Gonadal Hormones and Inhibitors: Androgens
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Hypo-Ant Pit-Gonad axes
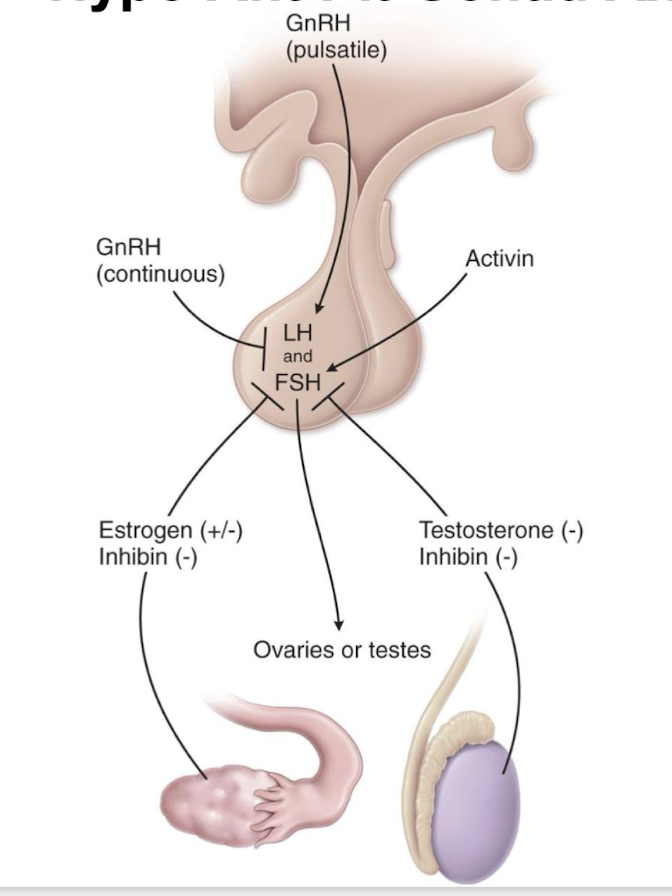
what is GnRH
a decapeptide produced by hypothalamic neurofibers
what is GnRH release influenced by
other hormones such as cortisol, insulin, IGF-1, prolactin. gonada steroids
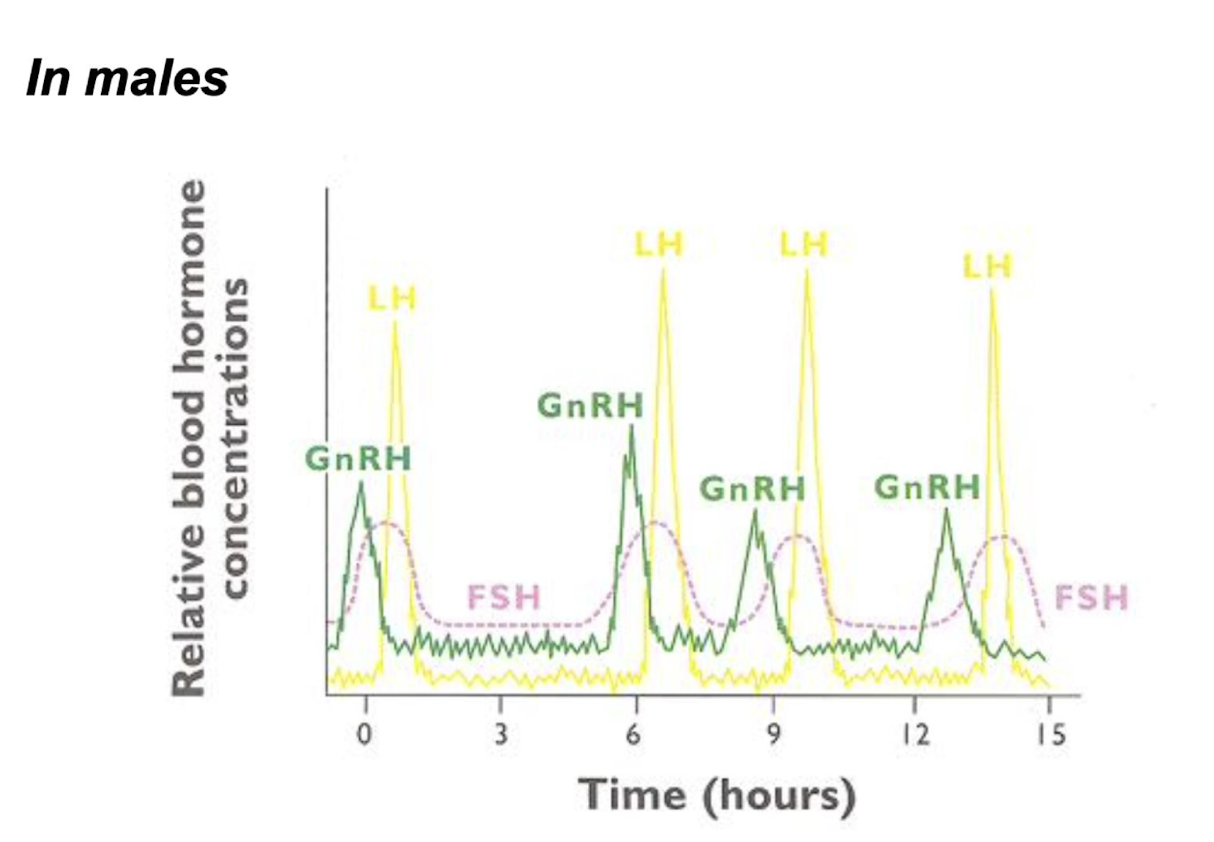
in which manner is GnRH released
a pulsatile manner to bind to GnRH receptors on the anterior pituitary -LH/FSH
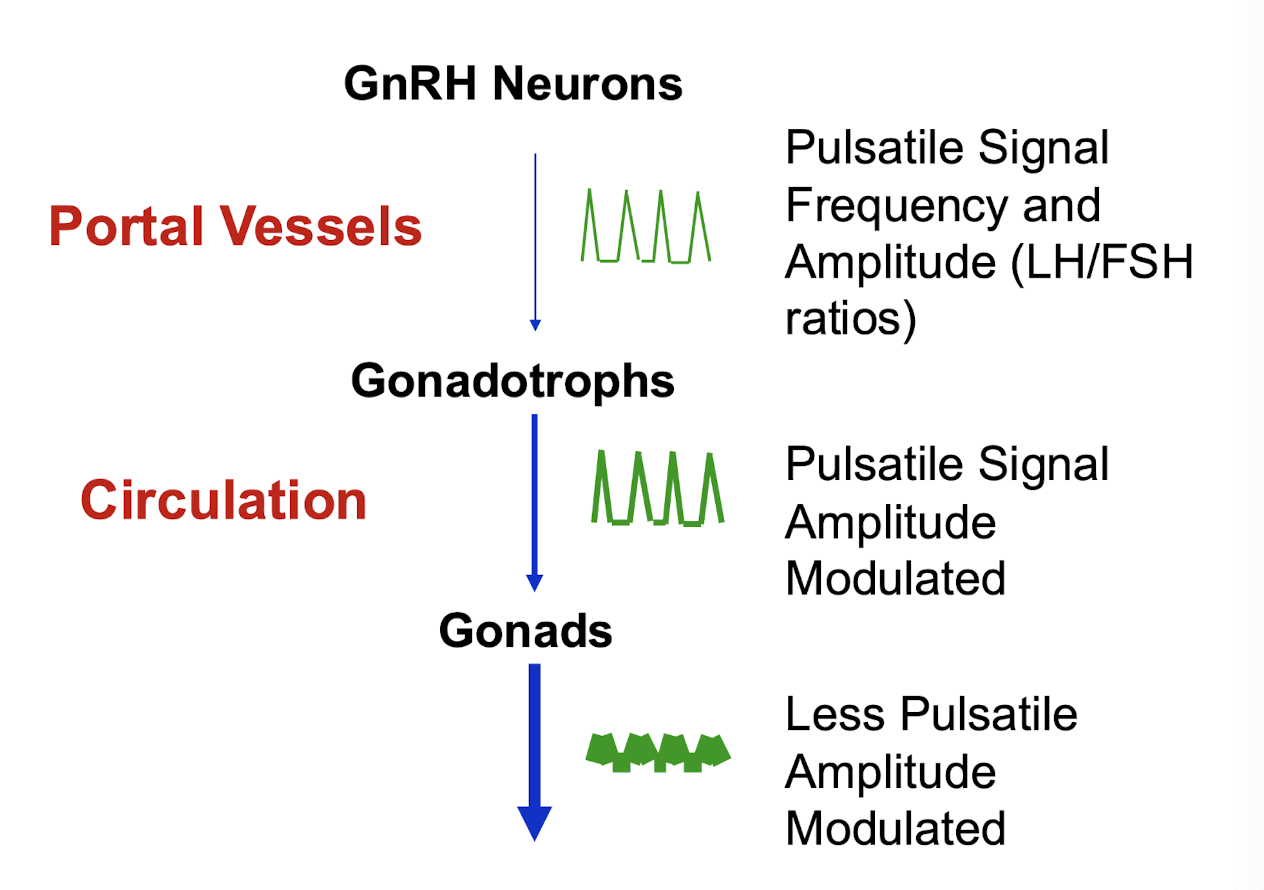
what does continuous stimulation and release of GnRH result in
GnRH receptor down-regulation
what is inhibin
produced by the Sertoli cells (testes) and granulosa cells (developing follicles) inhibits further FSH release
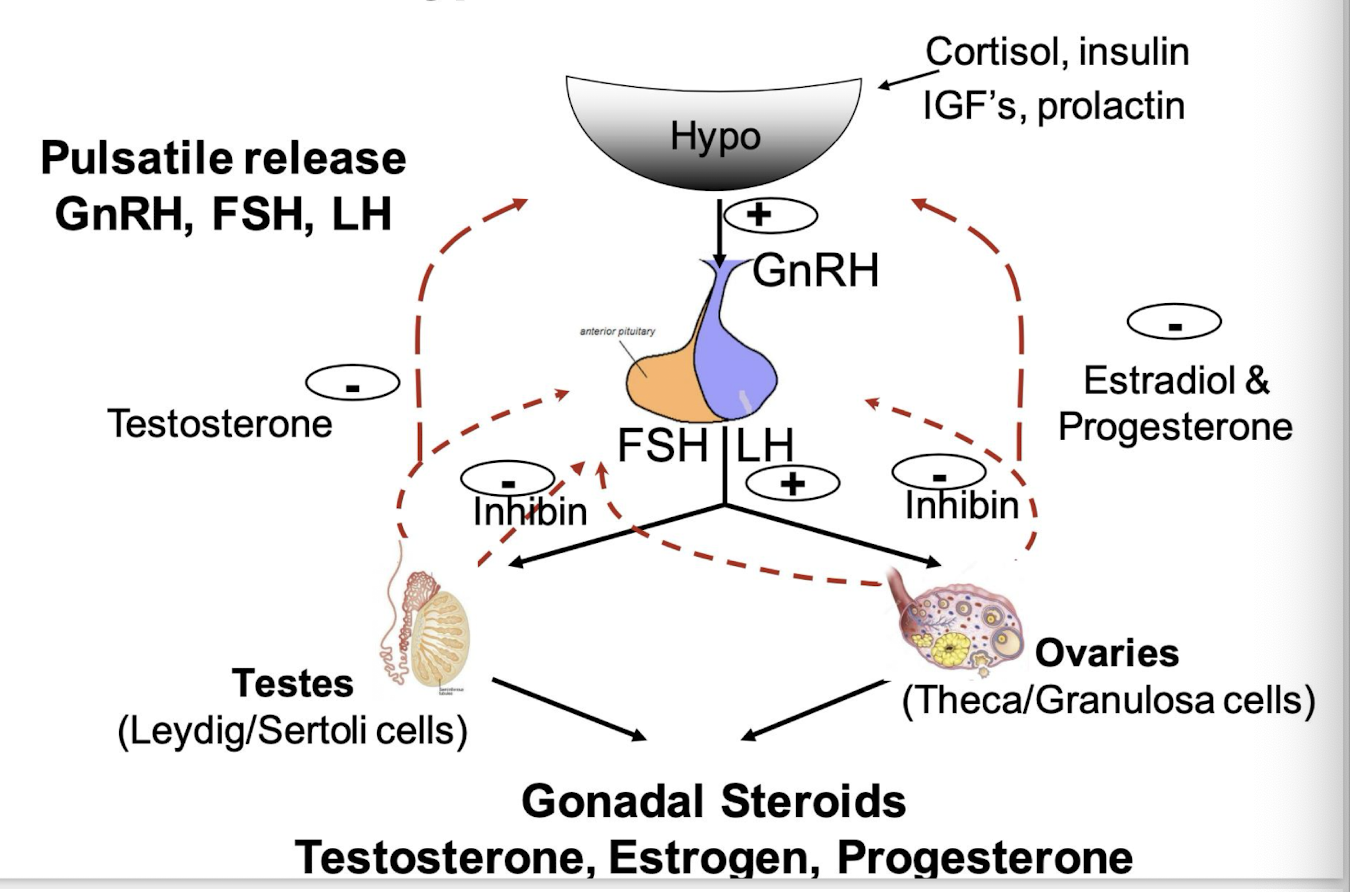
FSH and LH
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone) are structurally similar to glycoproteins
upon release they bind to surface receptors on the cells of the ovaries and testes
Ovary and hormones
FSH stimulates follicular development
LH stimulates ovulation
both LH/FSH are needed for steroidogenesis by the follicular cells
testes and hormones
LH is the major regulator of testosterone production via activation of Leydig cells. Testosterone feeds back to suppress LH
FSH acts on Sertoli cells → spermatogenesis. inhibin from sertoli cells feeds back to suppress pituitary FSH
GnRH stimulation
gonadorelin - used in both sexes for infertility caused by hypothalamic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism — less popular now
pulsatile therapy via a portable pump; programmed for pulsatile delivery about every 90 mins
GnRH suppression - most common use of GnRH
Leuprolide → used to induce hypogonadism when given continuously
receptor down regulation on pituitary and reduced LH/FSH production
Uses:
prostatic cancer and benign hyperplasia
uterine fibroids, endometriosis
central precocious puberty
assisted reproductive technology procedures
FSH analogues
hMG (menopur); FSH-like activity and LH-like activity
human menopausal gonadotropins are extracted from the urine of postmenopausal women
used to stimulate ovarian follicular development in women and spermatogenesis in men
need to be used in conjunction with LH in both sexes
ovulation and implantation in women
testosterone production in men
recombinant FSH also available - more expensive
LH analogues
hCG - human chorionic gonadotropins
produced by the human placenta and excreted in the urine of pregnant women; similar to LH in structure
used in conjunction with hMG for infertility
Recombinant LH and recombinant hCG is also available — more expensive
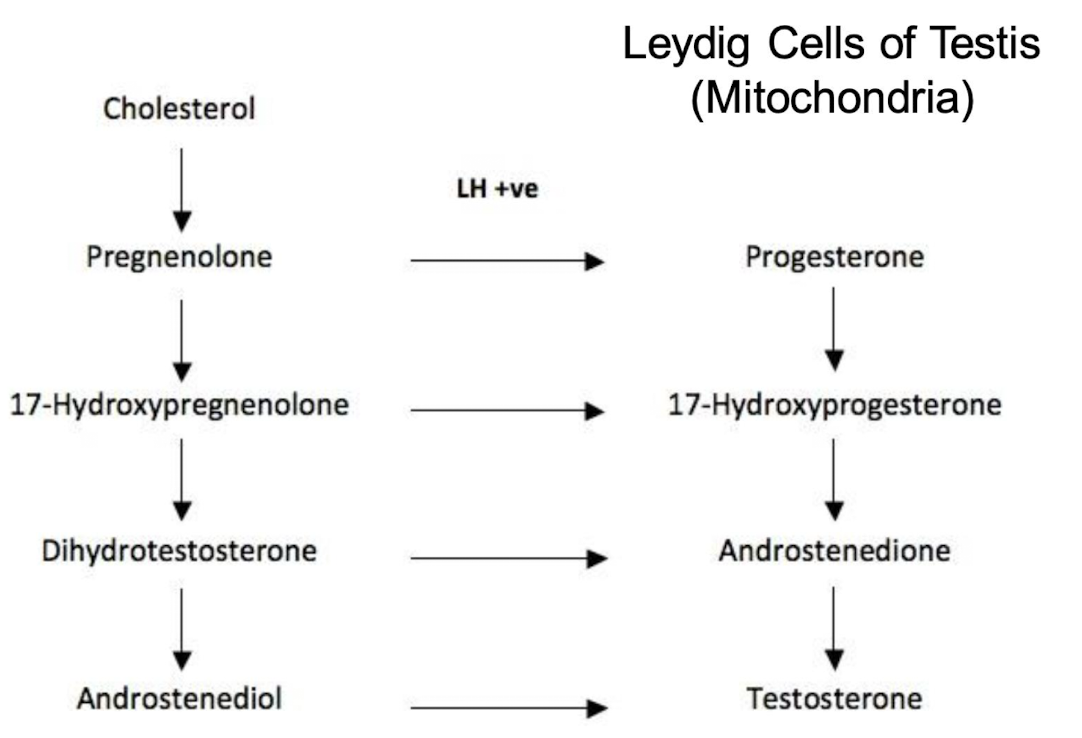
what is the most important androgen secreted by the testes (LH stimulated)
testosterone
what is testosterone secreted by
95% by Leydig cells and 5% by adrenals in men
small amounts of what also produced by the testes
dihydrotestosterone, DHEA and androstenedione also produced by testes
in women, small amounts of testosterone are derived from what? and what is it converted to
derived from ovaries and adrenals; some converted to estrogens in body fat and bone
is there storage of androgens
little to no storage of androgens upon synthesis
androgens actions and effects
circulating testosterone bound to what
SHBG; approx 1-2% free
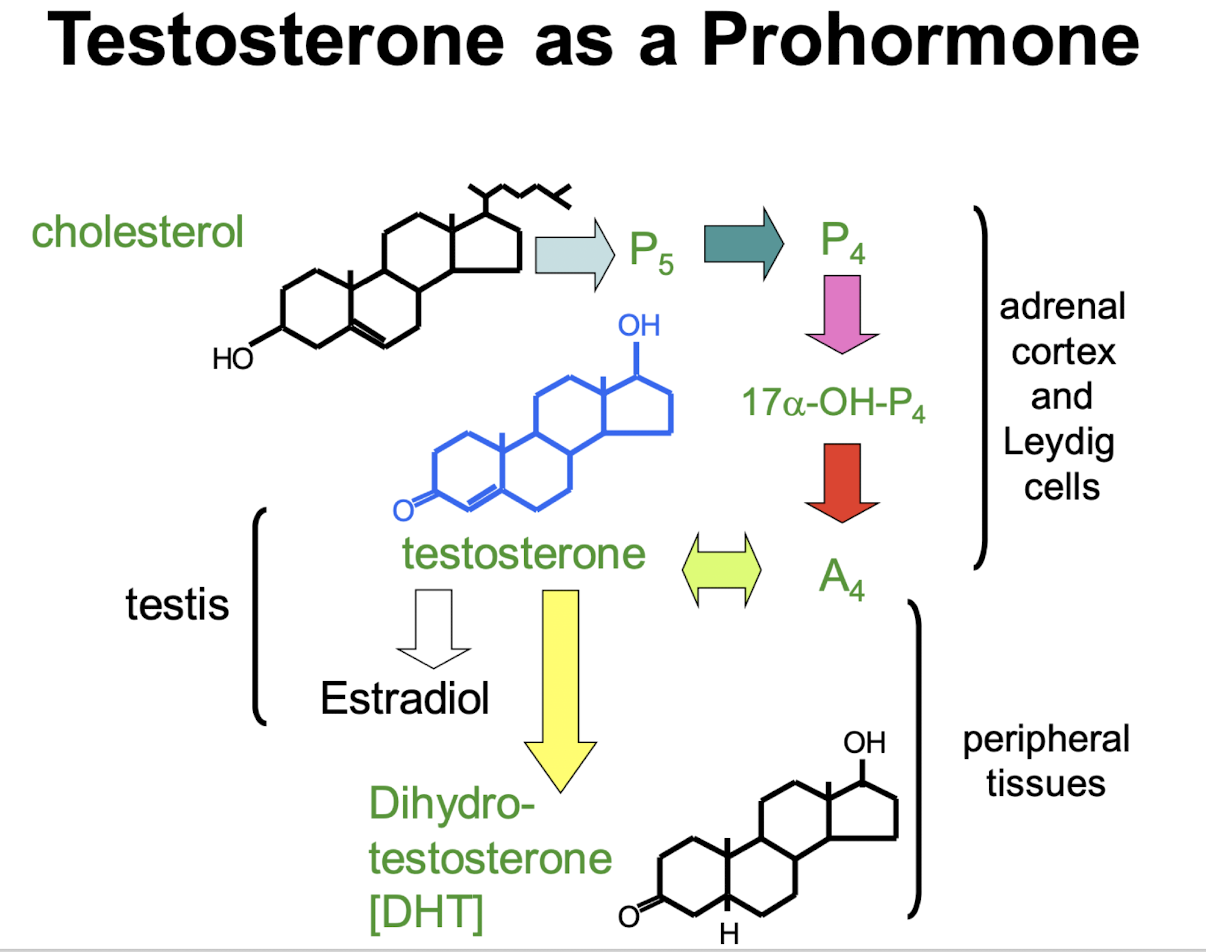
where is testosterone metabolized
in most tissues
what metabolizes testosterone
dihydrotestosterone by 5a-reductase; many sites
Estradiol by aromatase; liver, adipose, bone, brain
how do all affects of sex steroids in target cells occur
by way of steroid nuclear receptor mechanisms
what receptor do dihydrotestosterone and testosterone bind
androgen receptor
what hormone binds the androgen receptor with greater affinity
dihydrotestosterone
what receptor does estradiol bind
estrogen receptor
androgens actions and effects
responsible for secondary sex characteristics, virilization and growth promotion
spermatogenesis
genitalia and secondary sex glands
deepening of voice; facial hair
libido and behavioural changes
lean body mass
erythropoiesis, decrease HDL
estradiol - closure of growth plates in long bones
testosterone; androgenic and anabolic effects
testosterone has 1:1 androgen:anabolic ratio
attempts have been made to alter preparations to produce more anabolic versus androgenic effects
stanazolol, Nandrolone decanoate, Oxandrolone
goal of delivery is what
to provide reliable drug levels
oral preparations; must pass by liver
testosterone half-life varied by adding esters; allows for formulation of depot preparations → enanthate, cyprionate, undecanoate
transdermal delivery; patch or organogel
toxicity and side effects of androgen preparations
prostatic enlargement, acne, mood and behaviour
hepatic dysfunction/cancer
suppression of spermatogenesis - sterility
atherosclerosis and heart disease
women - masculinization - contraindicated in pregnancy
androgen replacement therapy - most common use
used to replace or augment endogenous androgens secretion in hypogonadal men (testes versus pituitary deficiency)
testosterone; PO, IM or transdermal available
if spermatogenesis required, then gonadotropins used until puberty, then testosterone used
Gynecological disorders
reduce breast engorgement post-partum (andorgens antagonize the growth-promoting effects of estradiol on the breast)
chemotherapy of inoperable breast cancer
enometriosis; Danazol (a weak synthetic androgen)
occasionally combined with estrogens; post-menopausal women - reduce bleeding from estrogens
use as a protein anabolic agent
following surgery, trauma, debilitating disease
growth stimulators and aging
stimulate growth in boys with delayed puberty
androgens decrease witha ge; supplementation has shown to increase lean mass and hematicrit while reducing bone turnover in older men
anabolic steroid abuse in sports
increase strength, aggressiveness, performance
side-effects: infertility, aggression, depression, liver dysfunction and liver cancer
the “Duchess”
a drug cocktail hard to detect
consisted of oral Turinabol, Oxandrolone and Methasterone which was dissolved in alcohol
swished in mouth to be absorbed by the buccal membrane and spat out
shortens the window of detectability
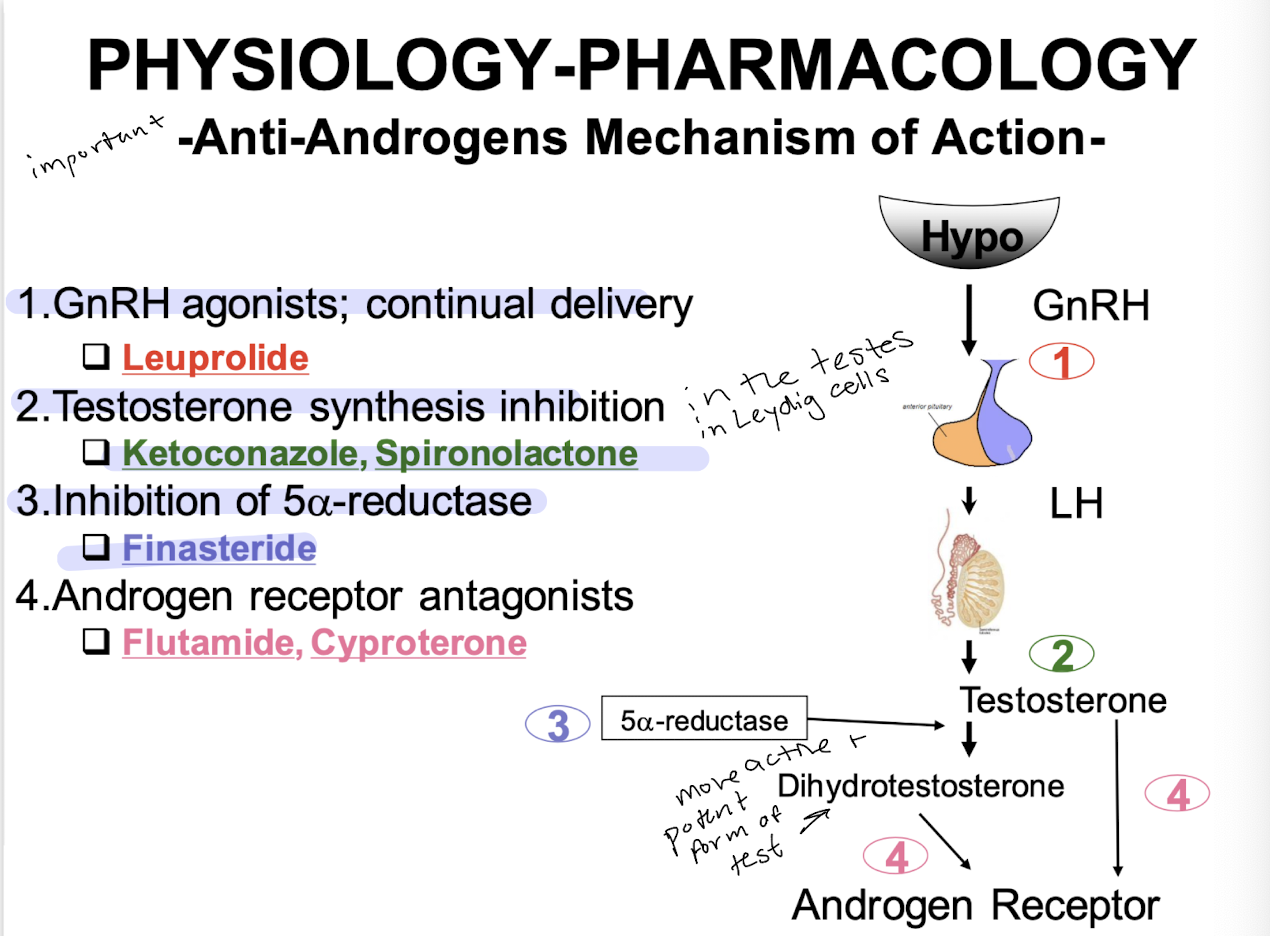
when would you use Androgen suppressors/antiandrogens
treatment of male prostatic cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia, endometriosis: in some women (e,g, women with PCOS and endometriosis) androgens are already high - therefore, reduce estrogen e.g. with oral contraceptives, then block the excess androgen
hirsutism in women; male pattern baldness'
excessive sex drive or behaviours in men; precocious puberty
anti androgens
leuprolide
Ketoconazole, spironolactone
finasteride
flutamide, cyproterone
mechanism of action of leuprolide
GnRH agonists; continual delivery
Ketoconazole, sprionolactone mechanism of action
testosterone synthesis inhibition
flinasteride mechanism of action
inhibition of 5a-reductase
Flutamide, Cyproterone mechanism of action
androgen receptor antagonists
what is the major androgen produced by the testes? what percent is bound in blood and what to
testosterone; 98% bound by testosterone-estradiol binding globulin
what is testosterone responsible for
male secondary sexual characteristics - muscle and bone development, facial and body hair, deeper voice, spermatogenesis, fat distribution, sexual behaviour
what is testosterone released from and what manner
95% from the Leydig cells, controlled by pulsatile hypothalamic GnRH, stimulates pituitary LH release
what are the effects of T amplified by
tissue conversion to DHT and estradiol by 5a-reductase
used for what
anabolic effects in wasting diseases (e.g. cancer), growth promotion in delayed puberty, reducing breast and endometrial growth in women
what are the side effects of testosterone abuse
cardiovascular effects and infertility
what suppresses LH and T
long acting GnRH analogs