Module 6 - The Skeletal Muscle System
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
skeletal muscles are attached to bone via...
tendons
Insertion
the point at which a muscle's tendon attaches to the more moveable bone
Orgin
the point at which a muscle's tendon attaches to the more stationary bone
Belly
the largest part of the muscle, which actually contains the muscle cells
biceps brachia and triceps brachia are one example of two muscles that _______________________
work together.
When two muscles work together to create the same movement, they are called.....
synergists
prime mover (agonist)
primarily responsible for movement
Antagonist
the muscle that works opposite of the agonist
Muscles tend to work as WHAT in the body?
levers
a lever consists of f a rigid bar called a _________________
fulcrum
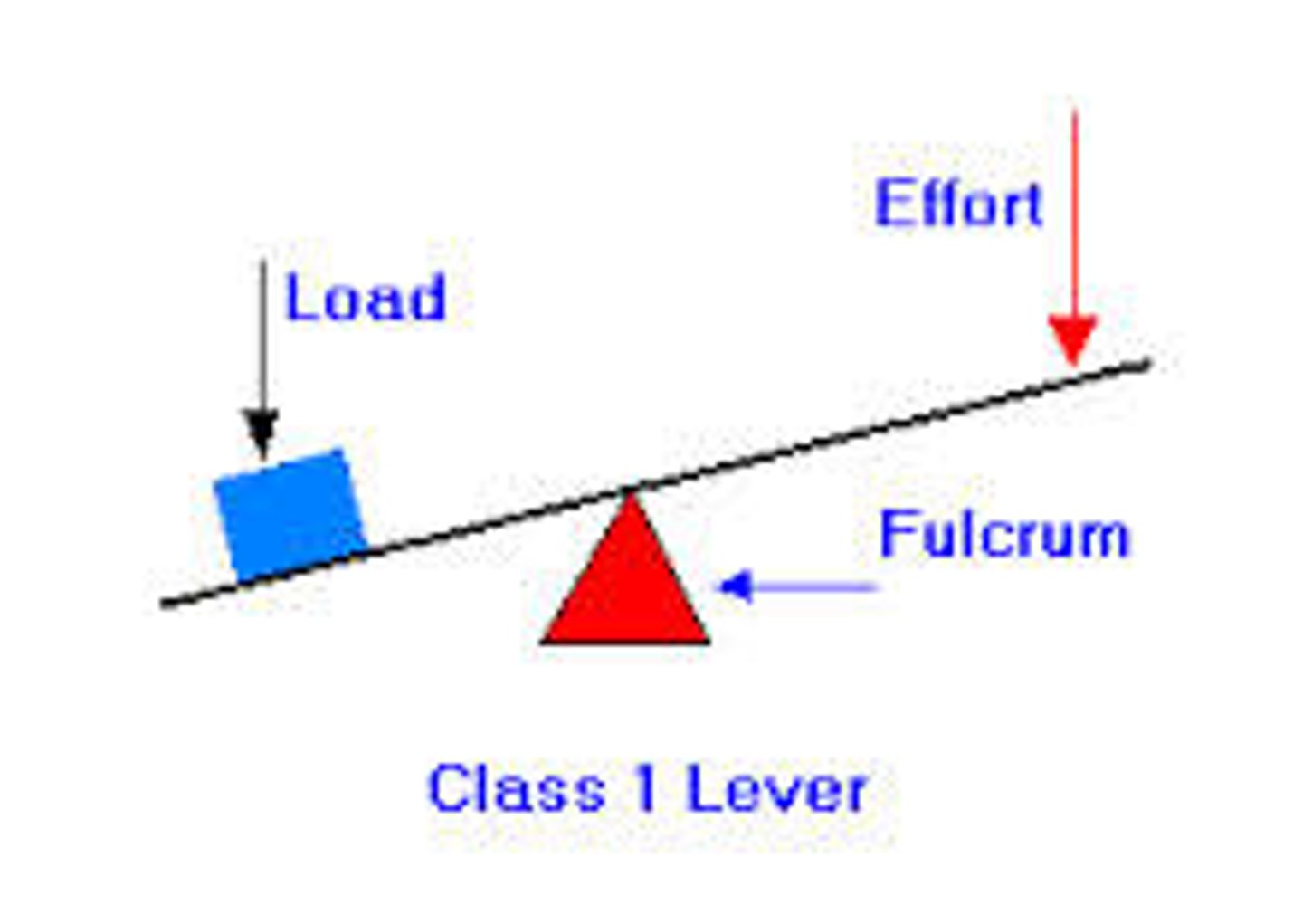
first class lever
in a first class lever the fulcrum is between the effort and the resistance
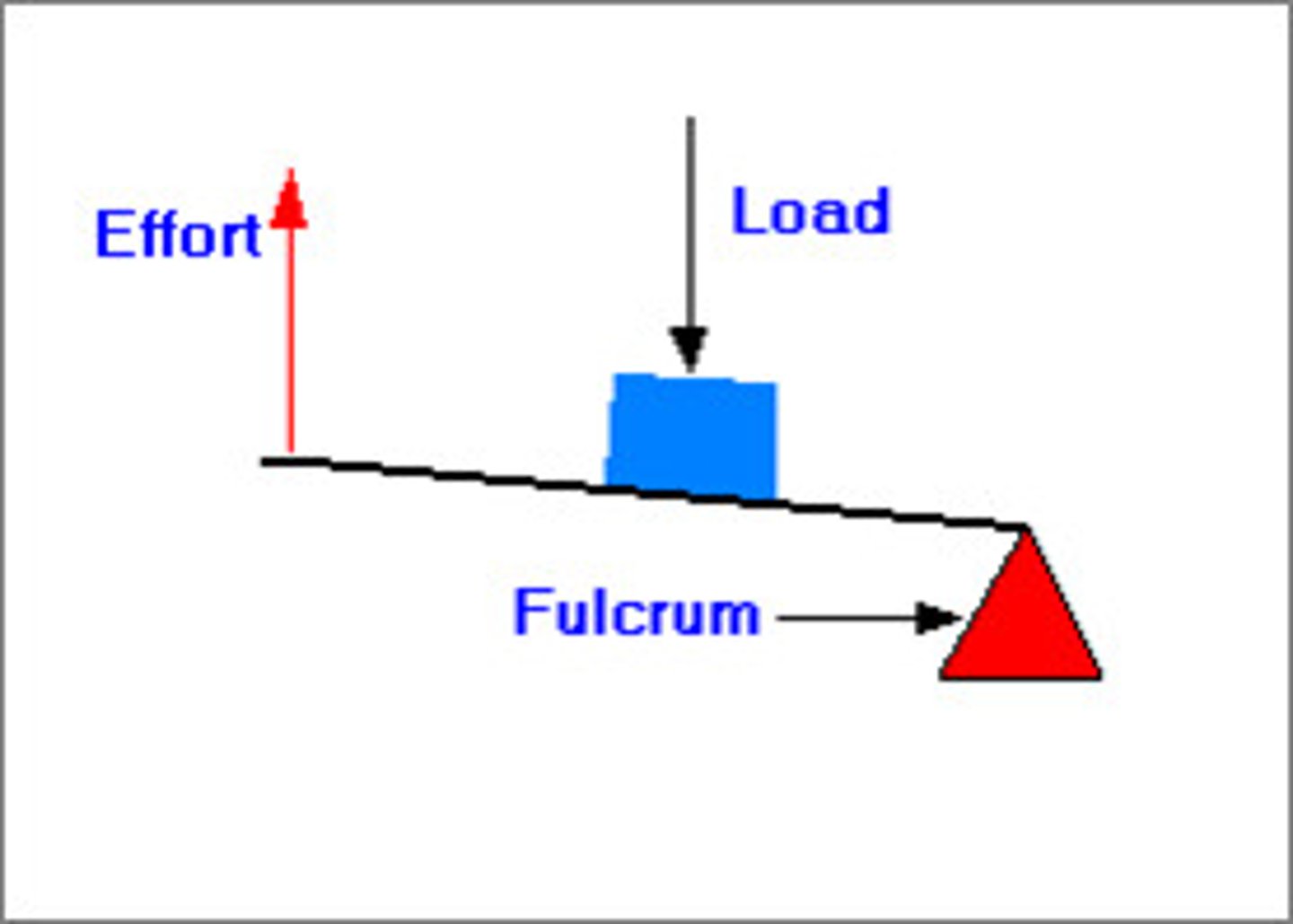
second class lever
in a second class lever the resistance is between the effort and the fulcrum
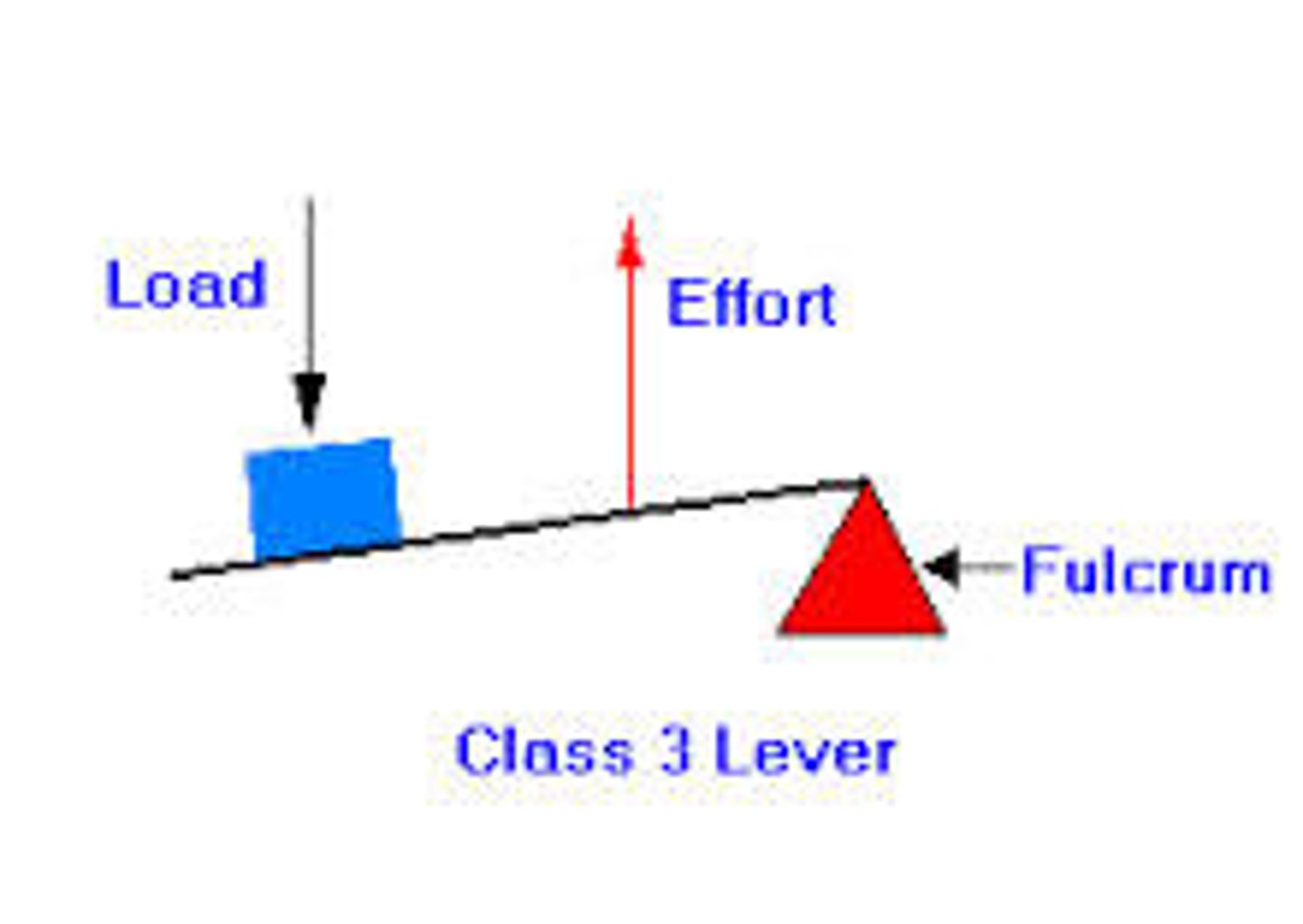
third class lever
in the third class lever, the effort is between the fulcrum and the resistance.
where can superficial skeletal muscles be found?
just underneath the layer of skin
what are the seven criteria used in naming a muscle?
(1). size, (2). Shape, (3). Location, (4). orientation of the fascicles , (5). origin and insertion, (6). number of heads, (7). function
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is the primer mover of a group of muscles which...
Rotate and flew the head
the frontal and occipitals muscles are often considered two bellies of a single muscle called the
occipitofrontalis muscle
the orbicular oculi circle the orbit and it used to _____________
close the eye.
Orbicular iris surrounds the lip and is used to ___________________. It is nicknamed the "___________________ ____________"
Purse the lips, Kissing muscle
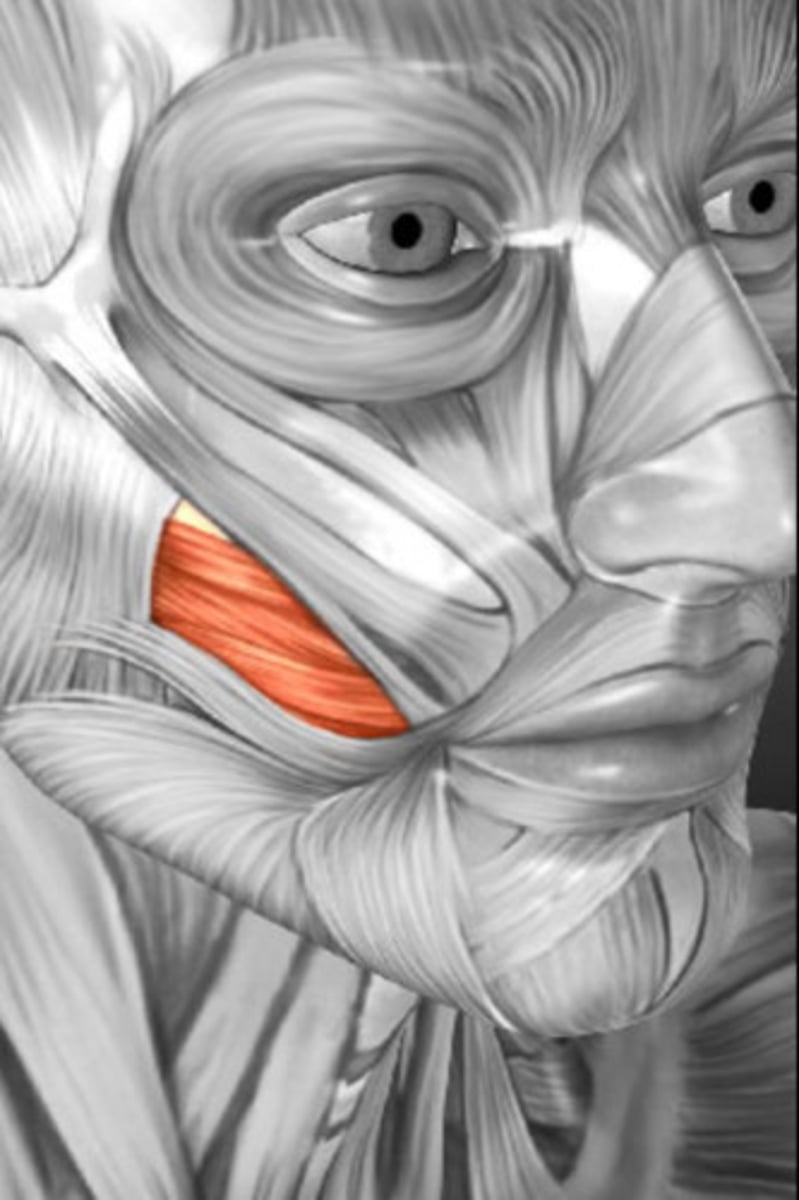
the buccinator (or cheek muscle) does what? what is one action that needs the use of the buccinator?
compresses the cheek, making rapid changes in volume of the oral cavity. Squirting water out of your mouth
Zygomaticus major and minor are two muscles needed for what?
smiling
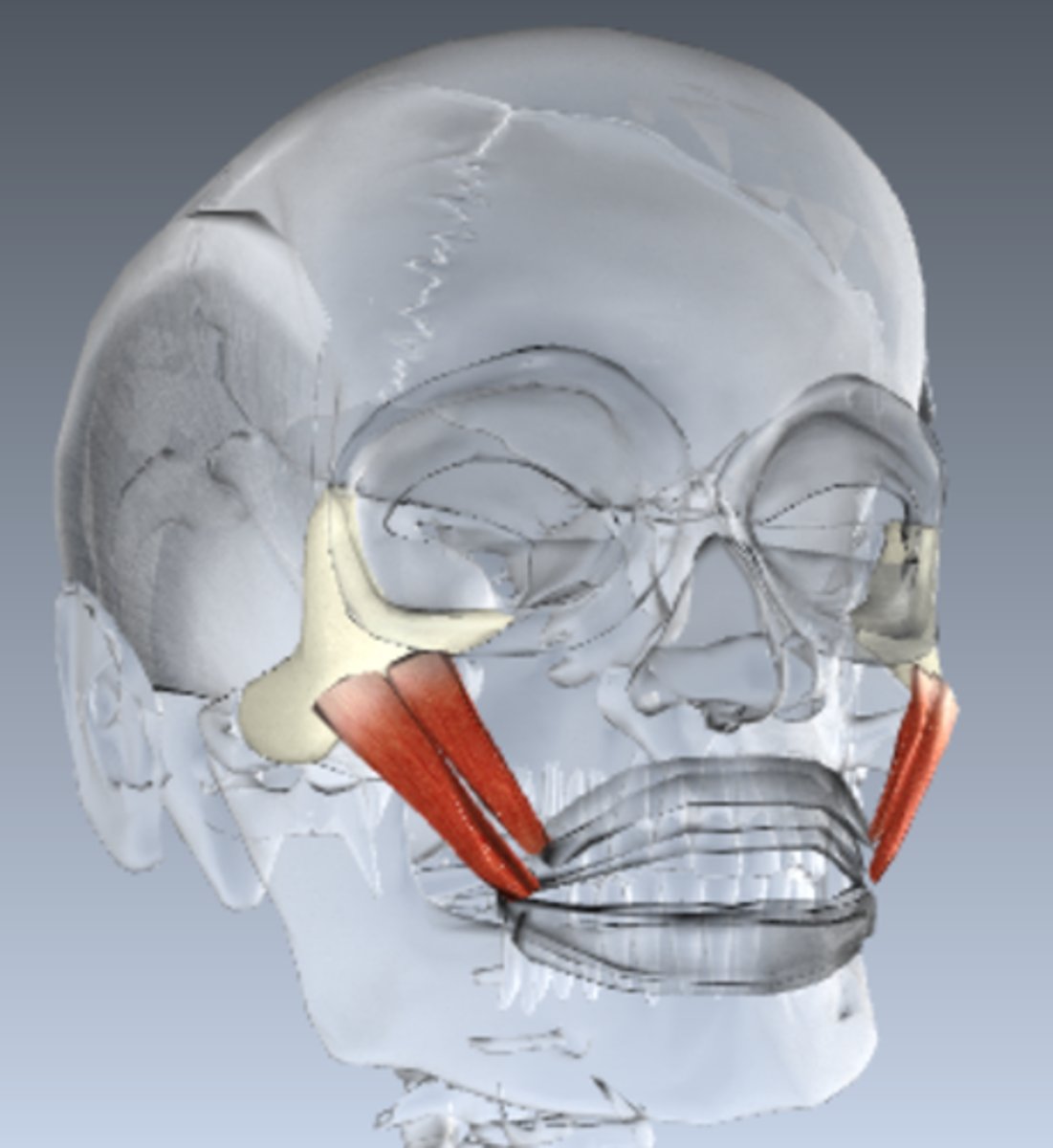
what if the action of the platysma?
frowning
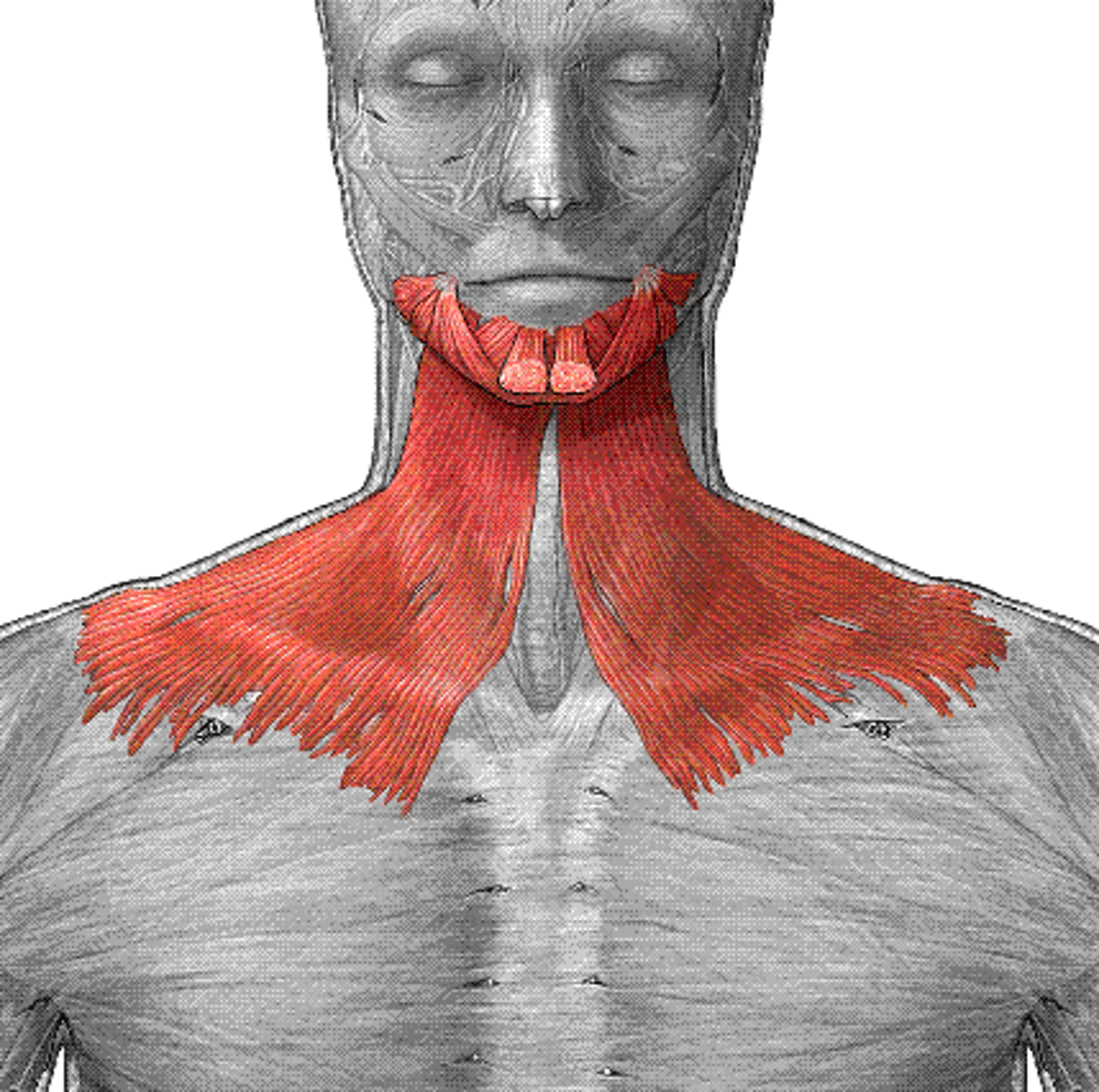
Mastcation
the process of chewing
the temporalis muscle's fascicles converge on the ___________________, enabling the temporals to ________________________________________
mandible, elevate the mandible powerfully.
masseter ________________________ and and it can be used to _________________
elevate the mandible powerfully, protract the mandible (to push the lower jaw forward)
lateral pterygoid
Depresses and protracts mandible and moves it from side to side
medial pterygoid
elevates mandible
the deltoid muscle packs how many groups of fascicles into one muscle?
3
pectoralis major action
Adducts, flexes, and medically rotates the arm.
pectorals minor action
depresses the scapula and elevates the ribs
Lines alba (white line)
a band of connective tissue that binds all of the abdominal muscles.
rectus abdominis is covered with a _______________________
sheath of connective tissue
lateral to the rectus abdominis is the ______________________. what is the action of ______________?
broad external oblique muscle, flexes the vertebral column but also rotates it
internal oblique does _________________________. It is located where?
does the same thing as the external oblique, which the internal oblique is located underneath.
what muscle is underneath the internal oblique
the transverses abdominis.
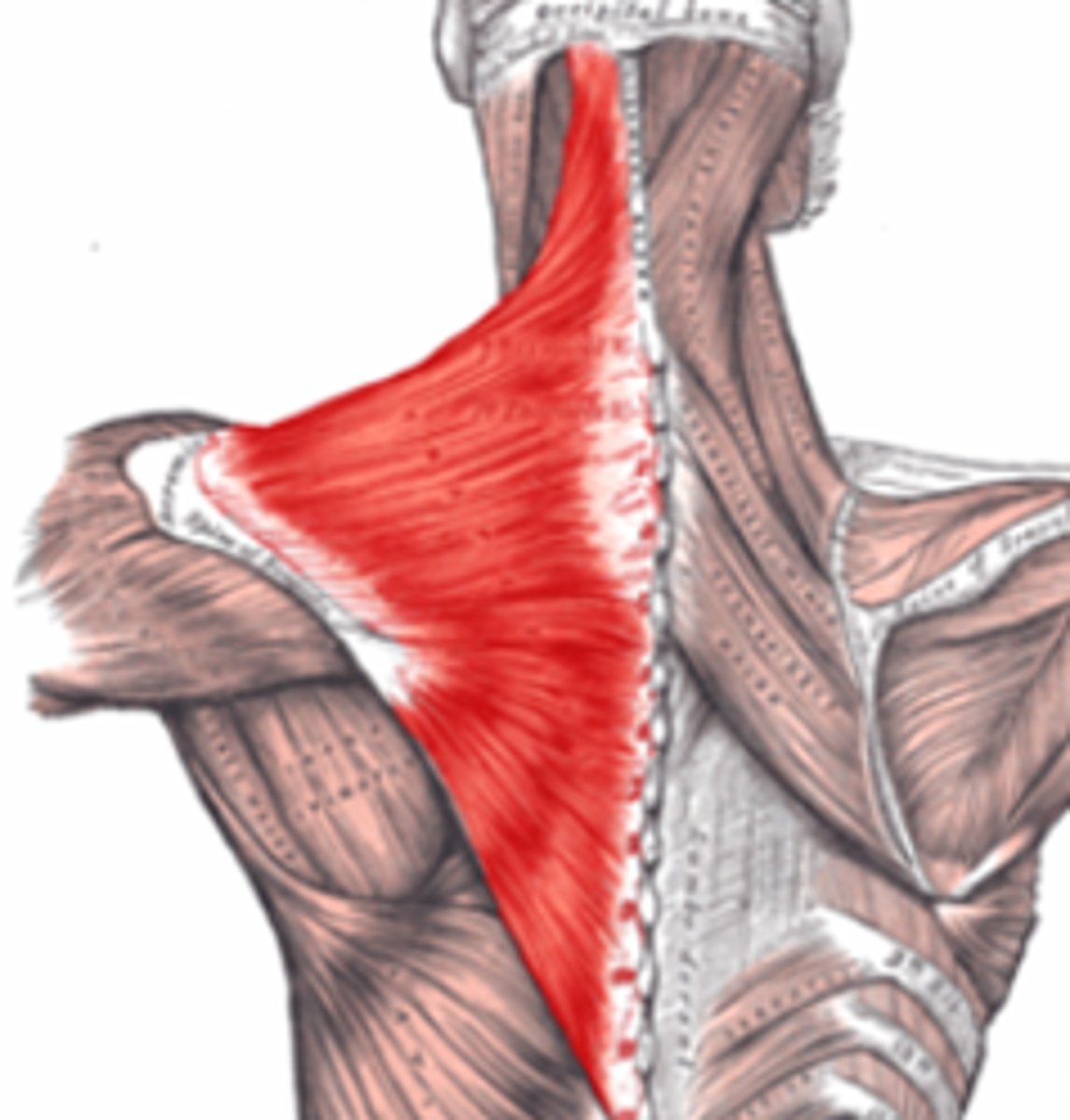
Trapezius location
extends up the neck to the shoulder and down the thoracic vertebrae.
latissimus dorsi
extends and adducts arm
the trees major works with the latissimus dorsi to
adduct, extend, and medially rotate the arm.
the rhomboideus major and rhomboideus minor work with the elevator scapulae, the trapezius, the serrates anterior, and the pectorals minor to move what?
the scapula
triceps brachii work to extend what?
the forearm at the elbow
the ball of the humerus is held into socket by muscle tension during muscle movement. what four. muscles cause this tension?
supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis
biceps brachia flexes the
forearm at the elbow
the Brachioradialis aids the biceps brachii in what?
flexing the forearm
The pronator teres __________(action)_________________ aided by the _____________________
pronates the forearm at the elbow, turning the forearm to a palms-down movement. pronator quadratus
supinator action
supinates the forearm
flexor capri radialis action
flexes and abducts the hand
flexor carpi ulnaris and the palmaris longs along with the flexor carpi radialis do what
flew the hand
the flexor digitorum superficialis flexes
both the wrist and the four fingers (not the thumb)
the flexor digitorum superficialis profundus aids ___________________.
the flexor digitorum superficialis flexes
the extensor carpi radialis longus and the extensor carpi radialis brevis _______________ (with help for the ____________________) and __________________
Extend (with help from the extensor carpi ulnaris) and abduct the hand
the extensor digitorum is the antagonist of the _________________________, as it extends the hand and the four fingers (not the thumb)
flexor digitorum superficialis
if it weren't for the ____________ ______________________ the extensor tendons would bow outward when the extensor contracts. Is ____________ ______________________ a muscle?
exstendor retinaculum. no
exstrinsic hand muscles
muscles in the forearm that create movement in the hands
Intrinsic hand muscles
Muscles in the hand that produce movement in the hand
the gluteus maximus action
extends, abducts and laterally rotates thigh
where is the gluteus medius located?
underneath the gluteus Maximus.
where is the gluteus minimus located?
underneath the gluteus medius
what three muscles are collectively known as the hamstring muscle group?
the biceps femurs, semimembranosus, and the semitendinosus.
the iliacus and the psoas major flex ______________, they are often considered one muscle called the __________________
thigh, iliopsoas
the quadriceps femurs is made up of what four muscles?
the rectus femoris, the cactus laterals, the vests intermedium, and the vests medialis.
What is the longest muscle in the body?
Sartorius
the adductor longs and adduscro Magnus work together to ___________________
adduct the thigh.
Gracilis (action)
adducts thigh and flexes leg
the calf is made up of what two muscles? They are inserted into the calcaneus (heel bone) via the ___________________
gastrocnemius and soleus, the calcanea tendon.
The tibia's anterior works to ___________ and ________________ the foot
dorsiflex and invert the foot
what two muscles ever the foot?
peroneus braves and peroneus longus
flexor digitorum longus _______ the four lateral toes (not the big toe) while the extensor digitorum longus ____________ the four lateral toes
flexes, extends
extensor hallicus longus action
dorsiflexion and inverts the foot, as well as extends the big toe
the peroneus terminus has the same origin as the other peroneus muscles but is really apart of the ________________________
extensor digitorum longus
What is the location of the patellar ligament?
extending from the patella