MCAT organic chemistry 1-4
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
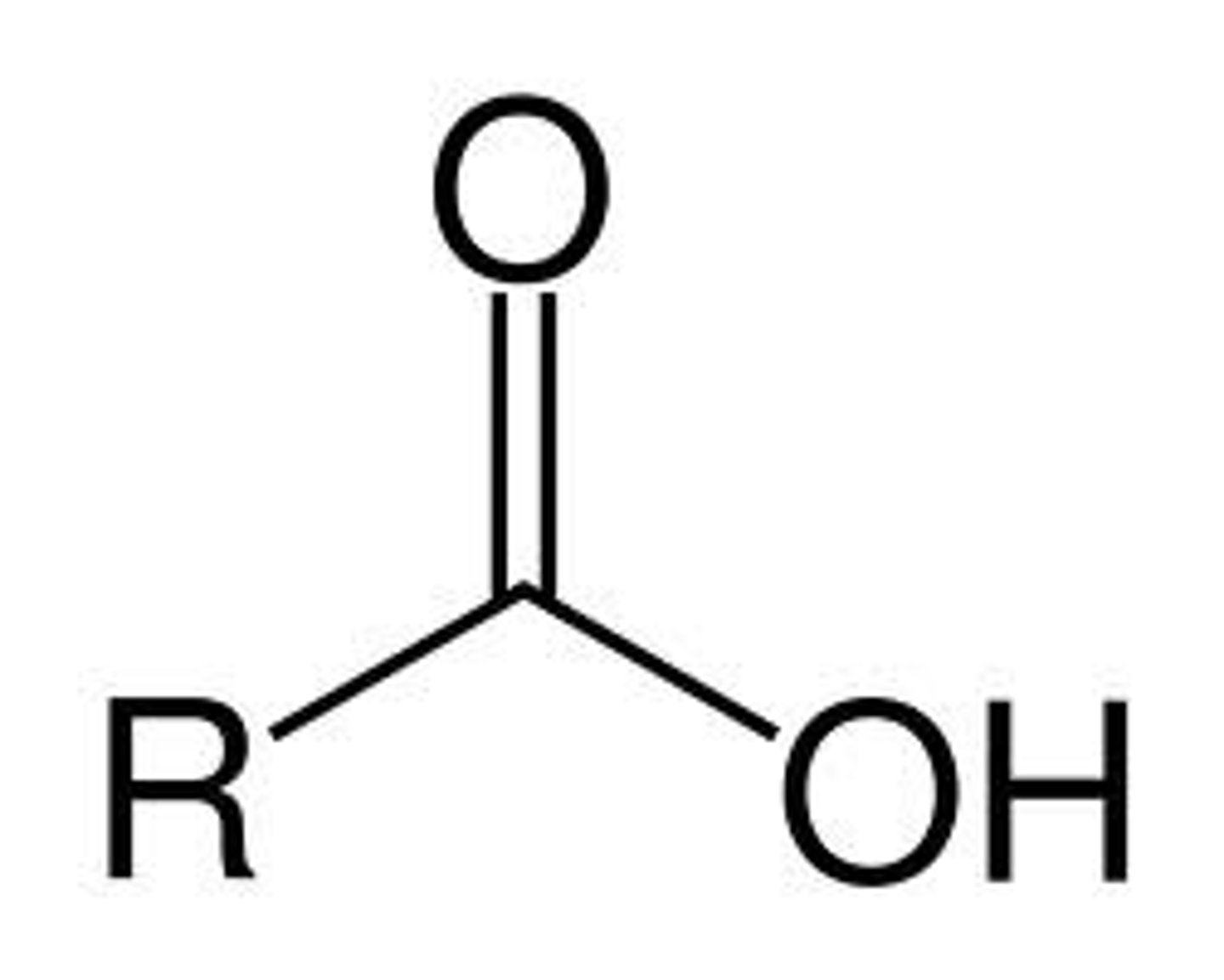
1. carboxylic acid
2. anhydride
3. ester
4. amide
5. aldehyde
6. ketone
7. alcohol
8. alkene or alkyne
9. alkane
functional group priority groups
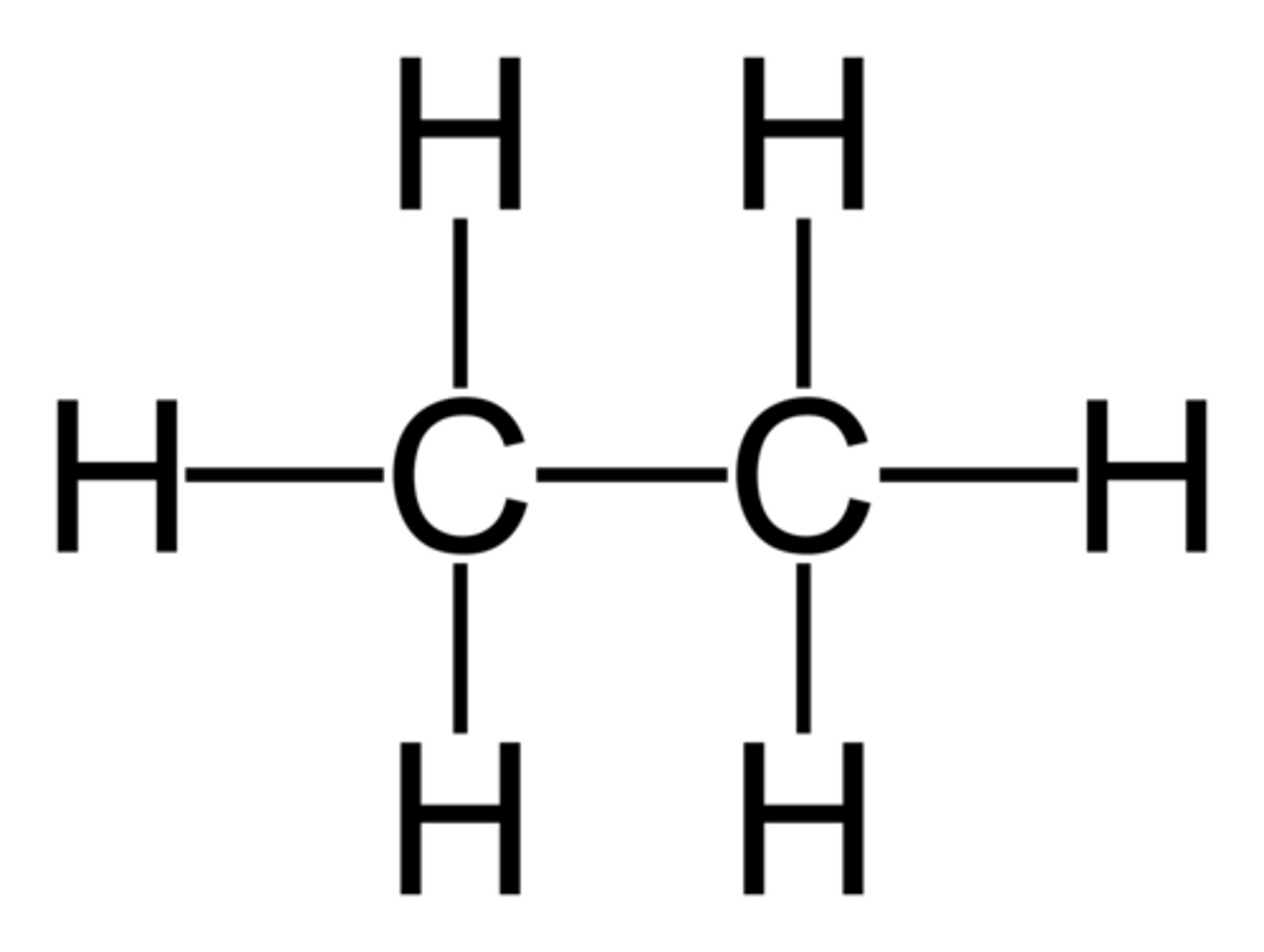
alkane
ane
Alkene
ene
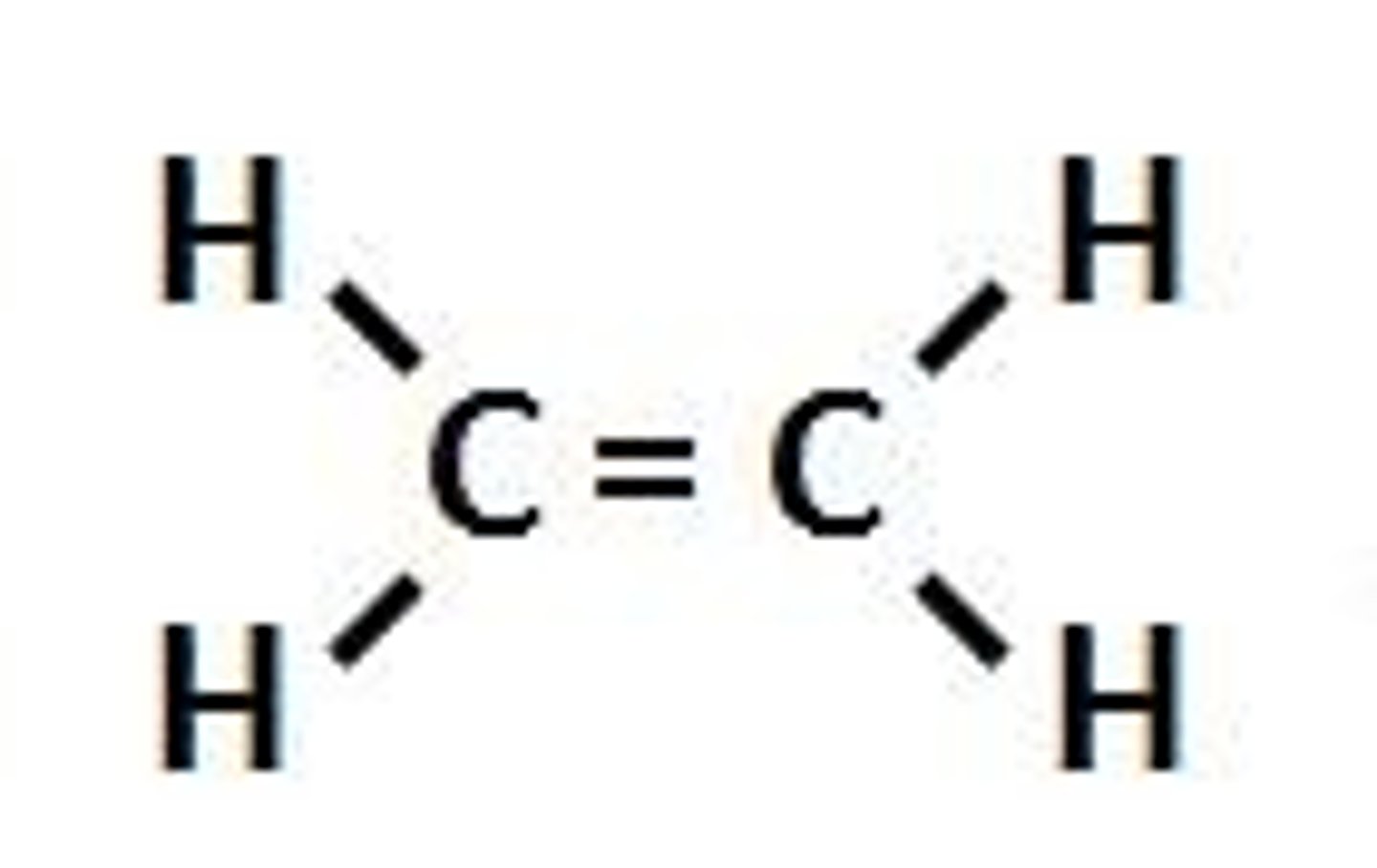
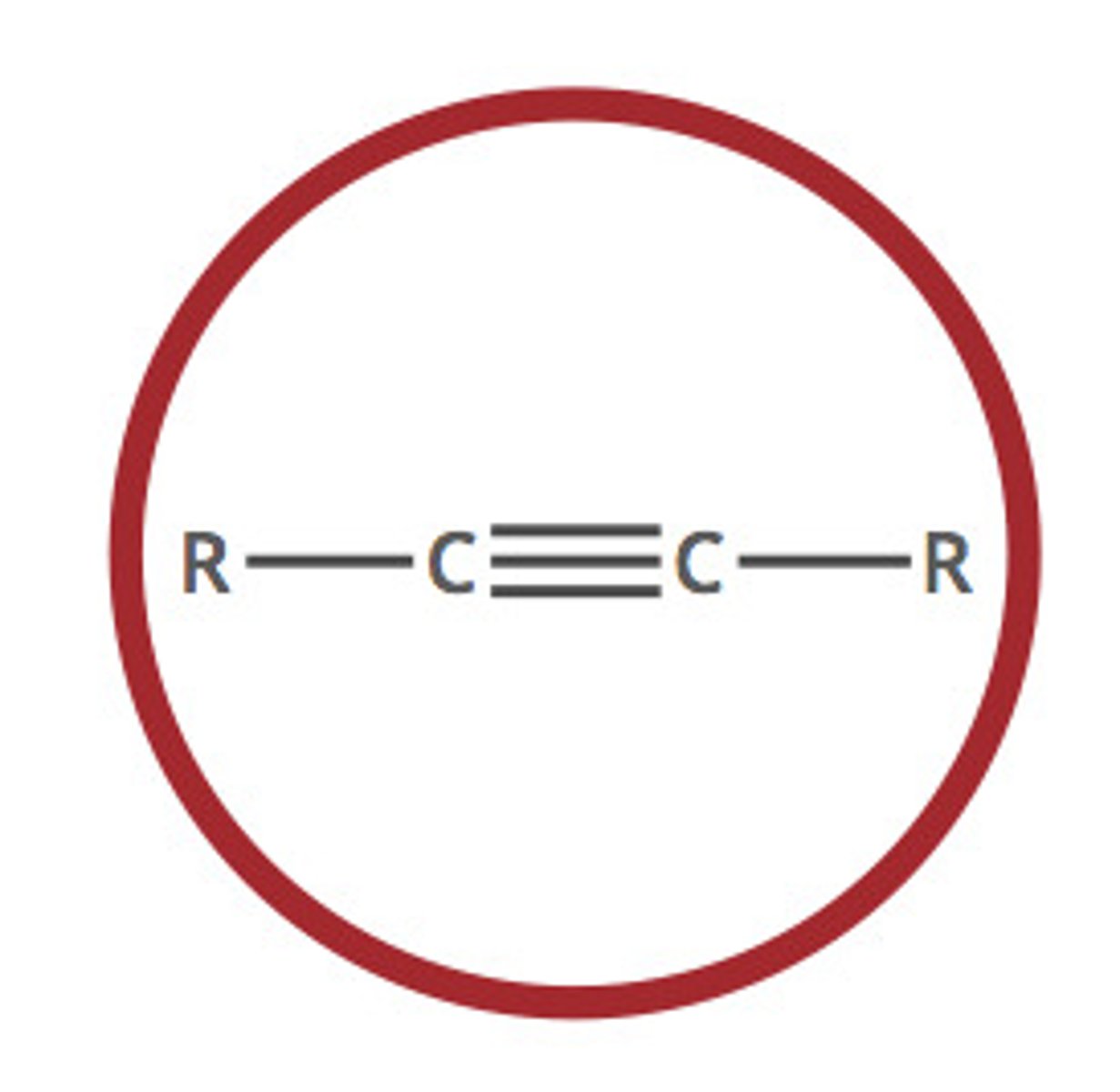
alkyne
yne
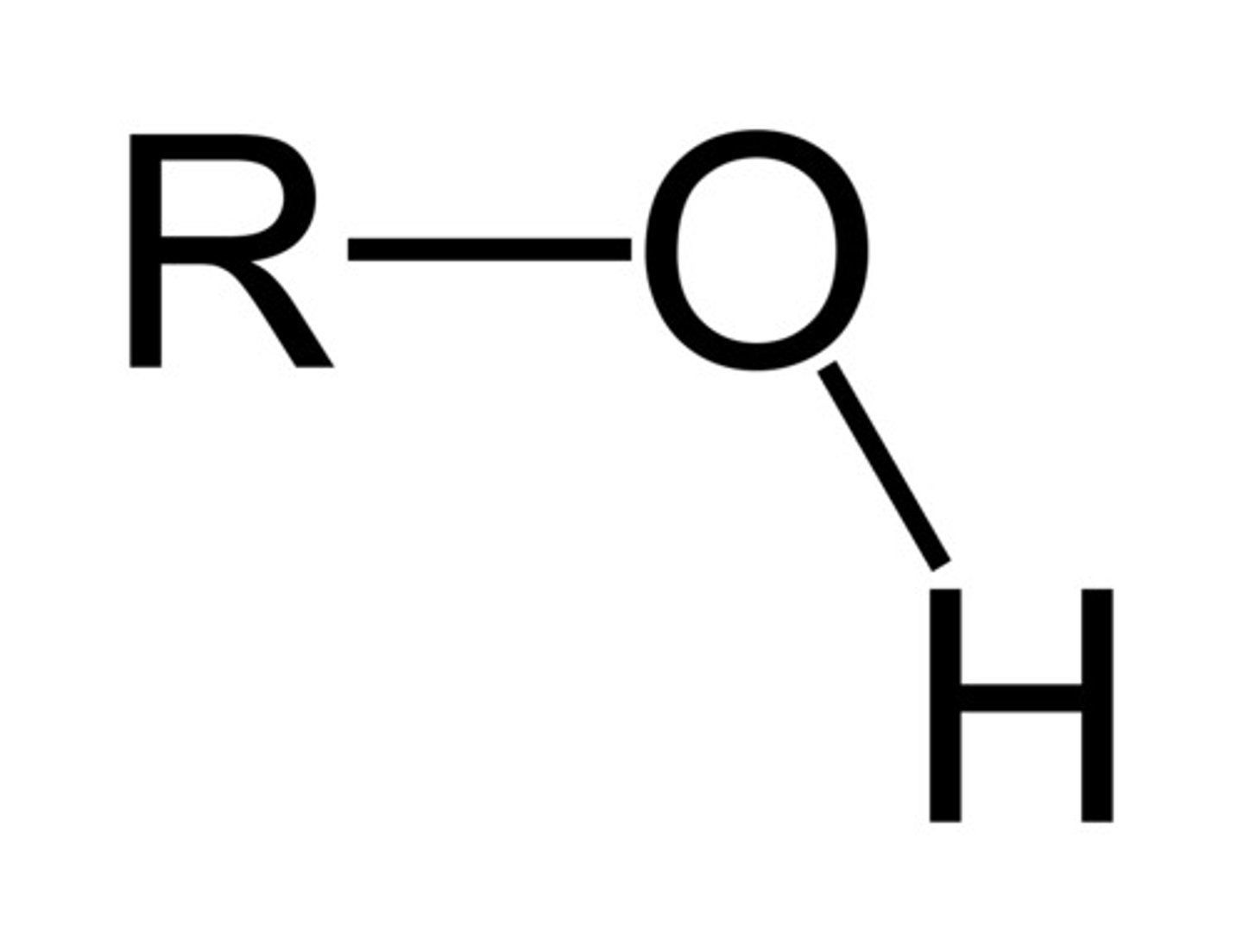
alcohol
-ol
hydroxy-
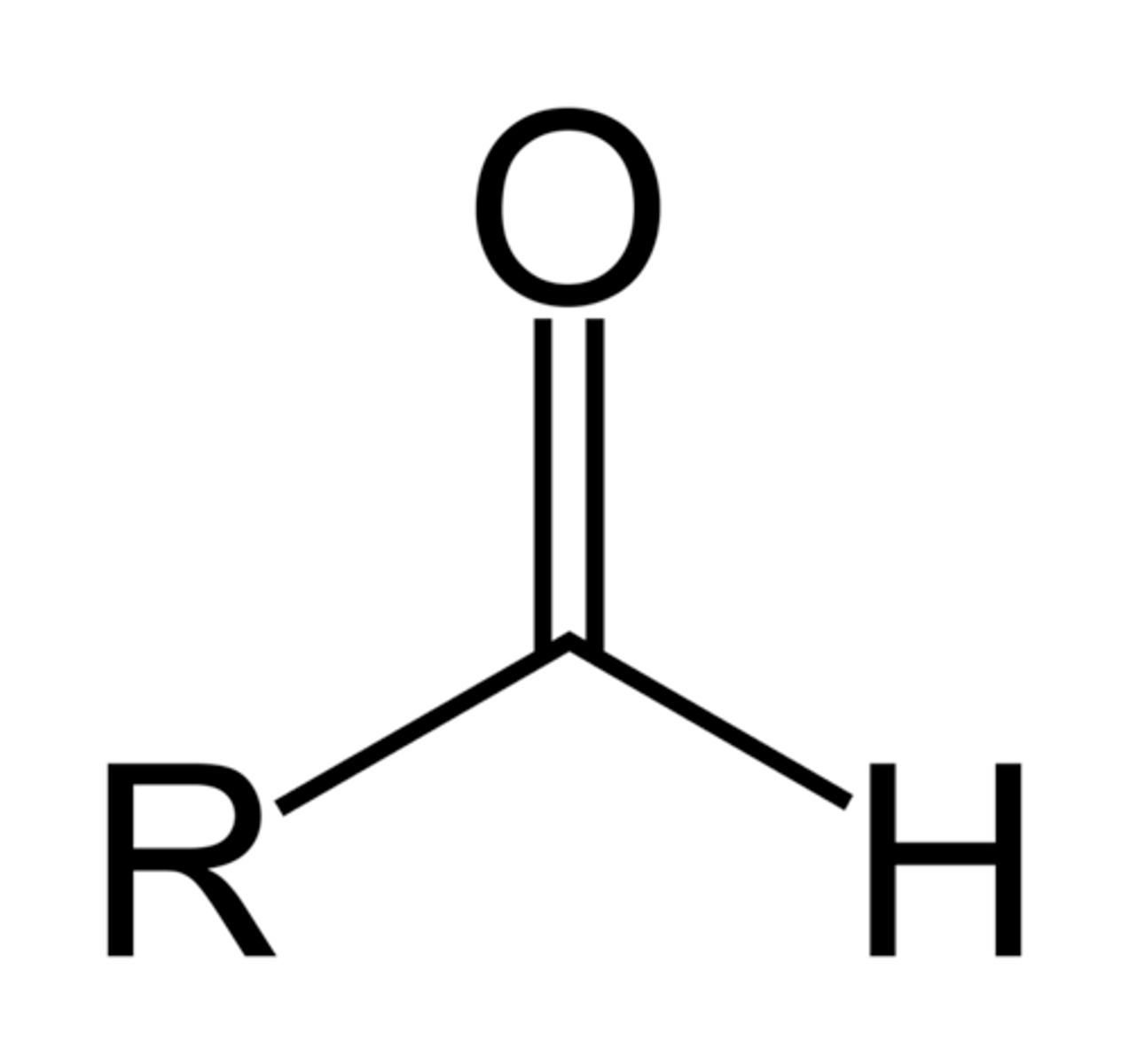
aldehyde
-al
oxo-
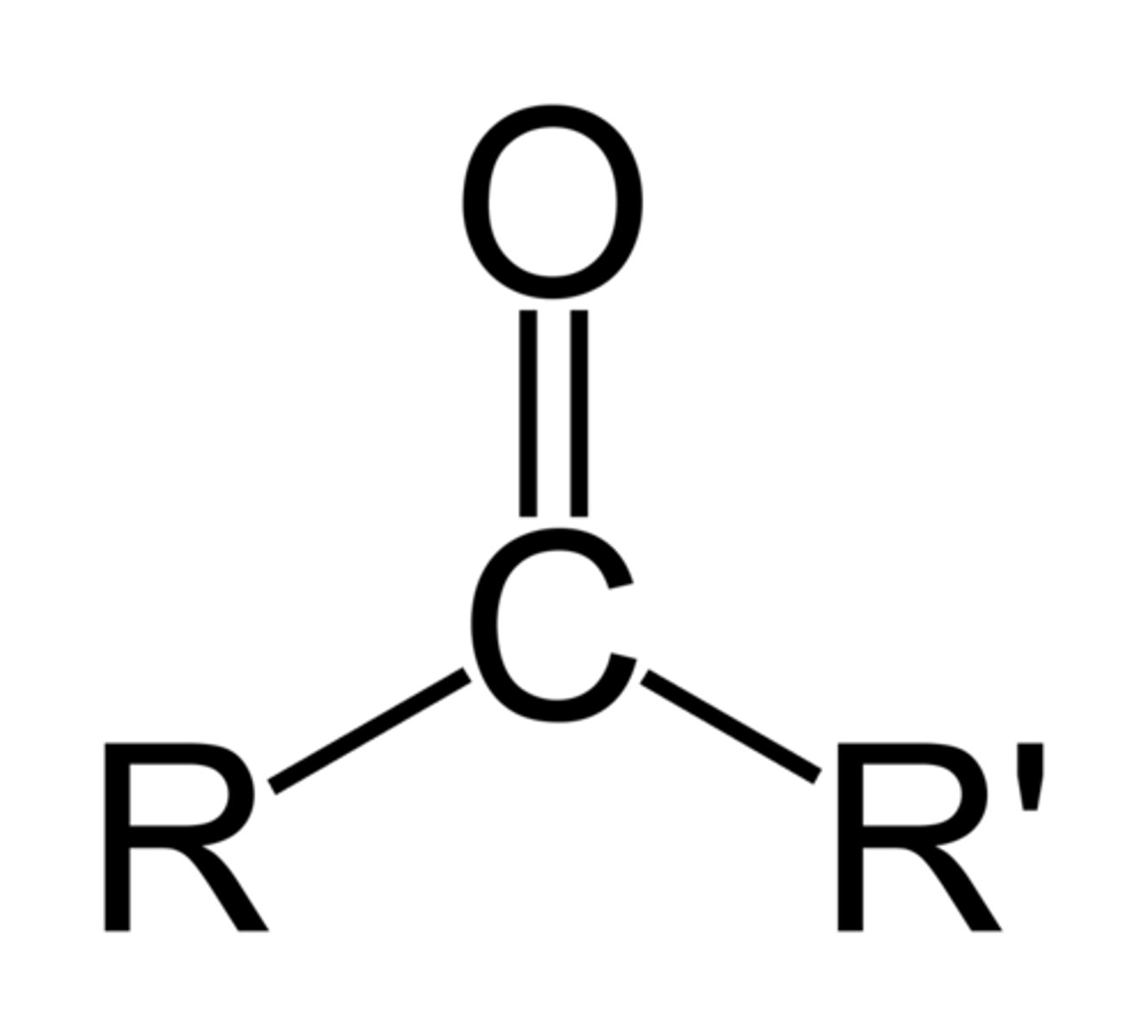
ketone
-one
oxo-
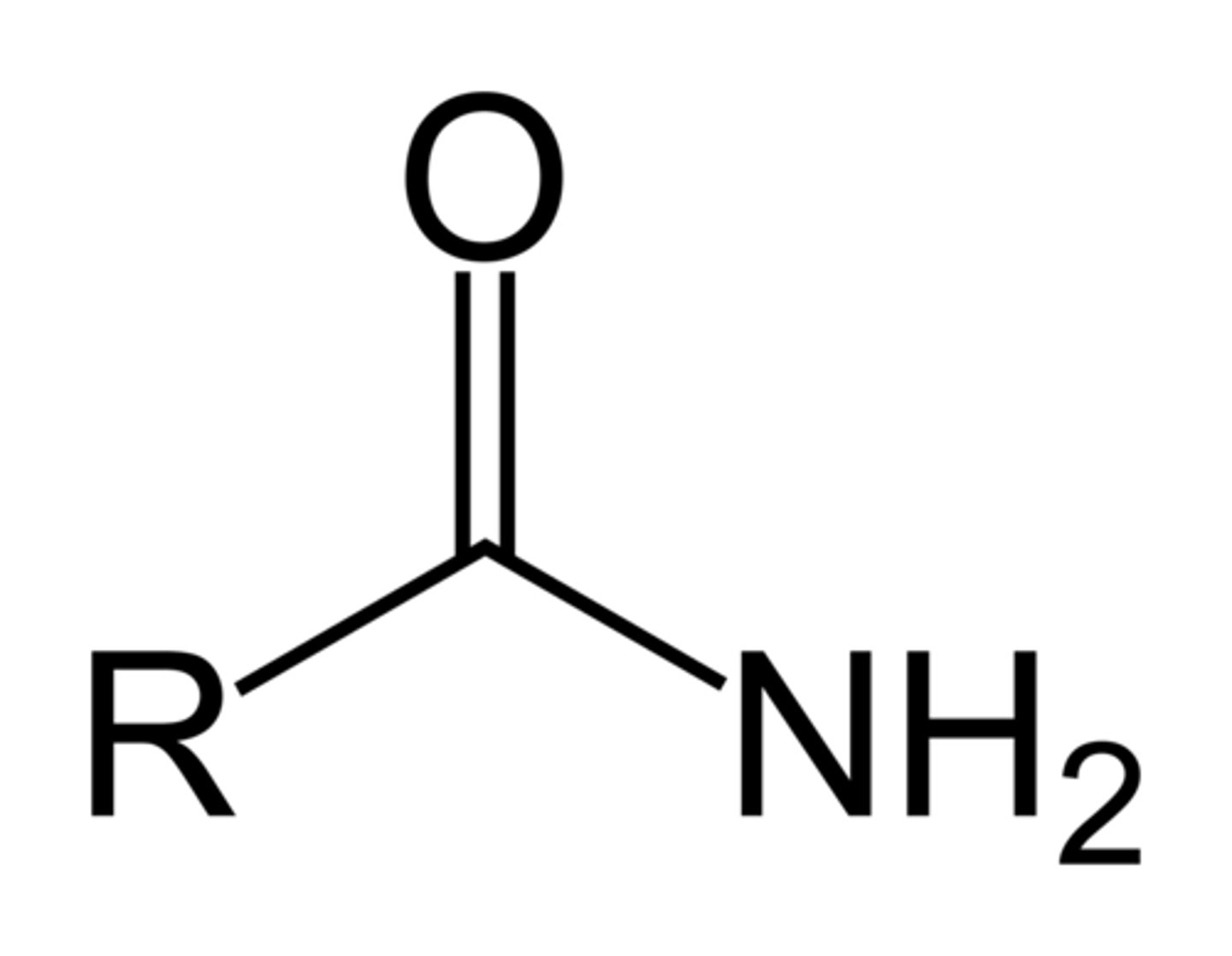
amide
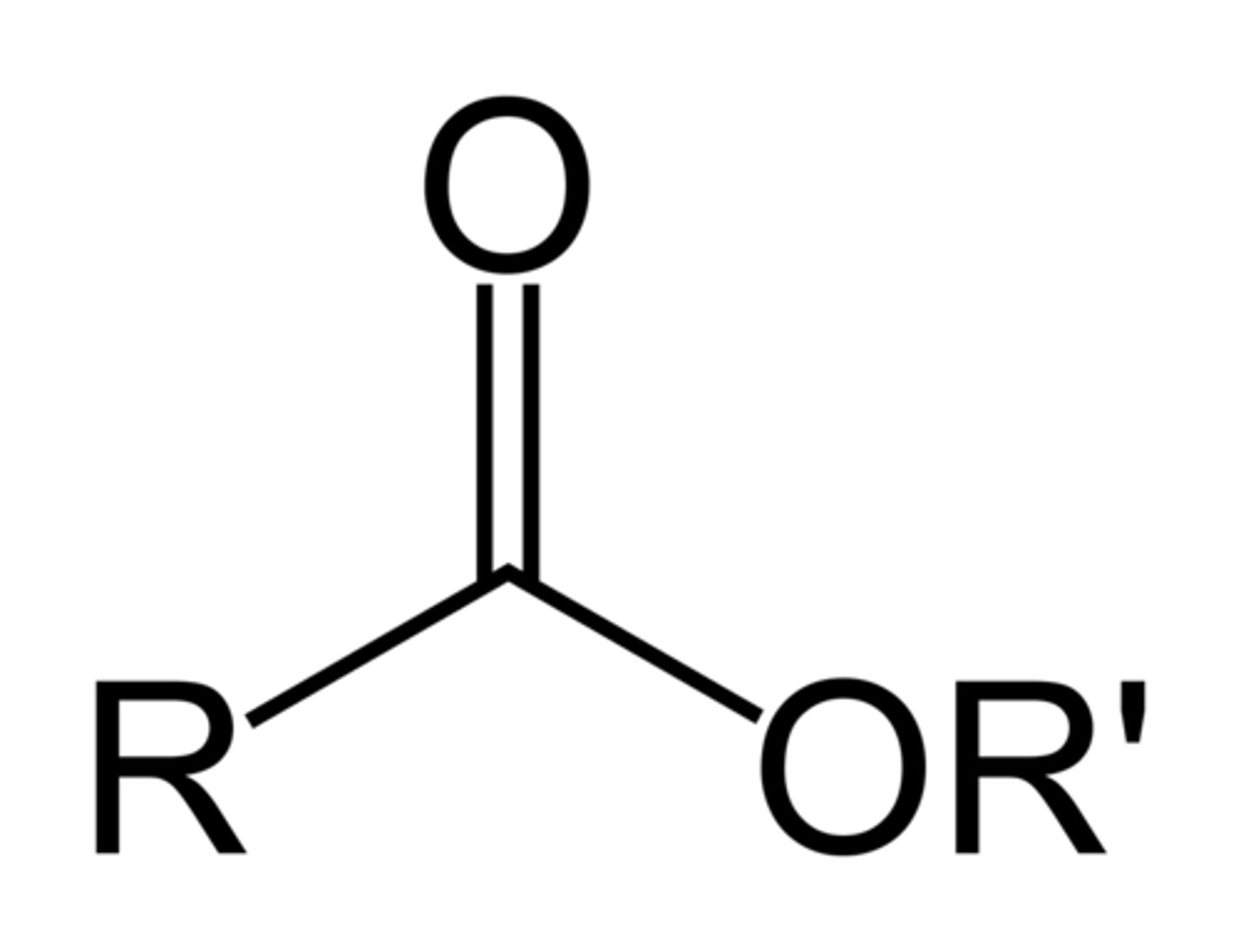
ester
-oate
alkoxycarbonyl-
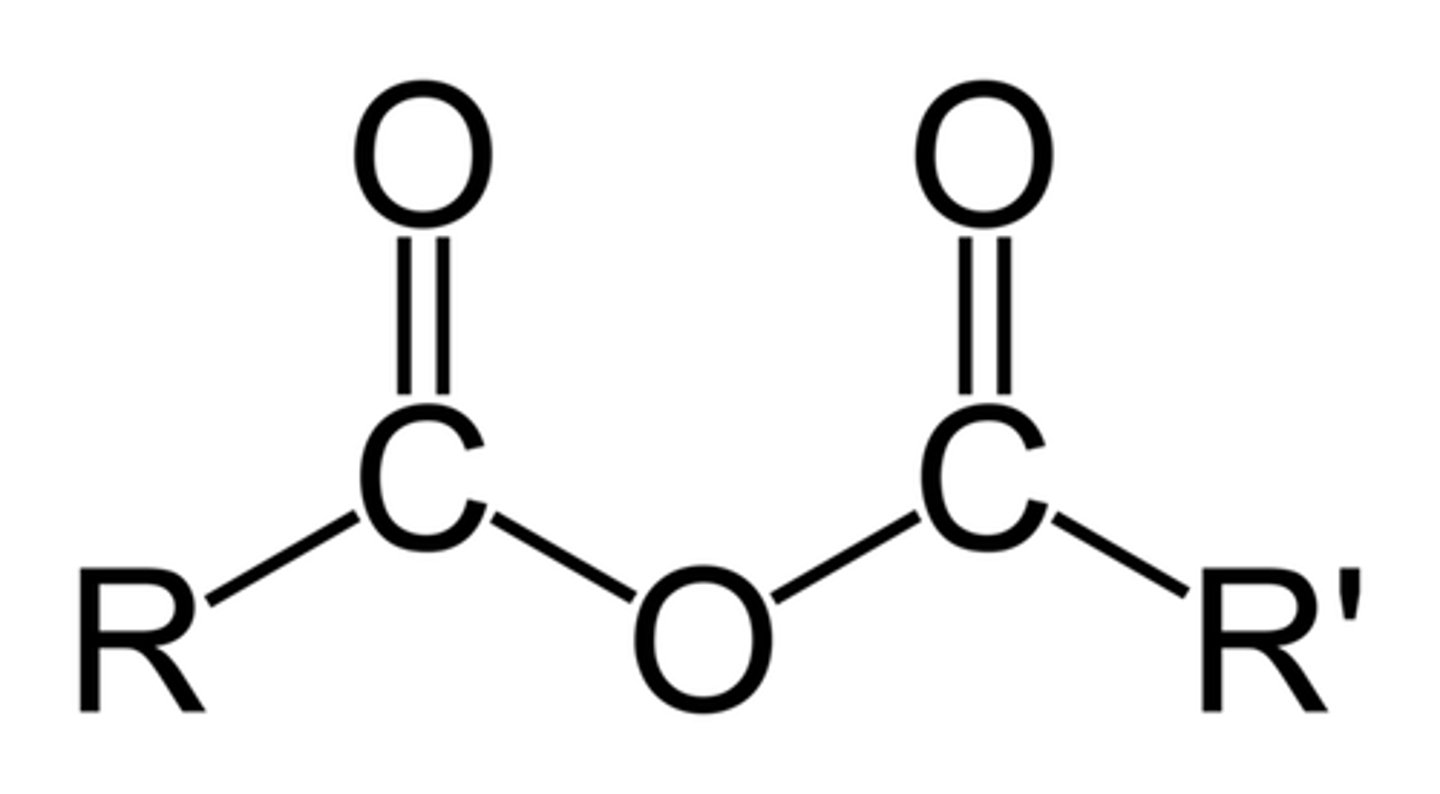
annhydride
reactive toward nucleophiles
carboxylic acid
-oic acid
carboxy-
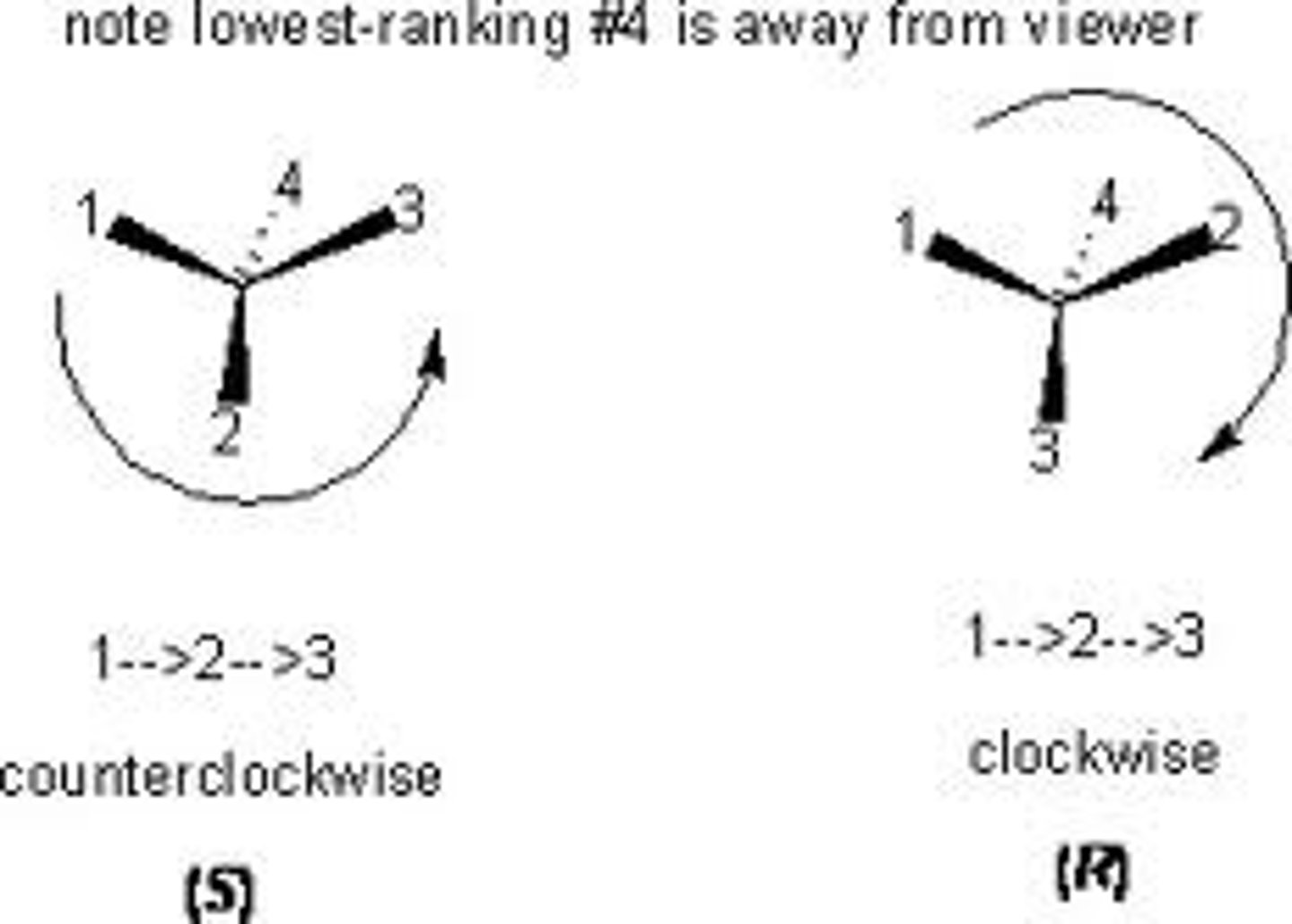
structural, conformational, configurational, enantiomers, diastereomers, cis/trans
isomers
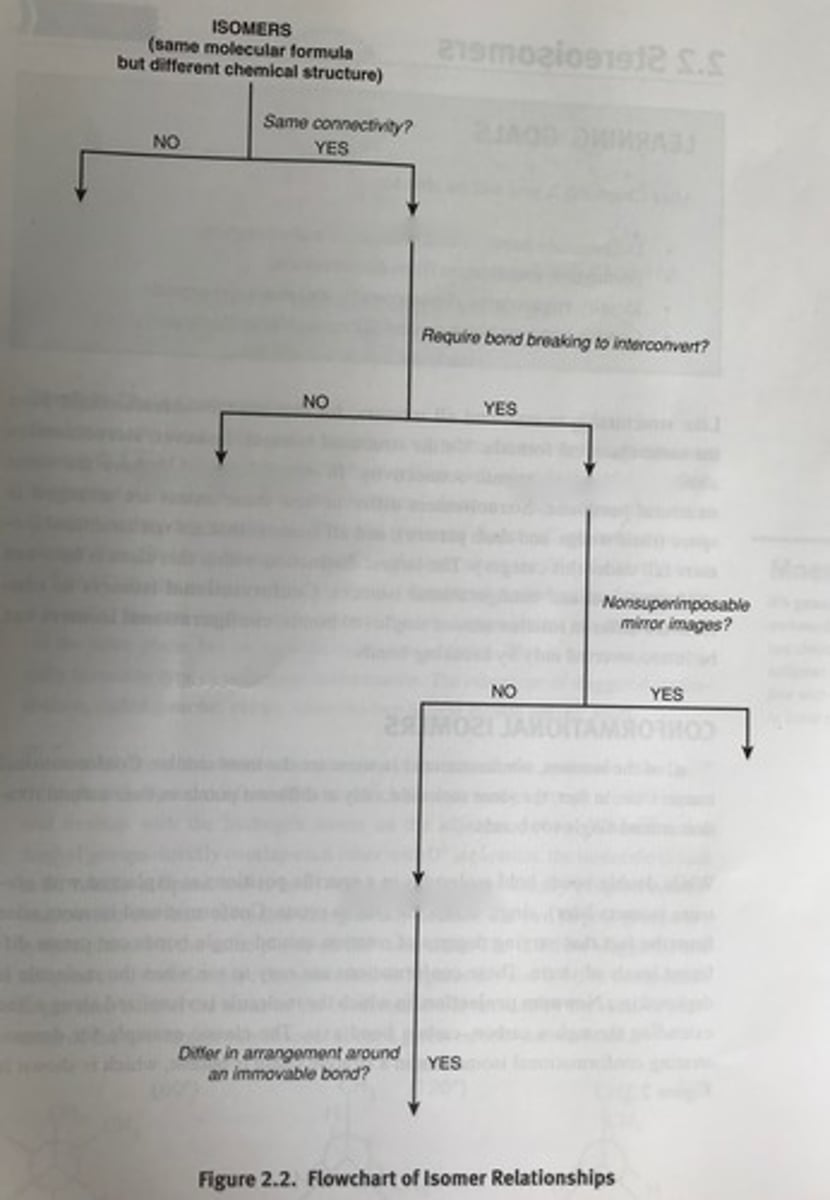
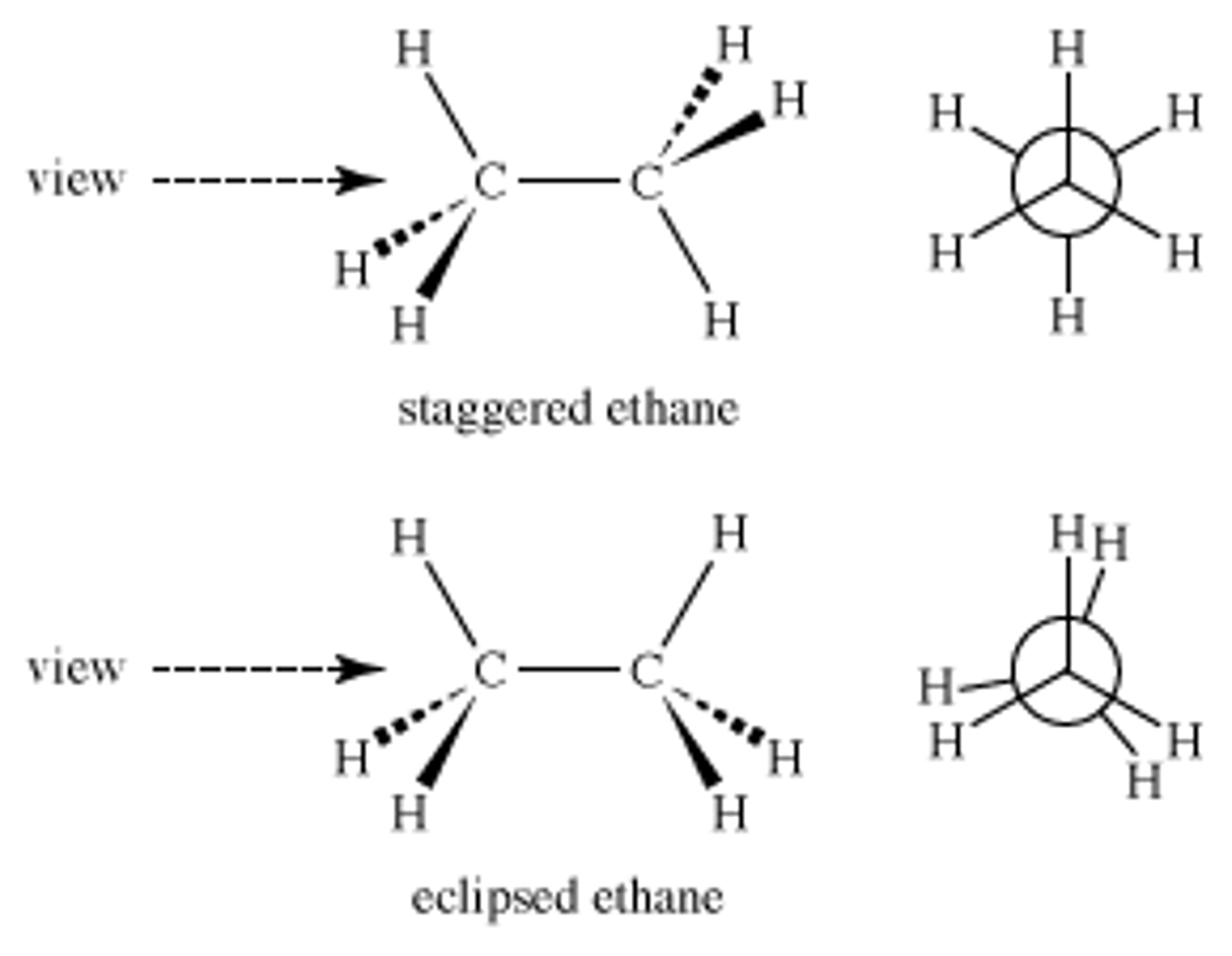
differ around a rotation on a sigma bond
conformational isomers
have to make/break bonds
configurational isomers
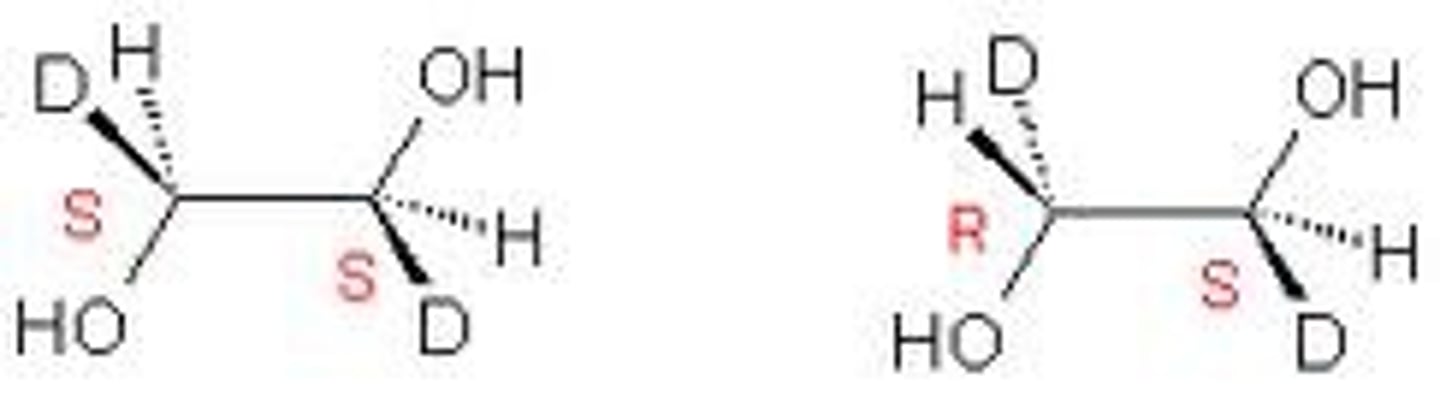
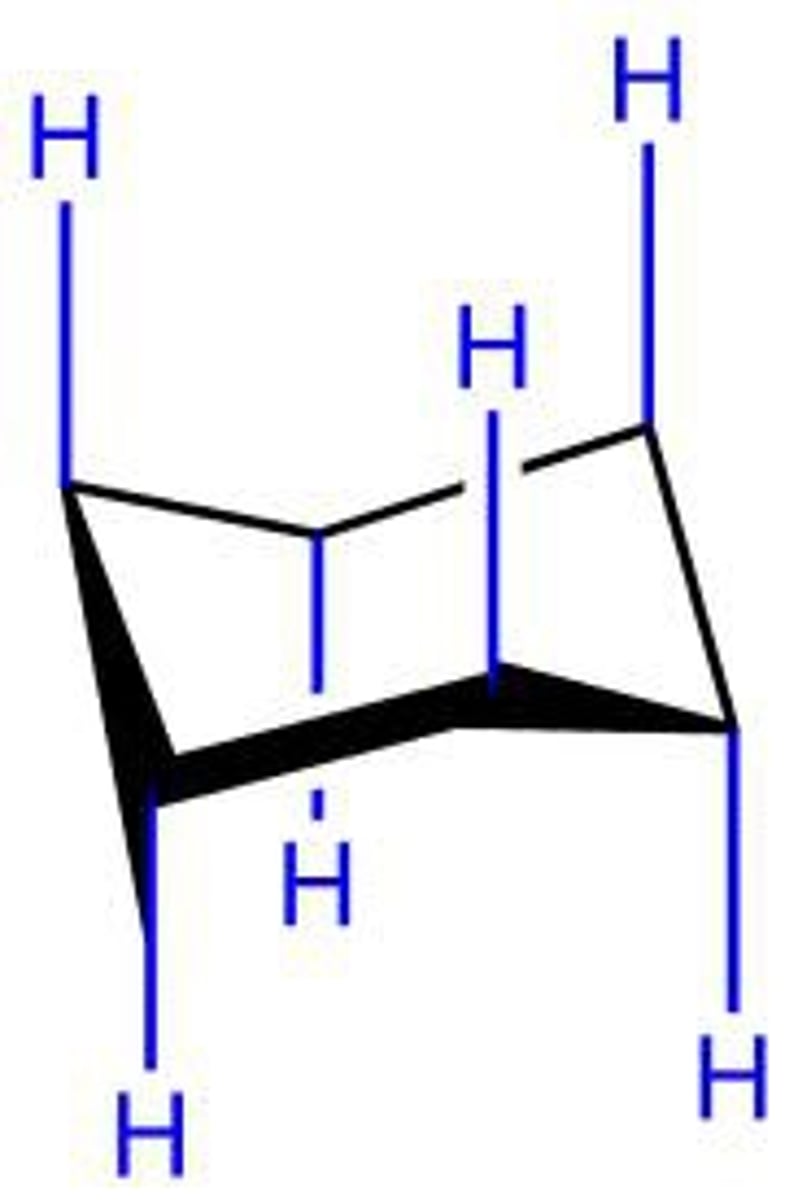
equatorial bond
a bond to a chair conformation of cyclohexane that extends from the ring roughly perpendicular to the imaginary axis through the center of the ring; a bond that lies roughly along the equator of the ring
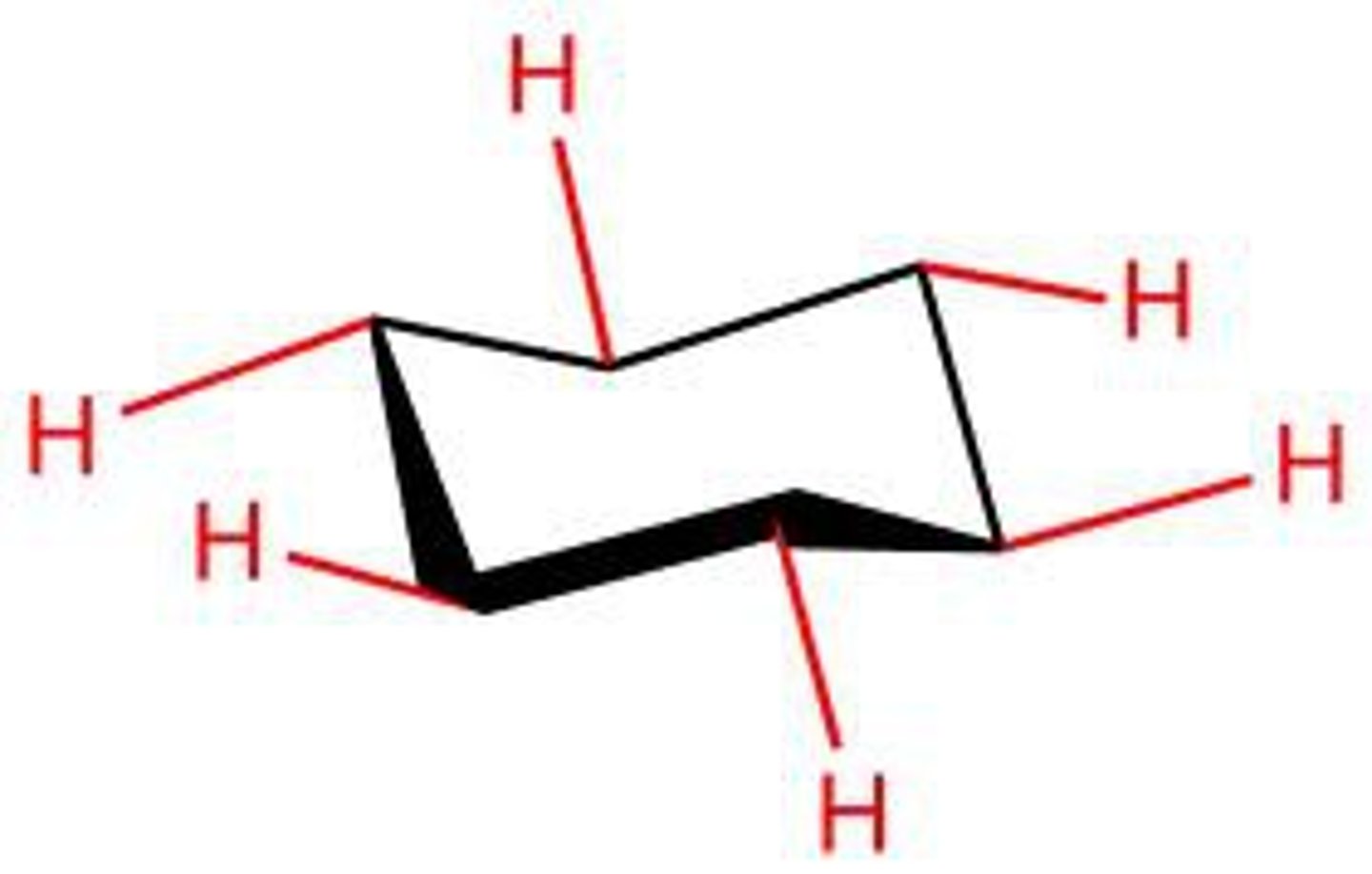
axial bond
a bond of the chair conformer of cyclohexane that points directly up or directly down
relative configuration
gives the stereochemistry of a compound in comparison to another molecule
absolute configuration
-determined by the 3D arrangement of the groups attached to the chiral carbon
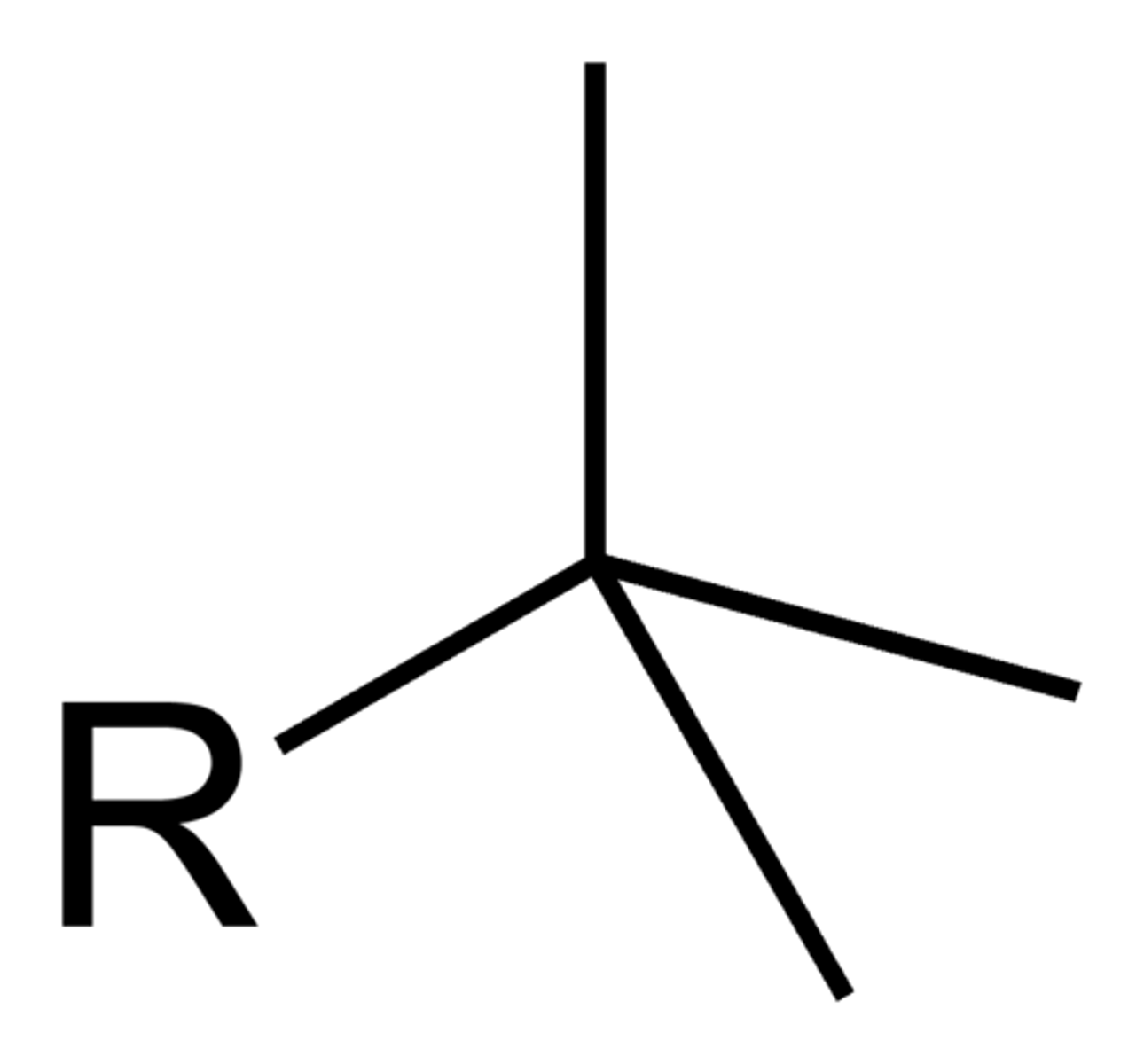
t-butyl
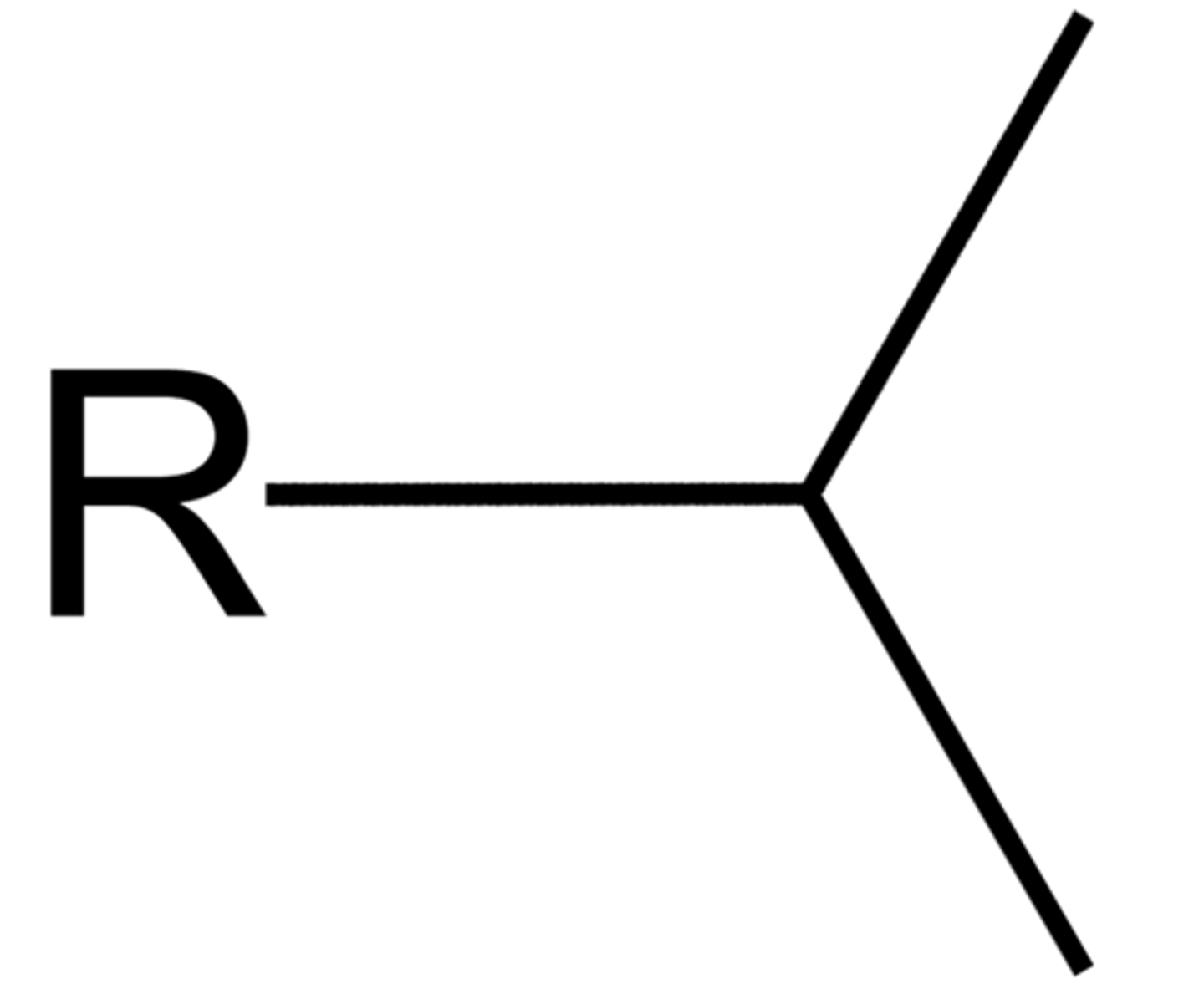
isopropyl
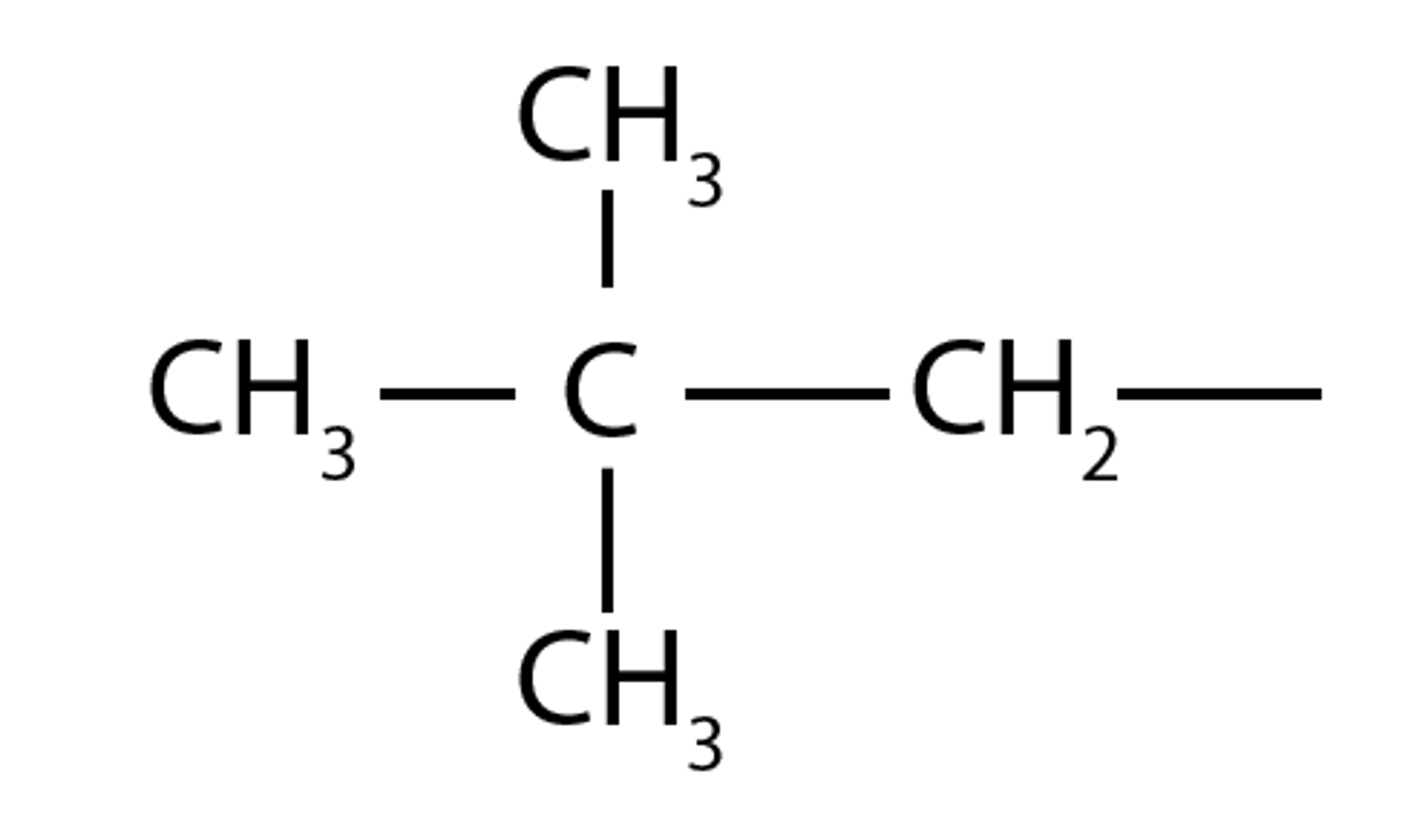
neopentyl
isobutyl
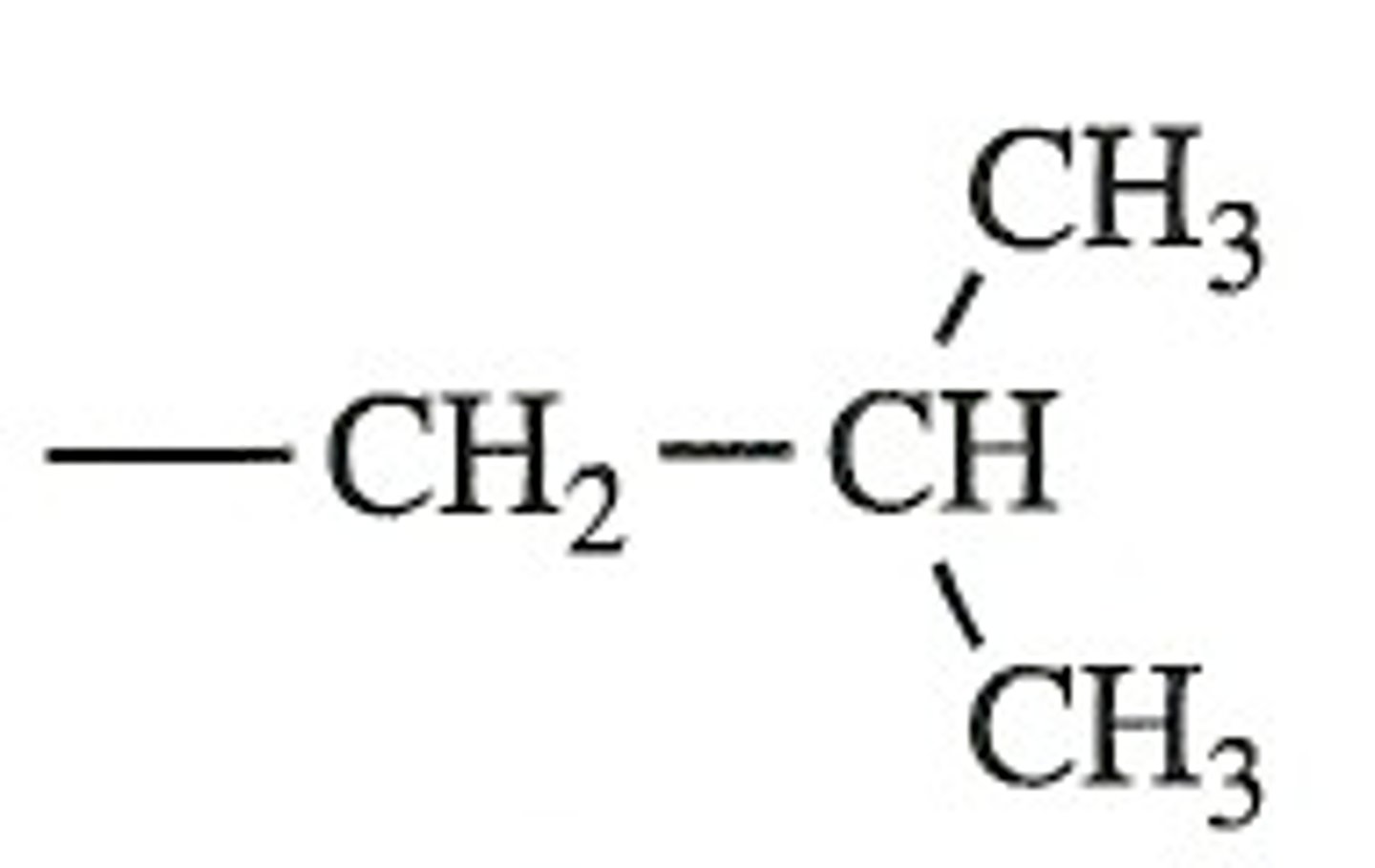
sec-butyl
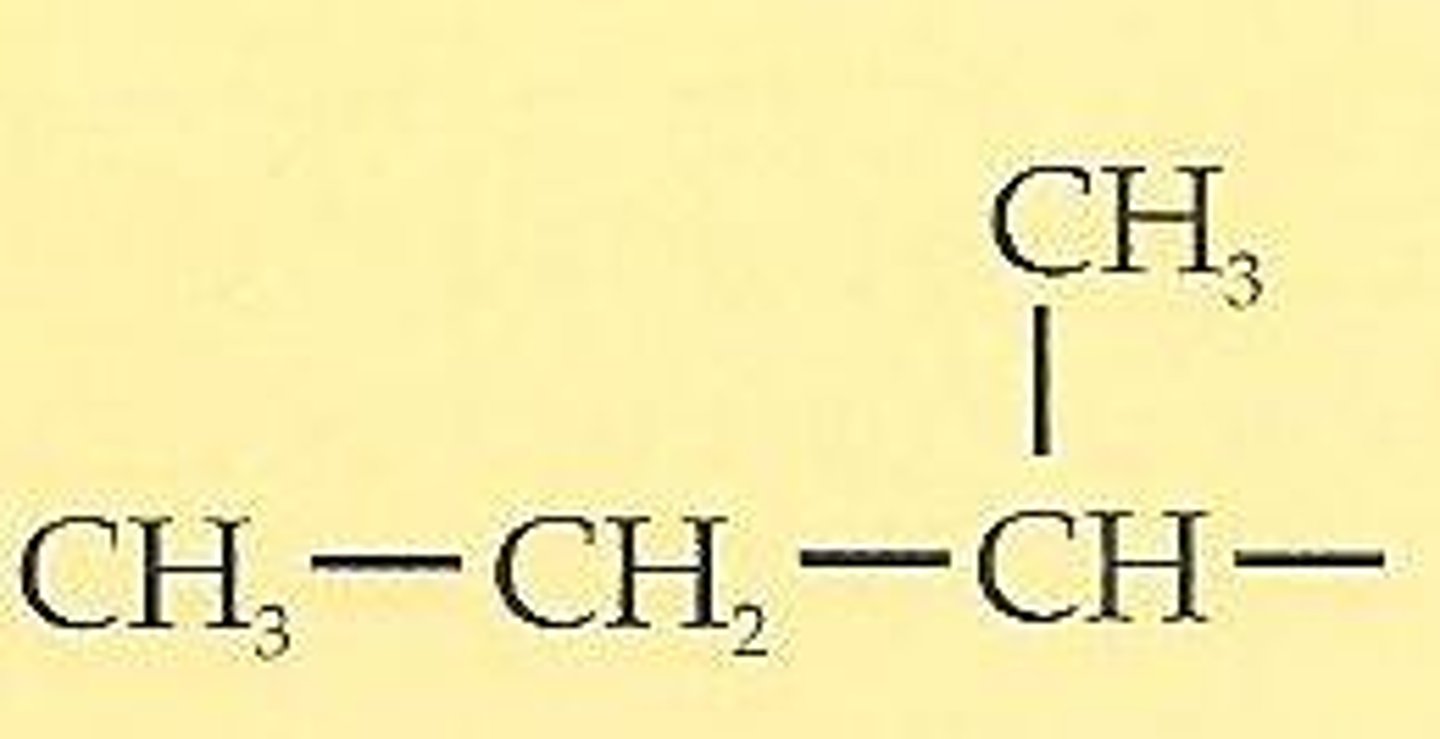
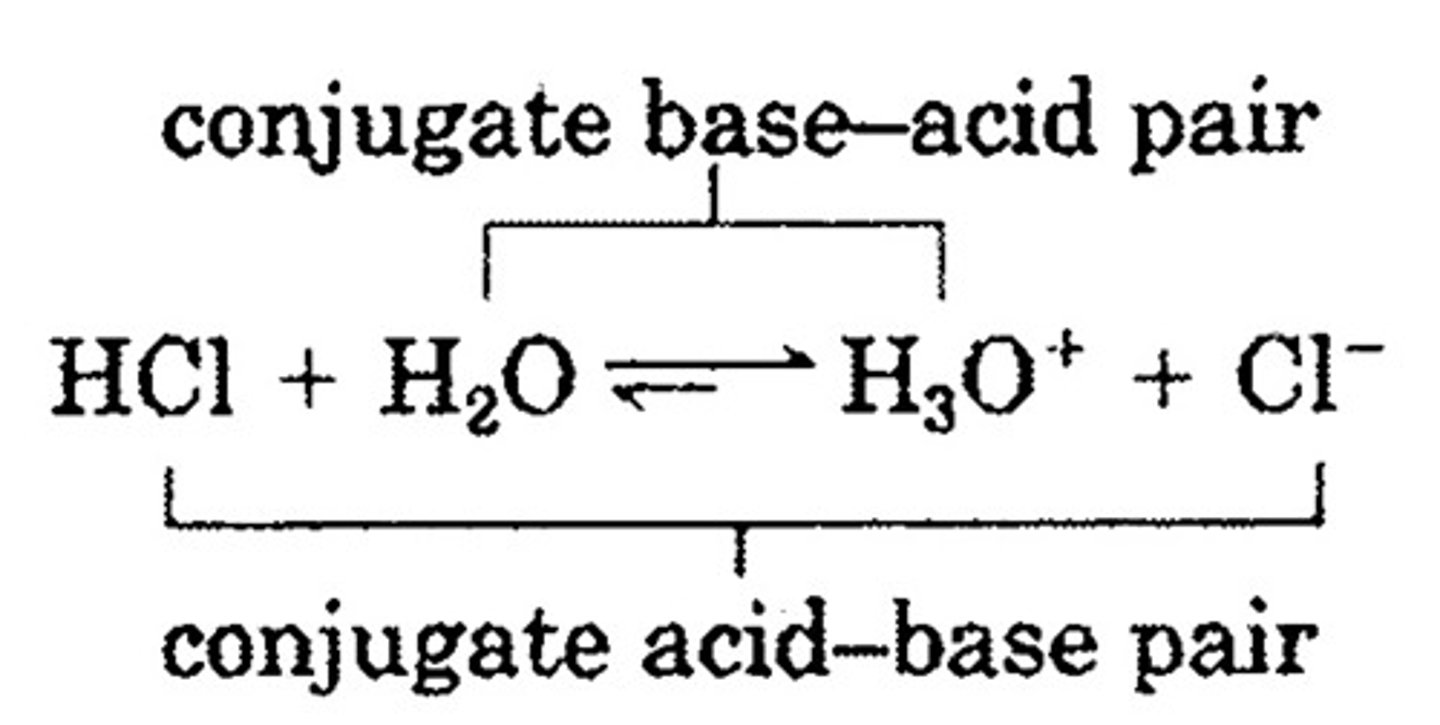
bronstead-lowry acid
proton donor
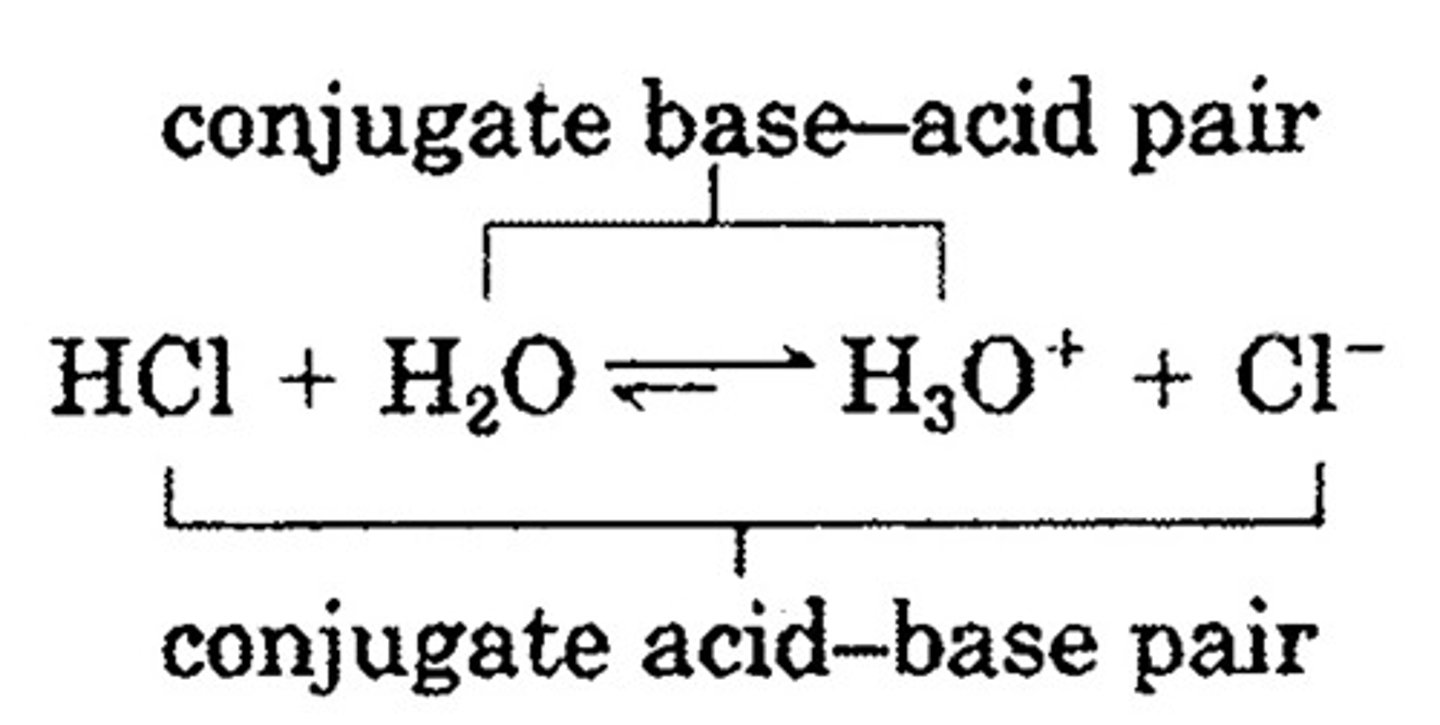
bronstead lowry base
proton acceptor
lewis acid
electron acceptor
lewis base
electron pair donor
pKa = -logKa
pKa equation
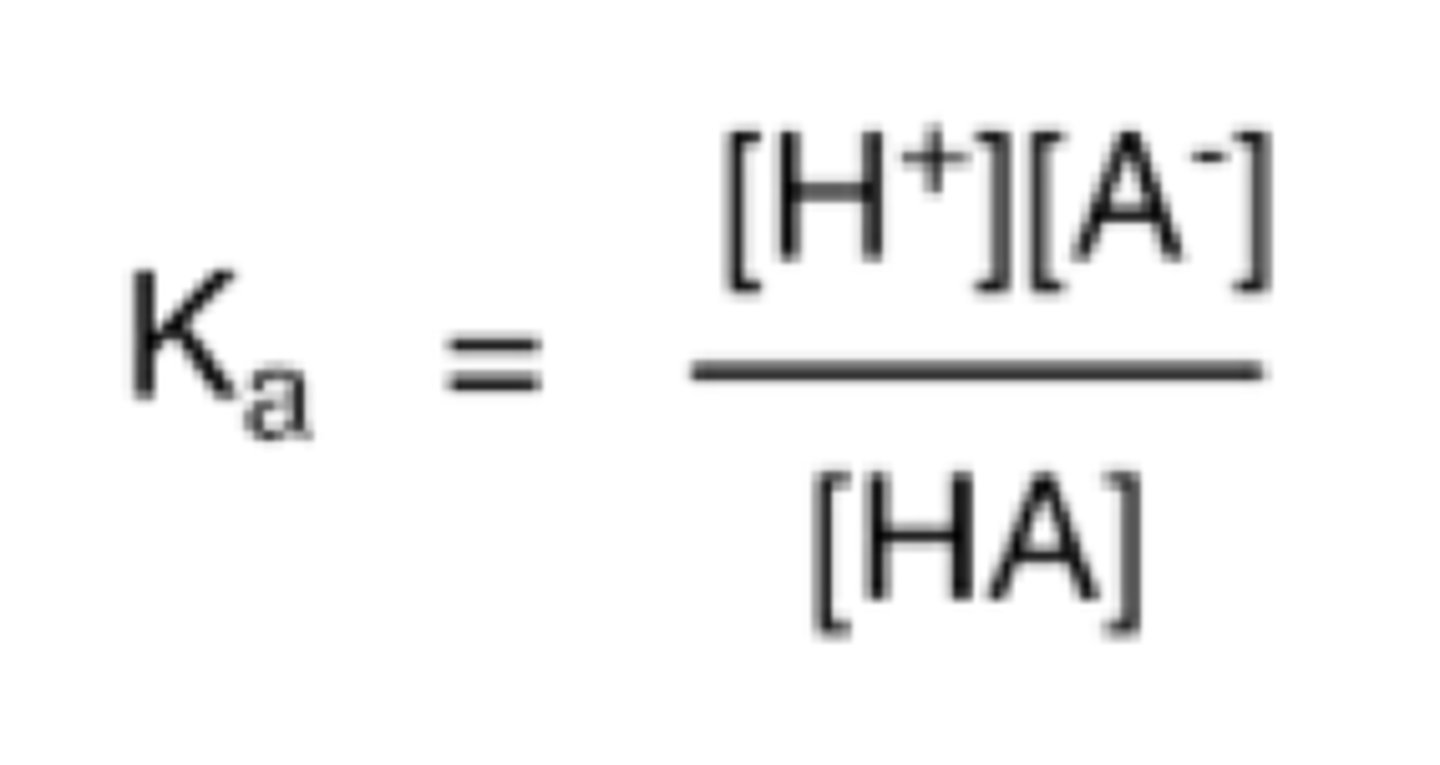
high pKa
weak acid, strong base
low pKa
strong acid and weak base
Alkane, alkene, hydrogen, alkyne, ester, ketone/aldehyde, alcohols, carboxylic acid, hydronium ion
weak to strong acids
determined by 4 factors : charge, electronegativity, steric hinderance, solvent
Nucleophilicity
anions, lone pairs and pi bonds
nucleophiles have
protic solvents
water, methanol, ethanol, ammonia, acetic acid
aprotic solvent
one that cannot donate protons (hydrogen ions) in an acid-base reaction
examples of aprotic solvents
DMF, DMSO, acetone
nucleophilicity increases down periodic table
trends in protic solvent
Electrophile
electron pair acceptor
leaving group
Atom or group that departs during a reaction.
carbonyl carbon
common reactive site
oxidation
increase in oxygen bonds, decrease in hydrogen bonding
Primary alcohol to aldehyde
PCC
primary alcohol to carboxylic acid
H2CrO4