METHANE
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Methane
- First in the series of Parrafin/Alkane (which is saturated)
- The simplest alkane and the primary component of natural gas.
- colorless/ odorless
- abundant hydrocarbon is a greenhouse gas, contributing to climate change
Water Displacement
Methane is insoluble in water and hence is conveniently collected by?
Alkaline KMnO₄
Bases
Acids
Alcoholic iodine
Methane is inert toward the common laboratory reagents such as?
90%
Natural gas contains approximately ____ methane; hence its synthesis is significant.
Marsh Gas
Natural Gas
Methane is often referred as?
Anhydrous Barium Hydroxide
may be used instead of soda lime. Methane prepared in this manner contains certain impurities.
CH4 + Na2CO3 + H2O
Synthesis of Methane
CH3COONa + CaO + NaOH →
Decomposition Reaction
type of chemical reaction in which a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. This process occurs when the original compound is subjected to heat, light, electricity, or other forms of energy.
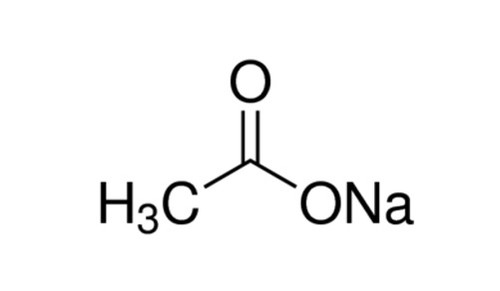
C₂H₃NaO₂
Chemical Structure of Anhydrous Sodium Acetate
Anhydrous Sodium Acetate
- Serves as the source of acetate ions (CH3COO-) in the reaction.
- Sodium salt form of acetic acid (vinegar)/ the ethanoate ion
- It's written as NaCH3COO or NaC2H3O2
heated
When ______, anhydrous sodium acetate decomposes to release acetate ions, which subsequently react with the components of soda lime to produce methane.
Soda Lime
a mixture of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and calcium oxide (CaO), acts as a strong base and dehydrating agent in the reaction.
Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3)
Water Vapor (H2O)
The sodium hydroxide component of soda lime reacts with anhydrous sodium acetate to form?
Calcium Oxide
What component helps in the dehydration of the reaction mixture, facilitating the elimination of water molecules
Soda Lime
It promotes the decomposition of anhydrous sodium acetate and facilitates the formation of methane gas.
Dry Ignition Tube
Burner
Reagents
Set Up of Synthesis of Methane
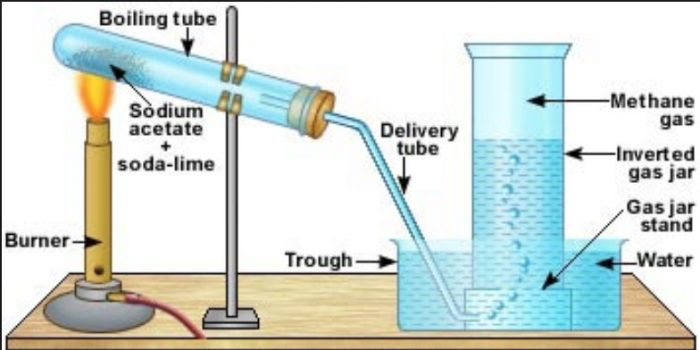
Dry Ignition Tube
Is a glass tube typically made of borosilicate glass, resistant to high temperatures. It provides a controlled environment for the chemical reaction to occur. The tube is dry to prevent any moisture from interfering with the reaction.
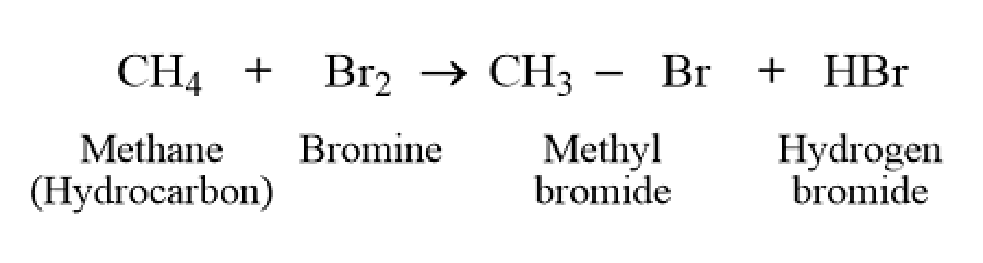
Reaction with Bromine
Reaction with Alcoholic Iodine
Reaction with Alkaline KMnO4
Tests for Unsaturation
Reaction with Bromine
The decolorization of bromine water indicates the absence of unsaturation in methane. Any persistence of color suggests the presence of unsaturated hydrocarbons as impurities.
Reaction with Bromine
What is this?
Reaction to Alcoholic Iodine
What is this?
No Reaction
Alkanes do not react with Oxidizing Agents
Reaction to KMnO4
Combustion of Methane
Produces a clean, blue flame, indicating complete combustion to carbon dioxide and water. Any deviation from this observation may suggest impurities affecting the combustion process.
CO2 + 2H2O
Combustion Reaction of Methane
CH4 + 2O2 →
- Any discrepancies observed in the chemical tests could be attributed to impurities present in the synthesized methane. Common impurities may include ethylene, ethane, or other hydrocarbons with unsaturated bonds.
- The presence of impurities can affect the physical and chemical properties of methane, such as its reactivity with bromine and alkaline KMnO₄.
- Further purification techniques, such as fractional distillation or gas chromatography, may be required to isolate pure methane for specific applications.
Discussion of Combustion Reaction of Methane
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
- The preferred method of infrared spectroscopy.
- Determines the chemical bond between molecules/ bonding
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
- Use of Protons and determine the skeleton structure of the compound.
Ex: MRI (its function is like magnets)
Chromatography
Determines the compound based on its polarity
Test of Unsaturation
Determines if one carbon group is filled with hydrogen or not.
Instrumental Method
Best method to determine function group.
Recorded from 5000 to 400 cm−1 (2.0 to 25 μm), with special attention being given to the molecule's ν4 region (1300 cm−1, 7.69 μm) and the near-IR features at 4600 - 4100 cm–1 (2.17 - 2.44 μm)
Methane's IR spectra
Alcohols
- Organic compounds containing hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups attached to :
- saturated C atom of a simple alkyl group
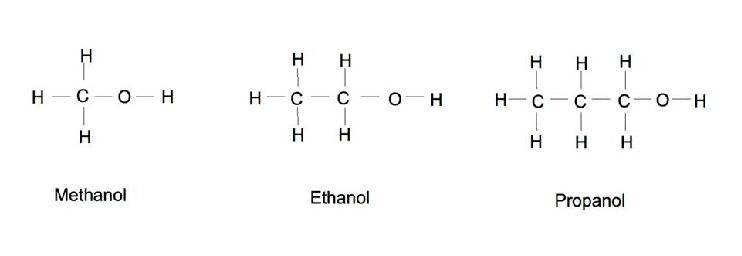
Primary Alcohol
OH group attached to a primary carbon atom
Ex: Ethanol
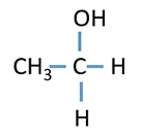
Secondary Alcohol
OH group attached to a secondary carbon atom
Ex: 2- Propanol
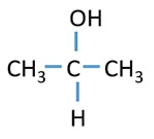
Tertiary Alcohol
OH group attached to a tertiary carbon atom
Ex: 2-methy-2-propanol
Aliphatic alcohols and lower aromatic alcohols
Highly branched alcohols and alcohols with twelve or more carbon atoms (solid at room temperature & fruity odors)
Physical state of alcohols
Polar
Alcohols are _____ compounds
Dipole-dipole Interaction
The attraction between the positive end of one dipole and the negative end of the other.
greater than
Boiling points of alcohols are higher _________ alkanes and chloroalkanes of similar relative molecular mass
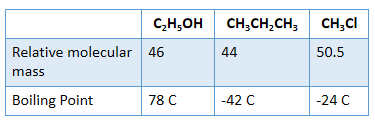
Boiling Point
Is the state of the internal pressure of hydrogen bond and surface pressure is equal.
- Alcohols with short carbon chains dissolve in water
- Solubility decreases sharply with the increasing length of the carbon chain
- Higher alcohols are insoluble in water
- Polyhydroxy alcohols are more soluble than monohydroxy
- Branched hydrocarbon increases the solubility of alcohol in water
Solubility of Alcohols in Water
In aqueous solution, alcohol will donated its proton to water molecule to give an alkoxide ion
Acidity of Alcohols
- Ethanol-solvent for varnishes, perfumes and flavorings, a medium for chemical reactions and in recrystallization
- Hypnotic (More chlorine causes depression)
Importance of Alcohols
- Grignard synthesis (more efficient because it can yield higher percentage of alcohols )
- Hydrolysis of alkyl halides
- Industrial and laboratory preparations
Preparation of Alcohol
Grignard reagents
are chemical compounds with the general formula R−Mg−X, where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl.
(The reaction will never happen if there is a presence of water)
Alcoholic Fermentation
- A process of using yeasts (fungi) to convert sugars into alcohol.
- May be classified as oxidation, reduction, cleavage and combination reaction, which are promoted or catalyzed by enzyme.
zymase
ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION
The enzyme known as ________, which yeast cells produce has the property of promoting the splitting of glucose by alcoholic fermentation with formation of ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide
invertase
C12H22O11 + H2O
C6H12O6
zymase
C6H12O6
2CH3-CH2OH + 2CO2
Only the primary and secondary alcohols are oxidized by hot acidified potassium permanganate or potassium dichromate
1◦ or 2◦
- The purple color of potassium permanganate
- The potassium dichromate changes from orange to green
Oxidation of Alcohols
Tertiary Alcohol
Lucas Test
-immediate cloudiness
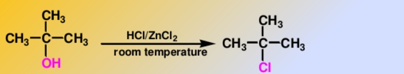
Secondary Alcohol
Lucas Test
-solution turns cloudy within about 5 minutes

Primary Alcohol
Lucas Test
- no cloudiness at room temperature

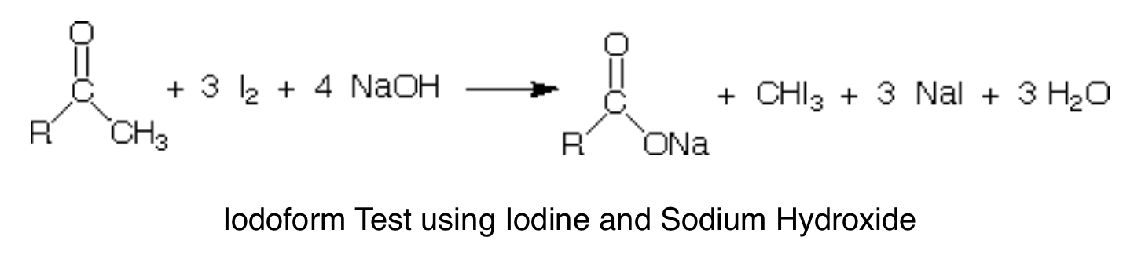
Iodoform Test
Ethanol and secondary alcohols containing the methyl alcohol group which react with alkaline solutions of iodine to form triiodomethane.
Phenols
Compounds that have –OH group attached directly to a benzene ring
- Colorless, crystalline, poisonous solid with phenolic odor
- Melting point 41C and Boiling Point 182C
-Sparingly soluble in water forming pink solution at room temperature
- Completely soluble above 68.50C
- Causes blisters on skin
- Used as disinfectants and in washrooms
Physical Properties of Phenols
- Phenols are more acidic than alcohol
- Basic Properties
- Test for the hydroxyl group
- Bromination of phenol
Properties of Phenols