CNS Depressants and Muscle Relaxants
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
SEDATIVES
•Sedatives
•Drugs that have an inhibitory effect on the CNS to the degree that they reduce:
•Nervousness
•Excitability
•Irritability
HYPNOTICS
•Cause sleep
•Much more potent effect on CNS than sedatives
•A sedative can become a hypnotic if it is given in large enough doses.
•Sedative-hypnotics:
DOSE DEPENDENT
LOW VS HIGH DOSES
•At low doses, calm the CNS without inducing sleep.
•At high doses, calm the CNS to the point of causing sleep.
3 GROUPS
•Barbiturates
•Benzodiazepines
•Miscellaneous drugs
CNS Depressants: Benzodiazepines
•Formerly the most prescribed sedative-hypnotic drugs
•Favorable adverse effect profiles, efficacy, and safety when used appropriately
•Non-benzodiazepines are currently more frequently prescribed.
Benzodiazepines:Mechanism of Action
•Depress CNS activity
•Affect hypothalamic, thalamic, and limbic systems of the brain
•Benzodiazepine receptors: Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
•Do not suppress rapid eye movement (REM) sleep as much as barbiturates do
•Do not increase metabolism of other drugs
Benzodiazepines: Drug Effects
•Calming effect on the CNS
•Useful in controlling agitation and anxiety
•Reduce excessive sensory stimulation, inducing sleep
•Induce skeletal muscle relaxation
Benzodiazepines: Indications
•Sedation
•Sleep induction
•Skeletal muscle relaxation
•Anxiety relief
•Anxiety-related depression
•Treatment of acute seizure disorders
•Treatment of alcohol withdrawal
•Agitation relief
•Balanced anesthesia
•Moderate or conscious sedation
BENZOS can have paradoxycal effects
opposite of what we want
-you want them to be calm they get agitated
Benzodiazepines: Contraindications
•Drug allergy
•Narrow-angle glaucoma :dilates the pupil so causes too much pressure
•Pregnancy-depress the fetus
Benzodiazepines: Adverse Effects
•Headache
•Drowsiness
•Dizziness
•Cognitive impairment
•Vertigo
•Lethargy
•Fall hazard for older adults
•"Hangover" effect or daytime sleepiness
-withdrawal wether its used short or long term
-short term- anxxiety issues and insomnia, dizzy, sweaty
-long term- more severe, delirium, paranoia, muscle spasms and teitching
TX for toxicity
•Flumazenil as an antidote
-symptomatic and supportive tx
Benzodiazepines: Toxicity and Overdose
-confusion
-drowsy
-lethargic
-resp depression
-cardiac arrest
-extreme HTN
-circulatory collapse with large dose
-vasodilation
-SERIOUS: RESP DEPRESSION (CAN DIE)
Benzodiazepines: Interactions
•Azole antifungals, verapamil, diltiazem, protease inhibitors, macrolide antibiotics, grapefruit juice
•CNS depressants (alcohol, opioids)
•Olanzapine
•Rifampin
•Herbal Interactions
•Food-drug Interactions
•Opioids
Herbal Products: Kava
•Used to relieve anxiety, stress, and restlessness and to promote sleep
•May cause temporary yellow skin discoloration (extended, continued intake) and visual disturbances
•Potential interactions with alcohol, barbiturates, and psychoactive drugs
•Contraindicated in liver disease, alcoholism, other conditions
•Patient should not operate heavy machinery during use
Herbal Products: Valerian
•Used to relieve anxiety, restlessness, and sleep disorders
•May cause CNS depression, hepatotoxicity, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, restlessness, insomnia
•Many interactions, including with CNS depressants, MAOIs, phenytoin, warfarin, and alcohol
•Contraindicated in cardiac and liver disease
•Patient should not operate heavy machinery during use.
Diazepam (Valium)
•First clinically available benzodiazepine drug. It has varied uses
•Treatment of anxiety
•Procedural sedation and anesthesia adjunct
•Skeletal muscle relaxation
-also for seizures in pregnancy only used when benefits outweigh risks
•Available in multiple forms:
•Oral
•Rectal
•Injectable
-contraindicated: alcohol intoxication
-cautions with breast feeding
-do not stop abruptly
-be careful and monitor mom and baby BP, slow rising to prevent faints can cause veins to become extravagated, used a large vein if given IV
Midazolam (Versed)
•Most used preoperatively and for moderate sedation
•Causes amnesia and anxiolysis (reduced anxiety) as well as sedation
•Normally administered by injection in adults
•Liquid oral dosage form is also available for children.
-GIVEN BUCCAL, NASAL, VEIN OR MUSCLE
-cns depressent short acting
-interacts with meds like cimetidine, rinitidine, omeprazole, contraceptives'
-crash cart close by
-usually given IM in large muscle monitor pt vcardoac and resp systems
-used to sedate kids in 3-5 mins
-rapidly absorbed
-crosses BBB amd breast milk
Temazepam (Restoril)
•Intermediate-acting benzodiazepine
•One of the metabolites of diazepam
•Normally induces sleep within 20 to 40 minutes
•Long onset of action, so it is recommended that patients take it about 1 hour prior to going to bed
•Still an effective hypnotic; however, it has been replaced by newer drugs
-no more than 7-10 days
-encourage patient to use non pharm method dotn wanna be on this for to long
Nonbenzodiazepine: Eszopiclone (Lunesta)
•First hypnotic to be FDA approved for long-term use
•Designed to provide a full 8 hours of sleep
•Considered a short- to intermediate-acting agent
•Patients should allot 8 hours of sleep time and should avoid taking hypnotics when they must awaken in less than 6 to 8 hours.
•Used csutiously in olds bc causes severe kidney and liver issues
•Avoid alcohol
•Low dependency risk
Nonbenzodiazepine: Ramelteon (Rozerem)
•Structurally like the hormone melatonin
•Works as an agonist at melatonin receptors in the CNS
•Technically, it is not a CNS depressant; used as hypnotic
•Not classified as a controlled substance
•Indicated for patients who have difficulty with sleep onset rather than sleep maintenance
-contreaindicated in ppl with liver disease, depression and COPD
-used for patient who have diffivulty with sleep onset
Nonbenzodiazepine: Zolpidem (Ambien)
•Short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic
•Lower incidence of daytime sleepiness compared with benzodiazepine hypnotics
•Ambien CR is a longer acting form with two separate drug reservoirs.
•Somnambulation
Barbiturates
•First introduced in 1903; were the standard drugs for insomnia and sedation
•Habit forming; low therapeutic index
•Only a handful commonly used today partly because of the safety and efficacy of benzodiazepines
Barbiturates: Mechanism of Action
•Site of action: brainstem (reticular formation)
•By potentiating the action of GABA, nerve impulses traveling in the cerebral cortex are inhibited
Barbiturates: Indications
•Ultrashort acting
•Anesthesia for short surgical procedures
•Anesthesia induction
•Control of seizures
•Reduction of intracranial pressure in neurologic patients
-intubation
•Short acting
•Sedation and control of seizures
•Intermediate acting
•Sedation and control of seizures
•Long acting
•Seizure prophylaxis
Barbiturates: Contraindications
•Drug allergy
•Pregnancy
•Significant respiratory difficulties
•Severe kidney or liver disease
•Caution in older adults
Barbiturates: Adverse Effects
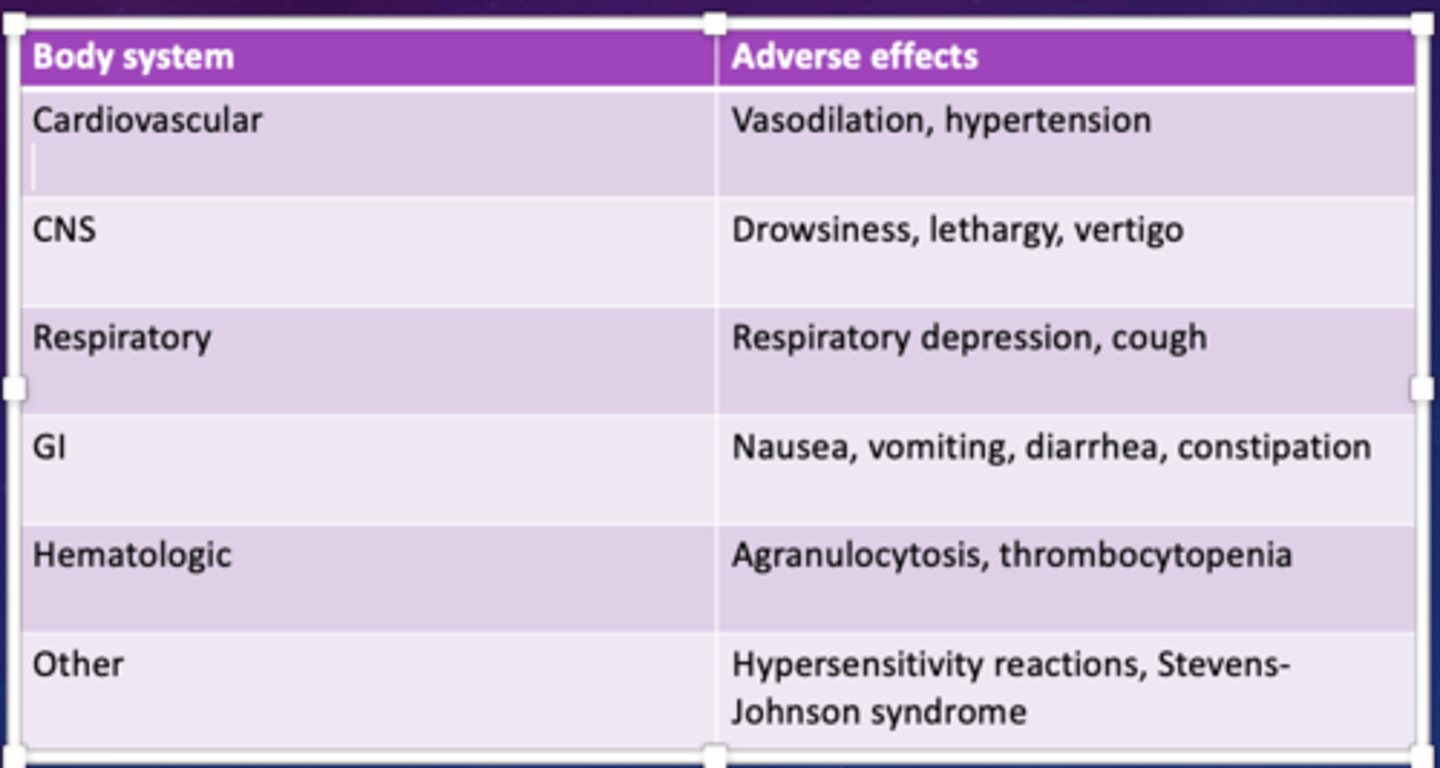
Barbiturates:Toxicity and Overdose
•Overdose frequently leads to respiratory depression and subsequent respiratory arrest.
•Overdose produces CNS depression (sleep to coma and death).
•Can be therapeutic
•Anesthesia induction
•Uncontrollable seizures: "phenobarbital coma
tx of barb OD
•Treatment of overdose
•Symptomatic and supportive
•Maintain adequate airway
•Assisted ventilation or oxygen therapy
•Fluids
•Pressor support
•Activated charcoal
Barbiturates: Drug Interactions
•Additive effects
•Alcohol, antihistamines, benzodiazepines, opioids, tranquilizers
•Inhibited metabolism
•MAOIs prolong the effects of barbiturates.
•Increased metabolism
•Reduces anticoagulant response, leading to possible clot formation
Phenobarbital
•Prototypical barbiturate
•Long-acting
•Uses:
•Prevention of generalized tonic-clonic seizures and febrile convulsions
•Hyperbilirubinemia in neonates
•Rarely used as sedative
•No longer recommended as a hypnotic
Muscle Relaxants
•Act to relieve pain associated with skeletal muscle spasms
•Majority are centrally acting.
•CNS is the site of action.
•Similar in structure and action to other CNS depressants
•Direct acting
•Act directly on skeletal muscle
•Closely resemble GABA
Muscle Relaxants: Indications
•Relief of painful musculoskeletal conditions
•Muscle spasms
•Management of spasticity of severe chronic disorders (multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy)
•Work best when used along with physical therapy
Muscle Relaxants: Adverse Effects
•Extension of effects on CNS and skeletal muscles
•Euphoria
•Lightheadedness
•Dizziness
•Drowsiness
•Fatigue
•Muscle weakness
Toxicity and Management of Overdose
•Primarily involve the CNS
•No specific antidote or reversal
•Best treated with conservative supportive measures
•If taken along with other CNS depressants
•Adequate airway must be maintained
•EKG monitoring
•Fluid management to avoid crystalluria
ABC
Common Muscle Relaxants
•Baclofen (Lioresal)
•Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)
•Tizanidine (Zanaflex)
•Methocarbamol (Robaxin)
Baclofen (Lioresal)
•Oral and injectable forms
•Treat chronic spastic muscular conditions
•Implantable baclofen pump device
Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)
•Oral and extended-release oral form (Amrix)
•Centrally acting muscle relaxer
•Most common used muscle relaxer
•Can cause marked sedation
Nursing Implications
•Before beginning therapy, obtain a thorough history regarding allergies, use of other medications, health history, and medical history.
•Obtain baseline vital signs and I&O, including supine and erect blood pressure.
•Assess for potential disorders and conditions that may be contraindications and for potential drug interactions.
•Give hypnotics 30 to 60 minutes before bedtime for maximum effectiveness in inducing sleep (depends on drug's onset).
•Most benzodiazepines cause REM rebound and a tired feeling the next day; use with caution in older adults.
•Instruct patients to avoid alcohol and other CNS depressants.
•Check with the prescriber before taking any other medications, including over-the-counter medications.
•Rebound insomnia may occur for a few nights after a 3- to 4-week regimen has been discontinued.
NURSING IMPLICATIONS CONTIN
•Safety is important:
•Keep side rails up or use bed alarms.
•Do not permit smoking.
•Assist patient with ambulation (especially older adults).
•Keep call light within reach.
•Monitor for adverse effects.
•Age-appropriate considerations
•Monitor for therapeutic effects:
•Increased ability to sleep at night
•Fewer awakenings
•Shorter sleep-induction time
•Few adverse effects, such as "hangover" effects
•Improved sense of well-being because of improved sleep
•For muscle relaxants: decreased spasticity, decreased rigidity
ALWAYS PICK
SAFETY