D1.1 DNA replication SL
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
DNA replication
Producing exact copies of DNA with identical base sequences
What is DNA replication needed for in multicellular organisms?
Reproduction
Growth + tissue replacement
What type of process is DNA replication?
Semi-conservative
Why is DNA replication a semi-conservative process?
Due to complementary base pairings
How is DNA a semi-conservative process?
Each newly synthesized double-stranded DNA molecule contains 1 og strand + 1 newly synthesized strand
Bc each parent strand acts as a template for DNA replication → determines order of bases → prevents errors
What does the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication + complementary base pairings allow for? and how?
High degree of accuracy in copying base sequences
Why is the semi-conservative nature of DNA replication important? (use slides)
2 important enzymes in DNA replication
Helicase
DNA polymerase
Helicase
Enzyme that unwinds (DNA double helix) + breaks hydrogen bonds betw DNA strands
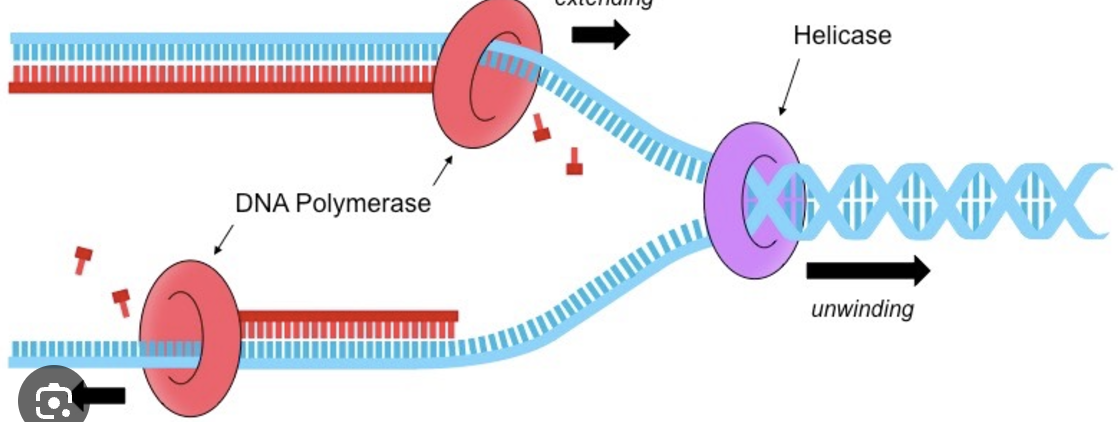
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that adds complementary bases / free DNA nucleotides to the template strands → creates new DNA strands (2 full DNA strands)
Moves along template strand
Adds free nucleotides to the new strand, creating a bond betw the phosphate of the free nucleotide + the sugar of the last nucleotide on the strand
Controls addition of free nucleotides to the developing DNA strand
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Amplifies DNA
Takes small quantity of DNA → copies al the nucleotides → makes millions copies of DNA
Only amplifies a targeted section of DNA
What is required for polymerase chain reaction?
Primers
Temp changes
Taq polymerase (enzyme)
Nucleotides
DNA samples
In PCR, what is added to the DNA sample instead of helicase + how?
Heat
Heat breaks hydrogen. bonds between parent strands
Primer
Short segment of DNA
Signals where to start copying
Complementary to the nucleotides at 1 end of the target DNA to be copied
Taq polymerase
Heat tolerant DNA polymerase enzyme
Taq = bacteria living in hot springs → heat resistant enzymes
Heat doesn’t denature the enzyme
What does Taq polymerase do in PCR?
Synthesizes new DNA strands by adding free nucleotides to a single-stranded DNA template
Why does Taq polymerase need to be heat resistant?
Needs to withstand high temps used to denature DNA
No need to add new enzymes after each cycle
What allows for fast replication in PCR?
Alternating heat (to break H bonds) + cooling (for binding)
3 steps of PCR
Denaturation
Annealing
Elongation
What happens in denaturation in the PCR process?
DNA is heated to separate the strands
H bonds holding the 2 strands of DNA (backbone) tog break
So bases are freely exposed
What happens in annealing in the PCR process?
Sample cooled down
Primers bind to specific (nucleotide) sequences on each of the single-stranded DNA.
What happens in elongation / extension in the PCR process?
Sample heated
Taq polymerase catalyses the building of new DNA strands by extending the primers + adding free nucleotides
Entire cycle is repeated
How much DNA does each cycle of PCR produce?
Each cycle of PCR doubles the amount of DNA
2^n
Gel electrophoresis
Separates DNA fragments
What does gel electrophoresis separate DNA based on?
Separated fragments of DNA according to size
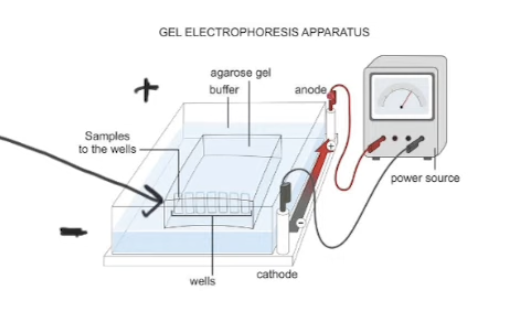
Steps of gel electrophoresis
Put fragments of DNA into 1 end of a porous gel
Apply electric current
Negative electrode must be at DNA end
Why does gel electrophoresis work when an electric current is applied?
DNA also negative
So negative end of electrode repels DNA
Repelling force moves DNA through the gel
Which fragments of DNA move further through the gel?
Shorter fragments
Applications of PCR + gel electrophoresis
DNA profiling for paternity + forensic investigations
Applications of PCR to test for coronavirus
Take swab + isolate viral RNA
Reverse transcribe. Use RNA to make DNA
PCR to amplify DNA + add fluorescent dyes to specific base sequences
Pros + cons of PCR to test for coronavirus
Pros
Specific, sensitive
Cons
Expensive, time-consuming
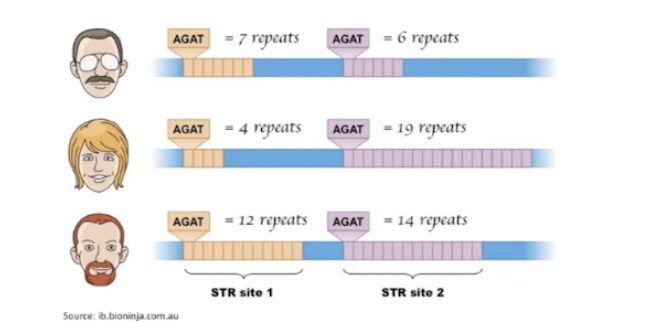
Short tandem repeats
Repeats of a certain sequence of bases
Diff people have diff no.s of those repeats
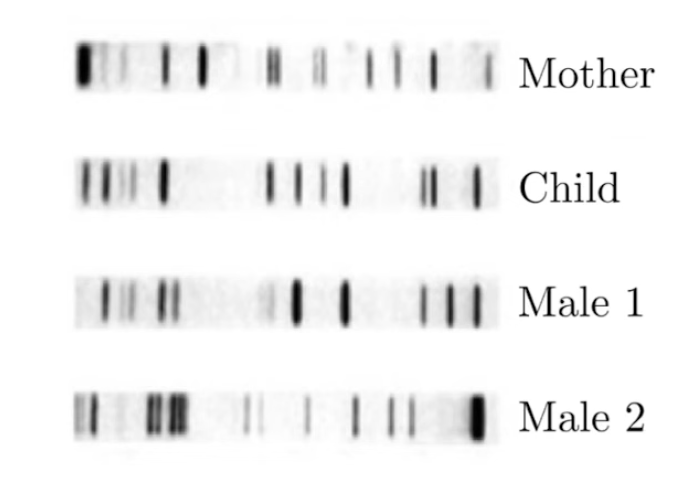
How is PCR + gel electrophoresis used for paternity testing?
Isolate short tandem repeats (using enzymes)
PCR to amplify the sample (of tandem repeats)
Separate them using GE
GE creates unique banding patterns for each individual
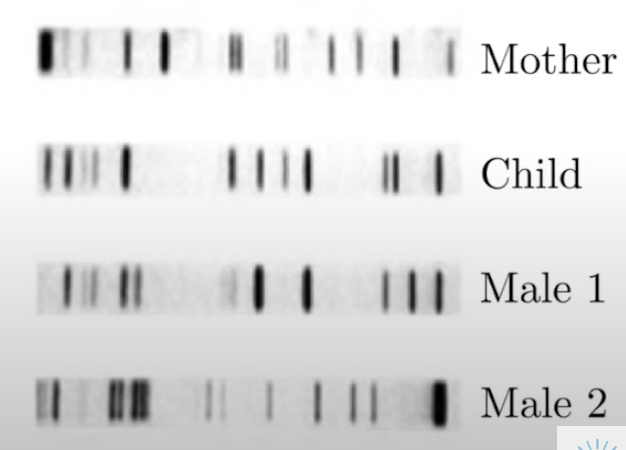
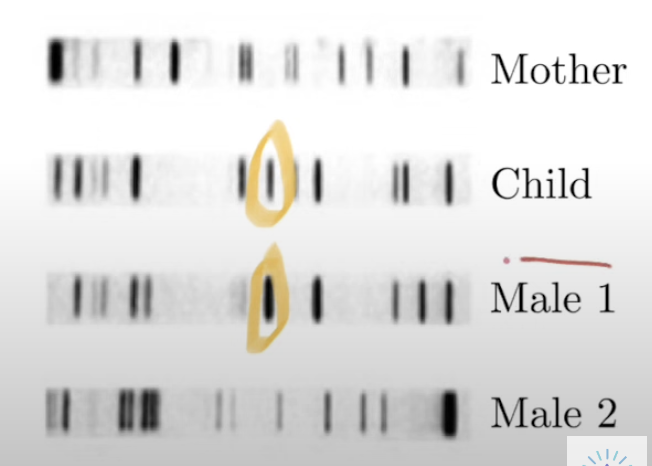
How to identify the parent of a child using banding patterns from gel electrophoresis?
Child gets ½ DNA from mom, ½ from dad
Ignore pieces of DNA that come from mom
Look at pieces of DNA that could come from other parent
½ bands identical with dad, ½ identical with mom
Process of DNA replication
complete
What enhances reliability in experiements>
Increase the no. of measurements in the test
In DNA profiling, how does increasing the number of markers used help?
Reduces the probability of a false match