PLUMBING VOCAB
1/211
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Plumbing Design and Estimate by Max B. Fajardo Jr. | Audio Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
212 Terms
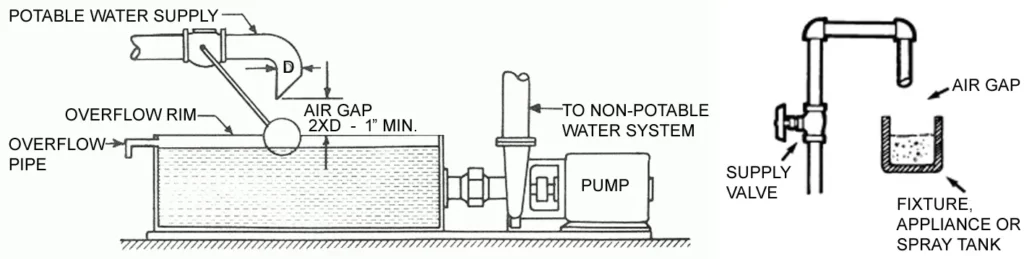
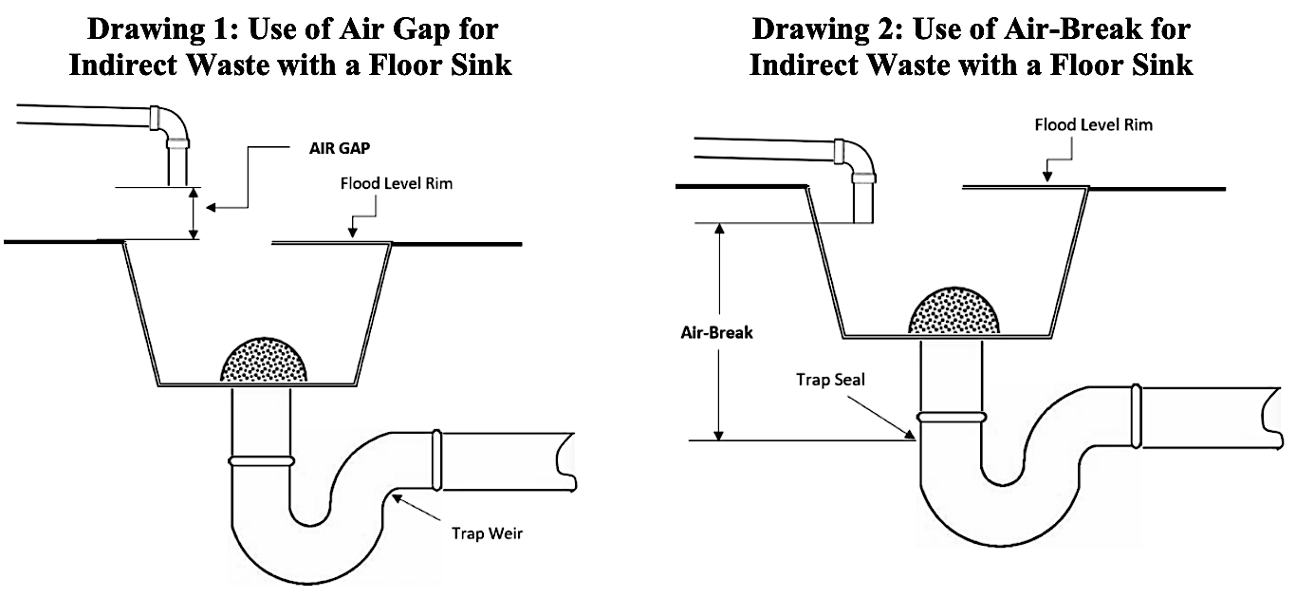
AIR GAP
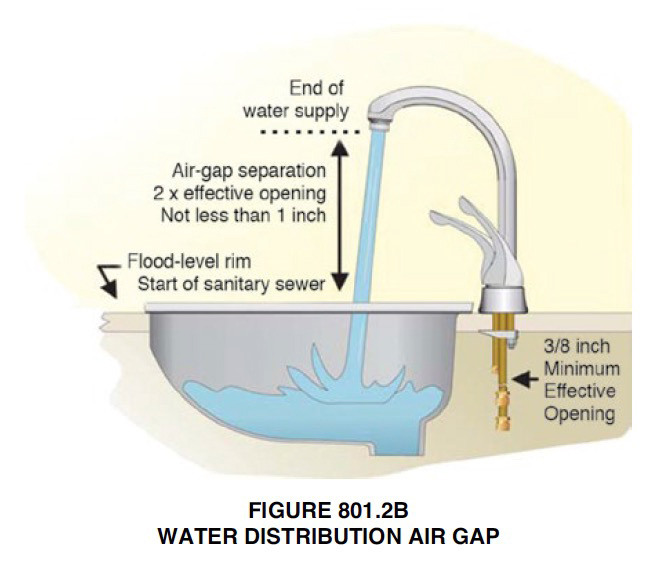
IN DRAINAGE: The unobstructed vertical distance (Usually 2 times the diameter of the supply pipe or more) through the free atmosphere between the lowest opening from any pipe or faucet supplying water to a tank, plumbing fixture, or other device and the flood level rim of the receptacle.
IN WATER DISTRIBUTION: The unobstructed vertical distance through the free atmosphere between the lowest opening from any pipe or faucet conveying potable water to the flood-level rim of any tank or fixture.
Typically required when there is a higher risk of backflow contamination or when there are strict codes in place to ensure the safety of potable water.
BACK FLOW
The flow of water or other liquids, mixtures, or substances into the distribution pipes of a potable supply of water from any source other than from its intended source.
BACK SIPHONAGE
The flowing back of used, contaminated or polluted water from a plumbing fixture or vessel into a water supply pipe due to a negative pressure in such pipe.
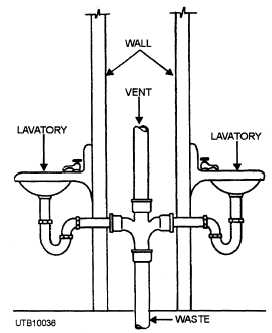
BATTERY OF FIXTURES
Any group of two (2) or more similar, adjacent fixtures which discharge into a common horizontal waste or soil branch.
BIBB
Synonymous with faucet, cock, tap, or plug.

BLOW OFF
A controlled outlet of a pipeline to discharge liquid or detritus.
A valve or system designed to release pressure, sediment, or trapped air from a system, often used in boilers or water mains to prevent damage or ensure proper operation.

BRANCH
Any part of the piping system other than a main, riser, or stack. Often used to connect fixtures to the main drainage or supply lines.
Can be either horizontal or vertical, depending on its function and orientation in the system.
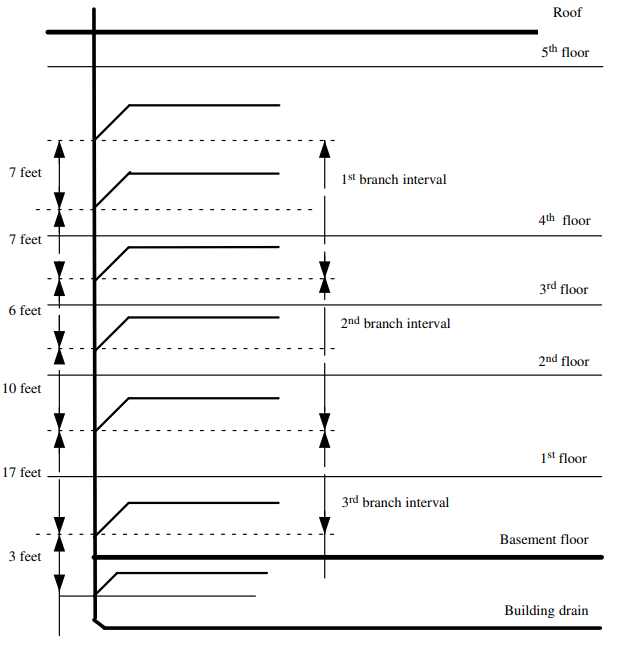
BRANCH INTERVAL
A length of soil or waste stack corresponding in general to a storey height, but in no case less than 2.43 meters within which the horizontal branches from one floor or storey of a building are connected to the stack.
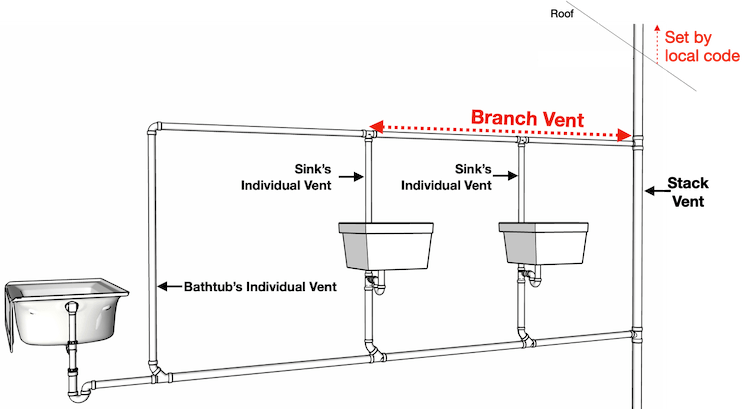
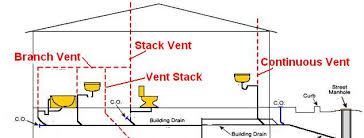
BRANCH VENT
Is a vent connecting one or more individual vents with a vent stack or stack vent.
CAULKING
Plugging an opening with oakum, lead or other materials that are pounded into the annular space.
Also, the material pounded into the annular opening.
Refers to using flexible materials like caulk or sealant to seal gaps and joints around fixtures, preventing leaks, water damage, and mold growth.
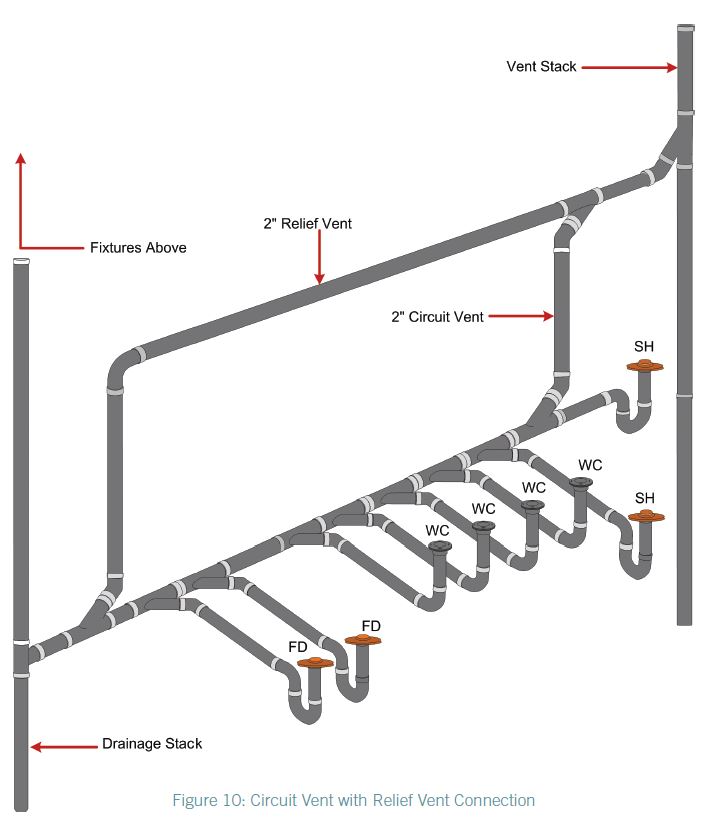
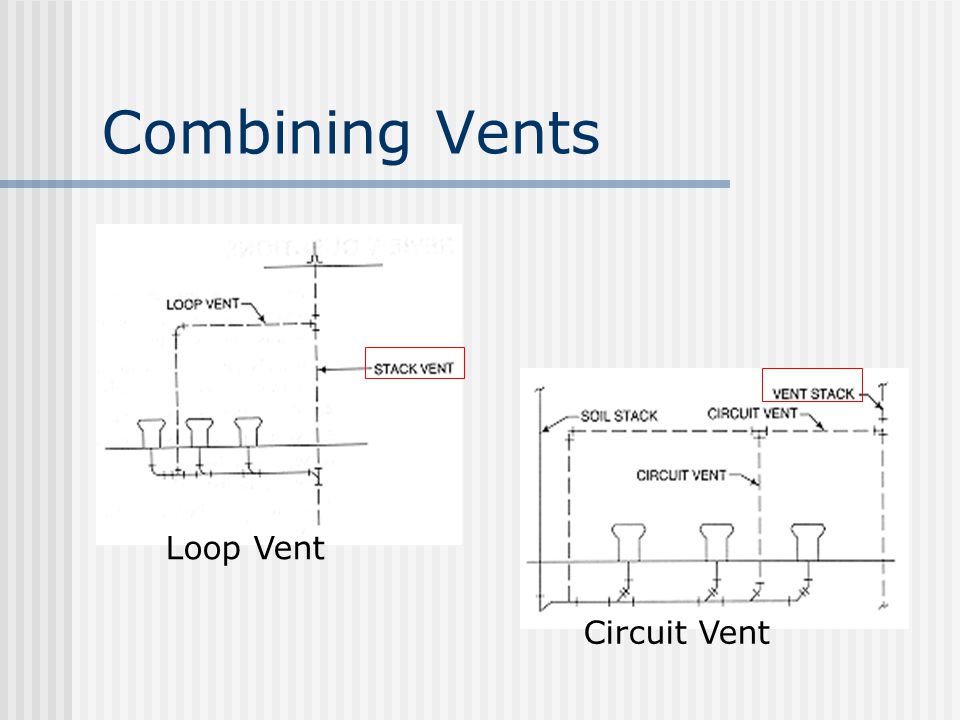
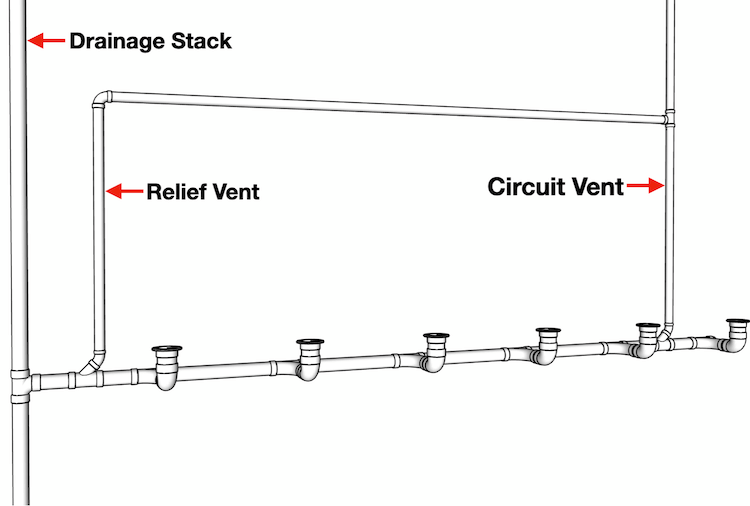
CIRCUIT VENT
A group of vent pipe which starts in front of the extreme fixture connection on a horizontal branch and connects to the vent stack.
CONTINUOUS VENT
Is a vertical vent that is a continuation of the drain to which the vent connects.
COMBINATION FIXTURES
A fixture combining one sink and tray or a two or three compartment sink or tray in one vent.
Single fixture that serves multiple functions using a common drain and trap. It is designed to save space and reduce plumbing complexity.
Examples:
Sink and Wash Tray Combination
Toilet and Sink Combination
Bathtub and Shower Combination
Kitchen Sink with Garbage Disposal

COMBINATION WASTE AND VENT SYSTEM (DWV - Drain-Waste-Vent system)
Especially designed system of waste piping embodying the horizontal wet venting of one or more sinks or floor drains by means of a common horizontal waste and vent pipe, adequately sized to provide free movement of air above the flow line of the drain.
Safely and efficiently remove wastewater from sinks, showers, toilets, and other fixtures, preventing sewer gases from entering the building.
COMMON VENT (Unit Vent or Dual Vent)
An arrangement of venting so installed that a single vent pipe will serve 2 traps.
CROSS-CONNECTION
Any connection or arrangement, physical or otherwise, between a potable water supply system and any plumbing fixture or any tank receptacle, equipment or device, through which enables non-potable, used, unclean, polluted, contaminated water or other substances to enter into any part of such potable water system under any condition.
Actual or potential connections between a potable and non-potable water supply. This may cause a backflow condition or a serious health hazard to occur.
DEAD END (Dead Leg)
The extended portion of a pipe that is closed at one end to which no connections are made on the extended portion, thus permitting the stagnation of liquid or air therein.
A section of a pipe that is no longer in use or has become isolated from the regular flow of water, potentially leading to water stagnation and increased risk of bacterial contamination.

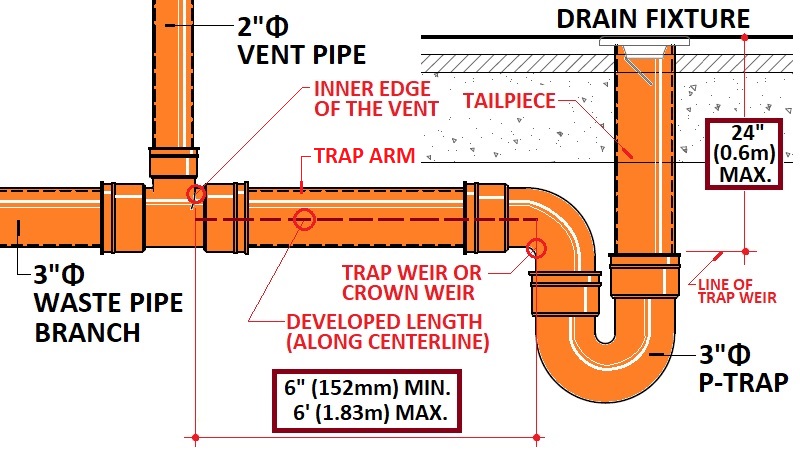
DEVELOPED LENGTH
The length of a pipe along its centerline and fittings.
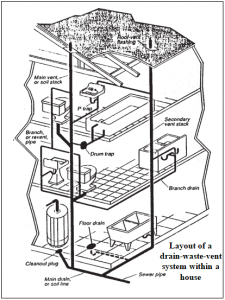
DRAINAGE SYSTEM
Network of pipes, drains, and fixtures designed to collect and remove wastewater, including sewage, rainwater, and other liquid waste, from a building, ensuring proper disposal and preventing sewer gases from entering.
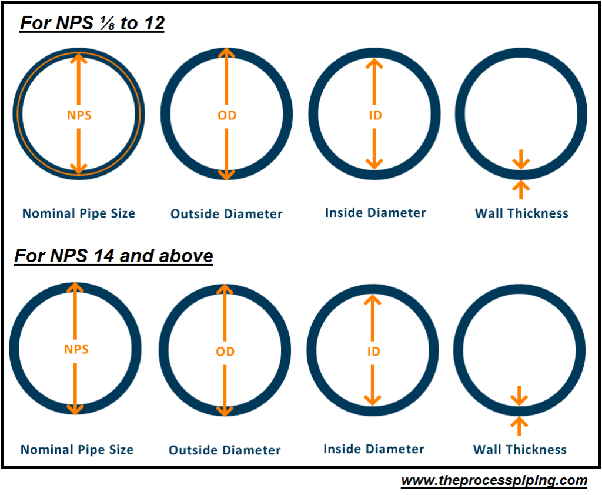
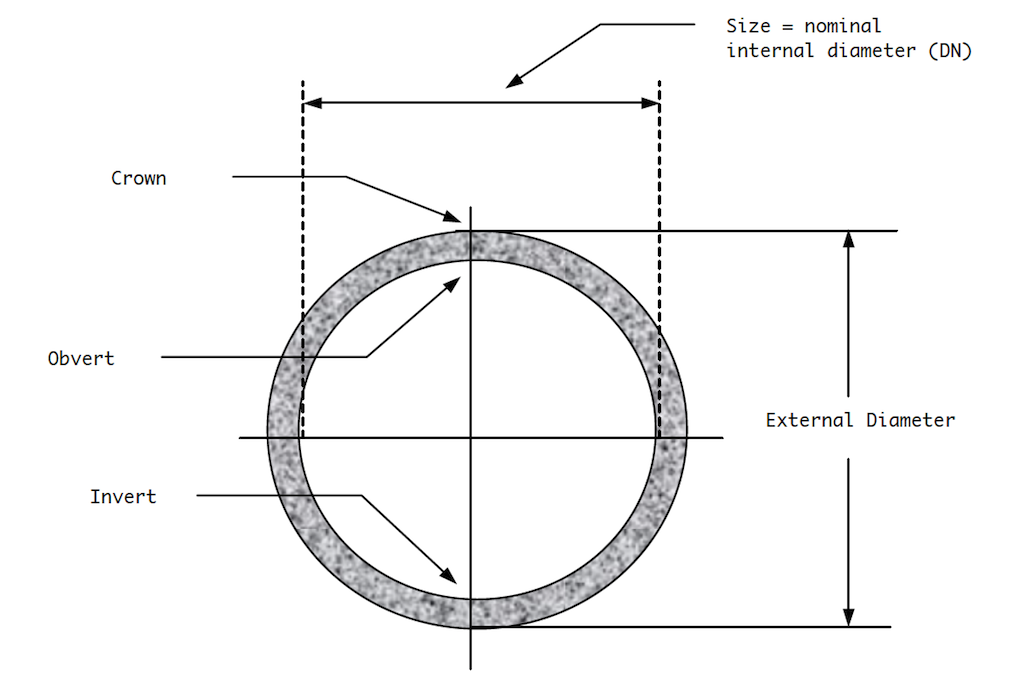
DIAMETER
Unless, specifically stated, the term, “diameter” is the nominal diameter as designated commercially.
Refers to the size of a pipe, measured as either the outside diameter (OD) or the inside diameter (ID), and is crucial for determining compatibility with fittings and ensuring proper flow rates and water pressure.
DRY VENT
A vent pipe that solely carries air and does not transport wastewater.
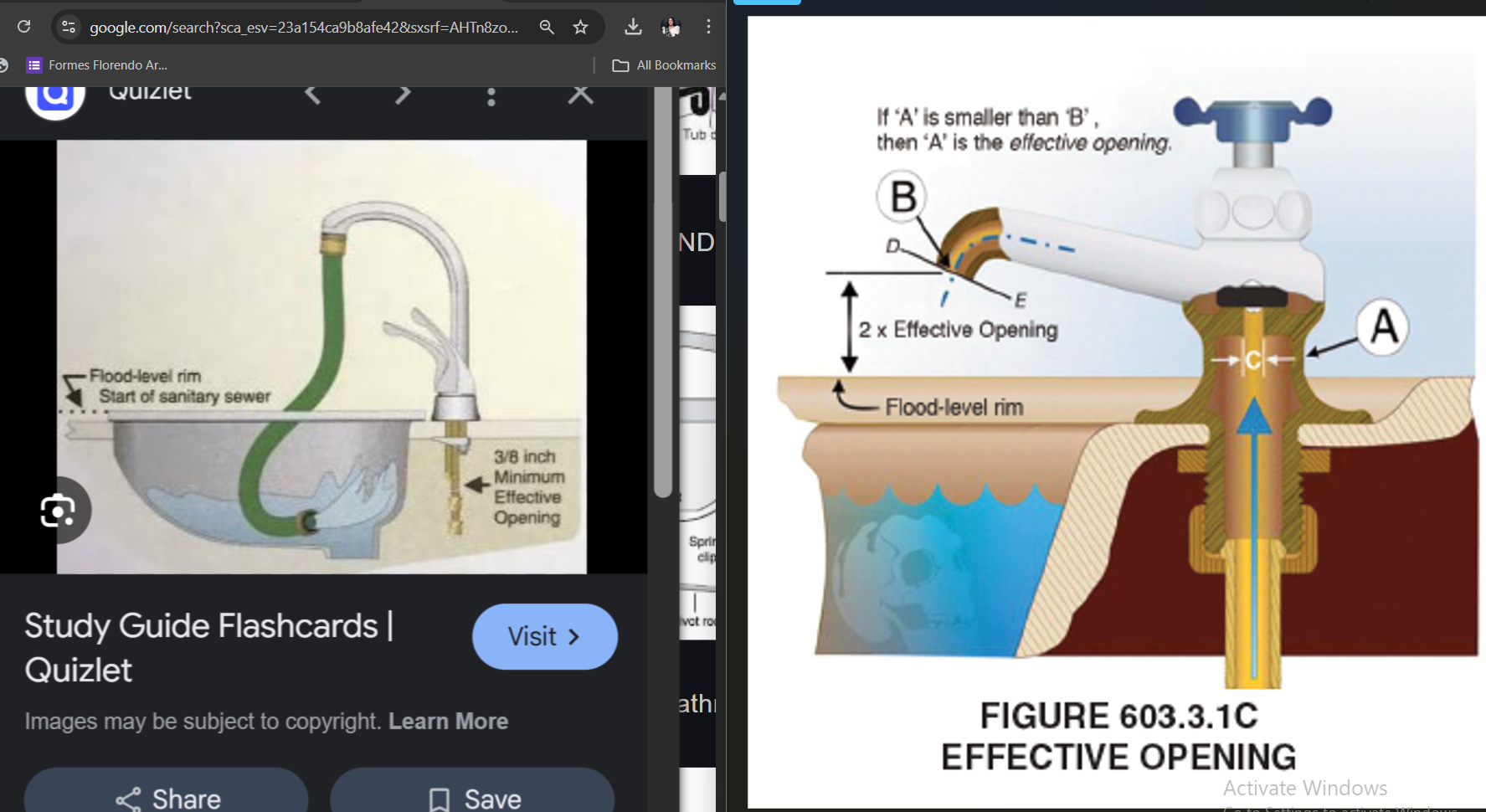
EFFECTIVE OPENING
the minimum cross-sectional area at the point of water supply discharge, measured or expressed in terms of diameter of a circle.
(If the opening is not a circle, the diameter of a circle that is equivalent to the cross sectional area.)
EXISTING WORK
That portion of a plumbing system that has been installed and approved prior to the contemplated addition, alteration, or correction
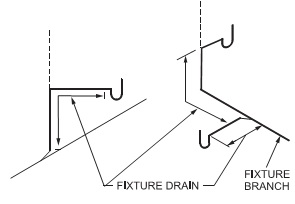
FIXTURE BRANCH
Drain pipe that serves 2 or more fixtures (excluding toilets) and conveys their waste to another drain or a stack.
Pipe connecting several fixtures
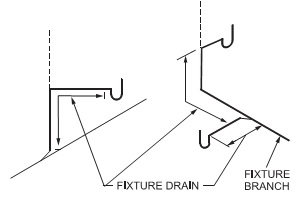
FIXTURE DRAIN
Connects a single fixture to a branch.
FIXTURE SUPPLY (Water Supply Line)
Is a water supply pipe connecting the fixture with the fixture branch
FIXTURE UNITS
Quantity in terms of which the load producing effects on the plumbing system of different kinds of plumbing fixtures are expressed on some arbitrarily chosen scale
FIXTURE UNIT FLOW RATE
Total discharge flow in gallons per minute of a simple fixture divided by 7.5 gallons that provides the flow rate of that particular plumbing fixture as a unit of flow.
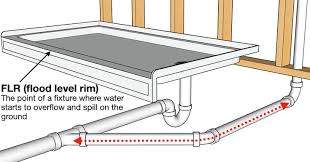
FLOOD LEVEL
Is a device located inside the tank for the purpose of maintaining water level for effective flushing of the water closet.
FERRULE
A small, cylindrical component, often made of metal or plastic, used to create a secure, leak-proof connection between a pipe or tube and a fitting.
A metallic sleeve called or otherwise joined to an opening in pipe into which a plug is screwed that can be removed for the purpose of cleaning or examining the interior of the pipe.

FLUSH VALVE
They serve as the mechanism that releases water from the toilet tank to the bowl, initiating the flush to remove waste.
Located at the bottom of the tank for flushing water closets and similar fixtures
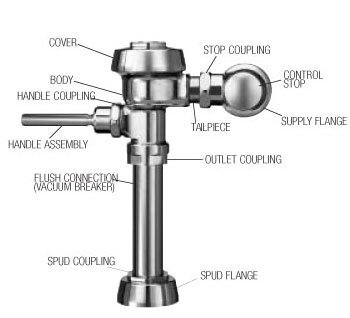
FLUSHOMETER VALVE
Commercial flush valve
Uses water pressure to flush toilets and urinals, instead of relying on a water tank like residential toilets.
Device that discharges a predetermined quantity of water to the fixture for flushing purposes activated by direct water pressure.

GRADE
Slope or fall of a pipe, typically expressed as a percentage to indicate the drop in feet (or meters) per hundred feet (or meters) of pipe length, ensuring proper drainage and preventing blockages.

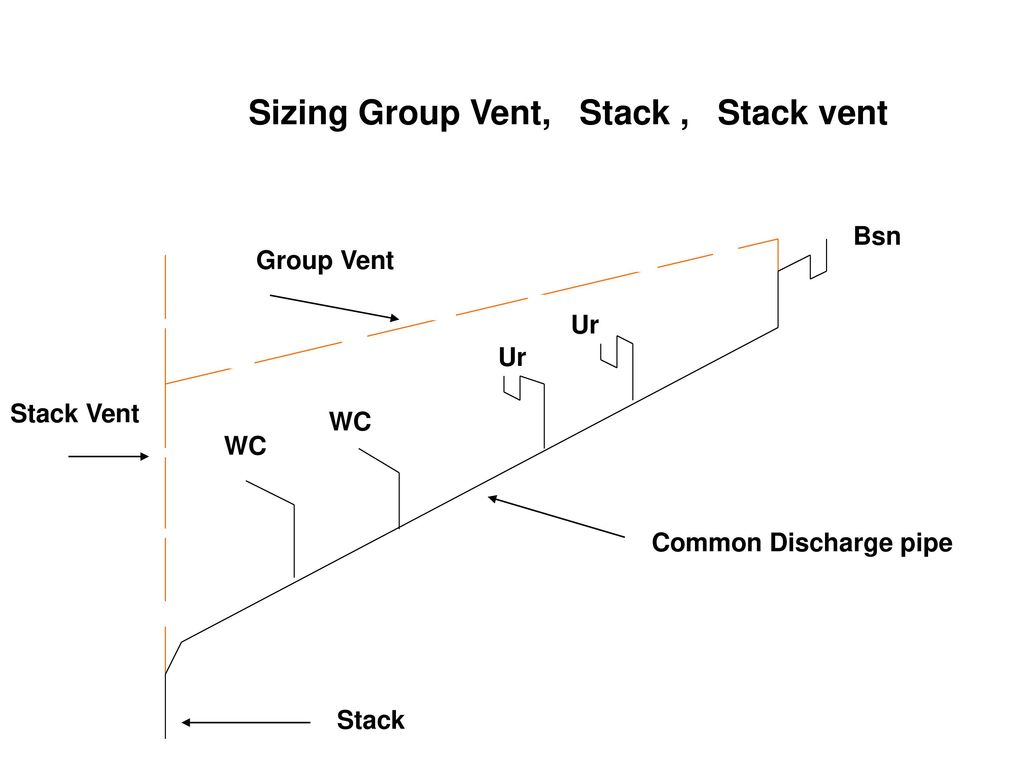
GROUP VENT
A branch vent that performs its function for two or more traps.
A system where multiple plumbing fixtures, like lavatories, bathtubs, or shower stalls, are vented by a single vent pipe, rather than each fixture having its own individual vent.
HORIZONTAL PIPE
Any pipe or fitting which makes an angle of more than 45 degrees with the vertical.
INVERT
Lowest portion of the inside of any pipe or conduit that is not vertical
LIQUID WASTE
Is the discharge from any fixture, appliance or appurtenance in connection with a plumbing system which does not receive fecal matter.
LOCAL VENT PIPE
Pipe on the fixture side of the trap that removes foul air or vapors from a room or fixture, conveying them to the outer air
Local - specific to a certain fixture or area
Different from individual vent. Not part of a drainage vent - more like an air exhaust.
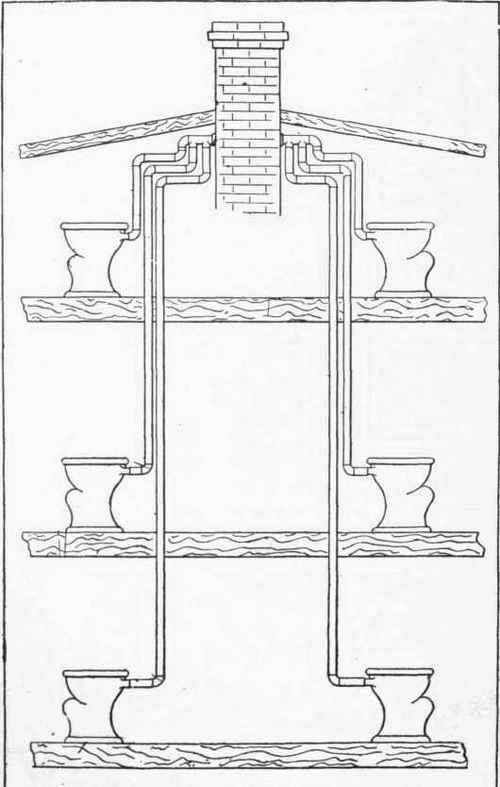
LOOPED VENT
Same as Circuit Vent except that it loops back and connects with a stack vent instead of a vent stack
Specific type of circuit vent
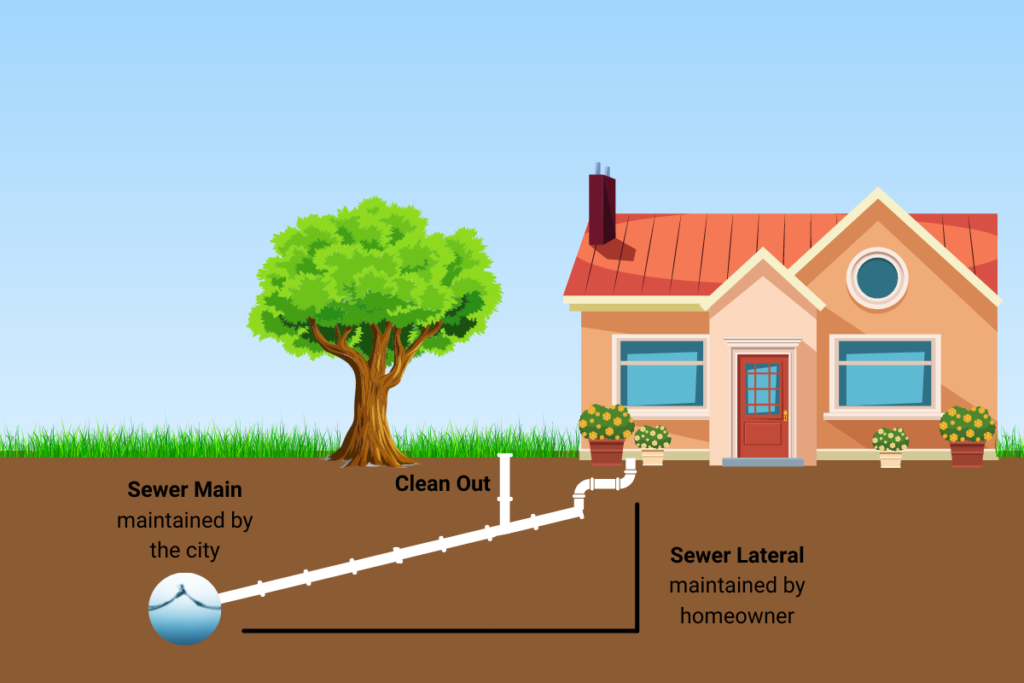
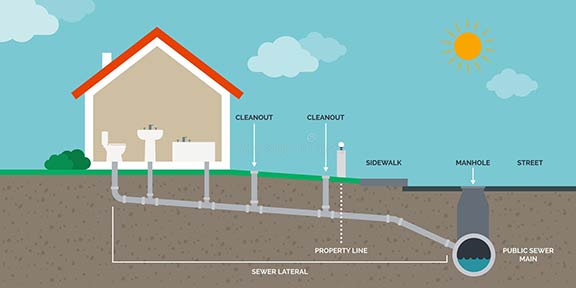
LATERAL (Sewer Lateral or Sewer Line)
In plumbing, a secondary pipe.
In sewage, a common sewer to which no other common sewer is tributary. It receives sewage only from the building sewer.
Refers to the pipe connecting a building’s plumbing system to the public sewer line, responsible for transporting wastewater from the home to the main sewer.

MAIN
principal artery of the system to which branches may be connected
MAIN SEWER
Is a sewer line or system directly controlled by public authority
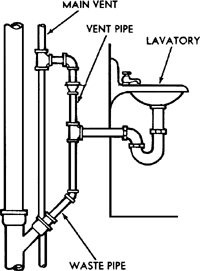
MAIN VENT (Vent Stack)
Principal artery of the venting system to which vent branches may be connected.
Vertical pipe that regulates airflow within the plumbing system, preventing sewer gases from entering the home and ensuring proper drainage
PLUMBING FIXTURES
Are installed receptacles, devices, or appliances which are supplied with water, or which receives or discharges liquid or liquid borne waste, with or without discharge into drainage system which maybe directly or indirectly connected.
PLUMBING SYSTEM
Includes the water supply distribution pipes, plumbing fixtures and traps, soil, waste and vent pipes, house drain and house sewers including their respective connections, devices, and appurtenances within the property line at premises, and water treating or water using equipment
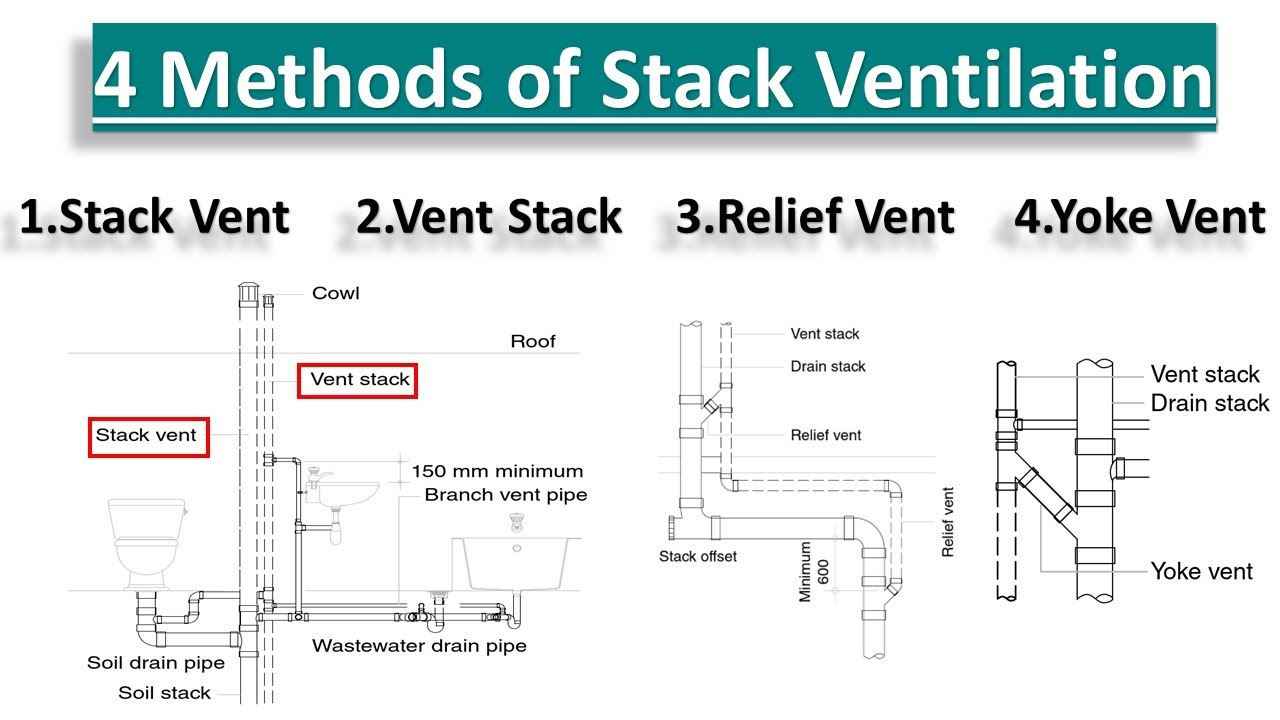
RELIEF VENT
Its primary function is to provide circulation of air between drainage and vent systems.
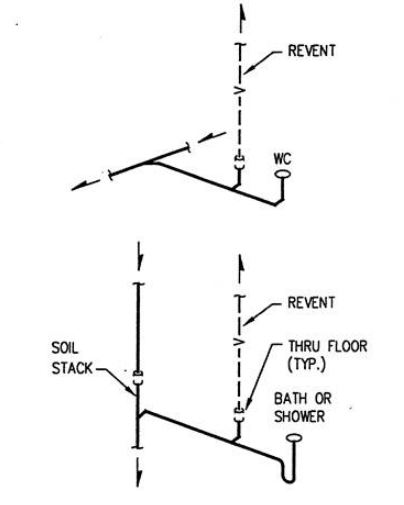
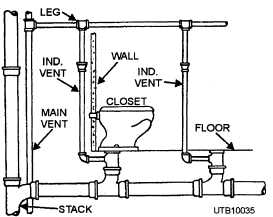
RE-VENT PIPE (Individual Vent)
That part of the vent pipeline which connects directly with an individual waste or group of wastes underneath or back of the fixture, and extend either to the main or branch vent pipe
PUBLIC SEWER
Common sewer directly controlled by public authorities where all abutters have equal rights of connection
SANITARY SEWAGE (Domestic Sewage)
The sewage containing human excrement and liquid household waste.
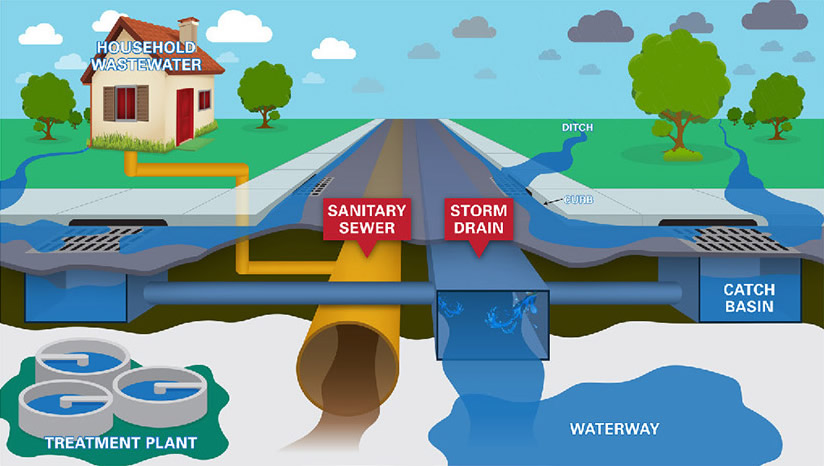
SANITARY SEWER
A sewer intended to receive sanitary sewage with or without industrial wastes and without the admixture of surface water, storm water or drainage.
SECONDARY BRANCH
Any branch in a building drain other than the primary branch.
Pipe that connects to a main branch or riser (often from fixtures like sinks or toilets). Connects a group of fixtures to the main system.
Sub-branch in a tree, coming off the main branch.
SEWERAGE OF SEWAGE WORK
Is a comprehensive term including all construction or collection, transportation, pumping, treatment and final disposition of sewage.
SIAMESE CONNECTION
Is a Y connection used on fire lines so that two lines of hose maybe connected to a hydrant or to the same nozzle.
A fitting with 2 or more inlets used to connect multiple hoses to a sprinkler system, allowing fire trucks to pump water into the system.
Fire Department Connection (FDC) that enables firefighters to quickly access a building’s fire suppression system.
STANDPIPE
A vertical pipe usually used for the storage of water, frequently under pressure.
SIDE VENT
A vent connecting to the drain pipe through a fitting at an angle not greater than 45 degrees or to the vertical.
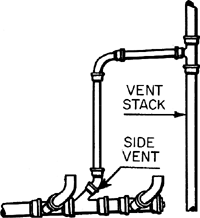
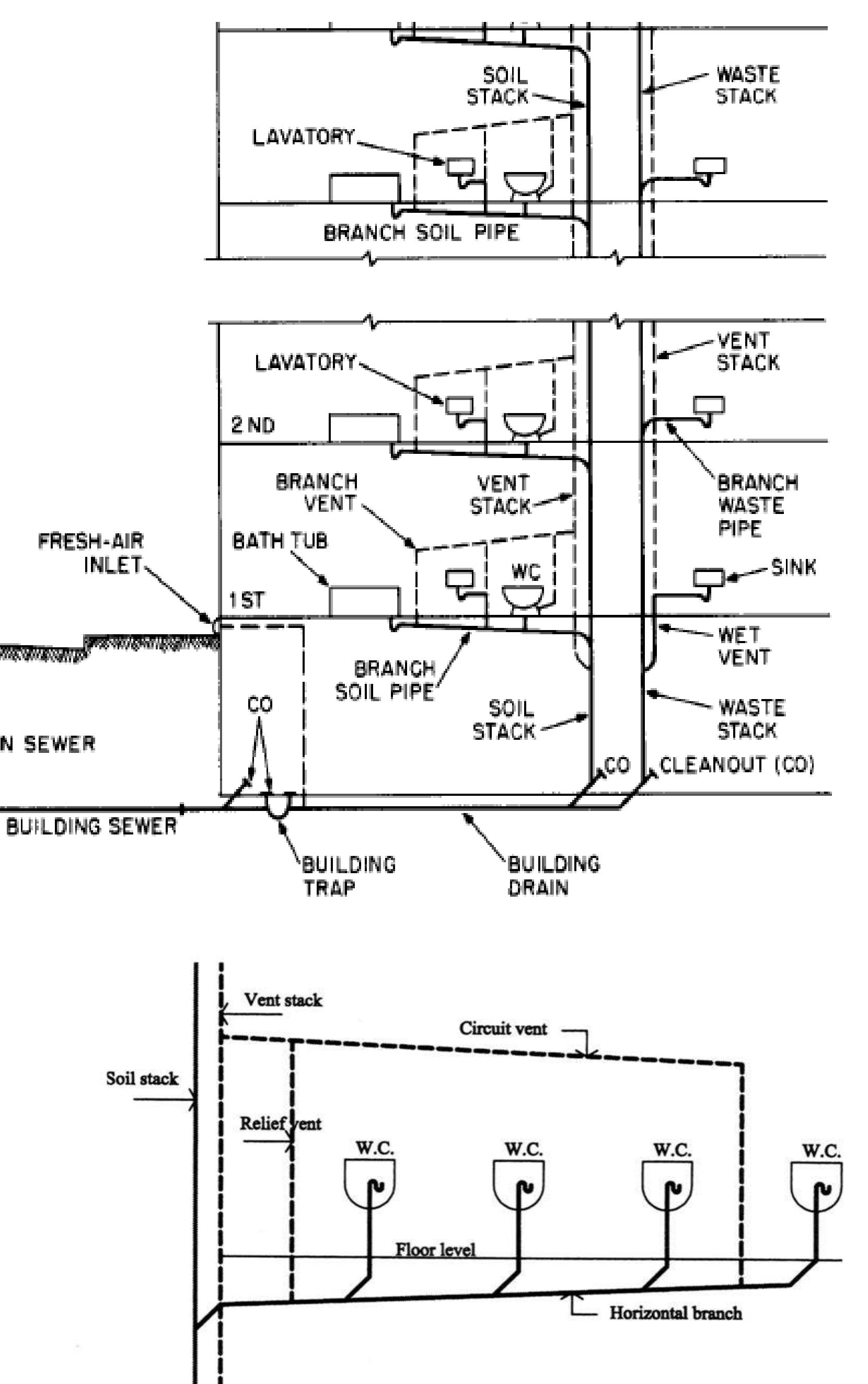
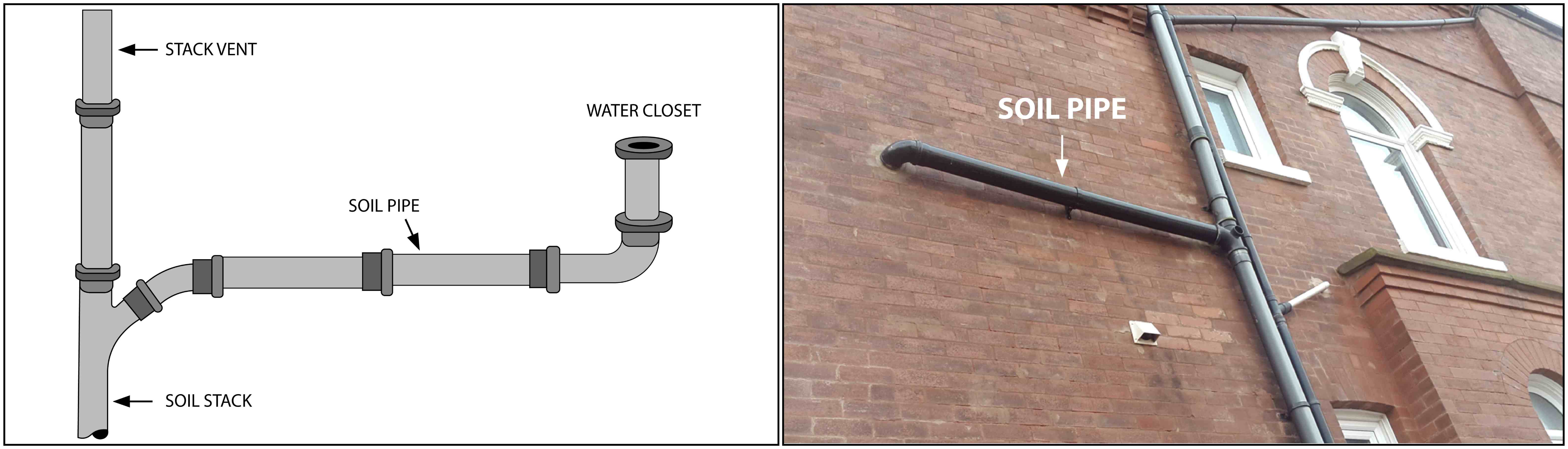
SOIL PIPE
Any pipe that conveys the discharge of water closets or fixtures having similar functions, with or without the discharge from other fixtures, to the building drains (house drain) or building sewer (house sewer)
STACK
The vertical main of a system of soil, waste, or vent pipe
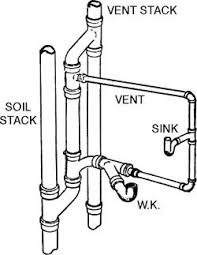
STACK GROUP
Term applied to the location of fixtures in relation to the stack so that by means of proper fittings, vents may be reduced to a minimum
STACK VENT (Soil or Waste Stack)
Extension of a soil or waste stack above the highest horizontal drain connected to the stack
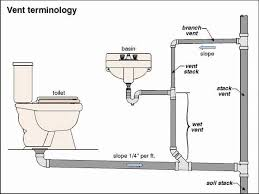
STACK VENTING
Method of venting a fixture or fixtures through the soil or waste stack.
SUBSOIL DRAIN
Are underground drain pipes that receive sub-surface or seepage water only and convey it to a place of disposal
SUMP
A pit or receptacle at a low point to which the liquid waste are drained.
Constructed pit or basin, typically located in a basement or crawl space, that collects excess water.
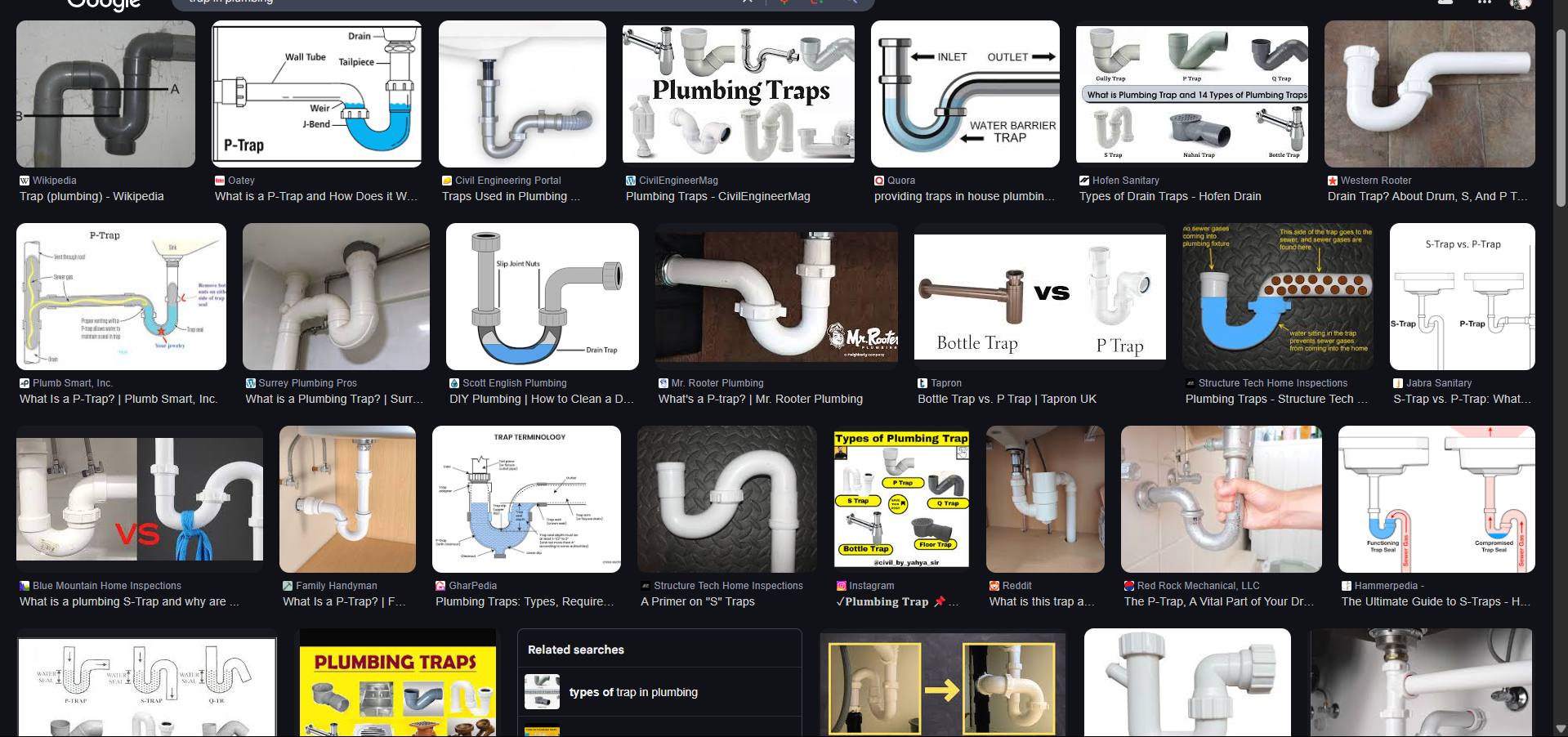
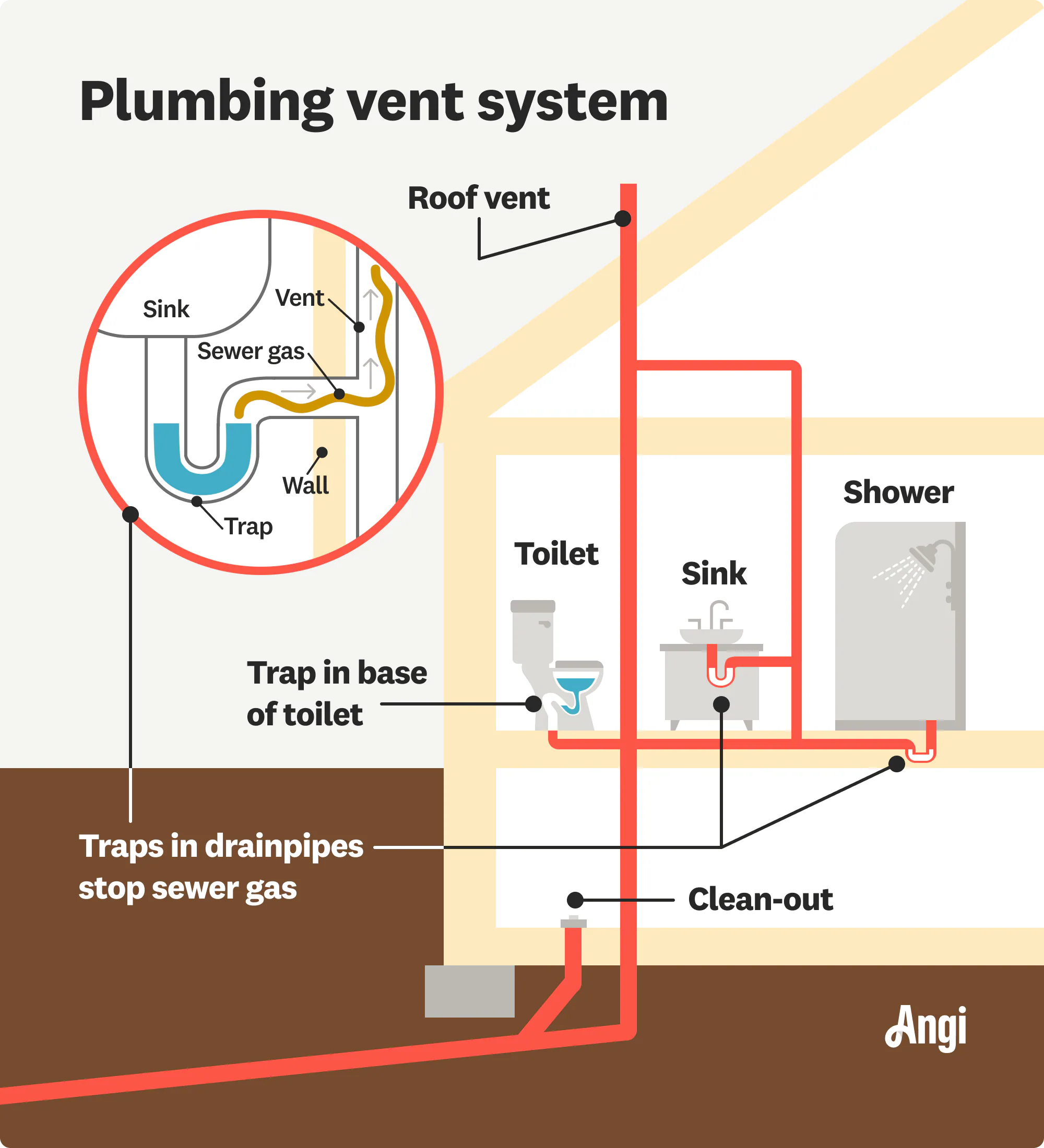
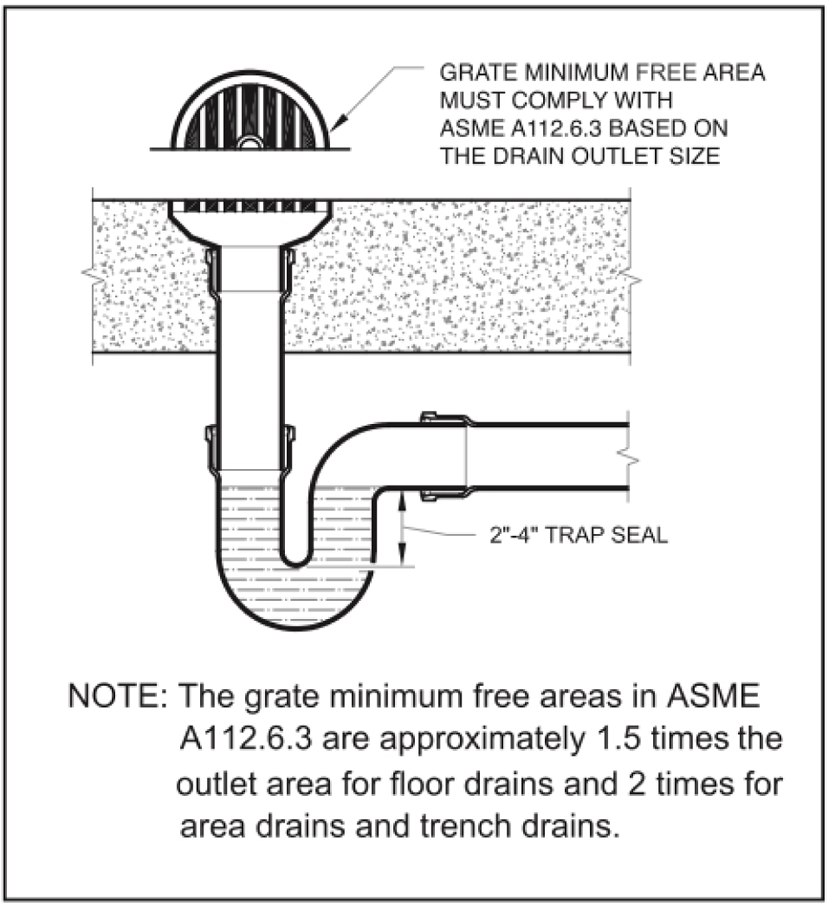
TRAP
Is a fitting or device so designed as to provide when properly vented a liquid seal that will prevent the back passage of air without materially affecting the flow of sewage through it.
TRAP SEAL
Maximum vertical depth of liquid that trap will retain, measured between the crown weir and top of the dip of the trap
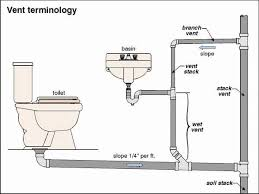
VENT STACK
Vertical pipe installed primarily for the purpose of providing circulation of air to different parts of the drainage system
VENT SYSTEM
Pipe/Pipes installed to provide a flow or circulation of air within the plumbing system to protect trap seals siphoning and back pressure.
VERTICAL PIPE
Is a pipe installed in a vertical position or at an angle of not more than 45 degrees with the vertical
WASTE PIPE
Pipe that conveys liquid waste from fixture that is free of fecal matter
WATER DISTRIBUTING PIPE
Pipe that conveys water from the water service pipe to the plumbing fixtures and other water outlets
WATER SERVICE PIPE
Pipe from the water main or other source of water supply to the building served
WATER SUPPLY SYSTEM
Consists of the water service pipes, the water distributing pipes, and the necessary connecting pipes, fitting, control valves, and all appurtenances in or adjacent to the building or premises.
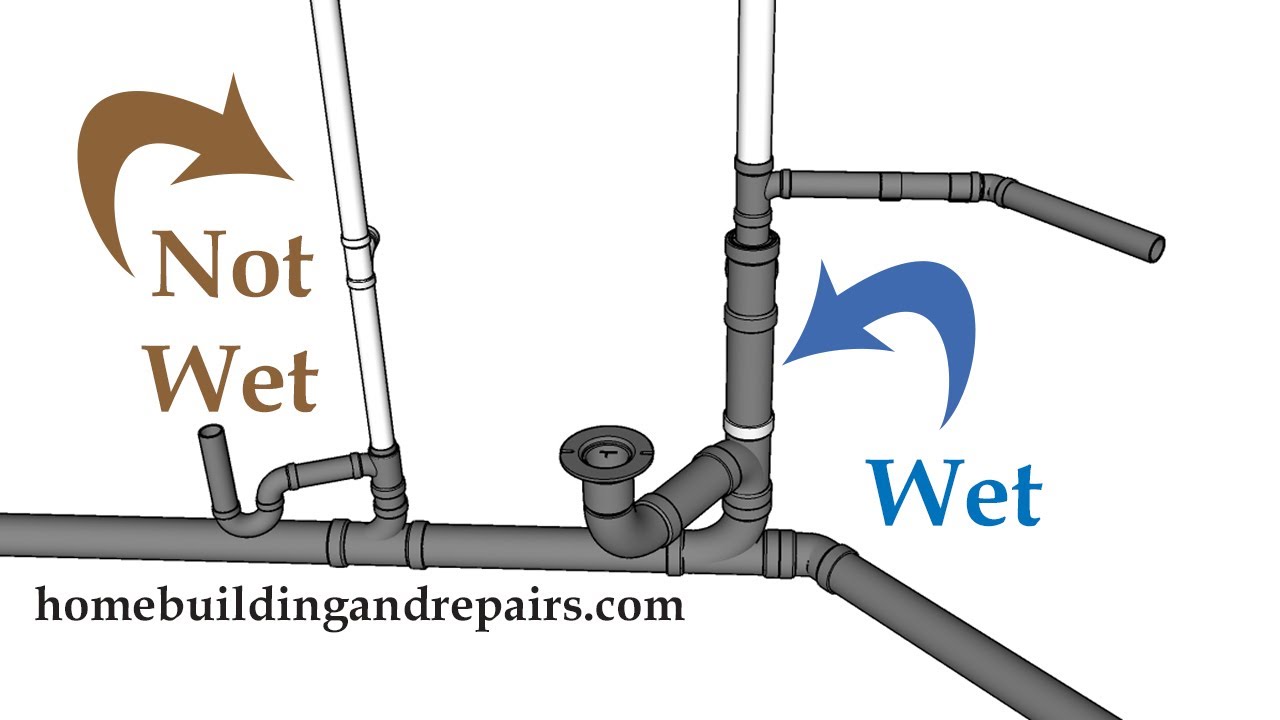
WET VENT
Is a vent that receives the discharge from wastes other than water closet
PLUMBING
The art and science of installing pipes, fixtures, and other apparatus to convey and supply water in the buildings, and to dispose and discharge waste water and other liquids, gases, and other substances out of buildings in a safe, orderly, healthy and sanitary way to ensure the health and sanitation of life and property.
PLUMBER
A person who is skilled in the field of sanitation.
PLUMBARIUS
Refers to an individual who worked in the sanitary field of Ancient Rome.
PLUMBUM
Lead. A metal used as plumbing material by the Romans, preferred for its twin properties of malleability and resistance to acid.
17th CENTURY
English Parliament passed the first plumbing apprentice law.
SEPTIC TANK
A buried, watertight tank designated and constructed to receive and partially treat raw domestic sanitary wastewater. It is a proper sewage disposal system.
ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene)
Black plastic pipe commonly used for drainage, sewage, and vent. Good at handling severely cold temperatures, but can warp with exposure to direct sunlight. Maybe used in buried or above ground DWV applications.

AIRBREAK
Physical separation between the potable water system and a waste system. It is created by providing an open vertical space between the end of a pipe that carries potable water and the wastewater or drain it is discharging into.
Typically used when the risk of backflow is lower, or when it’s allowed by local plumbing codes in less critical applications.
APPRENTICE PLUMBER
An entry level plumber, learning the trade. May work with a journeyman, under the supervision of a master plumber.
AREA DRAIN
A receptor designed to collect surface or storm water from an open area
RECEPTOR
A fixture that receives waste from appliances and fixtures. It can be a floor drain, standpipe, hub drain, or floor sink.
Typically used to receive discharge from fixtures or appliances that are required to discharge through an air break or air gap.
ASPIRATOR
A device, like a fitting or suction apparatus, that uses fluid under pressure to create a vacuum, often used for removing fluids or air, similar to an ejector.

VACUUM
Refers to a negative pressure condition in the pipes that can occur when the pressure inside the drainage system becomes lower than the atmospheric pressure.
BACKFLOW CONNECTION
A condition or any arrangement whereby reverse flow can occur.
BACKPRESSURE BACKFLOW
Type of unwanted reverse flow in a plumbing system where the pressure downstream (in the building or fixture) exceeds the pressure in the supply line, forcing contaminated water back into the potable water system.
Occurs due to an increased reverse pressure above the supply pressure. This maybe due to pumps, boilers, gravity, or other source of pressure.
BACK FLOW PREVENTER
Device or means to prevent flow of liquid from returning to the source of supply. It is also known as vacuum breaker.

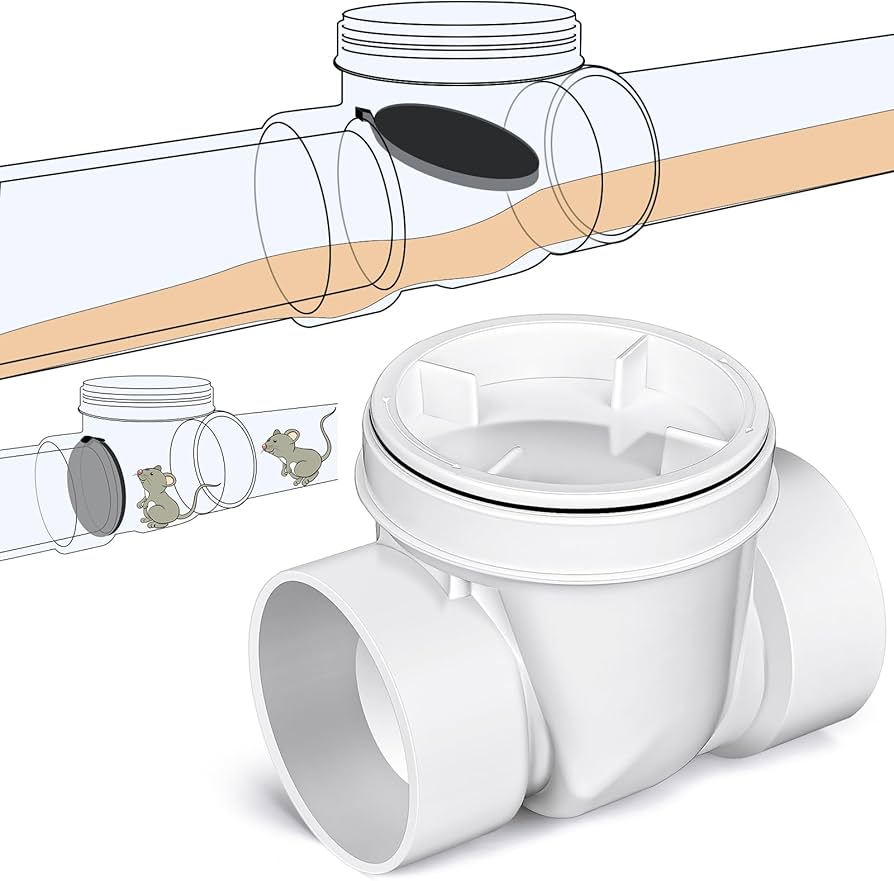
BACKWATER VALVE
A device installed in a drainage system to prevent reverse flow.
VALVE
A device that controls the flow of fluids through pipes, either by opening, closing, or partially obstructing the passage.
Used to direct flow, shut off water access, prevent backflow, and adjust water pressure within a system.
BACKVENT PIPE (Individual vent)
The part of a vent line, which connects directly with an individual trap underneath or behind the fixture and extends to the branch or main vent pipe at any point higher than the fixture or fixture traps it serves.
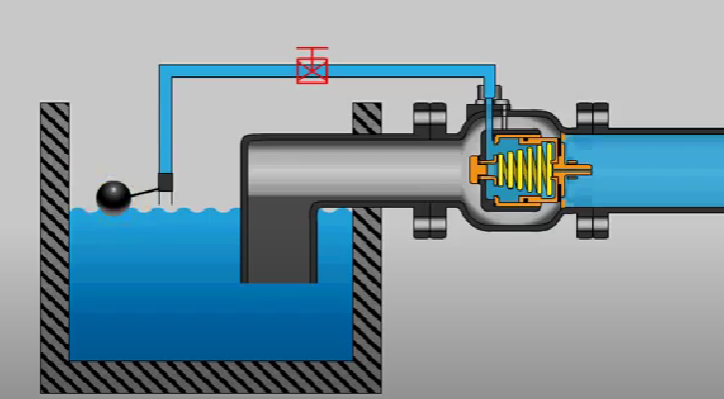
BALL COCK
A valve opened and closed by the fall and rise, respectively, of an attached ball floating on the surface of the liquid.
Vital component in plumbing, specifically in toilet tank mechanisms. It controls the flow of water into the tank and maintains the water level.
BALL JOINT
A type of pipe connection in which a ball shaped end is held in a cuplike shell and allows movements in every direction.

BATHROOM
A room equipped with a shower stall or bathtub
TYPES OF BATHROOM
Full Bath - Lavatory, Toilet, Shower Stall, and Bath Tub
¾ Bath - Toilet, Lavatory, and Shower Stall
½ Bath - Toilet and Lavatory
¼ Bath - aka Powder Room, Either Toilet or Shower
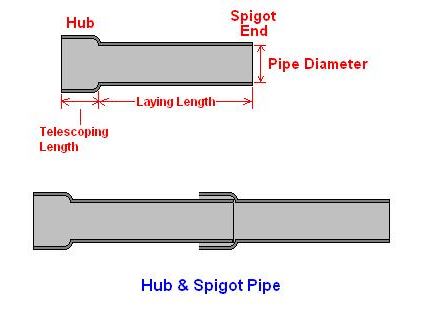
BELL OR HUB
That portion of a pipe which, for a short distance, is sufficiently enlarged to receive the end of another pipe of the same diameter for the purpose of making a caulked or push-on joint.
CAULKED JOINT
A joint that uses molten lead and oakum or hemp to seal the pipes. This type of joint is used in cast iron pipework.
These typically involve sealing the joint with a material like lead, which is poured or hammered into a space around the pipe to create a watertight seal.
Historical plumbing method. They are still used in specific applications, particularly for cast iron pipe in drainage and venting systems, but are less common than other modern joint types.

OAKUM
Loose fiber obtained by untwisting old rope, used especially in caulking wooden ships.
A preparation of tarred fibers used to seal gaps.

PUSH-ON JOINT
A type of connection, commonly used with ductile iron pipe, that uses a rubber gasket to form a watertight seal by simply pushing the pipe ends together.
GASKET
A mechanical seal, typically made of rubber or silicone, used to prevent leaks between two mating surfaces, ensuring a tight, waterproof seal when compressed between pipes, fittings, or other plumbing components.
