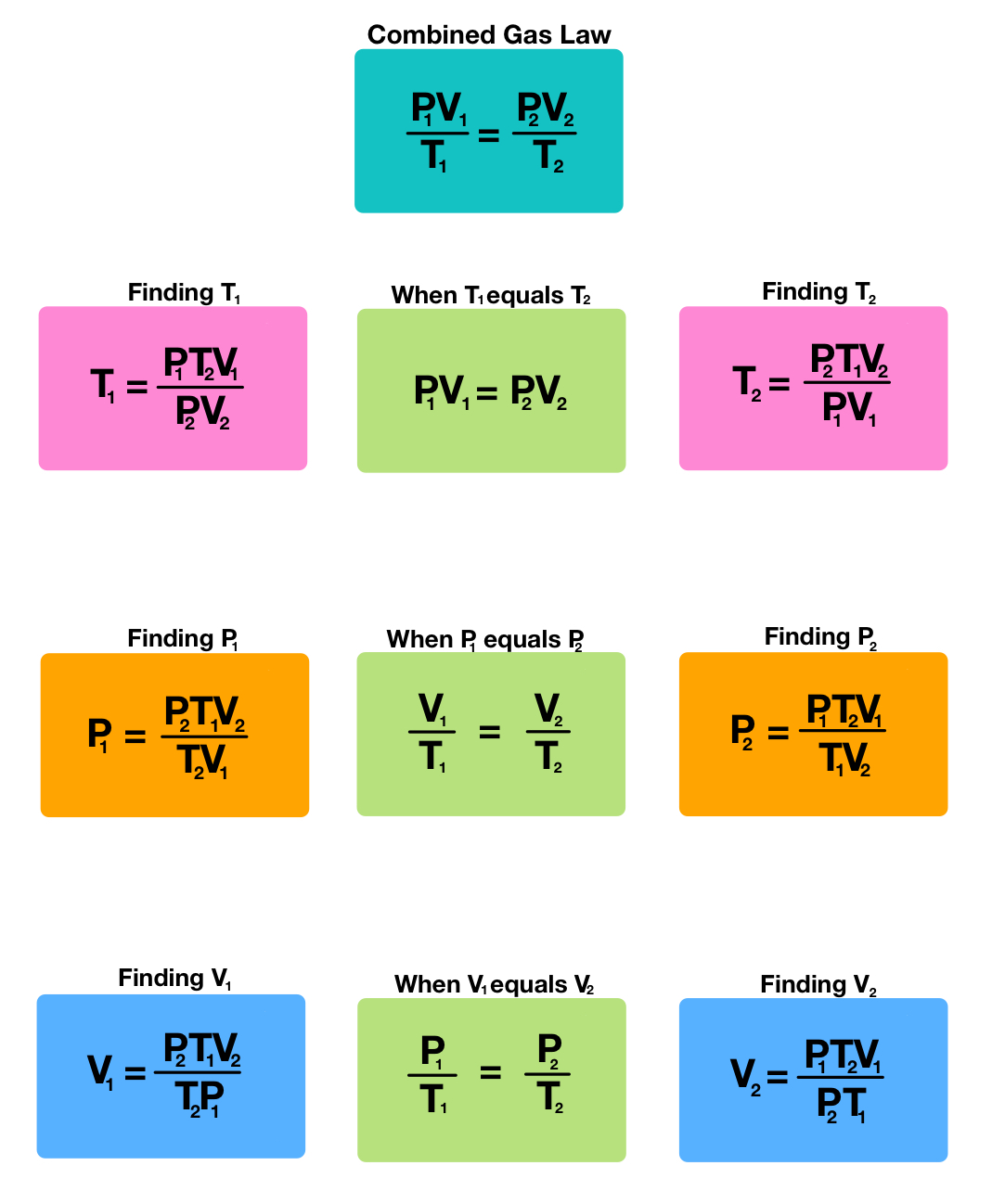
What equation do you need for T1

What equation do you need for P1
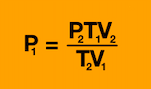
What equation do you need for V1

What equation do you need for T2

What equation do you need for P2
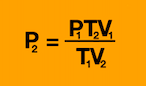
What equation do you need for V2
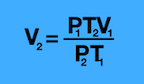
What is the only thing held constant in a combined gas law problem?
the amount of gas
Ideal Gas
A theoretical gas that perfectly follows the gas laws at all conditions, characterized by no intermolecular forces and that occupies no volume.
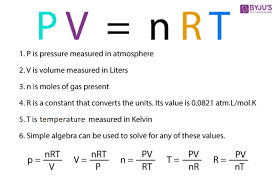
What equation do you need for N
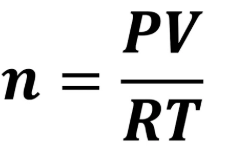
What equation do you need for V
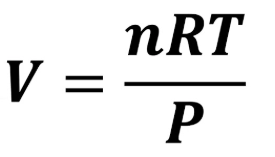
What equation do you need for P
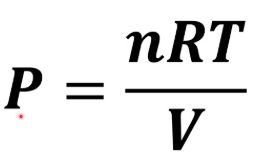
What equation do you need for T
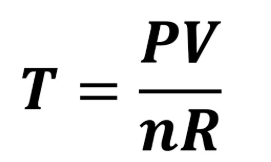
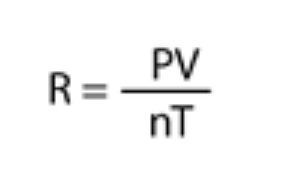
What equation do you need for R
In a combined gas law what can happen to the variables?
They can change while maintaining the relationship defined by the law.