Biogeochemical cycles
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
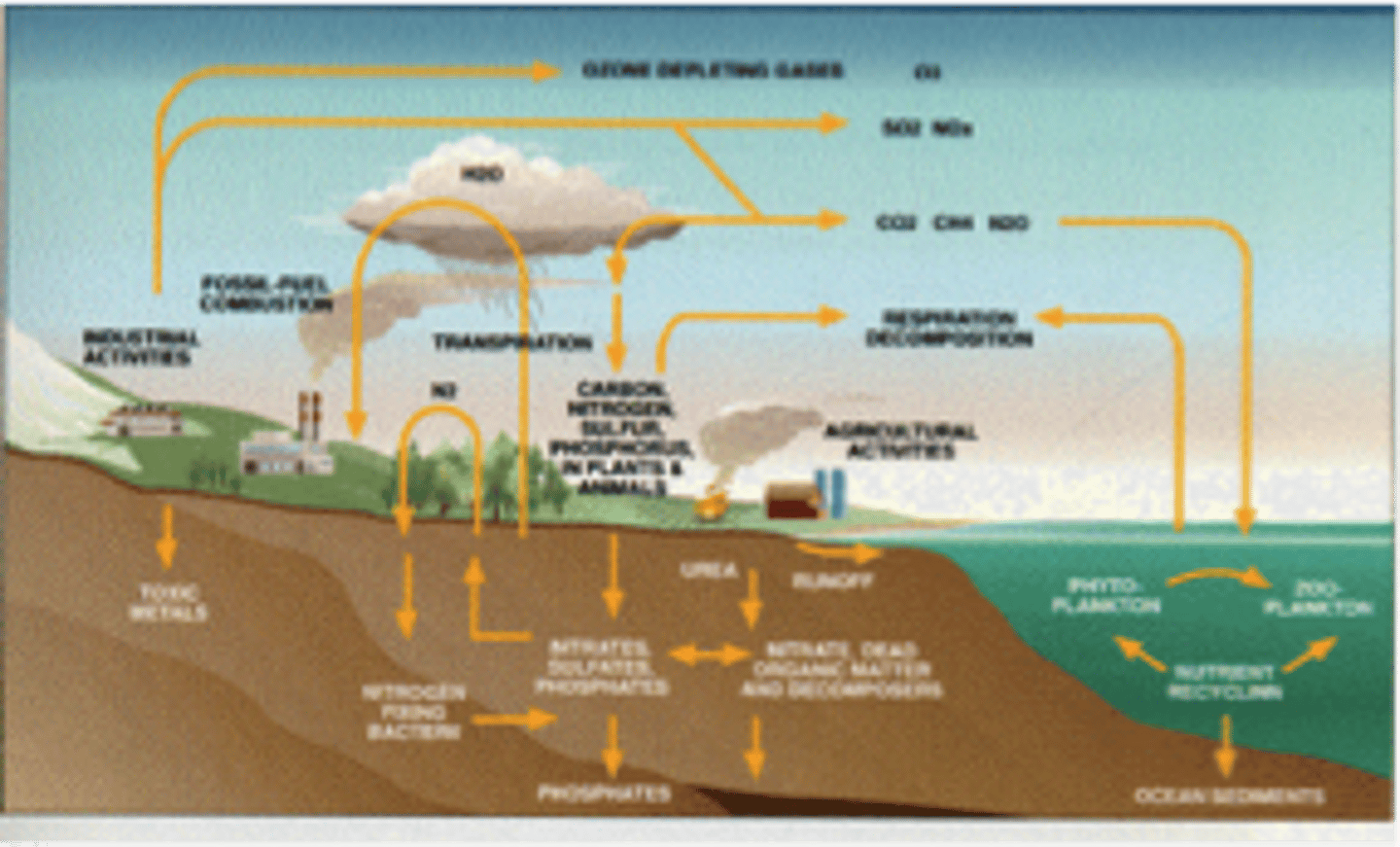
biogeochemical cycle
process in which elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from living organisms to the abiotic environment such as soil or the atmosphere.
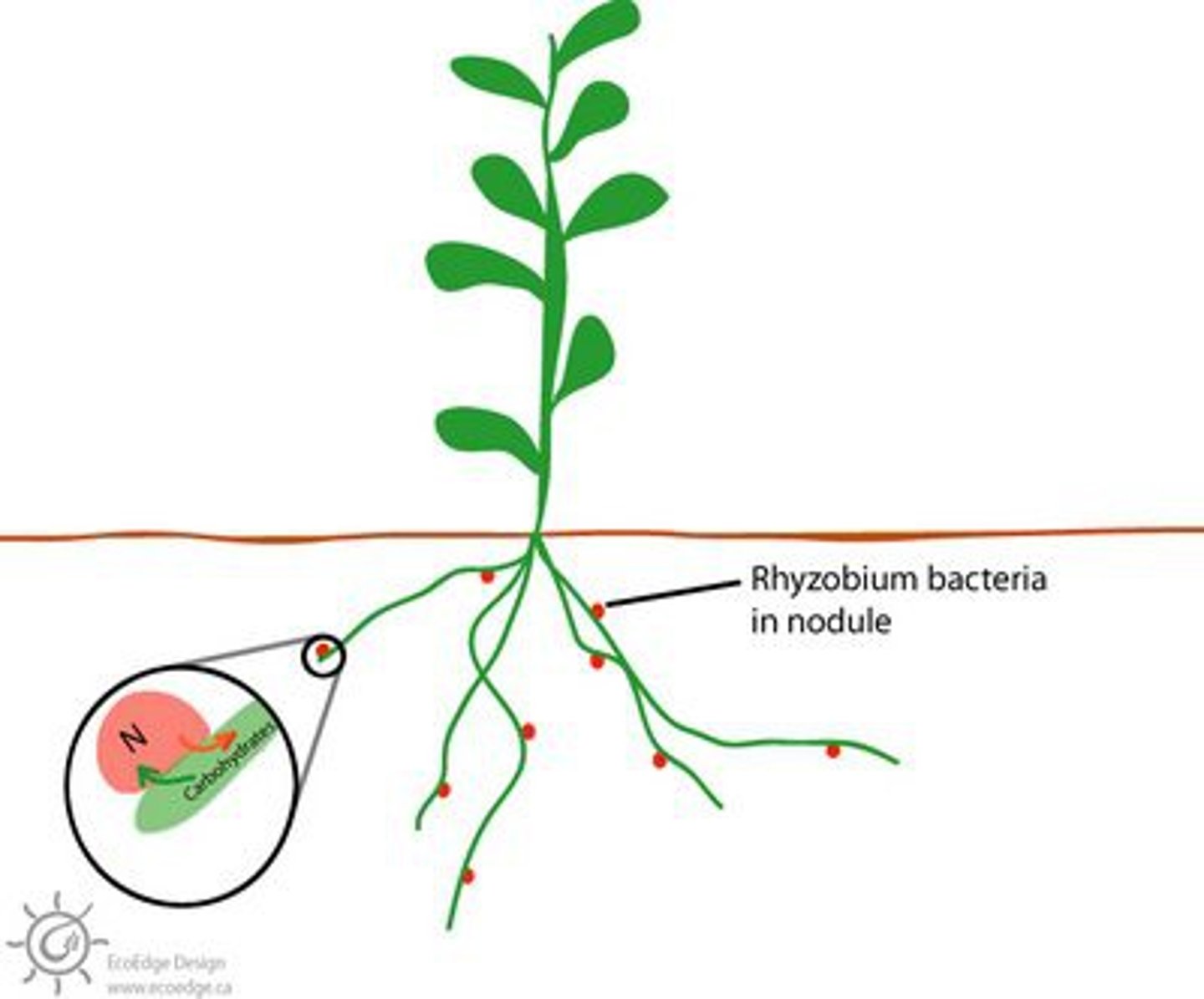
nitrogen fixation
the process of lightning or bacteria changing free nitrogen gas into usable nitrogen compounds such as nitrates that plants can absorb and use.
precipitation
any form of water that falls from clouds and reaches Earth's surface
condensation
the change of state from a gas to a liquid. This is what forms clouds in the atmosphere.
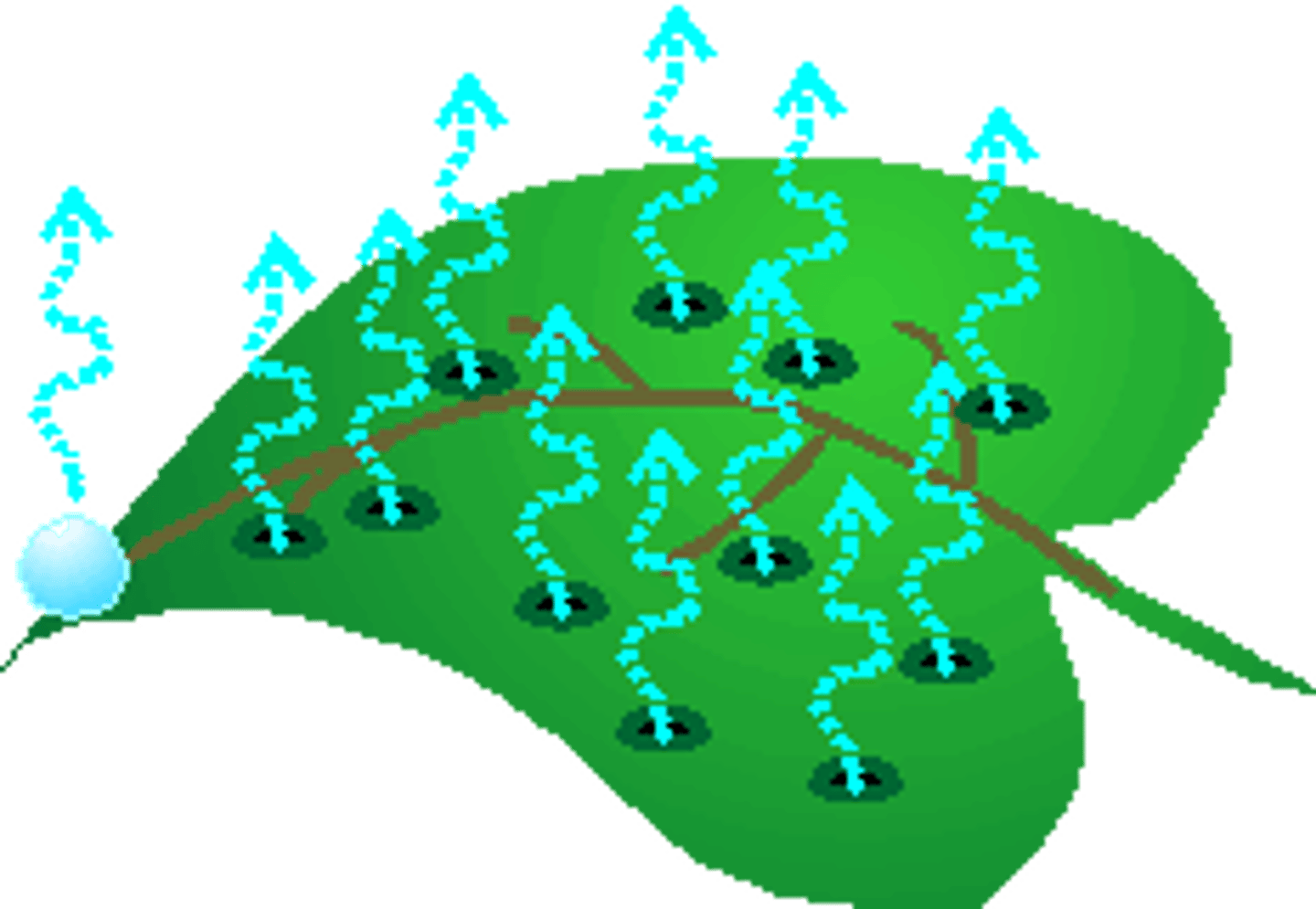
transpiration
evaporation of water from the leaves of plants
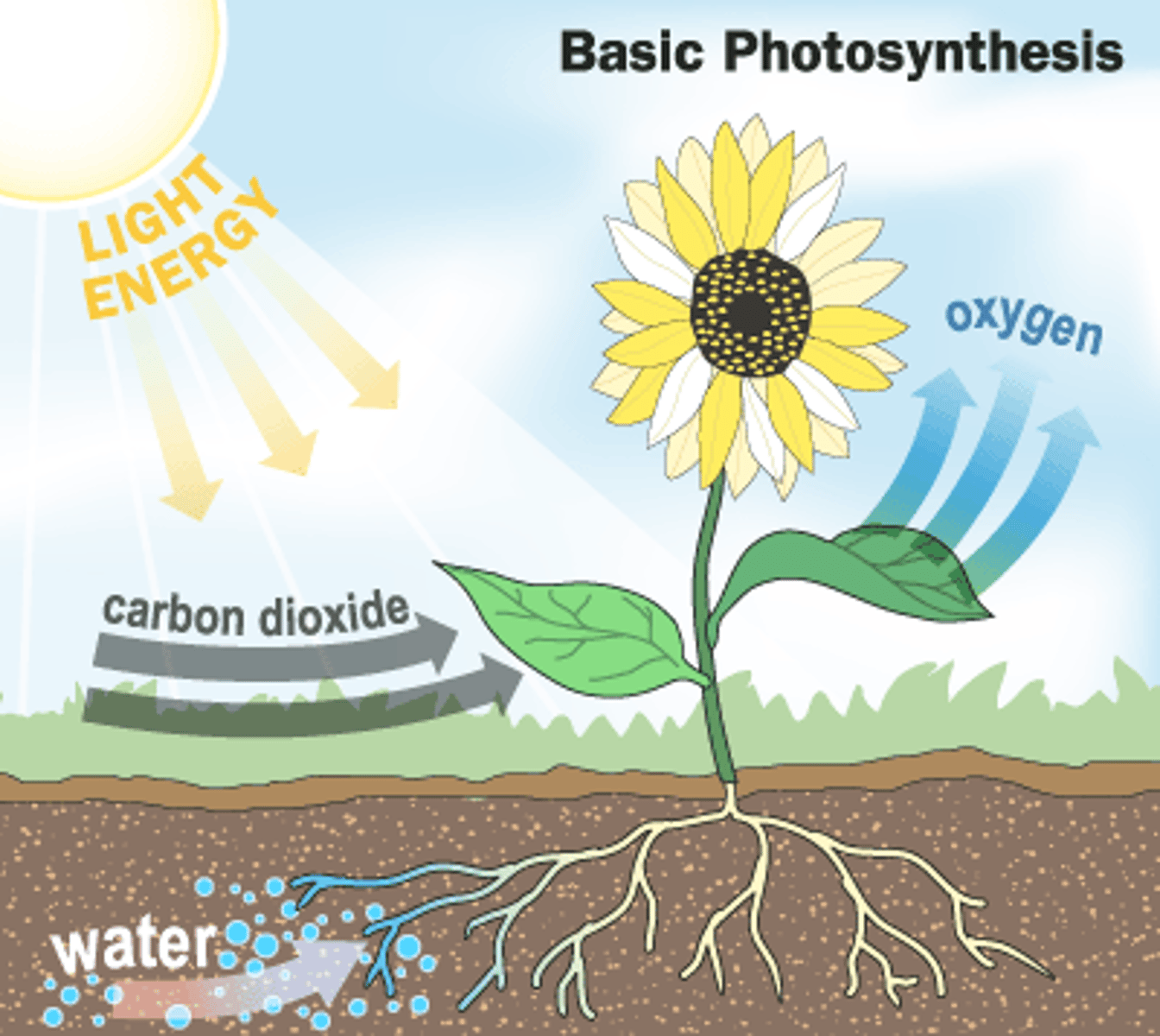
photosynthesis
conversion of light energy from the sun into the chemical energy of glucose. The process produces oxygen waste.
cellular respiration
process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen. The process produces carbon dioxide waste.

decomposition
the state or process of rotting. decomposition is responsible for recycling matter back into the environment.

denitrification
conversion of nitrates into nitrogen gas by denitrification bacteria.
evaporation
the change of a substance from a liquid to a gas

fertilizer
a substance that promotes plant growth by supplying essential nutrients such as nitrogen or phosphorus

fossil fuels
coal, oil, natural gas, and other fuels that are ancient remains of plants and animals

legumes
a group of plants that are part of nitrogen cycle; have nodules on their roots that house bacteria that can convert atmospheric nitrogen into a form that plants can use (ex. soybeans)

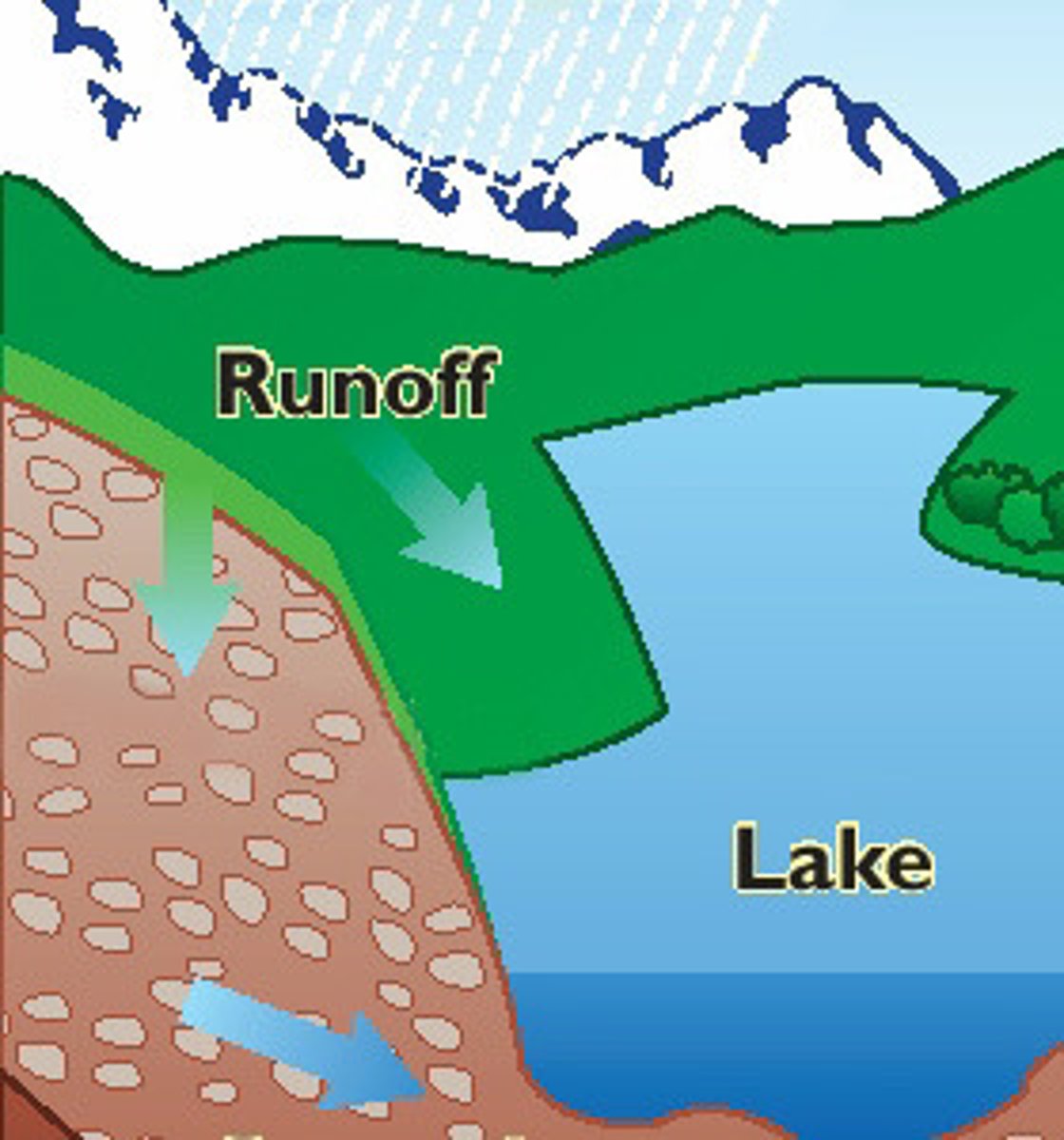
runoff
water that flows over the ground surface rather than soaking into the ground
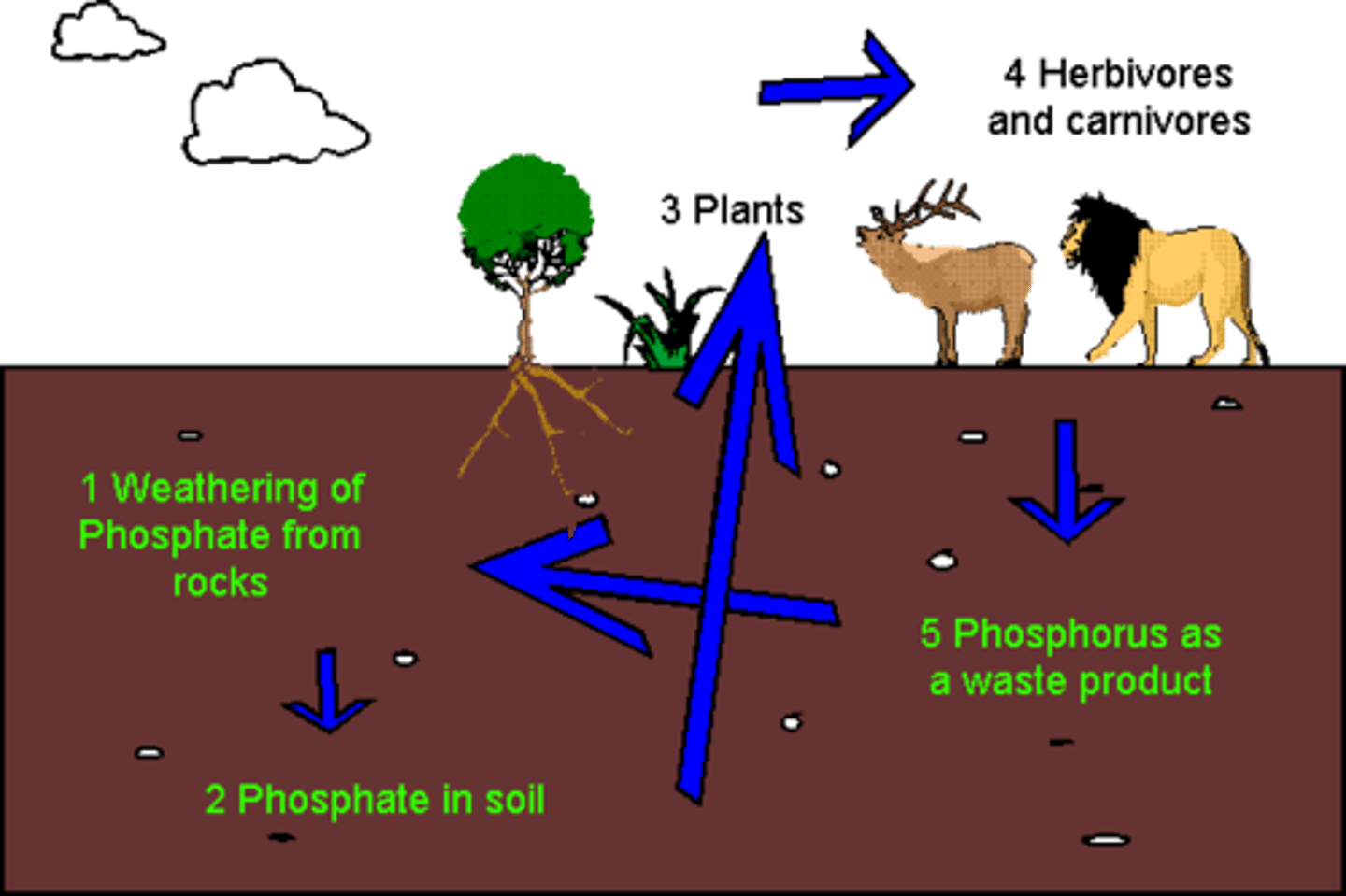
phosphorus cycle
phosphate in rocks enters the soil, the phosphate is absorbed by plans, the phosphates pass from organisms to organism in a food chain or food web, until decomposers recycle the phosphates into the soil again
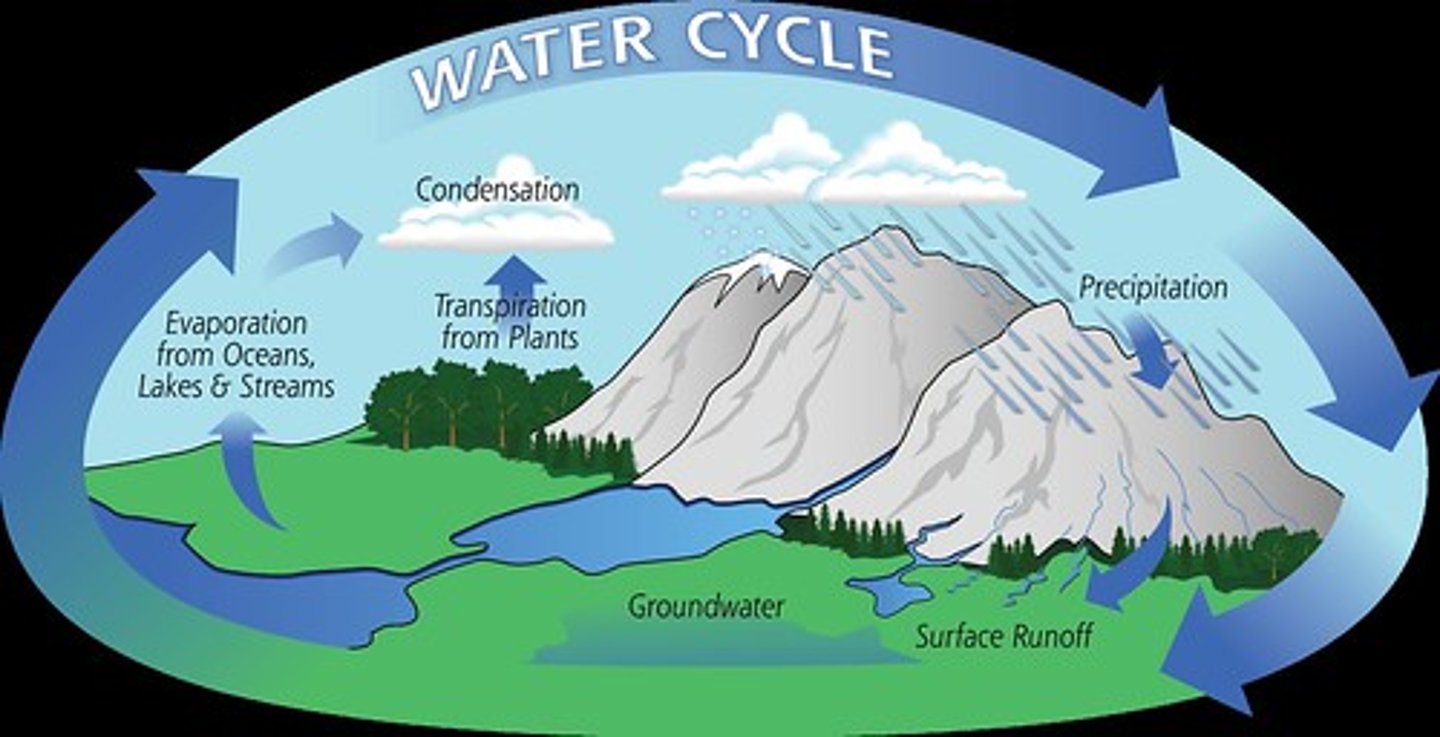
water cycle
bodies of water evaporate, plants transpire, and animals respire water into the atmosphere. The water vapor cools and condenses into clouds then the water precipitates down as rain or snow. Some of the water runs off into bodies of water were it can be used by animals and some water percolates into the water table where it can be used by plants.
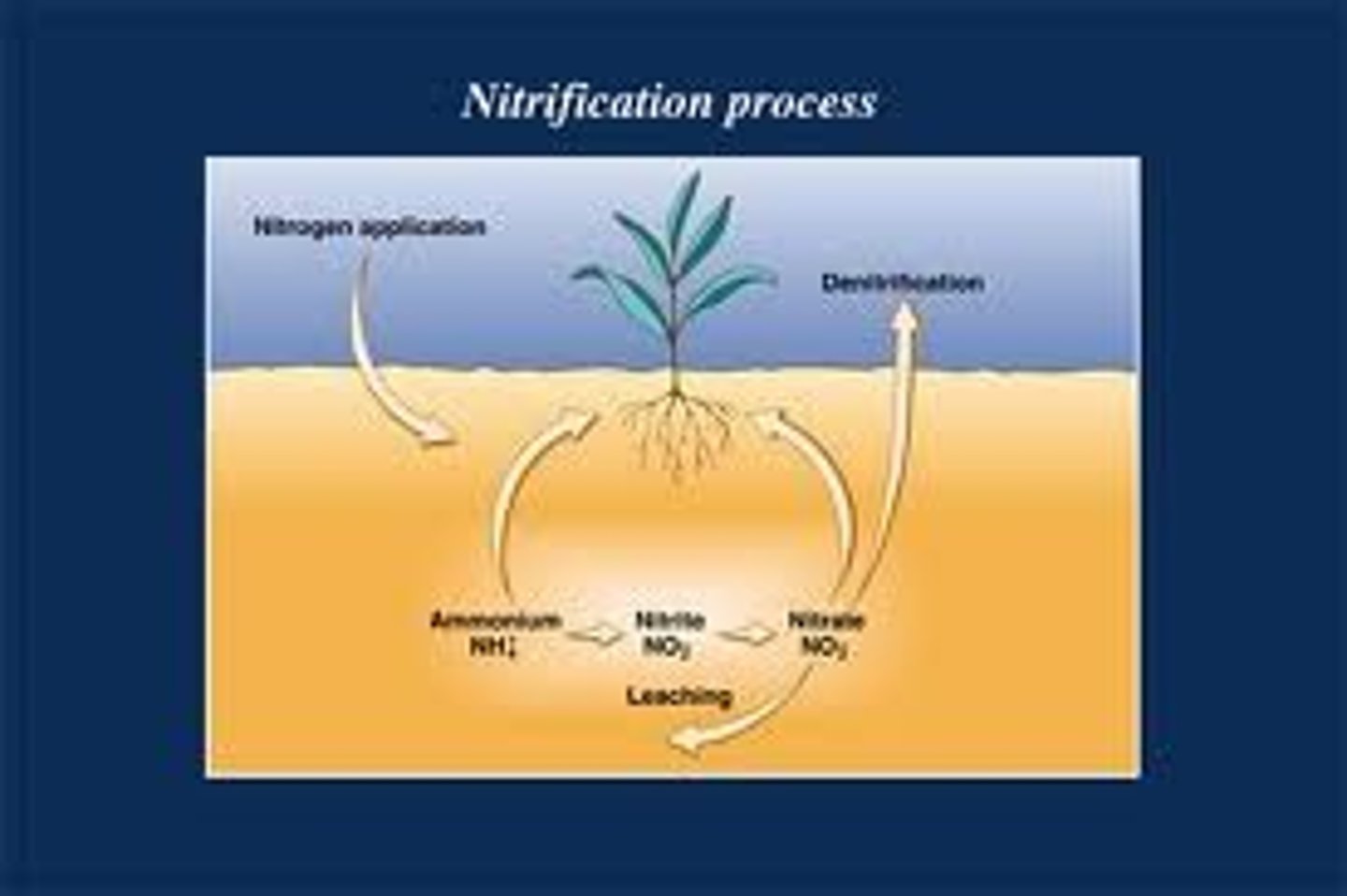
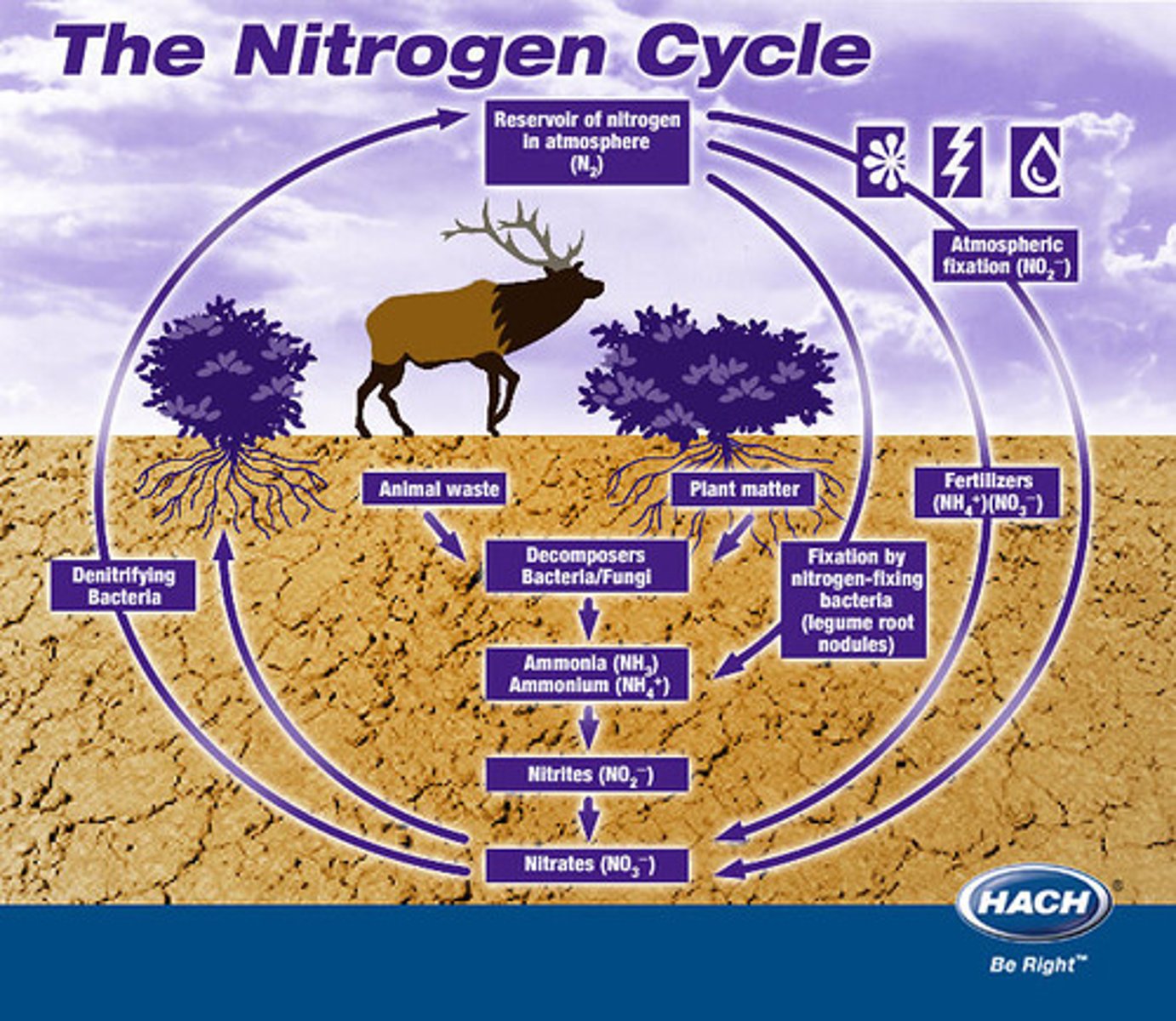
nitrogen cycle
unusable nitrogen gas in the atmosphere is fixed into usable nitrogen by lightning and bacteria. The usable nitrates are used by plants to make proteins. Animals consume the plants and each other to obtain nitrates. When consumers urinate or die decomposers return the nitrates to the soil.
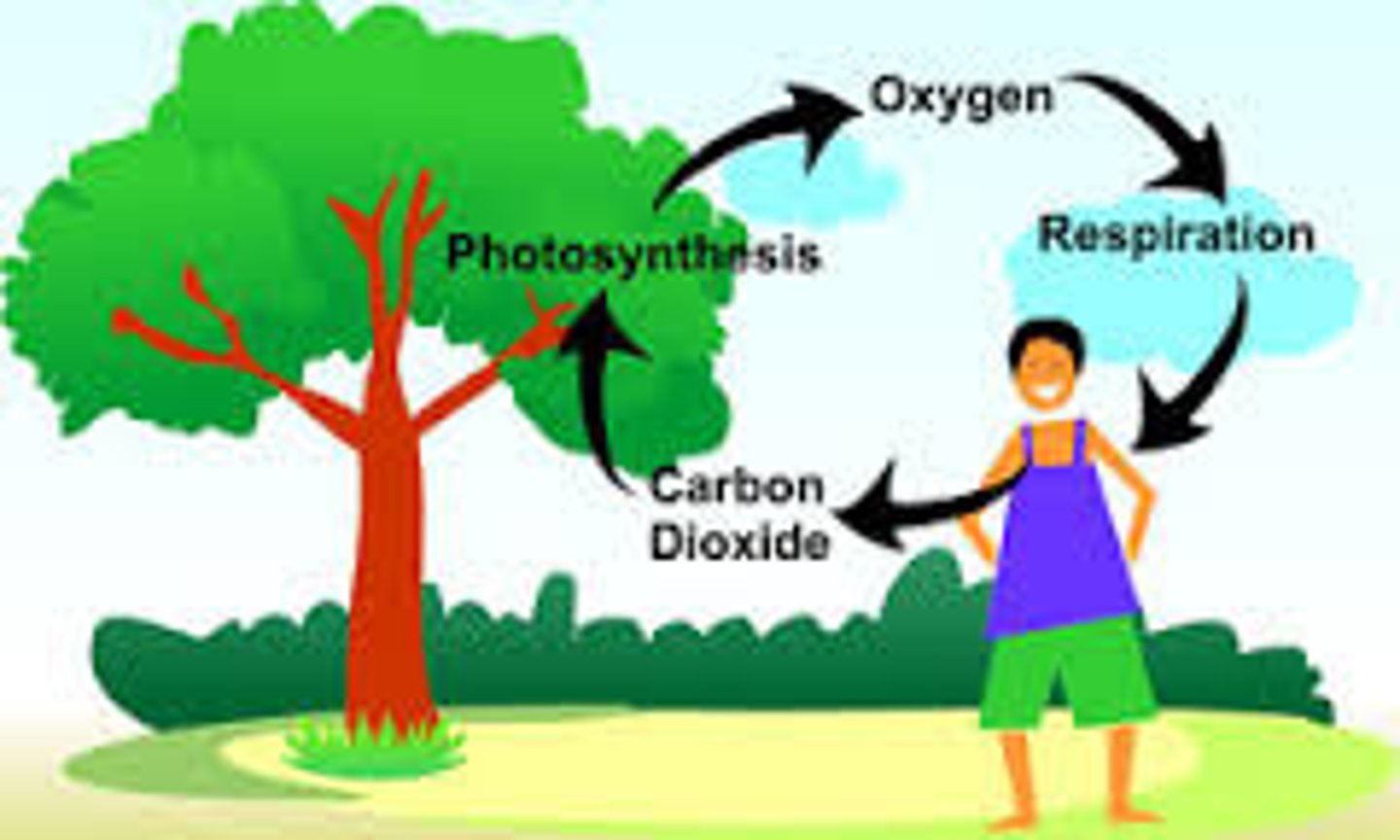
carbon dioxide cycle
carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is used by plants for photosynthesis. The plants use the carbon dioxide to make sugars (glucose) and release oxygen waste. All living organisms (including plants) use oxygen to break down sugars for energy in a process called cellular respiration. In the process they give off carbon dioxide waste.
ecological succession
the gradual process by which ecosystems change and develop over time.
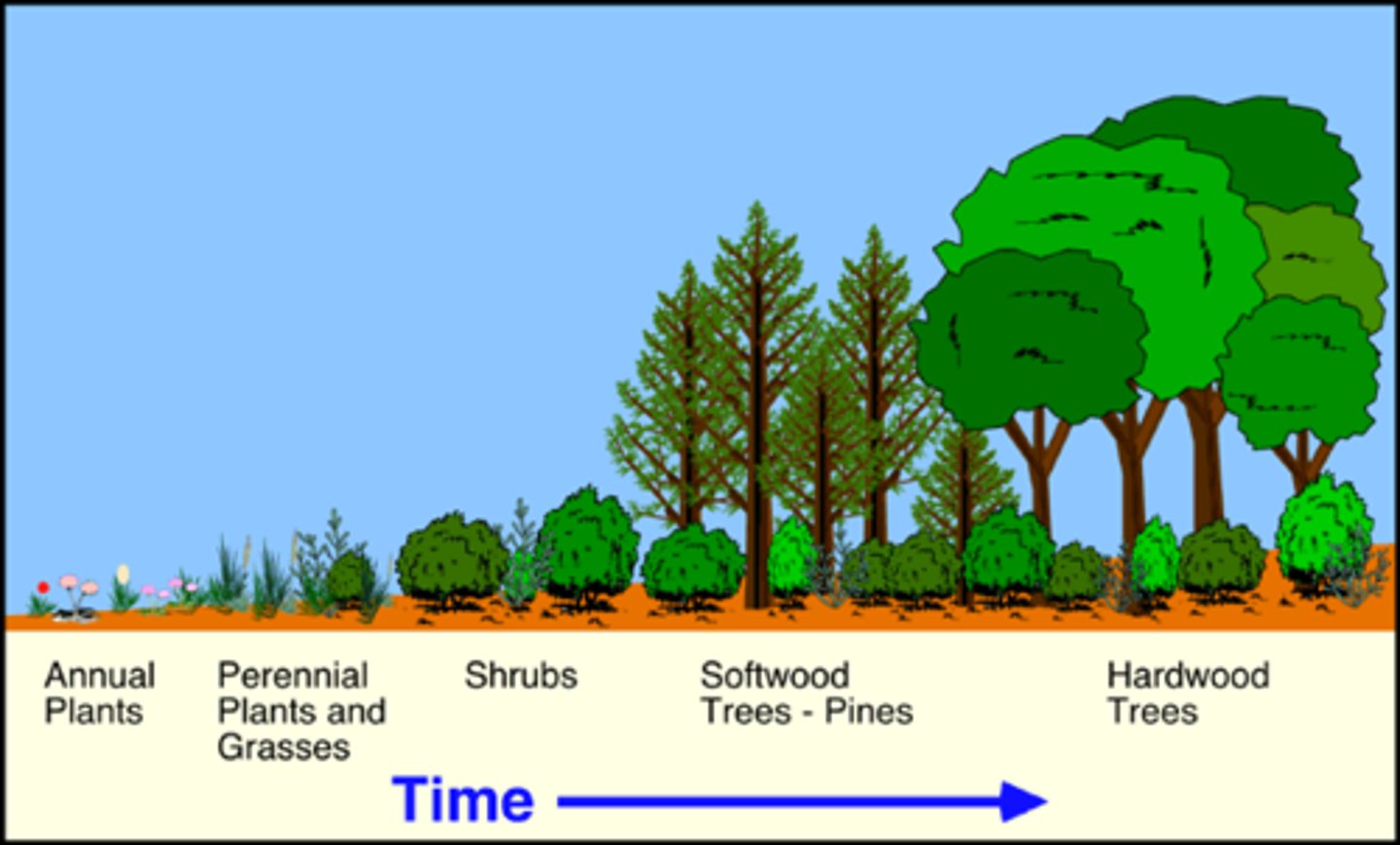
primary ecological succession
the series of community changes which occur on an entirely new habitat which has never been colonized before. For example, a newly quarried rock face

secondary ecological succession
the series of community changes which take place on a previously colonized, but disturbed or damaged habitat. For example, after land clearance or a fire.

pioneer species
the first group of organisms that can occupy a habitat. For example moss and lichen can occupy a rocky habitat

climax community
the final community in an ecosystem which is best adapted to the abiotic factors such as temperature, rainfall, and soil nutrients
