3. ECG Waveforms and Intervals
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the electrical charge inside a cardiac cell relative to the outside when it is electrically polarized?
The inside is negatively charged with respect to the outside.
How is electrical polarity maintained in cardiac myocytes?
Electrical polarity is maintained by membrane pumps that distribute potassium; sodium; chloride and calcium to keep the inside of myocytes electronegative.
What is the fundamental electrical event of the heart?
Depolarization.
Describe the process that occurs after depolarization to restore resting polarity in a myocyte
Repolarization occurs to restore myocyte resting polarity; this is through the use of membrane pumps that reverse the flow of ions.
What do all waveforms seen on EKG represent?
All waveforms seen on EKG are representative of depolarization and repolarization.
What are the three primary types of cardiac cells?
Pacemaker Cells; Electrical Conducting Cells; Myocardial Cells.
Which type of cardiac cell depolarizes spontaneously to initiate a cardiac cycle?
Pacemaker Cells.
What is the primary pacemaker of the heart?
Sinoatrial node (SA).
At what intrinsic rate does the SA node fire?
60-100 bpm.
Which system influences the firing rate of the SA node?
The autonomic nervous system.
What structure rapidly carries electrical current from the right atrium to the left atrium?
Bachmann’s Bundle.
What system consists of the electrical conducting cells (cells that rapidly carry current to distant parts of the heart) of the ventricles?
Purkinje system.
Which type of cardiac cell makes up the largest part of heart tissue and performs the "heavy lifting"?
Myocardial Cells.
What process links depolarization to contraction in myocardial cells?
Excitation-contraction coupling; where depolarization causes calcium to be released within the cell; and results in contraction.
Which waveform on the EKG represents atrial depolarization and contraction?
The P wave.
Does the firing of the SA node appear on the EKG?
No; the electrical activity of the SA node firing spontaneously is not seen on EKG.
How is the P wave divided anatomically?
The first part of the P wave represents RA depolarization and the second part of the P wave represents LA depolarization.
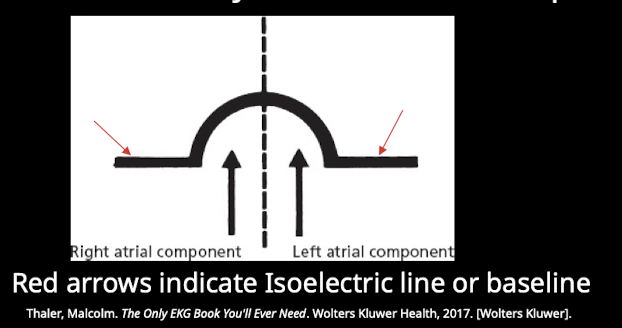
When does the EKG become electrically silent after atrial depolarization?
Once electrical activity has spread through both atria the EKG becomes electrically silent (isoelectric line-no myocardial cells are depolarizing).
Why is the AV node referred to as "the gatekeeper"?
Electrical current cannot conduct from atria to ventricles unless it is through the interventricular septum via the atrioventricular (AV) node.
What is the physiological purpose of the delay in electrical conduction through the AV node?
This delay is designed to give the atria time to empty blood into the ventricles.
A patient presents with complete heart block where no atrial impulses are conducting to the ventricles. Which structure is likely responsible for blocking the current flow?
The atrioventricular (AV) node; as current cannot conduct from atria to ventricles unless it is through the interventricular septum via the AV node.
What are the components of the ventricle conducting system?
The Bundle of His; Bundle branches; and the terminal Purkinje fibers.
Which major fascicles make up the left bundle branch?
The septal fascicle; anterior fascicle; and the posterior fascicle.
Which fascicle depolarizes the interventricular septum and in which direction? What do the other faciles do?
The septal fascicle; which depolarizes the interventricular septum in the left to right direction.

What is the final pathway for electrical current delivery to the ventricular myocardium?
Purkinje fibers.
Which EKG waveform represents ventricular depolarization and subsequent contraction?
The QRS complex.
Why does the QRS complex typically exhibit a higher amplitude than the P wave?
The higher amplitude of the QRS complex on EKG is due to the fact that the ventricles have greater muscle mass than the atria.
Define the Q wave on an EKG
The Q wave is the first downward deflection of the QRS complex.
Define the R wave on an EKG
The R wave is the first upward deflection of the QRS complex.
Define the S wave on an EKG
The S wave is the first downward deflection that follows an upward deflection.
What electrical event does the earliest part of the QRS complex represent?
The earliest part of the QRS complex represents depolarization of the interventricular septum by the septal fascicle of the left bundle branch.
Why does the left ventricle account for the majority of the QRS complex morphology?
The majority of the QRS complex represents contraction of the left and right ventricles; but the majority is attributed to the left ventricle because the muscle mass is much higher on the left.
During what period are myocardial cells resistant to further stimulation?
The refractory period; which occurs during repolarization.
Why is atrial repolarization not seen on a standard EKG tracing?
Atrial repolarization coincides with ventricular depolarization and is therefore hidden on EKG.
What EKG waveform represents ventricular repolarization?
The T wave.
Why is the T wave typically a wider waveform than the QRS complex?
Ventricular repolarization takes longer than depolarization; therefore the T wave is a wider waveform.
It should also have lower voltage than the QRS
Define the PR interval
The PR interval measures the time from start of atrial depolarization to the start of ventricular depolarization.

Define the QRS interval
The QRS interval measures the time of ventricular depolarization.

Define the QT interval
The QT interval measures the time from the start of ventricular depolarization to the end of ventricular repolarization.

Define the ST segment
The ST segment records the time from the end of ventricular depolarization to the start of ventricular repolarization.

A wave of depolarization is moving directly toward a positive electrode. What type of deflection will be observed on the EKG?
A positive (upward) deflection. (A)
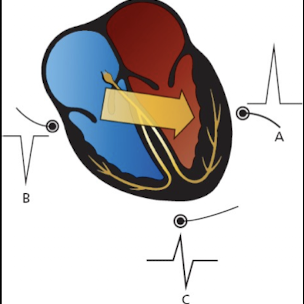
A wave of depolarization is moving directly away from a positive electrode. What type of deflection will be observed on the EKG?
A negative (downward) deflection. (B)

If a depolarization wave moves perpendicular to a positive electrode; what morphology will the deflection exhibit?
It will initially cause an upward deflection followed by a downward deflection. (C)
