IOS_1 RESPIRATORY_HISTOLOGY_RESPIRATORY_PORTION
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the composition of the alveoli?
Alveolar epithelium delimiting the sacs, within a region of highly vascularized (capillaries) fibroelastic connective tissue.
This is the region where exchange will take place.
VERY THIN WALLS. EMPTY SPACES -> ALVEOLAR SACS WILL BE FILLED WITH AIR
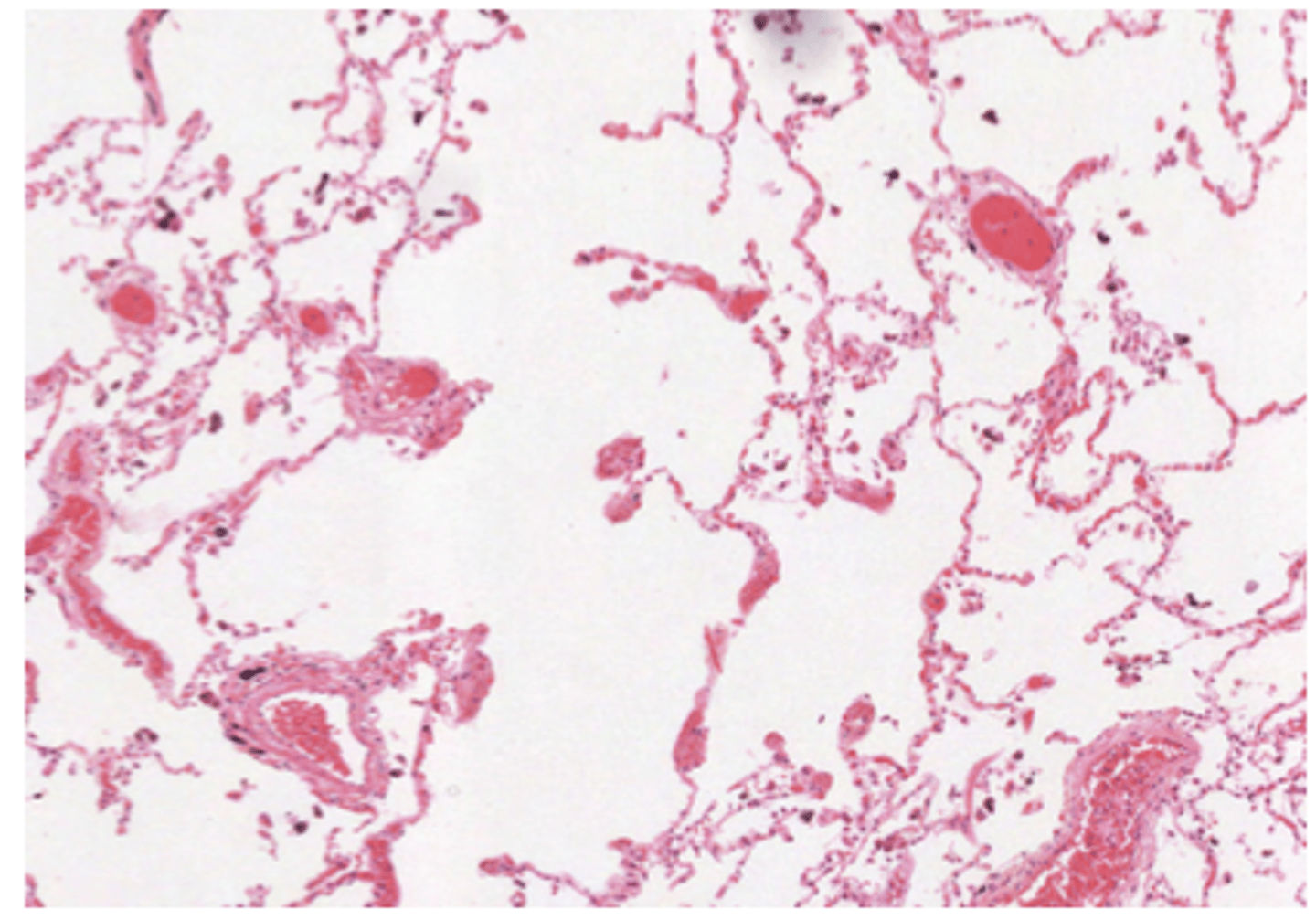
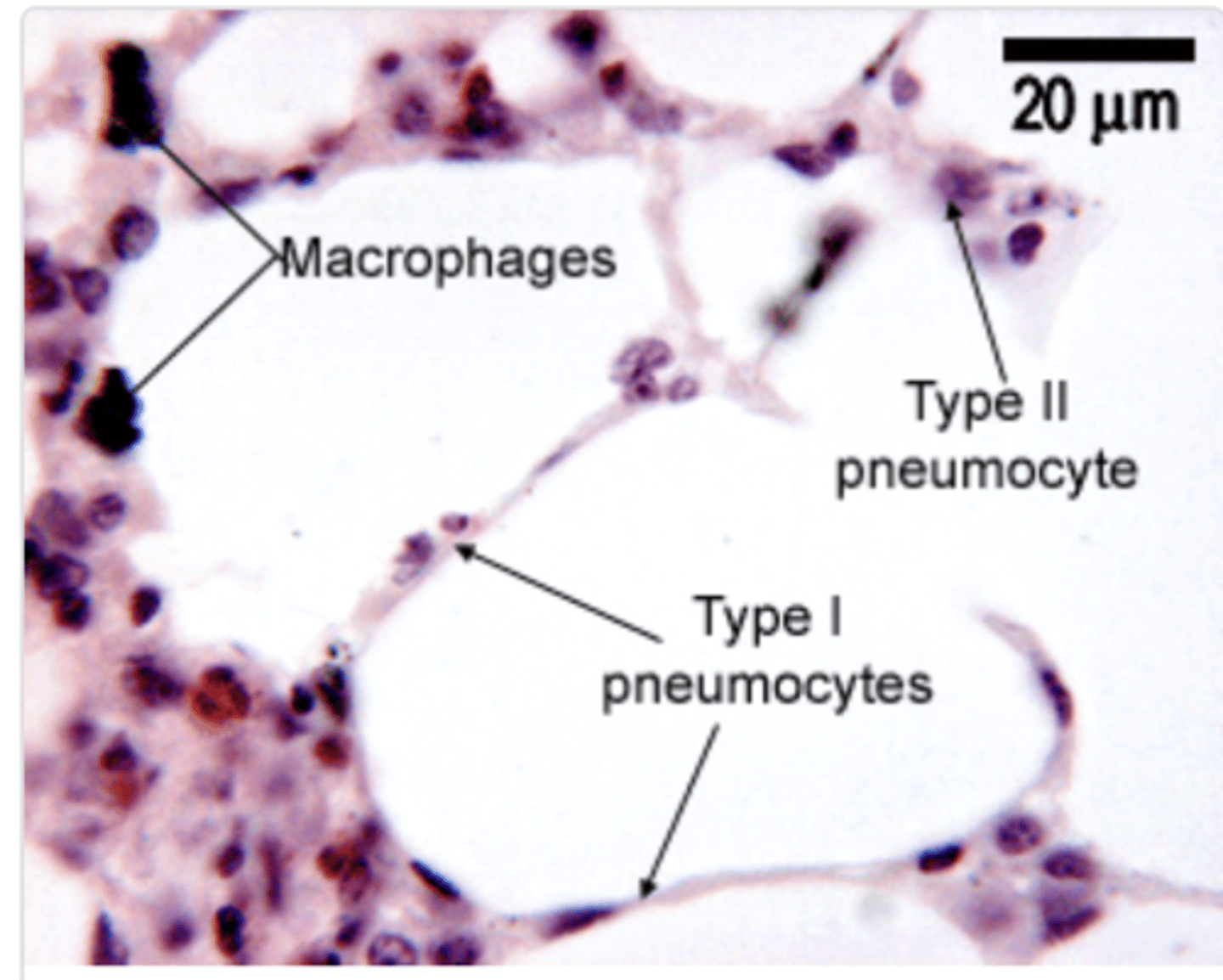
What are the cells found in the alveolar epithelium?
. Type I pneumocytes
.Type II pneumocytes
. Brush cells
. Pulmonary macrophages
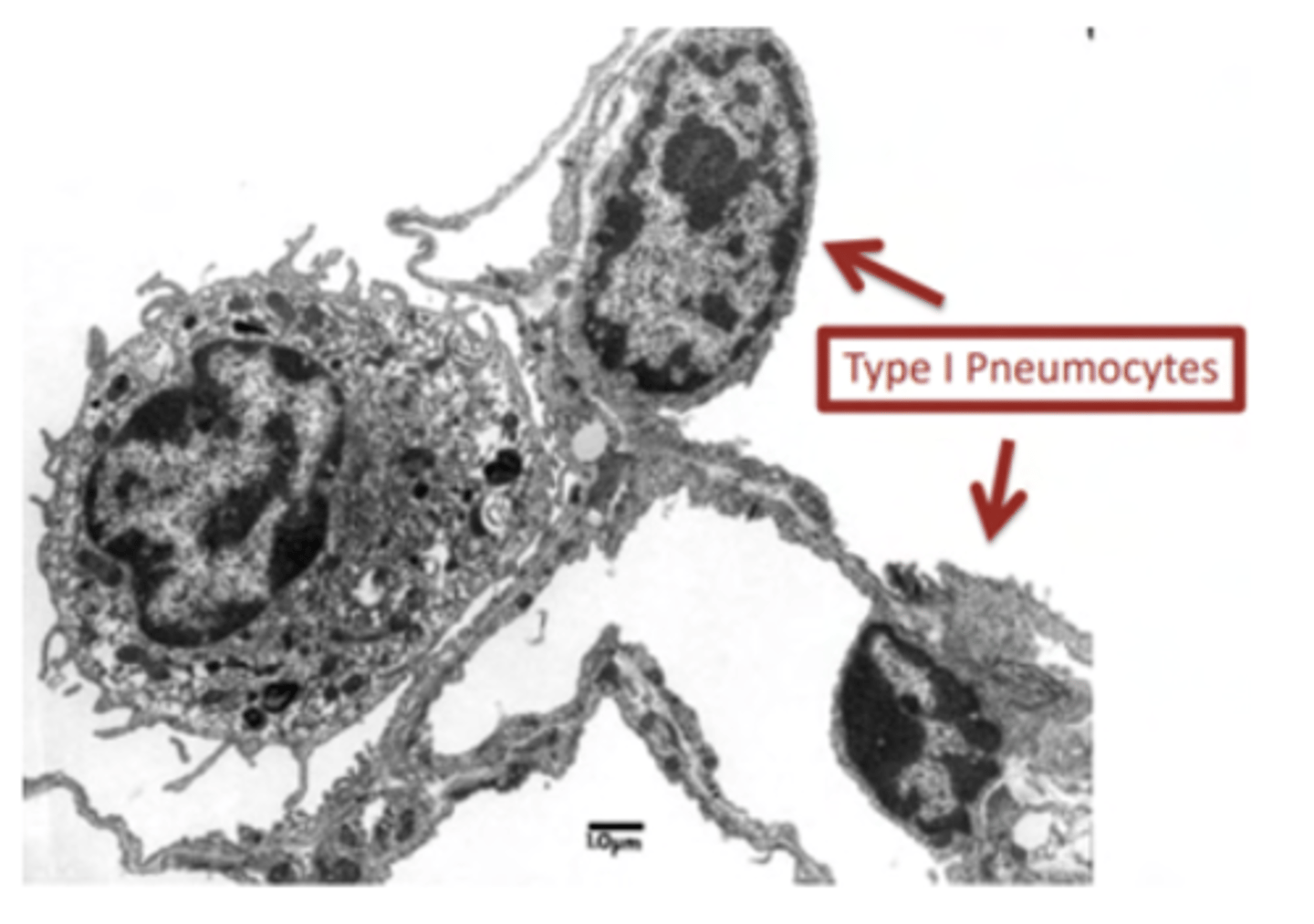
What's the role of pneumocytes type I?
They are involved in gas exchange
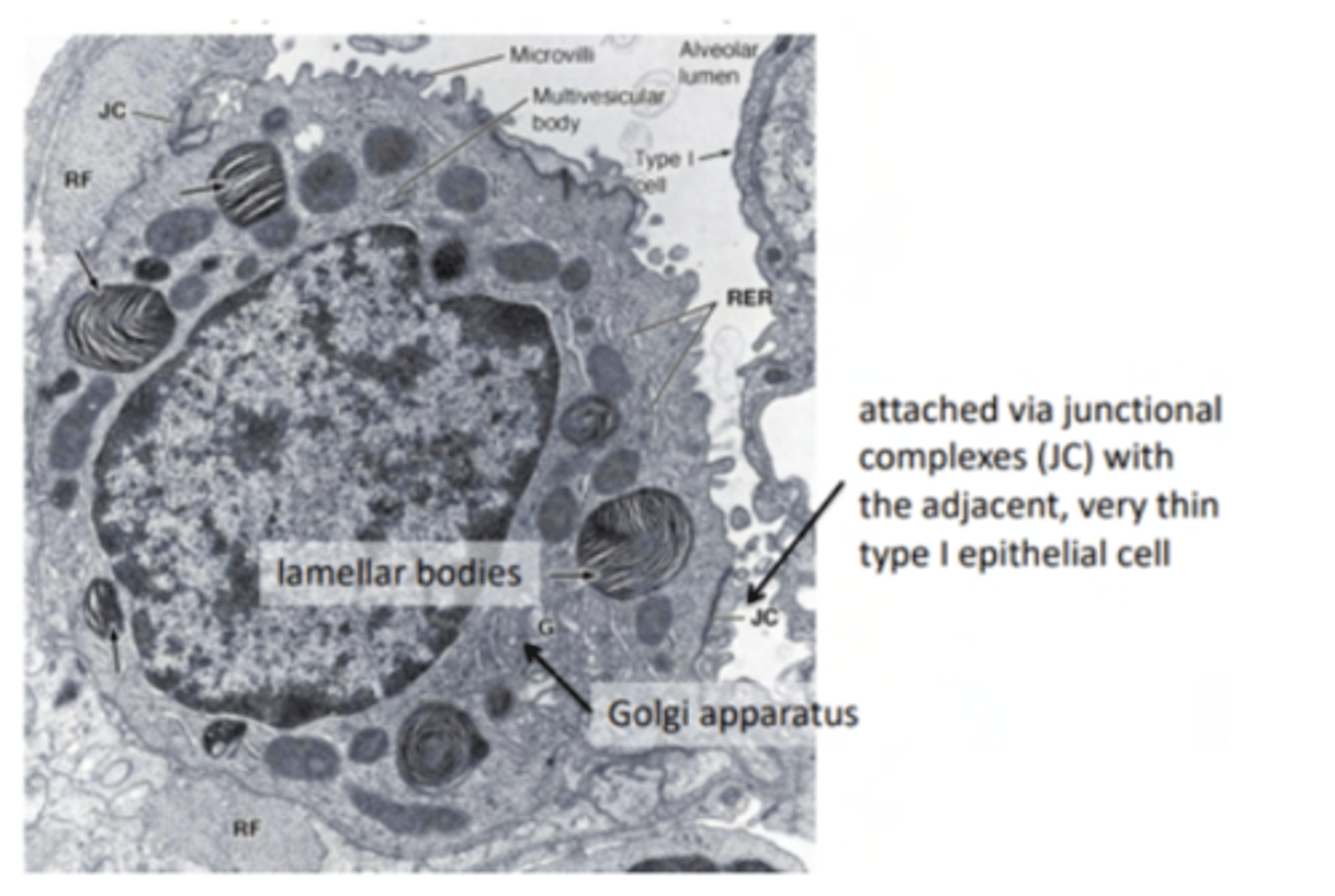
What's the role of pneumocytes type II?
secrete surfactant (mix of protein and lipids). They are analogue to Clara cells
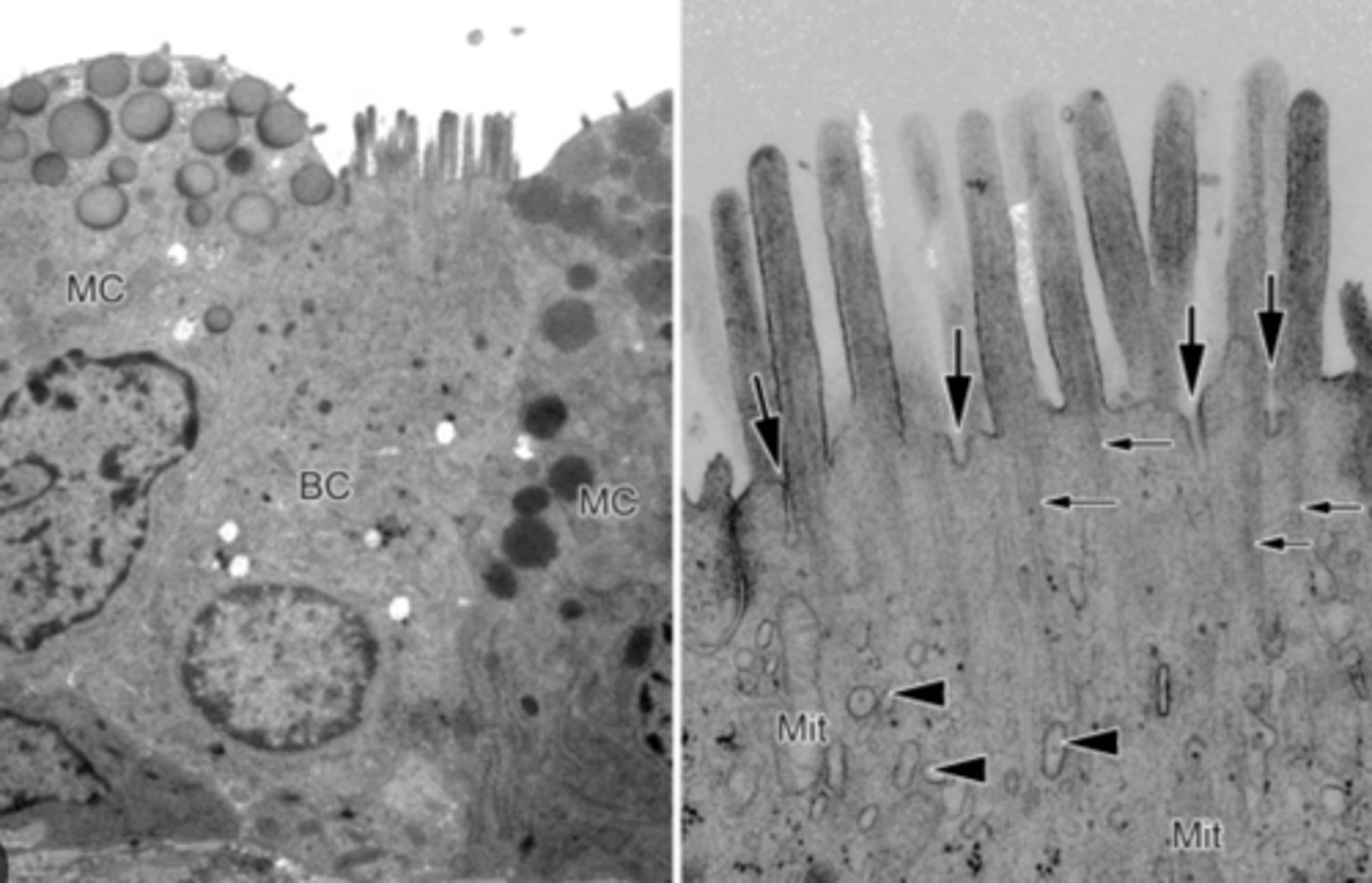
What's the role of brush cells?
Sensory receptors
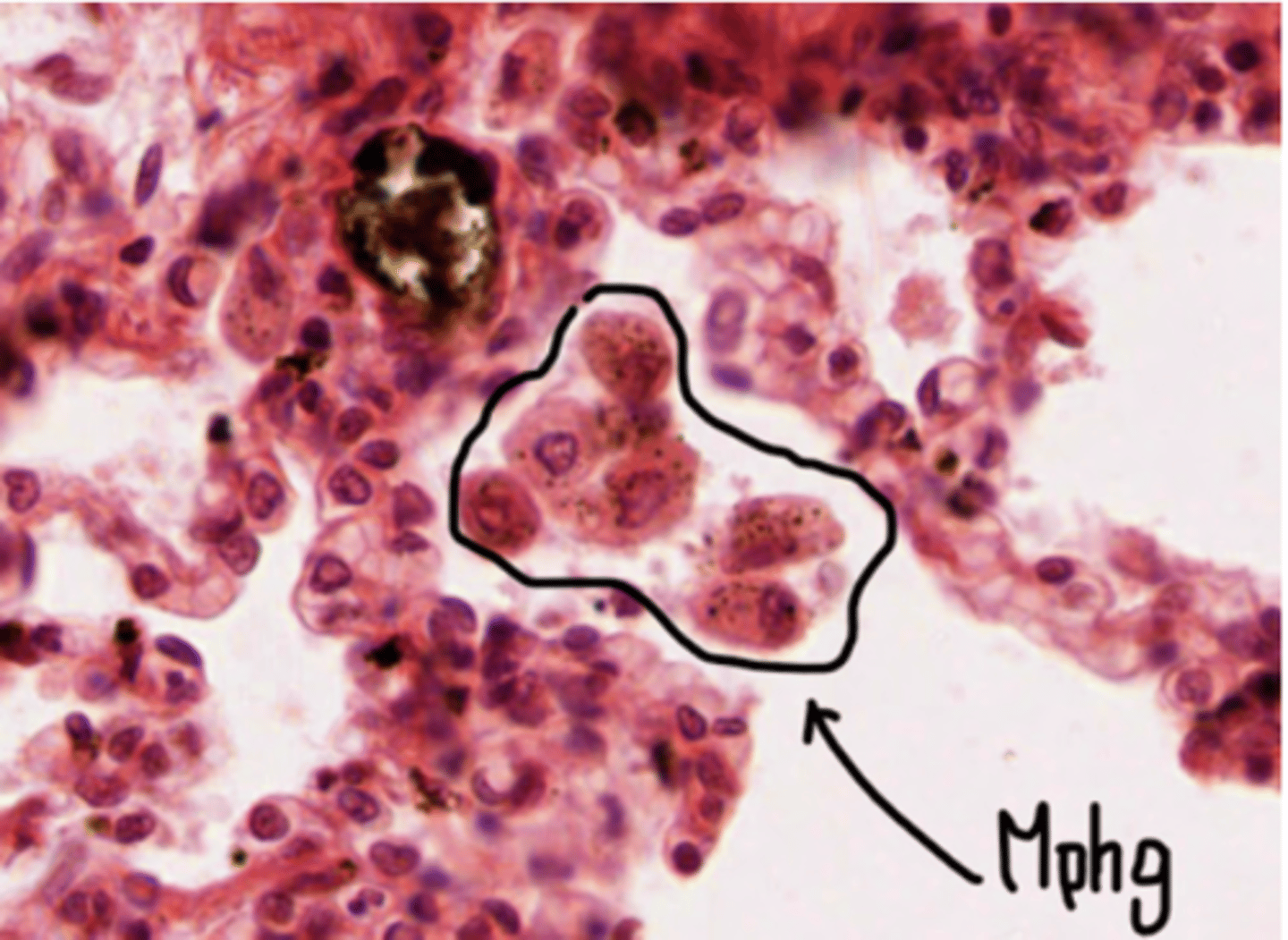
What's the role of pulmonary macrophagues (dust cells)?
carry out phagocytosis
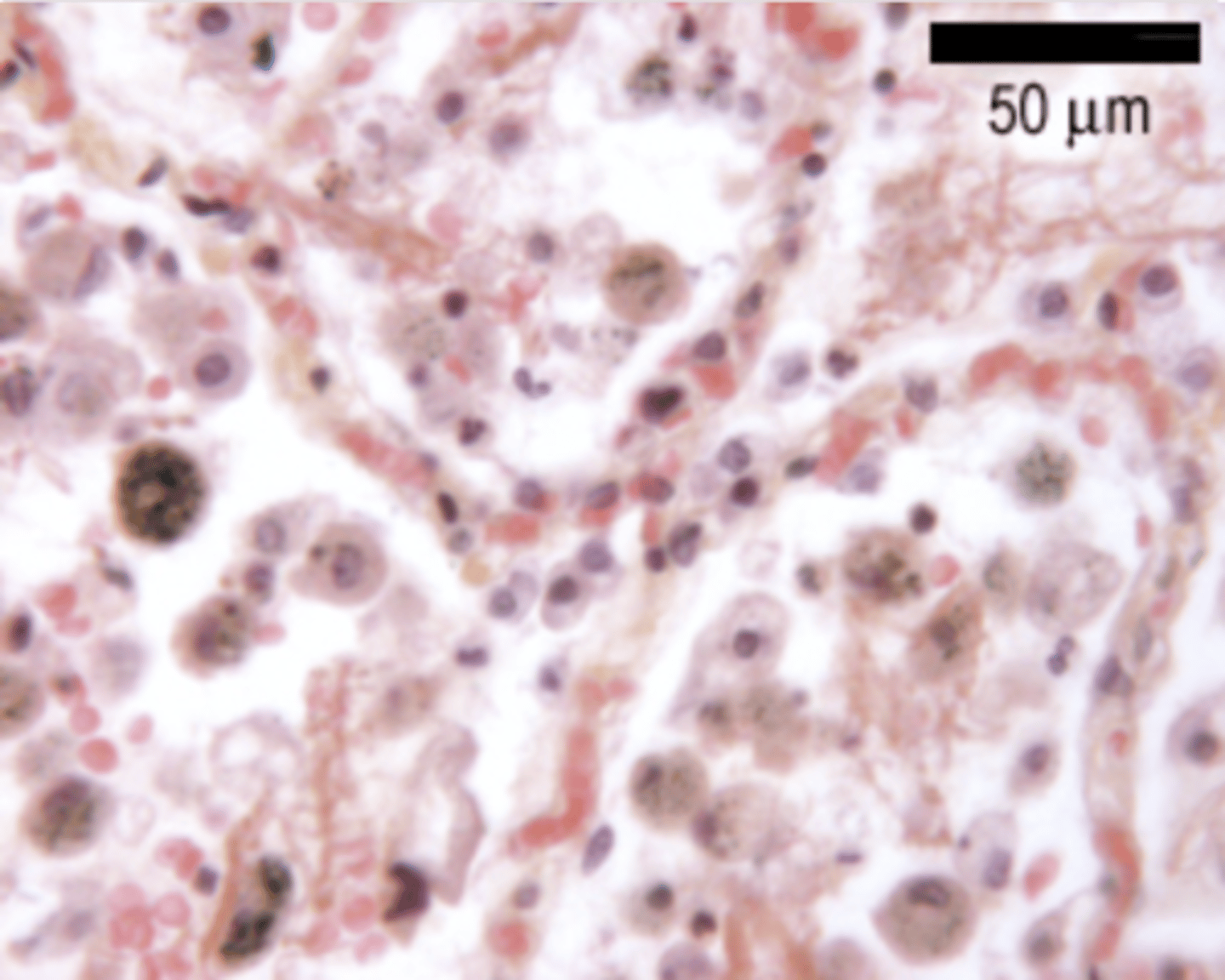
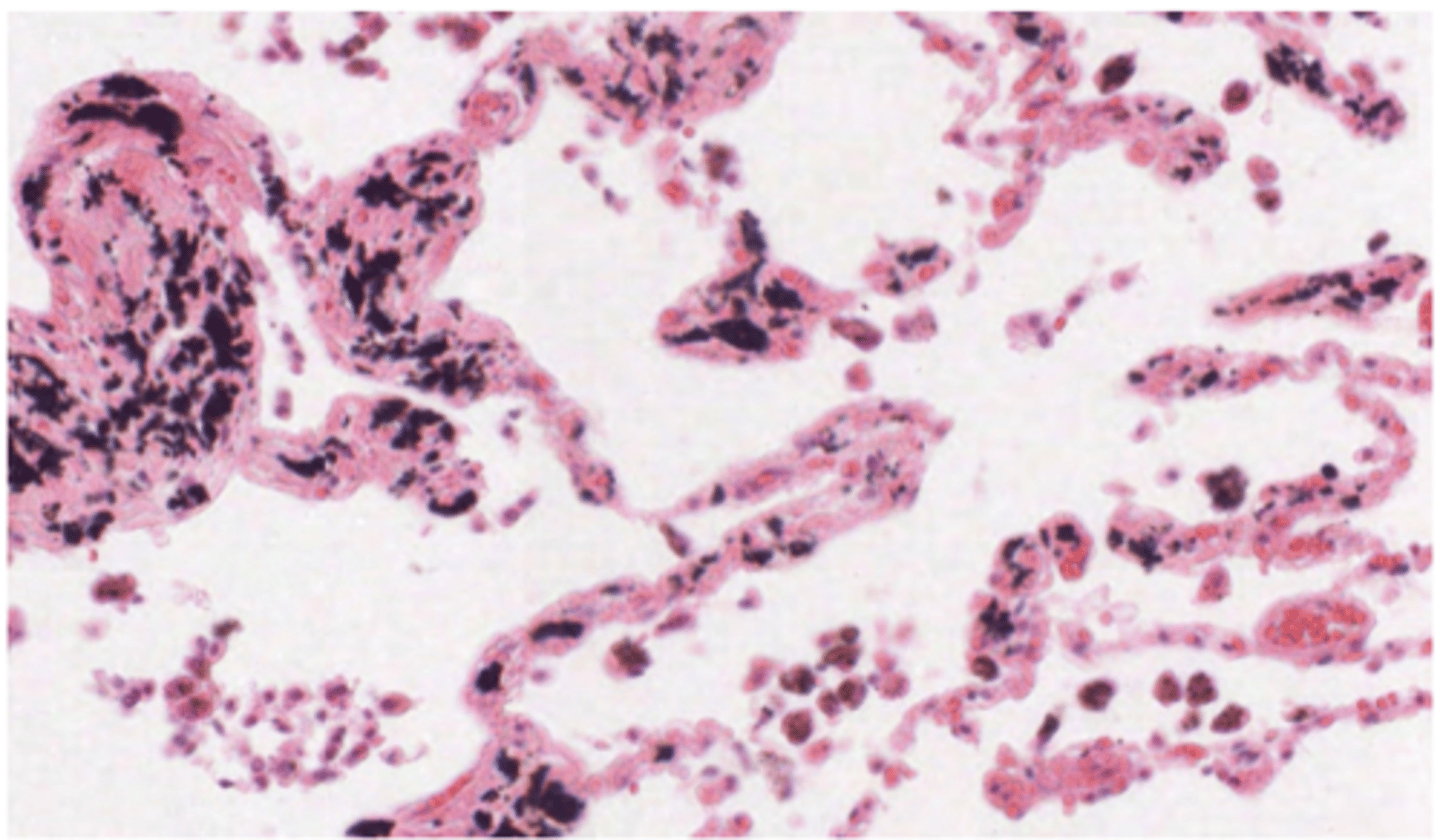
What are the black particles in the alveoli?
anthracotic pigment (anthracotic = black). Smokers will present many more . Particles present in the air
Pulmonary macrophages will be responsible for removing these particles, which is why they are generally seen containing black stuff inside of them.
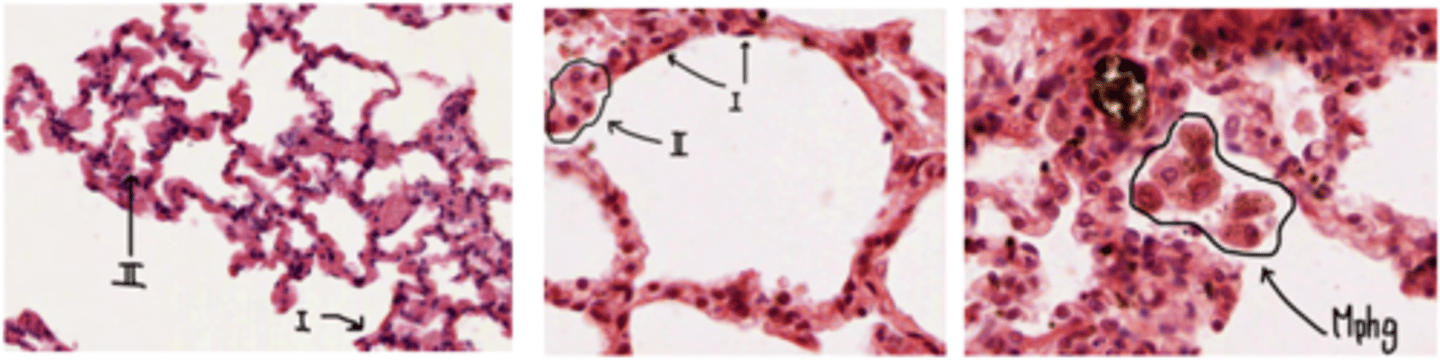
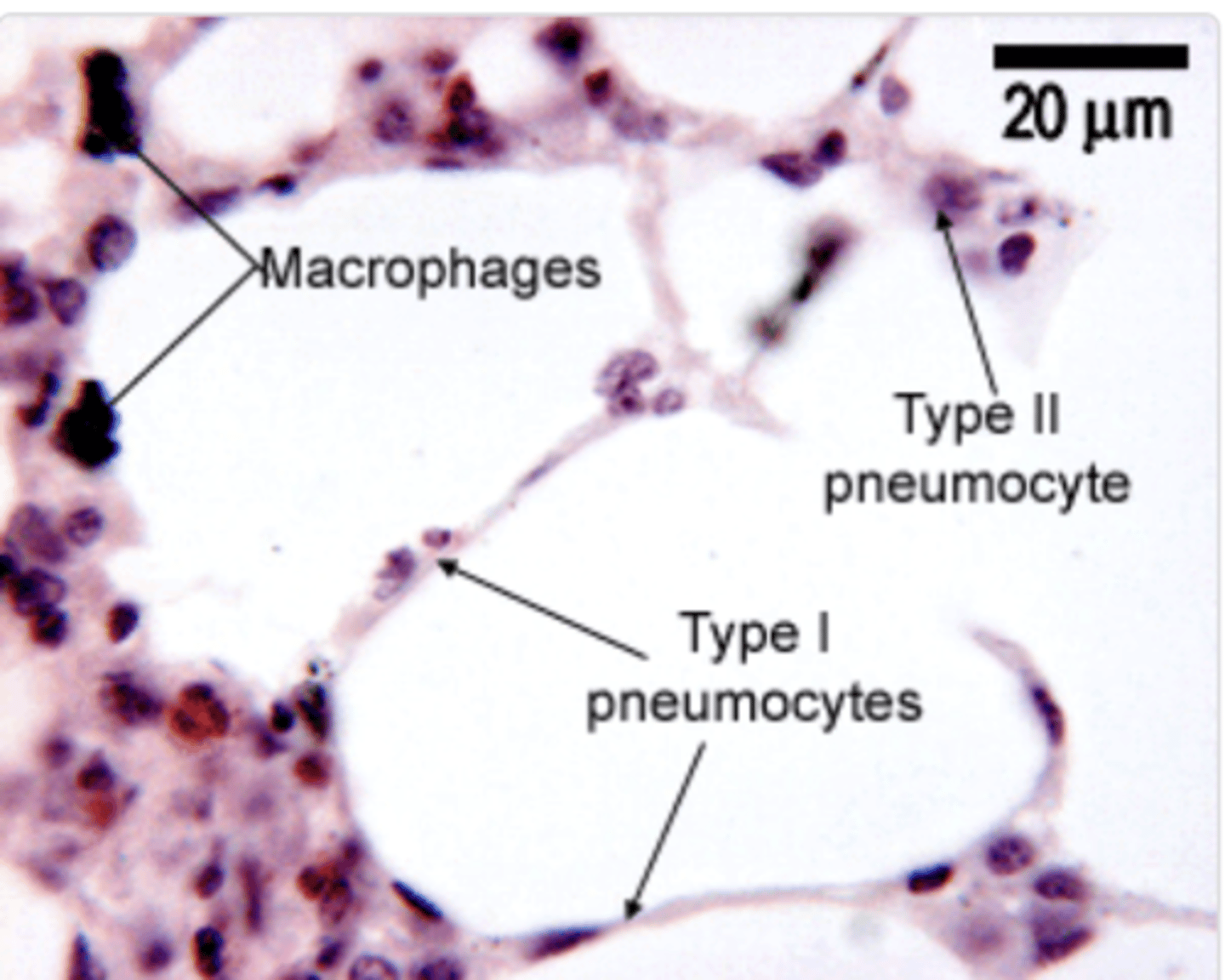
How to distinguis Type I pneumocytes?
Nucleus occupies almost the whole of the cell, very little cytoplasm = practically seen as deep purple dots.
They are lining in the alveoli
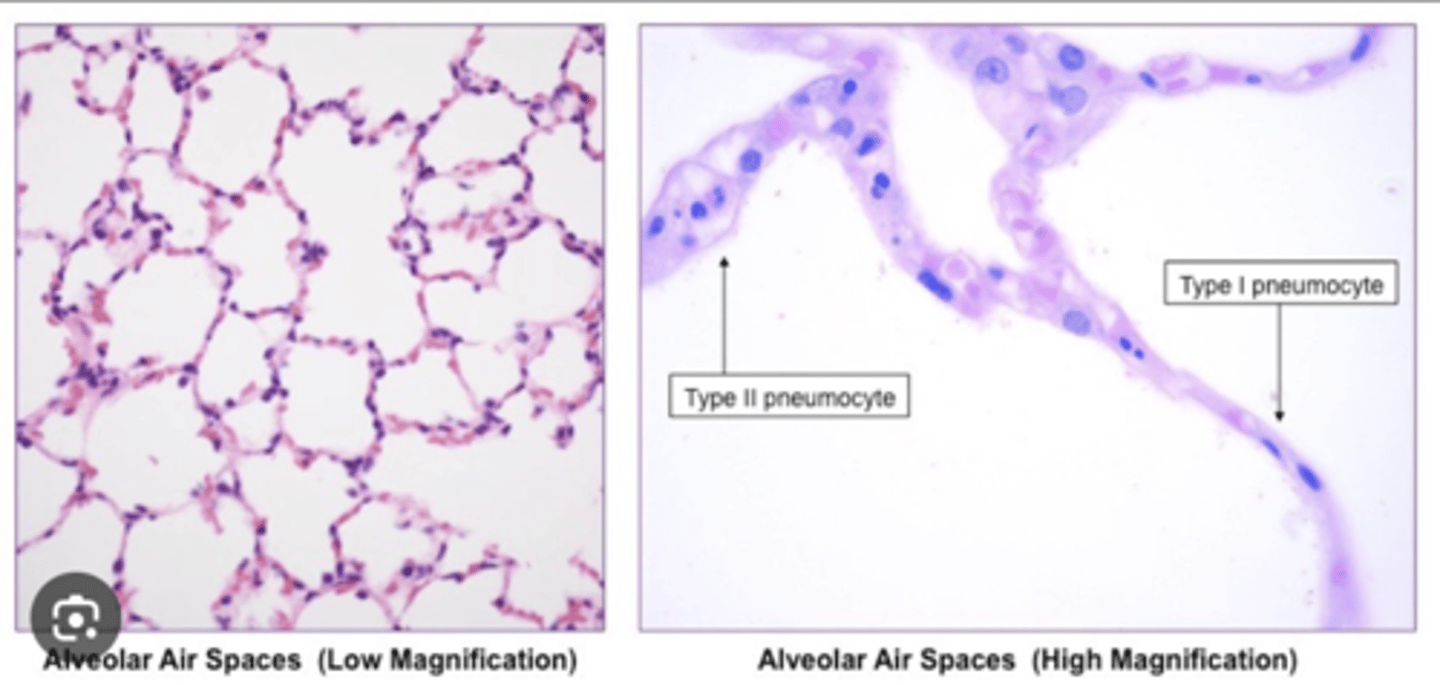
How are the epithelial cells of the Type I pneumocytes?
simple squamous epithelial cells and cover the majority of the
alveolar surface (97%).
Are pneumocytes type I able to replicate?
unable to replicate, and are susceptible to damage caused by toxic agents.
Where it happens the gas exchange?
Across the thin walls of alveoli, which are small air sacs in the lungs.
How it happens: It's driven by diffusion, where gases move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration (e.g., oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli).
How it happens the gas exchange in the alveoli?
Diffusion, where gases move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration (e.g., oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood, and carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into the alveoli).
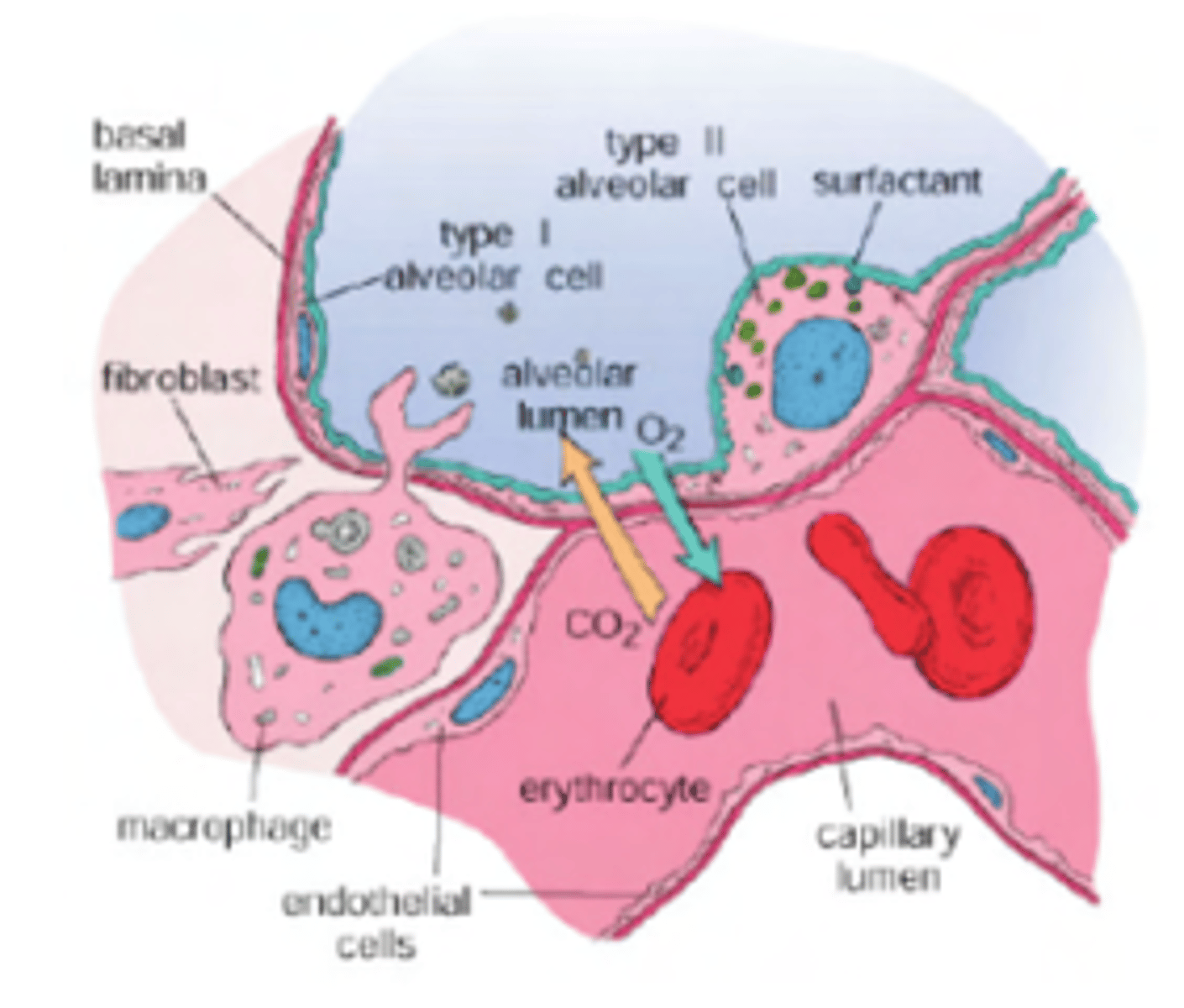
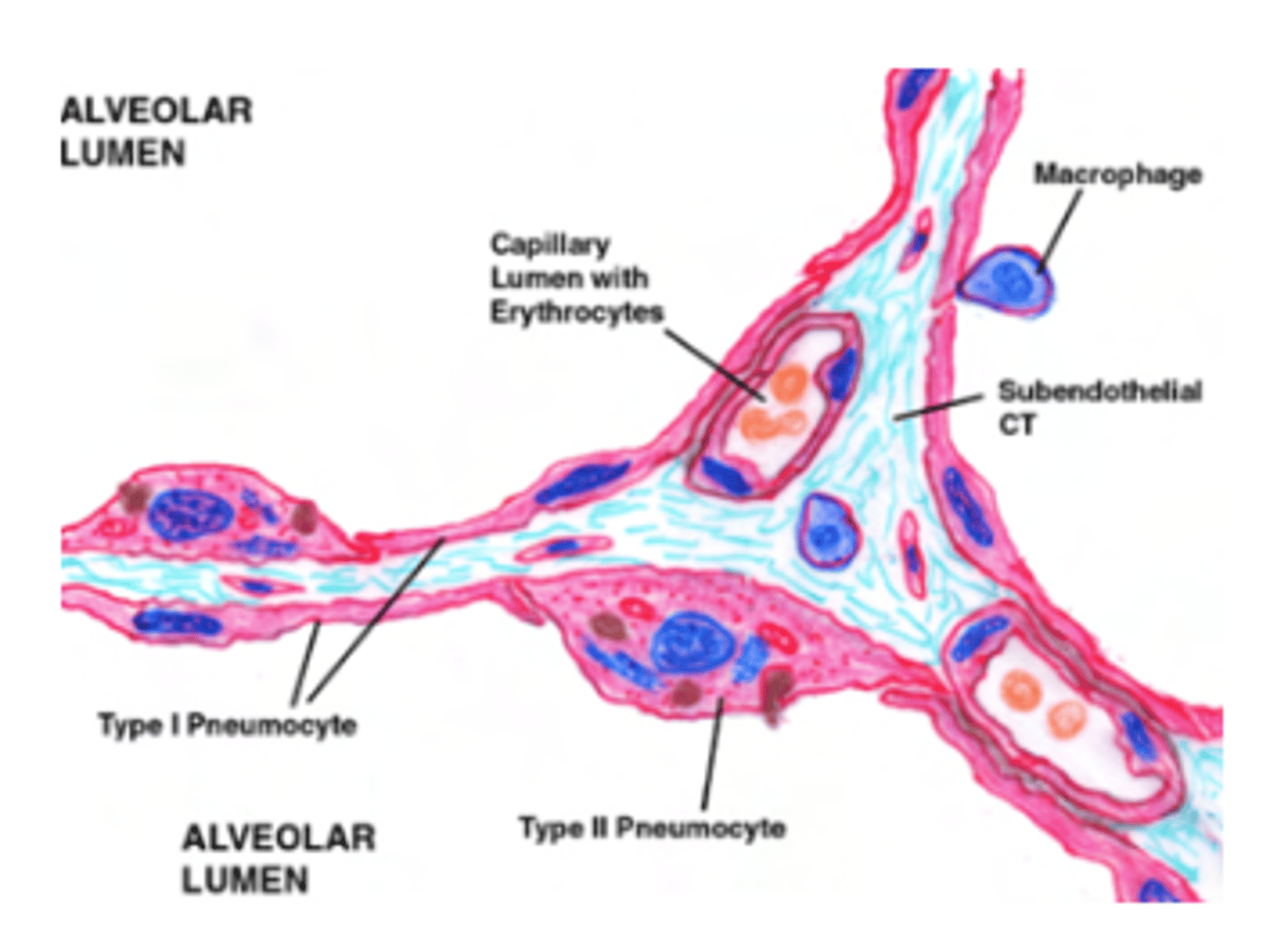
What are the 3 cell layers envolved in gas exchange?
. Pneumocytes Type I: primary role is to form a very thin surface for gas exchange.
Basement Membrane: between the alveolar epithelium and the capillary endothelium. It anchors the epithelial cells and the capillary structure, serving as a "glue" that fuses the two layers together.
Endothelium: The inner lining of the capillaries, made of simple squamous epithelium, which is also very thin to allow gas to pass through.
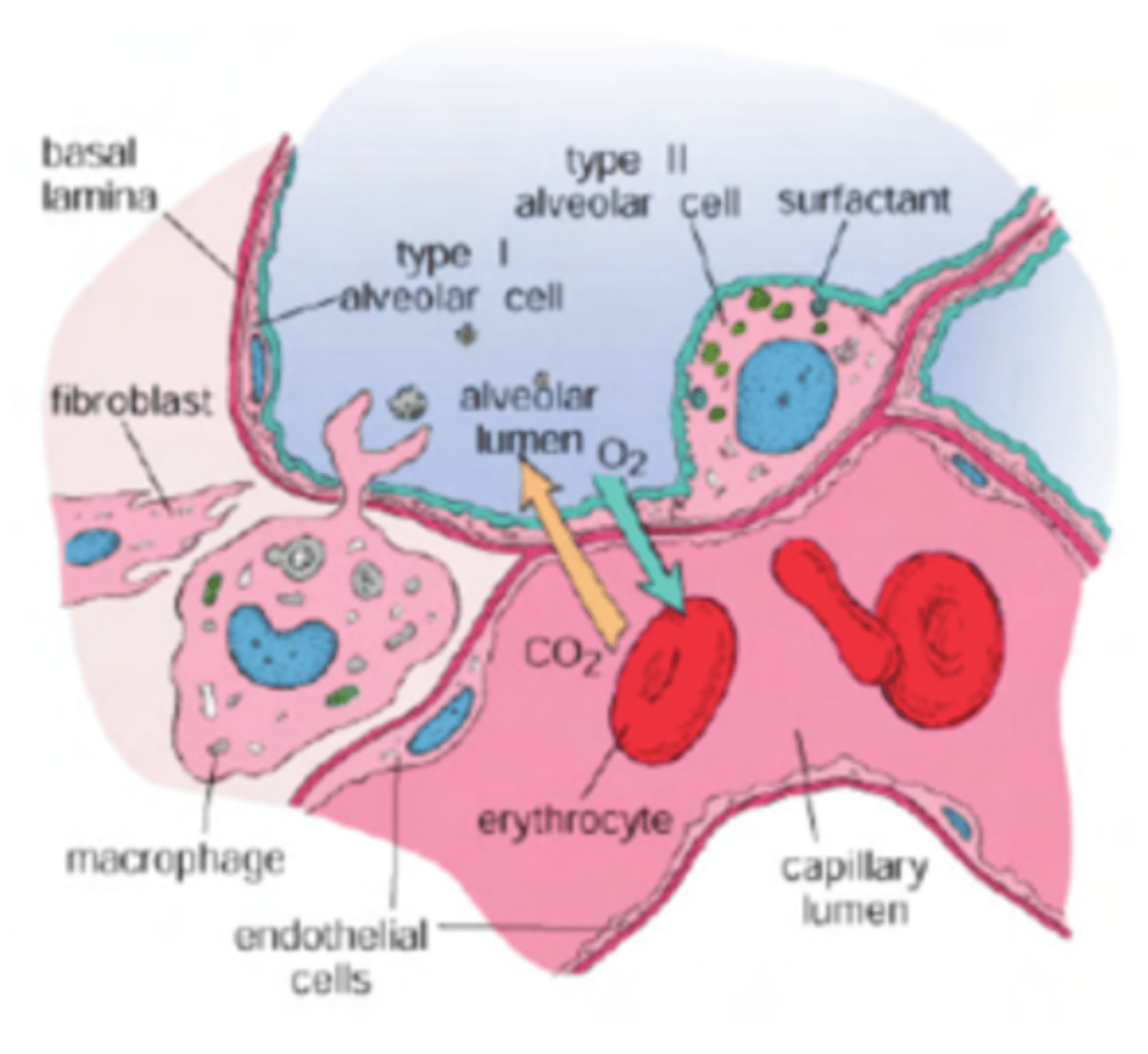
What is the gas pathway?
go through a 3 layered membrane in order to leave or reach the blood.
Membrane formed by:
. Pneumocytes type I (epithelial cells)
. Basement membrane (present in all epitheliums, to anchor it to surrounding tissue. Glues the 2 structures together)
. Endothelium (simple squamous
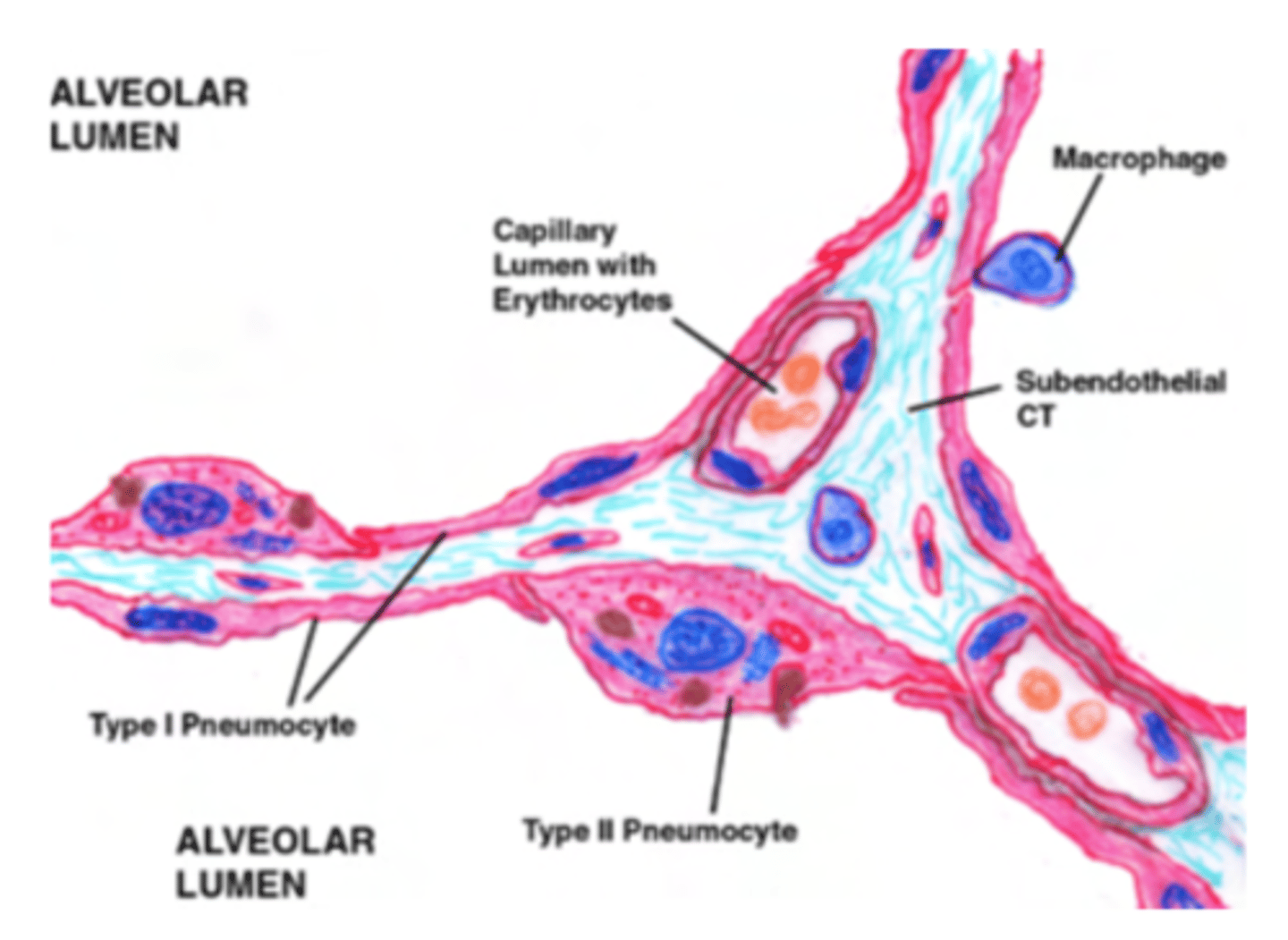
What are type II pneumocytes?
large and rounded cells with a vacuolated cytoplasm (filled with small vacuoles or spaces).
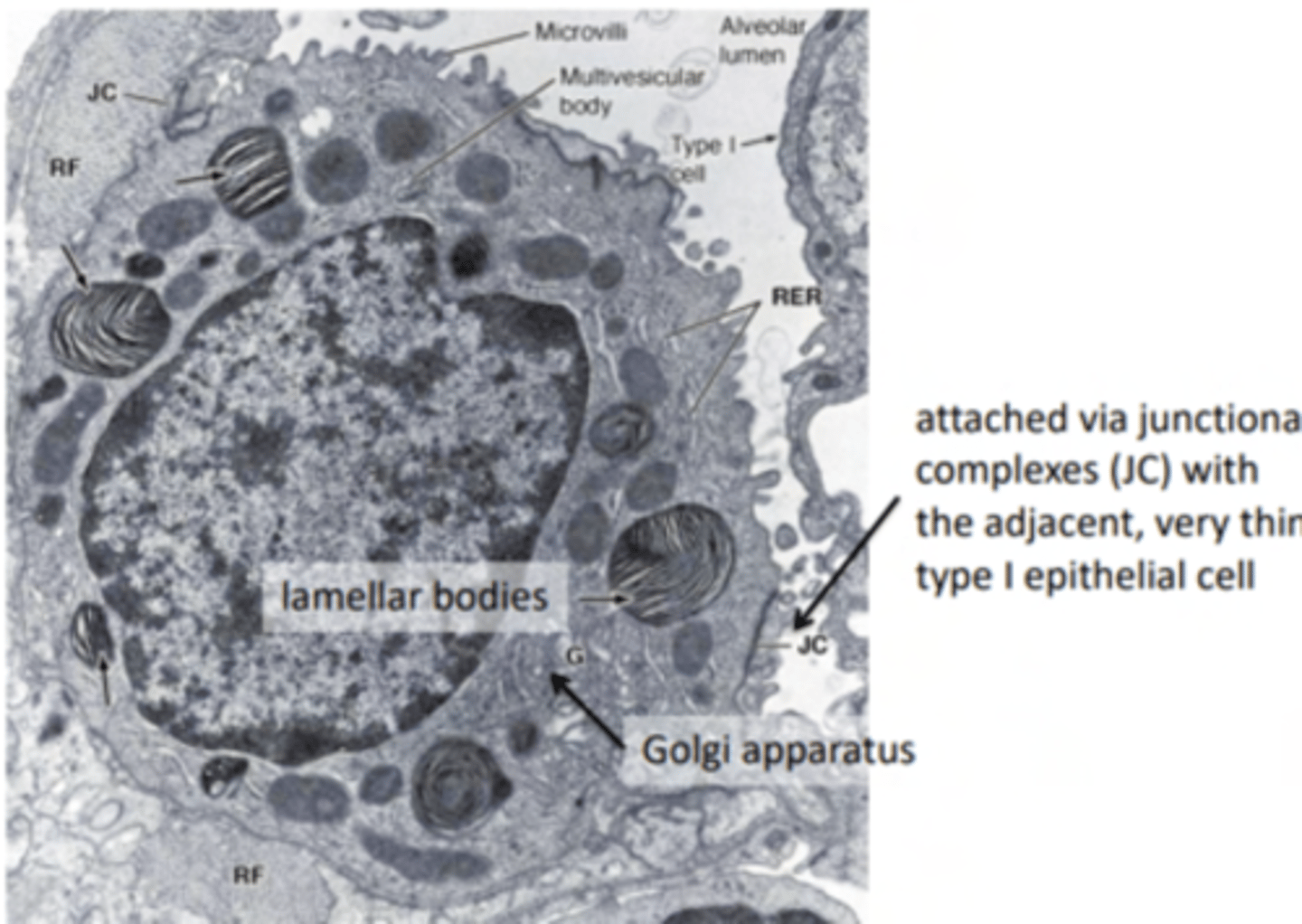
Where are the type II pneumocytes located?
Found in the alveolar-septal junction. Positioned between the alveolar epithelium and the connective tissue septum.
The septum is a connective tissue region between adjacent alveoli in the lungs.
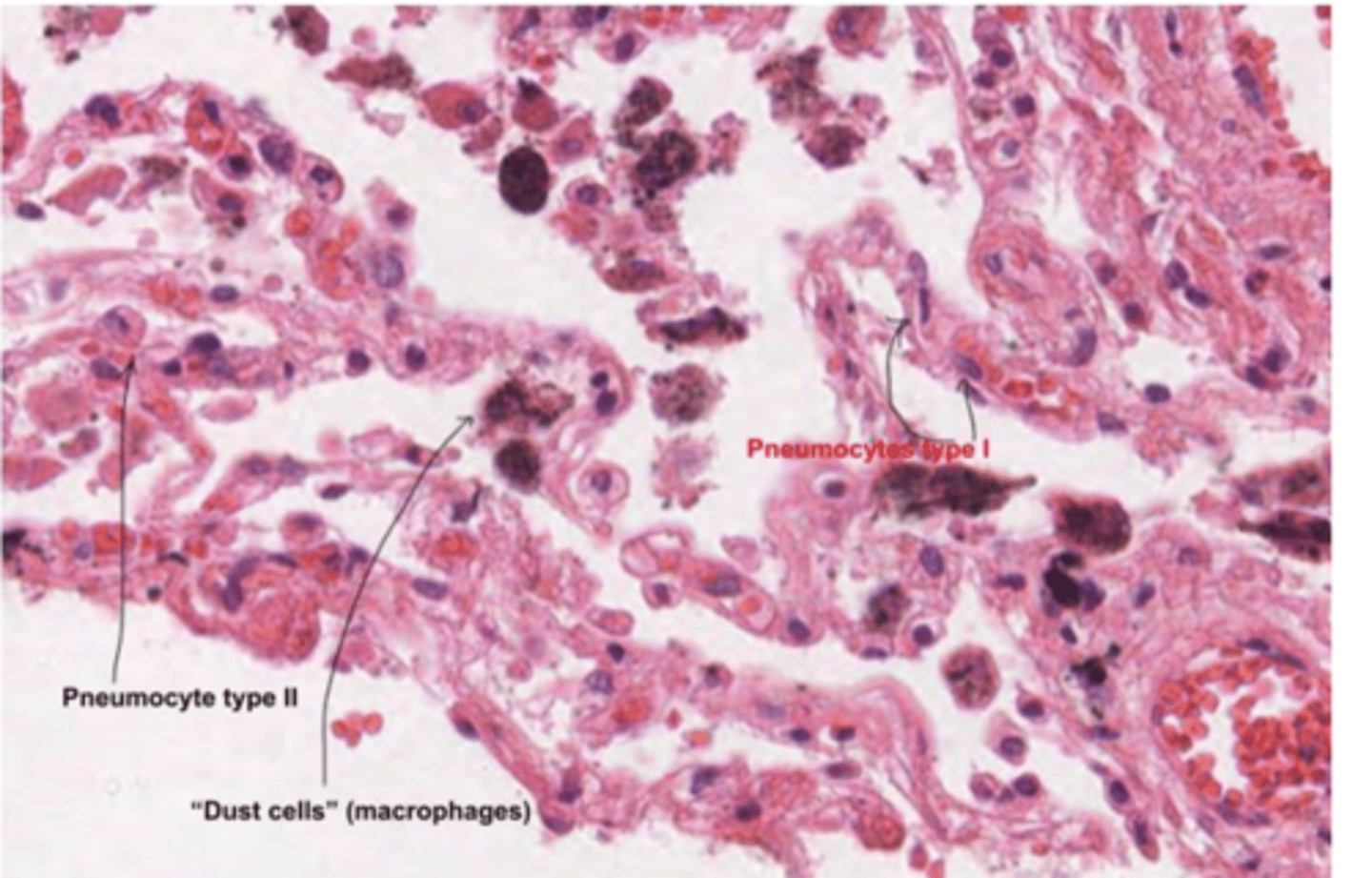
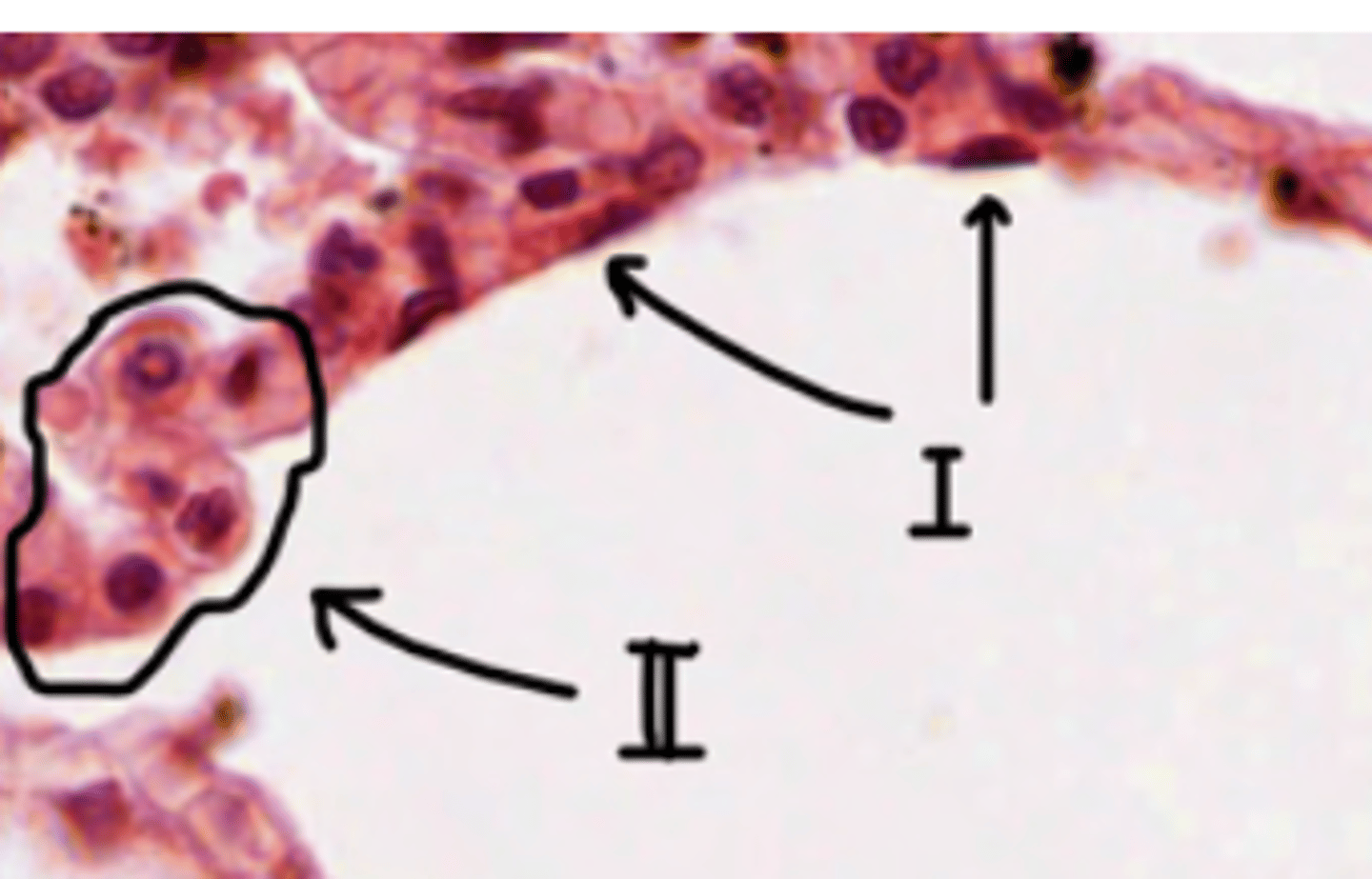
How to differentiate type I and type II pneumocytes?
type I: flat cell, little cytoplasm. Recovering most of the alveolus
type II: round, bigger cell, more cytoplasm.
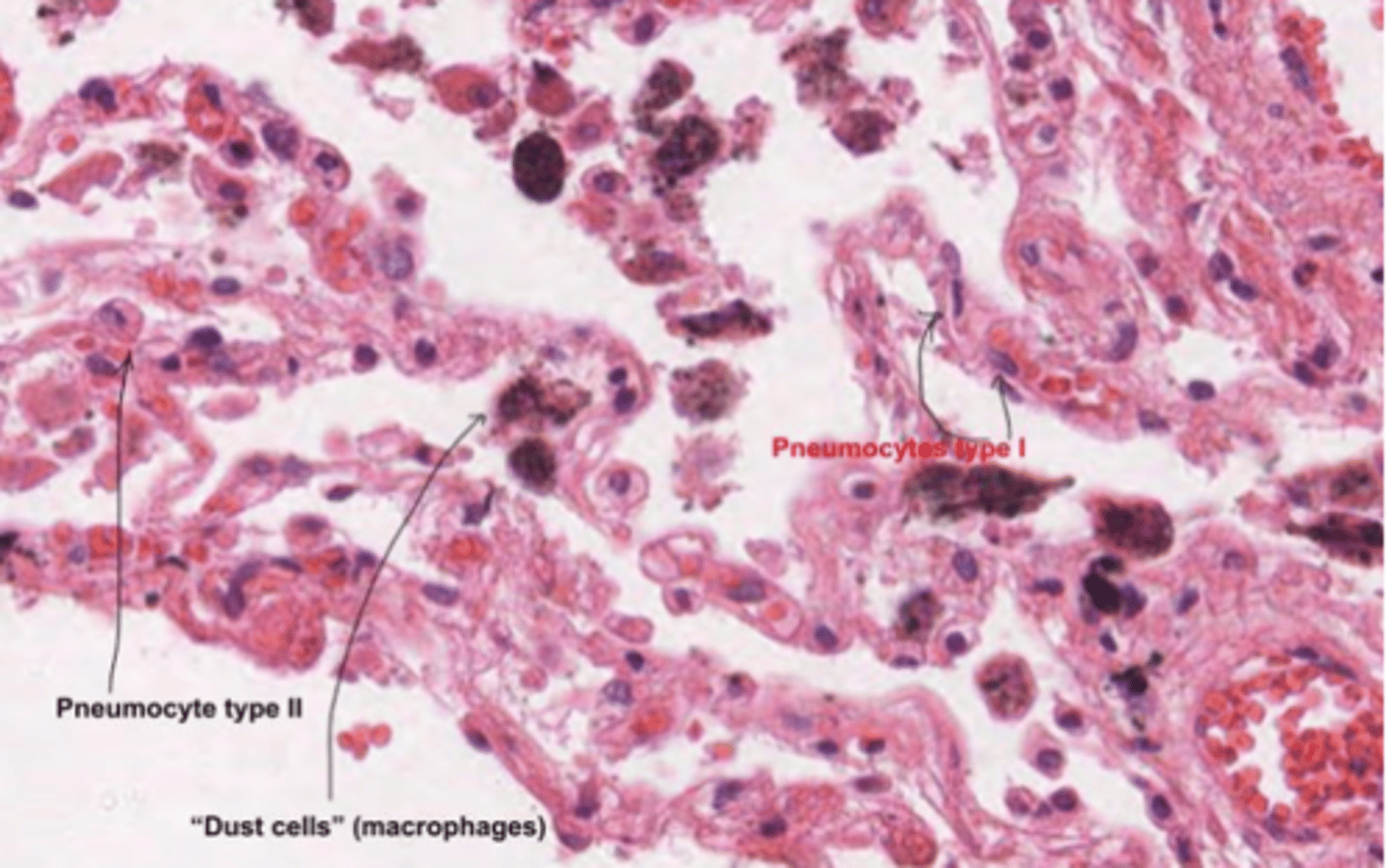
What is the role of pneumocyte type II in alveolar maintenance?
can also act as progenitor cells, replacing damaged Type I pneumocytes when needed. They are critical for alveolar repair and regeneration.
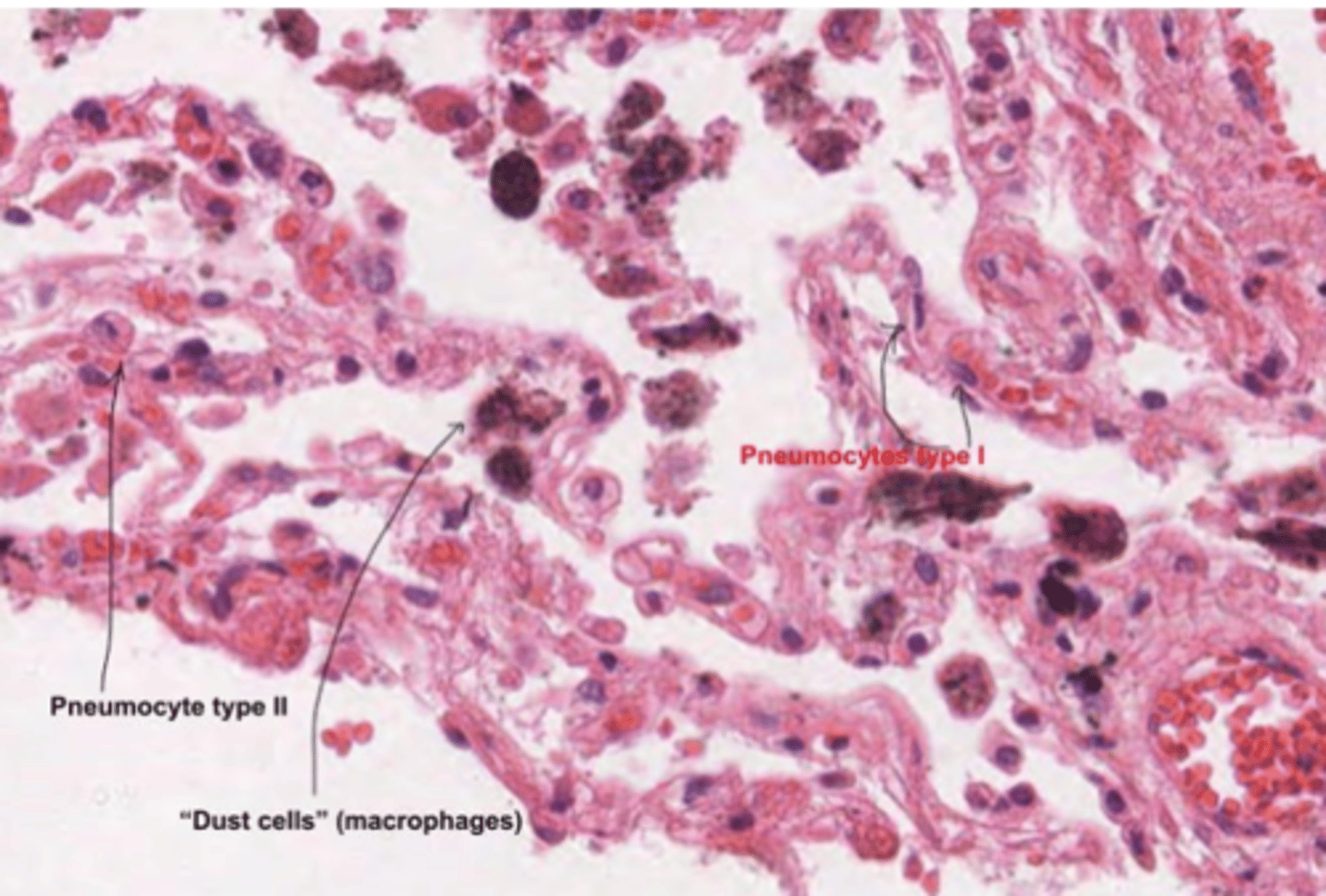
What are the macrophagues or dust cells?
are specialized immune cells in the alveoli of the lungs. Are the first line of defense in the respiratory tract, maintaining sterility in the alveolar spaces.
They also play a role in the clearance of dead cells and recycling surfactant components.
What happens to the lungs in an emphysema?
The alveoli become over inflated, and the walls break down. This leads to a decrease in respiratory function, and breathlessness.